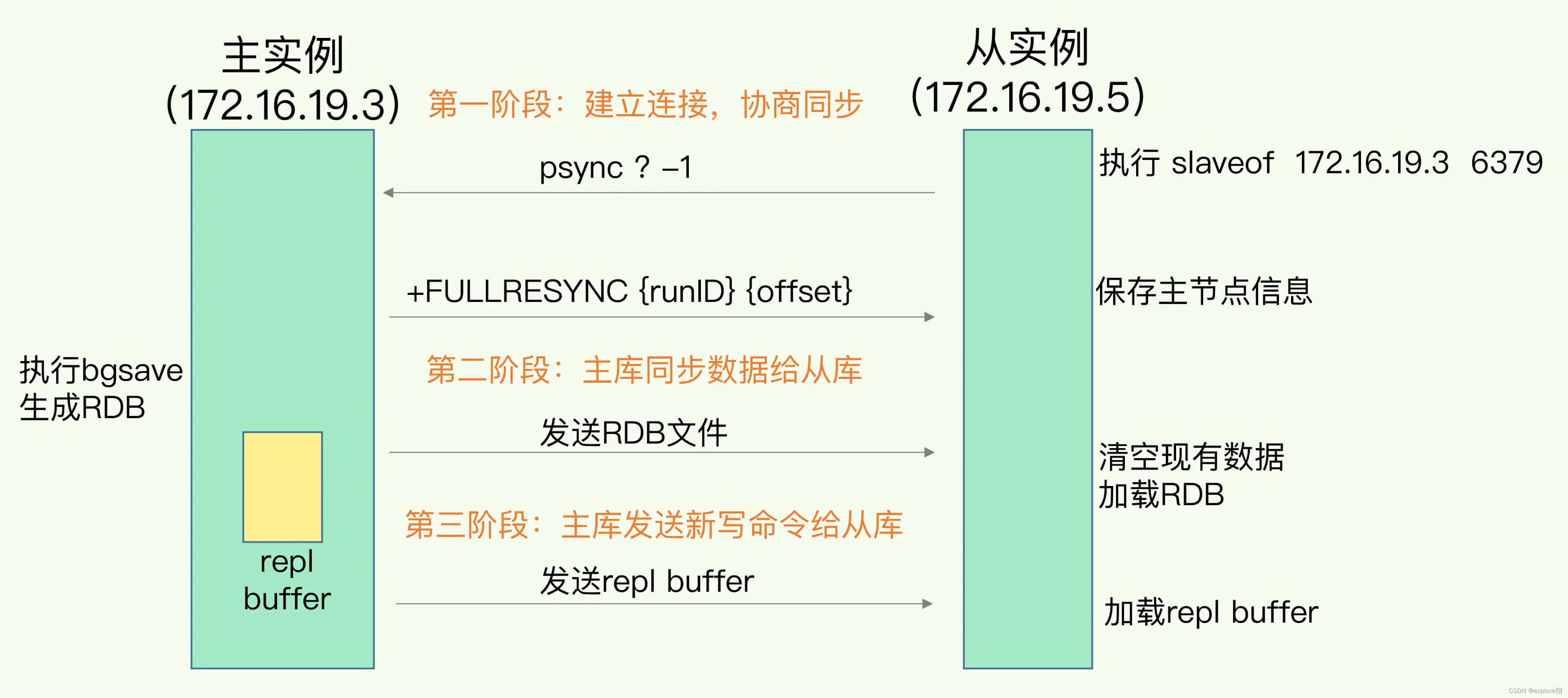
JavaSE-线程池(5)- ThreadPoolExecutor常用方法
invokeAll
ExecutorService 接口中定义的方法,给定一组任务,在所有任务执行完成时返回一个 Futures 列表,其中包含它们的状态和结果。
/**
* Executes the given tasks, returning a list of Futures holding
* their status and results when all complete.
* {@link Future#isDone} is {@code true} for each
* element of the returned list.
* Note that a <em>completed</em> task could have
* terminated either normally or by throwing an exception.
* The results of this method are undefined if the given
* collection is modified while this operation is in progress.
*
* @param tasks the collection of tasks
* @param <T> the type of the values returned from the tasks
* @return a list of Futures representing the tasks, in the same
* sequential order as produced by the iterator for the
* given task list, each of which has completed
* @throws InterruptedException if interrupted while waiting, in
* which case unfinished tasks are cancelled
* @throws NullPointerException if tasks or any of its elements are {@code null}
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if any task cannot be
* scheduled for execution
*/
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
invokeAll 使用方式
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest {
static class MyTask implements Callable<Boolean> {
private int id;
public MyTask(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
try {
System.out.println(
"time:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " " + Thread.currentThread() + " execute task " + id +
" start");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(
"time:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " " + Thread.currentThread() + " execute task " + id +
" finish");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 40, 5000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2));
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
List<Callable<Boolean>> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
tasks.add(new MyTask(i));
}
List<Future<Boolean>> futures = null;
try {
futures = executor.invokeAll(tasks);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("time:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " 主线程会等待invokeAll执行完成才继续执行");
for (int i = 0; i < futures.size(); i++) {
try {
System.out.println(futures.get(i).get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
如打印结果所示,主线程会等待 invokeAll 方法中的任务执行完后才继续执行
time:1677229181926 Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] execute task 1 start
time:1677229181927 Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] execute task 2 start
time:1677229181928 Thread[pool-1-thread-3,5,main] execute task 3 start
time:1677229181929 Thread[pool-1-thread-4,5,main] execute task 4 start
time:1677229181930 Thread[pool-1-thread-5,5,main] execute task 5 start
time:1677229183942 Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] execute task 2 finish
time:1677229183942 Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] execute task 1 finish
time:1677229183942 Thread[pool-1-thread-3,5,main] execute task 3 finish
time:1677229183942 Thread[pool-1-thread-5,5,main] execute task 5 finish
time:1677229183942 Thread[pool-1-thread-4,5,main] execute task 4 finish
time:1677229183965 主线程会等待invokeAll执行完成才继续执行
true
true
true
true
true
耗时:2141
一般在使用 invokeAll 方法时建议加上等待时间,防止任务执行时间过长线程一直阻塞,方法定义如下:
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
如果在 1 秒钟时间内任务没有结束将会被取消
futures = executor.invokeAll(tasks,1,TimeUnit.SECONDS);
执行结果如下:
time:1677231068880 Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] execute task 1 start
time:1677231068881 Thread[pool-1-thread-3,5,main] execute task 3 start
time:1677231068880 Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] execute task 2 start
time:1677231068881 Thread[pool-1-thread-4,5,main] execute task 4 start
time:1677231068881 Thread[pool-1-thread-5,5,main] execute task 5 start
java.lang.InterruptedException: sleep interrupted
at java.lang.Thread.sleep(Native Method)
at test.executors.ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest$MyTask.call(ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest.java:27)
at test.executors.ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest$MyTask.call(ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest.java:13)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run$$$capture(FutureTask.java:266)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:750)
。。。省略部分报错
java.util.concurrent.CancellationException
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:121)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)
at test.executors.ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest.main(ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest.java:59)
java.util.concurrent.CancellationException
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:121)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)
at test.executors.ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest.main(ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAllTest.java:59)
。。。省略部分报错
time:1677231069895 主线程会等待invokeAll执行完成才继续执行
耗时:1113
invokeAny
ExecutorService 接口中定义的方法,给定一组任务,只要有一个任务执行完成就返回这个任务的结果
/**
* Executes the given tasks, returning the result
* of one that has completed successfully (i.e., without throwing
* an exception), if any do. Upon normal or exceptional return,
* tasks that have not completed are cancelled.
* The results of this method are undefined if the given
* collection is modified while this operation is in progress.
* 执行给定的任务,返回成功完成的任务的结果(即没有抛出异常),如果有的话。
* 在正常或异常返回时,未完成的任务将被取消。如果在执行此操作时修改了给定的集合,则此方法的结果是未定义的。
*/
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
invokeAny 使用方式
如下,有5个任务,每个任务等待时间为 0-3 秒,线程池调用 invokeAny 方法获取最终执行的任务名称
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException;
public class ThreadPoolExecutorInvokeAnyTest {
static class MyTask implements Callable<String> {
private int id;
public MyTask(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
Integer randomTime = new Random().nextInt(4) * 1000;
try {
System.out.println(
"time:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " " + Thread.currentThread() + " execute task " + id +
" start,random time :"+randomTime);
Thread.sleep(randomTime);
System.out.println(
"time:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " " + Thread.currentThread() + " execute task " + id +
" finish");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "";
}
return "task" + id;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor =
new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 40, 5000,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2));
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
List<Callable<String>> tasks = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
tasks.add(new MyTask(i));
}
String futureResult = null;
try {
futureResult = executor.invokeAny(tasks, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("time:" + System.currentTimeMillis() + " 主线程会等待invokeAny执行完成才继续执行");
System.out.println("执行的任务为:" + futureResult);
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println("耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start));
}
}
执行结果如下,task5等待0秒,所以 invokeAny方法返回结果为task5,其他任务等待时间都超过0秒,所以都被取消执行