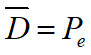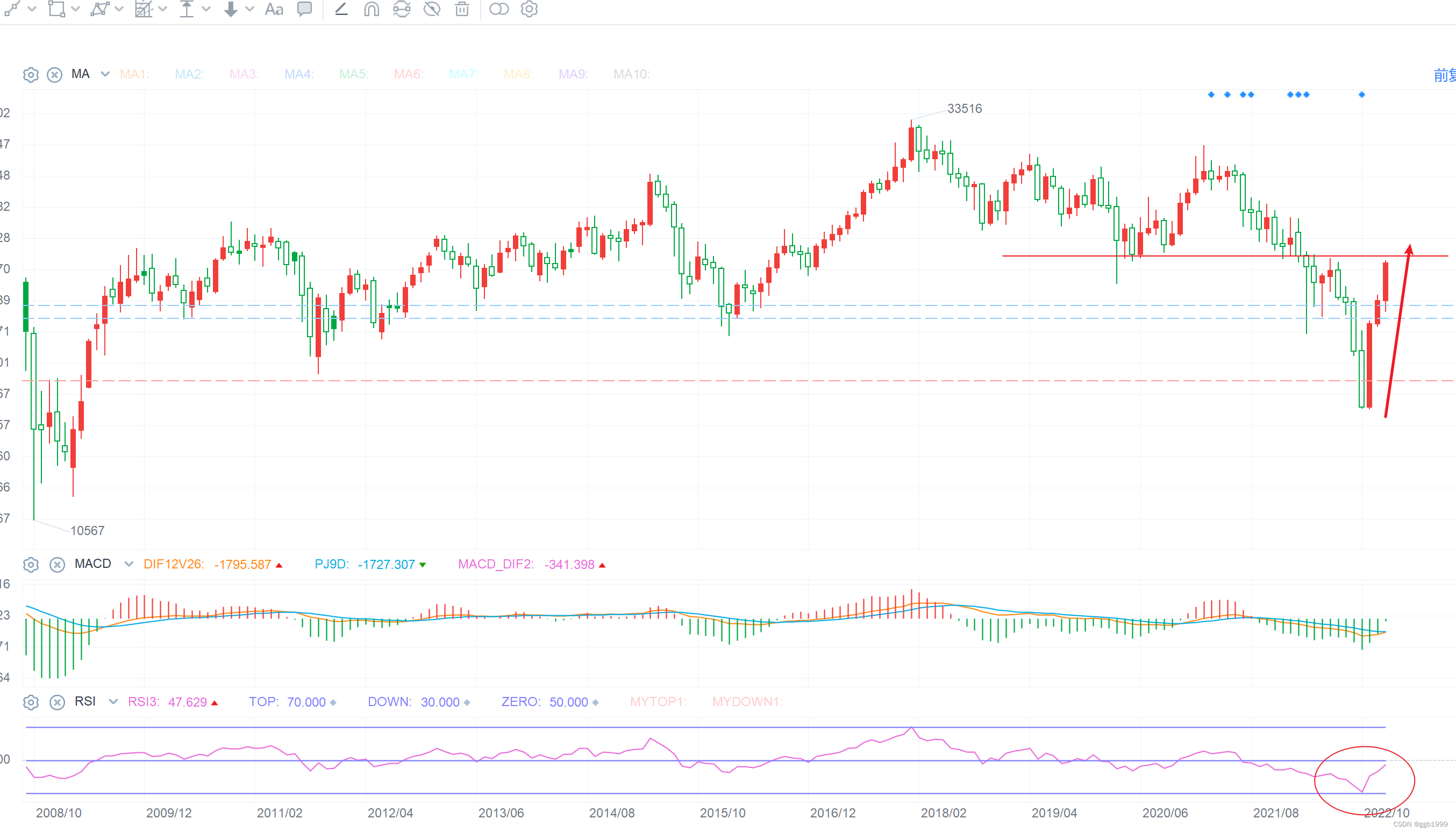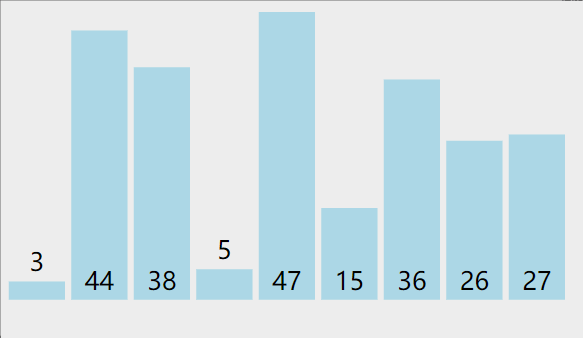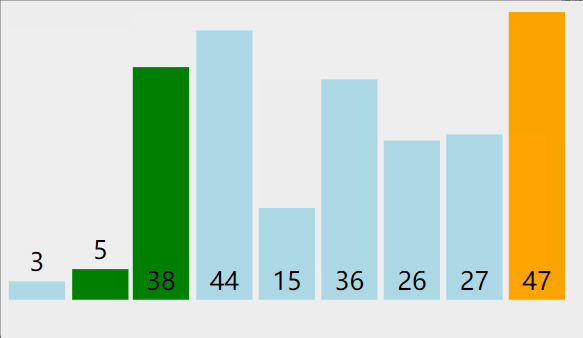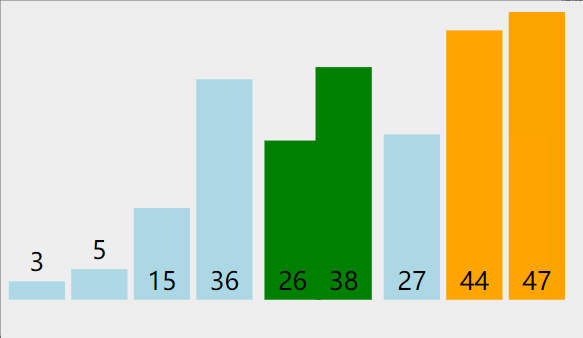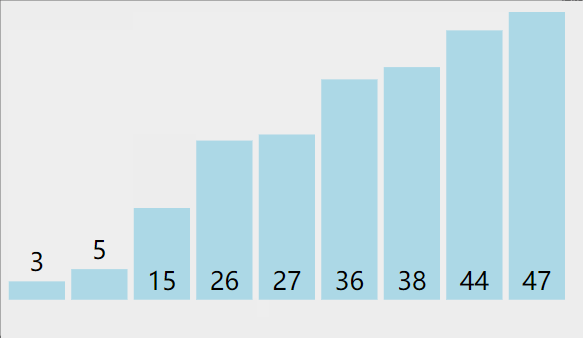

第 1 天
栈与队列(简单)
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
class CQueue {
public:
CQueue() {}
void appendTail(int value) {
s1.push(value);
}
int deleteHead() {
while(!s1.empty())
{
s2.push(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
int res;
if(!s2.empty())
{
res = s2.top();
s2.pop();
}
else
return -1;
while(!s2.empty())
{
s1.push(s2.top());
s2.pop();
}
return res;
}
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
};
剑指 Offer 30. 包含min函数的栈
【解法一】一个栈存放一个结构体结点
typedef struct Node { int num; int min; }Node; class MinStack { public: /** initialize your data structure here. */ MinStack() {} void push(int x) { Node a; a.num = x; a.min = x; if(!s.empty() && s.top().min<x) a.min = s.top().min; s.push(a); } void pop() { s.pop(); } int top() { return s.top().num; } int min() { return s.top().min; } stack<Node> s; };【解法二】使用俩个栈
class MinStack { public: /** initialize your data structure here. */ MinStack() { } void push(int x) { num.push(x); if(minnum.empty()) { minnum.push(x); } else { if(minnum.top()>=x) minnum.push(x); } } void pop() { if(num.empty()) return; else { if(num.top()==minnum.top()) minnum.pop(); num.pop(); } } int top() { if(!num.empty()) return num.top(); return -1; } int min() { if(!num.empty()) return minnum.top(); return -1; } stack<int> num; stack<int> minnum; };
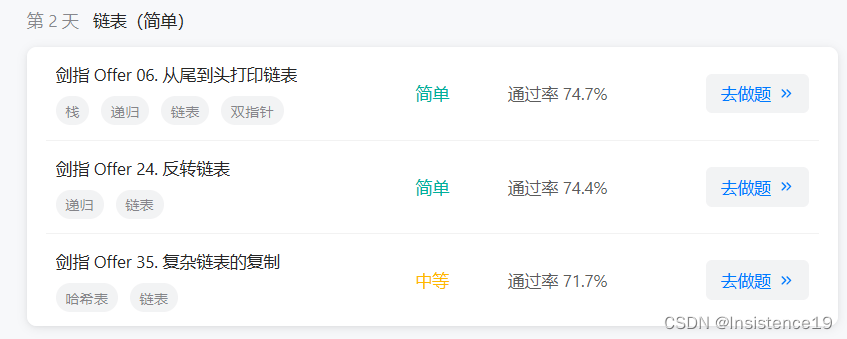
第 2 天
链表(简单)
剑指 Offer 06. 从尾到头打印链表
【解法一】使用vector存储,并反转结果
class Solution { public: vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { ListNode* cur = head; vector<int> res; while(cur) { res.push_back(cur->val); cur = cur->next; } reverse(res.begin(), res.end()); return res; } };【解法二】使用递归思想
class Solution { public: vector<int> res; vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { if(!head) return res; reversePrint(head->next); res.push_back(head->val); return res; } };【解法三】使用一个辅助栈
class Solution { public: vector<int> reversePrint(ListNode* head) { vector<int> res; if(!head) return res; stack<int> s; while(head) { s.push(head->val); head=head->next; } while(!s.empty()) { res.push_back(s.top()); s.pop(); } return res; } };
剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
【解法一】迭代
class Solution { public: ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { if(!head)return head; ListNode* cur = head; ListNode* Next = head; ListNode* prev = NULL; while(cur) { Next = cur->next; cur->next = prev; prev = cur; cur = Next; } return prev; } };【解法二】递归
class Solution { public: ListNode* recur(ListNode* cur, ListNode* prev) { if(cur==nullptr)return prev; ListNode* res = recur(cur->next, cur); cur->next = prev; return res; } ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) { return recur(head, nullptr); } };
剑指 Offer 35. 复杂链表的复制