#! https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/598780689
bresenham algorithm
全象限区域bresenham algorithm计算的python/c++实现
bresenham algorithm为计算机图形学中使用像素点显示直线的算法,算法使用整数运算,能大幅提升计算速度。最近概率栅格建图算法中涉及到直线绘制,故推导学习了下。
公式推导
主要是第一象限斜率小于1的区域的公式推导,其他区域可以转换到该区域计算。

斜率公式如下,其中d为上图中每移动一个像素,y轴上增加的数值,即斜率
y
1
−
y
0
x
1
−
x
0
=
δ
y
δ
x
=
d
\frac{y_1 - y_0}{x_1 - x_0} = \frac{\delta y}{\delta x} = d
x1−x0y1−y0=δxδy=d
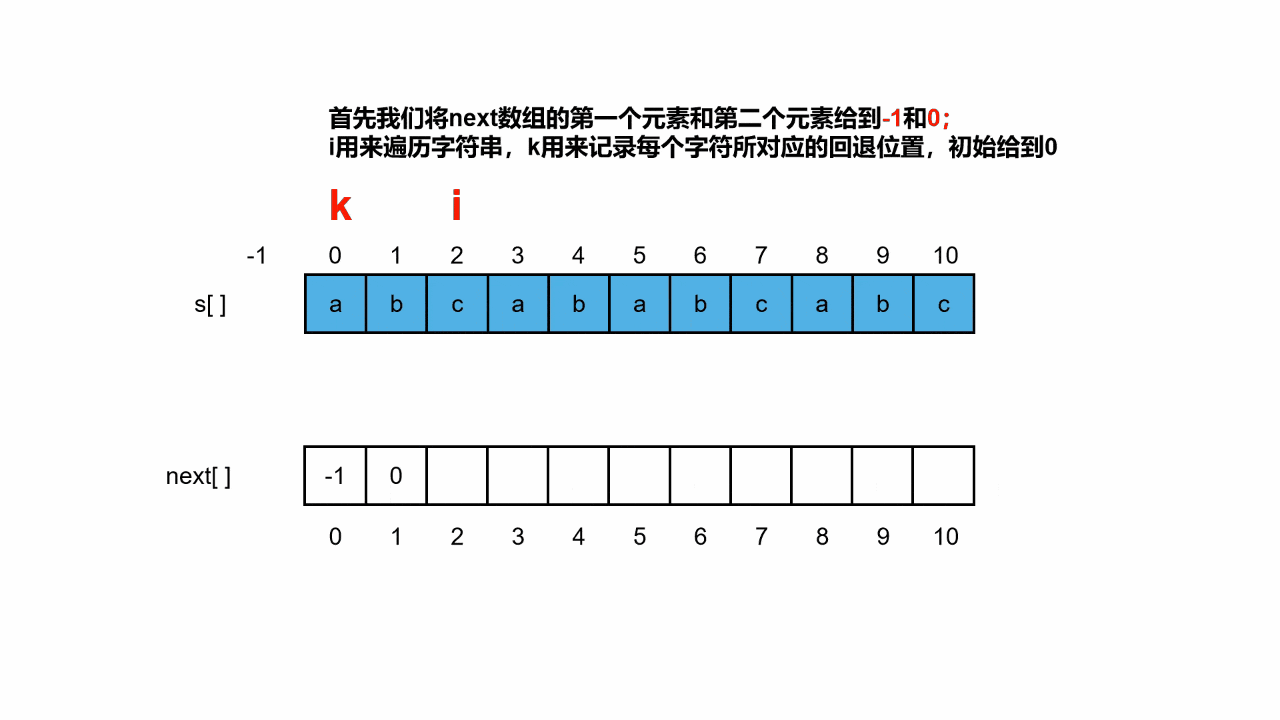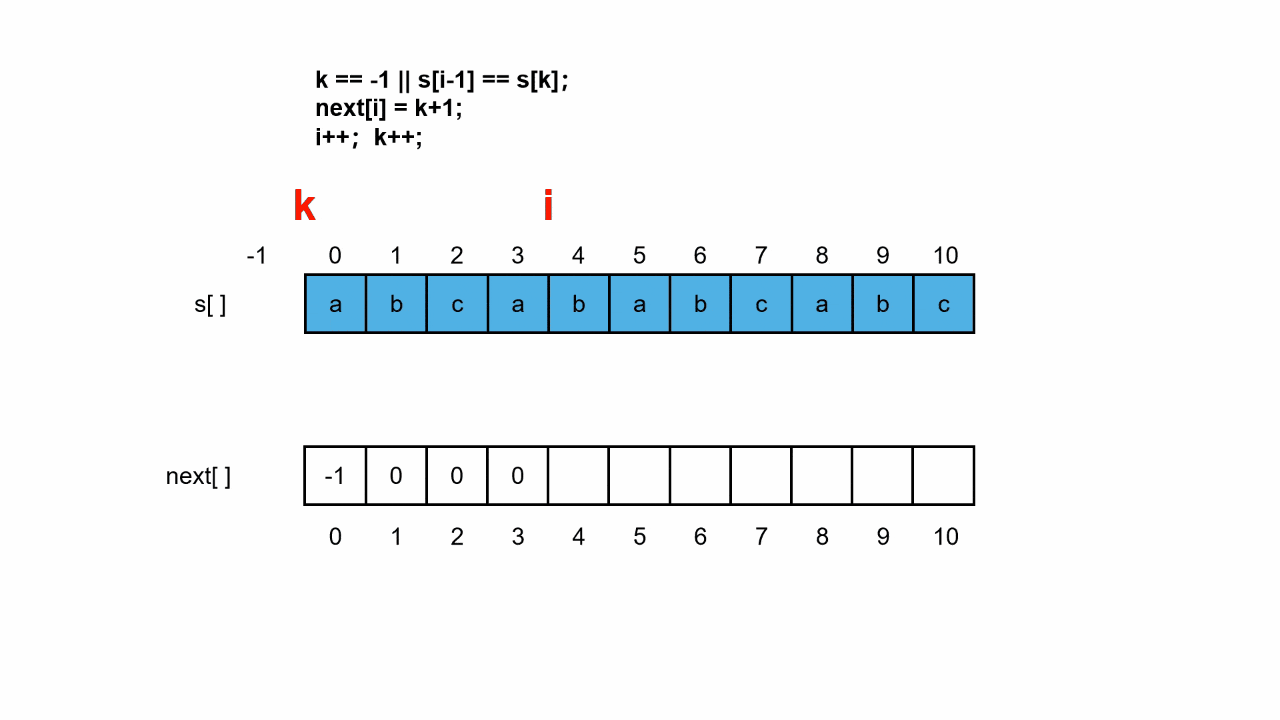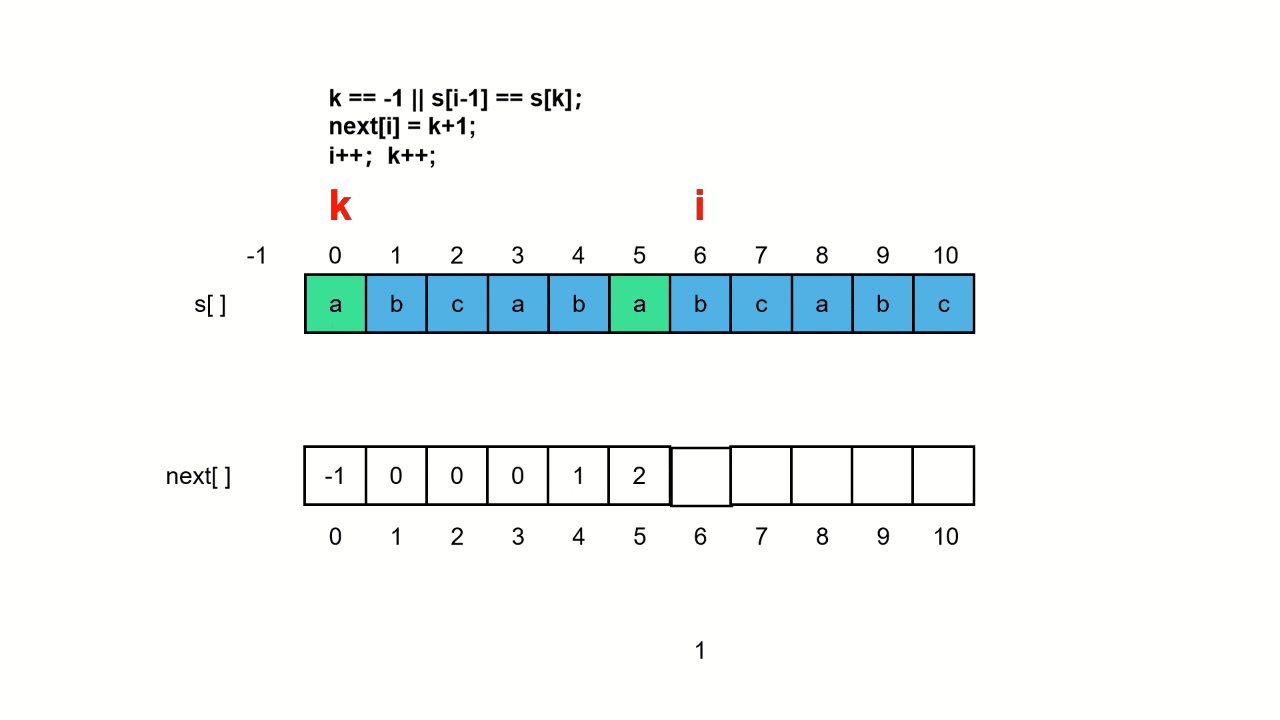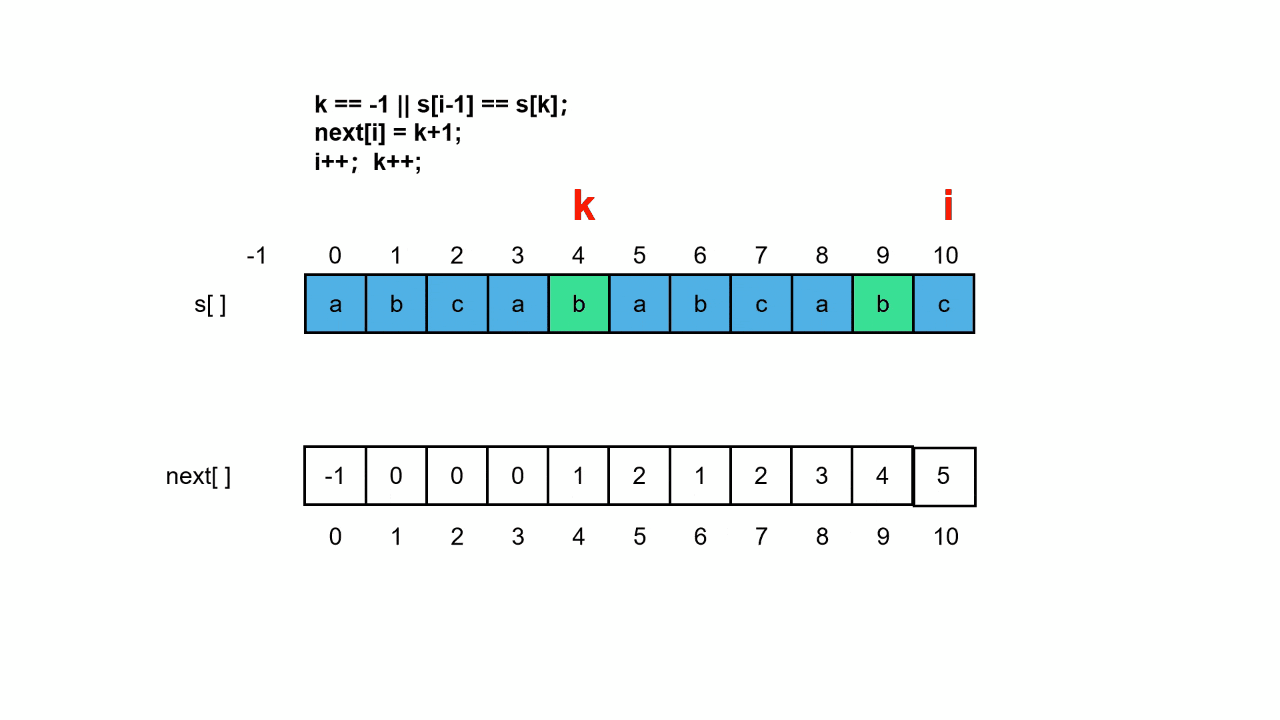
此时判断每次x增长时,纵轴的增值,对第一个像素判断d>0.5,是则y+1,下一个像素则判断2d>1.5,否则y不变,下一个像素则判断2d>0.5。
因为上一个像素没变,对比的阈值依旧保持不变。如上图示例:
当
x
=
x
1
=
x
0
+
1
x=x_1 = x_0+1
x=x1=x0+1时,d>0.5,则
y
1
=
y
0
+
1
y_1=y_0+1
y1=y0+1,y向上移动一个像素。d-0.5>0 => 2*dy-dx > 0
当
x
=
x
2
=
x
0
+
2
x=x_2 = x_0+2
x=x2=x0+2时,2d<1.5,则
y
2
=
y
1
y_2=y_1
y2=y1,y保持不变,此时1.5保持不变 2d-1.5>0 => 2*dy-dx + 2*dy-2*dx<0
当
x
=
x
2
=
x
0
+
3
x=x_2 = x_0+3
x=x2=x0+3时,3d>1.5,则
y
3
=
y
2
+
1
y_3=y_2+1
y3=y2+1,y向上移动一个像素 3d-1.5>0 => 2*dy-dx +2*dy-2*dx + 2*dy>0
递推公式如下:
D
k
=
{
2
∗
d
y
−
d
x
k
=
0
D
k
−
1
+
2
∗
d
y
k
>
0
且
D
k
−
1
<
0
D
k
−
1
+
2
∗
d
y
−
2
∗
d
x
k
>
0
且
D
k
−
1
>
0
D_k = \begin{cases} 2 * dy -dx &k = 0 \\ D_{k-1} + 2*dy & k>0且D_{k-1} < 0 \\ D_{k-1} + 2*dy-2*dx & k>0且D_{k-1} > 0 \\ \end{cases}
Dk=⎩
⎨
⎧2∗dy−dxDk−1+2∗dyDk−1+2∗dy−2∗dxk=0k>0且Dk−1<0k>0且Dk−1>0
伪代码如下:
plotLine(x0, y0, x1, y1)
dx = x1 - x0
dy = y1 - y0
D = 2 * dy - dx
y = y0
for x from x0 to x1
plot(x, y)
if D > 0
y = y + 1
D = D - 2*dx
end if
D = D + 2*dy
再精简为如下:
plotLine(x0, y0, x1, y1)
dx = x1 - x0
dy = y1 - y0
D = 0
y = y0
for x from x0 to x1
plot(x, y)
D += dy
if 2 * D > 0
D = D - dx
y = y + 1
end if
所有情况讨论
以(x0,y0)为原点,可分为如下8种+平行xy轴的10种情况讨论

以下实现以(x0,y0)为原点实现,如果(x0,y0)不是原点,需要先把数据平移到原点,再平移回去,或者修改TransformQuadrant函数
python实现及可视化

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 只支持x0=0,y0=0,要支持其他原点需要先平移到原点,再平移回去
def BresenhamAlgorithm(x0, y0, x1, y1):
# 1.process parallel situation
if x0 == x1 and y0 == y1:
return [x0, y0]
elif x0 == x1:
if y0 < y1:
y_min = y0
y_max = y1
else:
y_min = y1 + 1
y_max = y0 + 1
result = []
for y in range(y_min, y_max):
result.append([x0, y])
return result
elif y0 == y1:
if x0 < x1:
x_min = x0
x_max = x1
else:
x_min = x1 + 1
x_max = x0 + 1
result = []
for x in range(x_min, x_max):
result.append([x, y0])
return result
situation = 0
if x1 > x0 and y1 > y0:
if (y1 - y0) < (x1 - x0):
situation = 11
else:
situation = 12
elif x1 < x0 and y1 > y0:
if (y1 - y0) < (x0 - x1):
situation = 24
else:
situation = 23
elif x1 < x0 and y1 < y0:
if (y0 - y1) < (x0 - x1):
situation = 35
else:
situation = 36
elif x1 > x0 and y1 < y0:
if (y0 - y1) < (x1 - x0):
situation = 48
else:
situation = 47
# transform quadrant-2/3/4 to quadrant-1, or transform back
def Swap(xt, yt):
tmp = xt
xt = yt
yt = tmp
return xt, yt
def TransformQuadrant(xt, yt, pose, back=False):
if pose == 12:
xt, yt = Swap(xt, yt)
elif pose == 23:
xt = -xt
xt, yt = Swap(xt, yt)
elif pose == 24:
xt = -xt
elif pose == 35:
xt = -xt
yt = -yt
elif pose == 36:
xt = -xt
yt = -yt
xt, yt = Swap(xt, yt)
elif pose == 47:
yt = -yt
xt, yt = Swap(xt, yt)
elif pose == 48:
yt = -yt
if back:
if pose == 23 or pose == 47:
xt = -xt
yt = -yt
return xt, yt
# 3. transform to quadrant-1_1
# print(f"before {x1 - x0}, {y1 - y0}")
x1, y1 = TransformQuadrant(x1, y1, situation)
# print(f"after {x1 - x0}, {y1 - y0}")
# 4. compute grid in line
delta_x = x1 - x0
delta_y = y1 - y0
error = 0
y = y0
result = []
for x in range(x0, x1):
result.append([x, y])
error += delta_y
if 2 * error > delta_x:
error -= delta_x
y += 1
# 5. transform back to original quadrant
for pos in result:
pos[0], pos[1] = TransformQuadrant(pos[0], pos[1], situation, True)
return result
# grid map range
range_max = 70
grid_map = [[0 for i in range(range_max)] for j in range(range_max)]
# 设置x0,y0
xx, yy = 10, 10
# xx, yy = 0, 0
test_pts = [
[xx - 10, yy], [xx + 10, yy], [xx, yy - 10], [xx, yy + 10], # 平行轴
[xx + 15, yy + 10], [xx + 10, yy + 15], # 第一象限
[xx - 15, yy + 10], [xx - 10, yy + 15], # 第二象限
[xx - 15, yy - 10], [xx - 10, yy - 15], # 第三象限
[xx + 15, yy - 10], [xx + 10, yy - 15] # 第四象限
]
grid_idx = []
move_dis = 20
for pt in test_pts:
plt.plot([xx + move_dis, pt[0] + move_dis], [yy + move_dis, pt[1] + move_dis])
res = BresenhamAlgorithm(0, 0, pt[0] - xx, pt[1] - yy)
for a in res:
a[0] += xx
a[1] += yy
grid_map[a[1] + move_dis][a[0] + move_dis] = 5
grid_idx.append(a)
print(grid_idx)
plt.imshow(grid_map, cmap=plt.cm.hot, interpolation='nearest', vmin=0, vmax=10)
plt.colorbar()
plt.xlim(0, 20)
plt.ylim(0, 20)
my_x_ticks = np.arange(0, range_max, 1)
my_y_ticks = np.arange(0, range_max, 1)
plt.xticks(my_x_ticks)
plt.yticks(my_y_ticks)
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
C++实现
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <gtest/gtest.h>
/**
* @details implement of bresenham algorithm from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bresenham%27s_line_algorithm
* @param x0
* @param y0
* @param x1
* @param y1
* @return intersection grid indexes
*/
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> BresenhamAlgorithm(int x0, int y0, int x1, int y1)
{
using GridIndex = std::pair<int, int>;
// 1. process parallel situation
if (x1 == x0 && y1 == y0)
{
return { GridIndex(x0, y0) };
}
else if (x1 == x0)
{
GridIndex tmp_index;
std::vector<GridIndex> result;
result.reserve(static_cast<size_t>(std::abs(y1 - y0)));
int y_min = 0;
int y_max = 0;
if (y0 < y1)
{
y_min = y0;
y_max = y1;
}
else
{
y_min = y1 + 1;
y_max = y0 + 1;
}
for (int y = y_min; y < y_max; ++y)
{
tmp_index.first = x1;
tmp_index.second = y;
result.emplace_back(tmp_index);
}
return result;
}
else if (y1 == y0)
{
GridIndex tmp_index;
std::vector<GridIndex> result;
result.reserve(static_cast<size_t>(std::abs(x1 - y0)));
int x_min = 0;
int x_max = 0;
if (x0 < x1)
{
x_min = x0;
x_max = x1;
}
else
{
x_min = x1 + 1;
x_max = x0 + 1;
}
for (int x = x_min; x < x_max; ++x)
{
tmp_index.first = x;
tmp_index.second = y1;
result.emplace_back(tmp_index);
}
return result;
}
// situation include eight parts of quadrant(counterclockwise)
enum class Situation : int8_t
{
kQuadrant1_1 = 0,
kQuadrant1_2 = 2,
kQuadrant2_3 = 3,
kQuadrant2_4 = 4,
kQuadrant3_5 = 5,
kQuadrant3_6 = 6,
kQuadrant4_7 = 7,
kQuadrant4_8 = 8
};
// 2. get situation from grid position
Situation situation = Situation::kQuadrant1_1;
if (x1 > x0 && y1 > y0)
{
situation = ((y1 - y0) < (x1 - x0)) ? Situation::kQuadrant1_1 : Situation::kQuadrant1_2;
}
else if (x1 < x0 && y1 > y0)
{
situation = ((y1 - y0) < (x0 - x1)) ? Situation::kQuadrant2_4 : Situation::kQuadrant2_3;
}
else if (x1 < x0 && y1 < y0)
{
situation = ((y0 - y1) < (x0 - x1)) ? Situation::kQuadrant3_5 : Situation::kQuadrant3_6;
}
else if (x1 > x0 && y1 < y0)
{
situation = ((y0 - y1) < (x1 - x0)) ? Situation::kQuadrant4_8 : Situation::kQuadrant4_7;
}
// transform quadrant-2/3/4 to quadrant-1, or transform back
auto TransformQuadrant = [&](int& x1, int& y1, Situation situation, bool back = false)
{
switch (situation)
{
case Situation::kQuadrant1_2:
std::swap(x1, y1);
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant2_3:
x1 = -x1;
std::swap(x1, y1);
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant2_4:
x1 = -x1;
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant3_5:
x1 = -x1;
y1 = -y1;
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant3_6:
x1 = -x1;
y1 = -y1;
std::swap(x1, y1);
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant4_7:
y1 = -y1;
std::swap(x1, y1);
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant4_8:
y1 = -y1;
break;
case Situation::kQuadrant1_1:
default:
break;
}
if (back)
{
if (situation == Situation::kQuadrant2_3 || situation == Situation::kQuadrant4_7)
{
x1 = -x1;
y1 = -y1;
}
}
};
// 3. transform to quadrant-1_1
TransformQuadrant(x1, y1, situation);
int delta_x = x1 - x0;
int delta_y = y1 - y0;
int error = 0;
int y = y0;
// 4. compute grid in line
GridIndex tmp_index;
std::vector<GridIndex> result;
for (int x = x0; x < x1; ++x)
{
tmp_index.first = x;
tmp_index.second = y;
result.emplace_back(tmp_index);
error += delta_y;
if (2 * error > delta_x)
{
error -= delta_x;
y += 1;
}
}
// 5. transform back to original quadrant
for (auto& grid_index : result)
{
TransformQuadrant(grid_index.first, grid_index.second, situation, true);
}
return result;
}
TEST(test_bresenham, test_bresenham)
{
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> ground_truth
{{ -9, 0 }, { -8, 0 }, { -7, 0 }, { -6, 0 }, { -5, 0 }, { -4, 0 }, { -3, 0 }, { -2, 0 }, { -1, 0 }, { 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 0 }, { 2, 0 }, { 3, 0 }, { 4, 0 }, { 5, 0 }, { 6, 0 }, { 7, 0 }, { 8, 0 }, { 9, 0 }, { 0, -9 },
{ 0, -8 }, { 0, -7 }, { 0, -6 }, { 0, -5 }, { 0, -4 }, { 0, -3 }, { 0, -2 }, { 0, -1 }, { 0, 0 }, { 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1 }, { 0, 2 }, { 0, 3 }, { 0, 4 }, { 0, 5 }, { 0, 6 }, { 0, 7 }, { 0, 8 }, { 0, 9 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 3 }, { 6, 4 }, { 7, 5 }, { 8, 5 }, { 9, 6 }, { 10, 7 }, { 11, 7 },
{ 12, 8 }, { 13, 9 }, { 14, 9 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 1, 2 }, { 2, 3 }, { 3, 4 }, { 3, 5 }, { 4, 6 },
{ 5, 7 }, { 5, 8 }, { 6, 9 }, { 7, 10 }, { 7, 11 }, { 8, 12 }, { 9, 13 }, { 9, 14 }, { 0, 0 }, { -1, 1 },
{ -2, 1 }, { -3, 2 }, { -4, 3 }, { -5, 3 }, { -6, 4 }, { -7, 5 }, { -8, 5 }, { -9, 6 }, { -10, 7 }, { -11, 7 },
{ -12, 8 }, { -13, 9 }, { -14, 9 }, { 0, 0 }, { -1, 1 }, { -1, 2 }, { -2, 3 }, { -3, 4 }, { -3, 5 }, { -4, 6 },
{ -5, 7 }, { -5, 8 }, { -6, 9 }, { -7, 10 }, { -7, 11 }, { -8, 12 }, { -9, 13 }, { -9, 14 }, { 0, 0 },
{ -1, -1 }, { -2, -1 }, { -3, -2 }, { -4, -3 }, { -5, -3 }, { -6, -4 }, { -7, -5 }, { -8, -5 }, { -9, -6 },
{ -10, -7 }, { -11, -7 }, { -12, -8 }, { -13, -9 }, { -14, -9 }, { 0, 0 }, { -1, -1 }, { -1, -2 }, { -2, -3 },
{ -3, -4 }, { -3, -5 }, { -4, -6 }, { -5, -7 }, { -5, -8 }, { -6, -9 }, { -7, -10 }, { -7, -11 }, { -8, -12 },
{ -9, -13 }, { -9, -14 }, { 0, 0 }, { 1, -1 }, { 2, -1 }, { 3, -2 }, { 4, -3 }, { 5, -3 }, { 6, -4 },
{ 7, -5 }, { 8, -5 }, { 9, -6 }, { 10, -7 }, { 11, -7 }, { 12, -8 }, { 13, -9 }, { 14, -9 }, { 0, 0 },
{ 1, -1 }, { 1, -2 }, { 2, -3 }, { 3, -4 }, { 3, -5 }, { 4, -6 }, { 5, -7 }, { 5, -8 }, { 6, -9 }, { 7, -10 },
{ 7, -11 }, { 8, -12 }, { 9, -13 }, { 9, -14 }};
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> test_pts{
{ -10, 0 }, { 10, 0 }, { 0, -10 }, { 0, 10 },
{ +15, +10 }, { +10, +15 },
{ -15, +10 }, { -10, +15 },
{ -15, -10 }, { -10, -15 },
{ +15, -10 }, { +10, -15 }
};
std::vector<std::pair<int, int>> results;
for (auto& pt : test_pts)
{
auto res = BresenhamAlgorithm(0, 0, pt.first, pt.second);
results.insert(results.end(), res.begin(), res.end());
}
EXPECT_EQ(results, ground_truth);
// for (auto& pt : results)
// {
// printf("[%d, %d], ", pt.first, pt.second);
// }
// printf("\n");
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
::testing::InitGoogleTest(&argc, argv);
return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
return 0;
}
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.21)
project(test_bresenham)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 14)
add_executable(test_bresenham main.cpp)
target_link_libraries(test_bresenham gtest pthread)
参考
- https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1364y1d7Lo/?vd_source=9408e8cab54b943547dbc522a9112342
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bresenham%27s_line_algorithm
- https://www.cs.montana.edu/courses/spring2009/425/dslectures/Bresenham.pdf