小白入门,跑着个代码头都给我跑秃了,文档说不详细吧似乎啥都和你说了,说它详细吧,看了几遍也跑不出来。记录一下我遇到的问题:
目录
一、确定待执行的程序
(1)那些年的undefined reference
(2)一些路径指示
(3)程序分析
二、编译gem5环境
三、popnet运行
(1)下载popnet源码
(2)编译与依赖
四、benchmark和测试文件
(1)测试gadia_receive和gadia_call函数: test.cpp
(2)进一步测试: test.cpp
(3)benchmark test01.cpp:矩阵乘法,
(3)benchmark test02.cpp:BFS
一、确定待执行的程序
(1)那些年的undefined reference
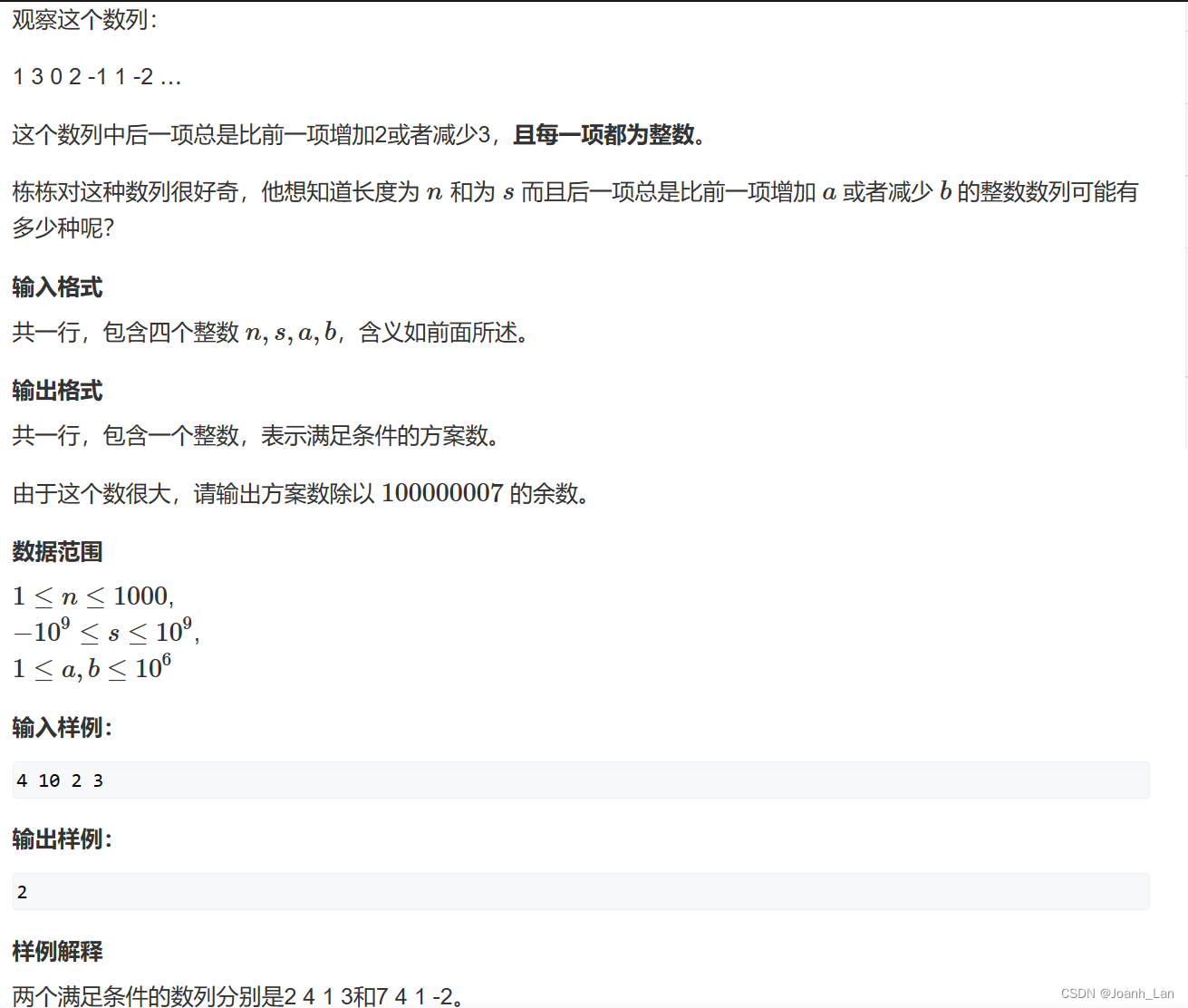
明明链接的路径没有问题(具体咋链接后面说),但是就是报reference错误,这篇文章比较详细地分析了undefined reference的一些原因及解决方案,如下:
"undefined reference to" 出现问题及解决方法_王老机的博客-CSDN博客_undefined reference to
我的文件结构如下:gem5/include/benchmark/待编译的源程序.cpp
关于g++的编译参数含义:
g++编译选项 - 紫long - 博客园
关于undefined reference to `pthread_create':+lpthread即可
undefined reference to `pthread_join'解决办法_iteye_3759的博客-CSDN博客
关于undefined reference to `m5_gadia_call':+./libm5.a即可
g++ -lm5 -L./ ./sourceCode.cpp -o a.out ./libm5.a
-l 指示库名称,比如我们指明了m5
-L 指明库的路径,我的是当前路径(其实我不明白为啥已经声明了./之后后面还要再声明一遍./libm5.a)
-o 重定义输出注意所有要在Gem5模拟器的FS模式下执行的程序都必须要提前编译好后,挂载到img文件中,在通过m5端连接系统进行执行,在linux中如果我要执行a.out文件,进入文件所在目录,执行如下命令即可:
./a.out(2)一些路径指示
libm5.a是啥?在哪儿?用来干啥
这个问题当初困扰了我很久,libm5.a是一个静态库文件,其中包含了被编译成二进制文件的一些程序或者代码片段,它们可以在其他程序中被链接使用。在gem5模拟器中,路径通常是~/gem5/include/libm5.a。静态库文件在编译期间就会被合并到其他程序中,因此可以减少运行时的资源开销。

-
静态库文件是一个由若干个目标文件打包生成的文件,由于静态库文件将所有的代码都包含在内,因此在生成的可执行文件中会包含所有的静态库文件内容。
-
动态库文件是一个独立的文件,它可以被多个程序共享,在生成的可执行文件中不会包含动态库文件的内容,而是将动态库文件的路径和名称记录在可执行文件的动态连接信息中,当可执行文件运行时,
静态库文件的文件后缀一般是 .a,动态库文件的文件后缀一般是 .so(Linux)、.dylib(macOS)或 .dll(Windows)。在 Linux 和 macOS 系统中,动态库文件名称通常会以 "lib" 开头,例如 libc.so、libstdc++.so 等。
(3)程序分析
关于Chiplet-Gem5-SharedMemory-main中benchmark涉及到的一些知识,主要是矩阵乘法test01.cpp
(24条消息) 傻白探索Chiplet,Gem5实例程序分析(九)_好啊啊啊啊的博客-CSDN博客
二、编译gem5环境
可以参考官教程:gem5: Building gem5
也可以看我记录的博客:
(24条消息) Gem5模拟器 for Ubuntu20.04_好啊啊啊啊的博客-CSDN博客_ubuntu20.04 gem5
如果遇到了以下这个问题:
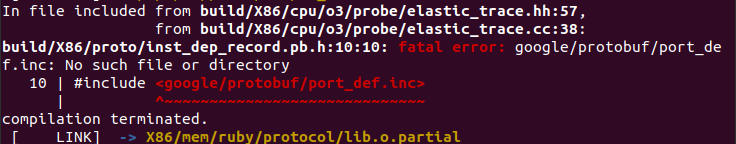
执行以下代码:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler libgoogle-perftools-dev
python3 `which scons` --clean --no-cache # cleaning the build folder
python3 `which scons` build/X86/gem5.opt -j 9 # re-compiling gem5
rm -rf build/ # completely removing the gem5
//如果重新编译还是不行,就把build整个文件夹删掉重来
build folder
python3 `which scons` build/X86/gem5.opt -j 9 # re-compiling gem5如果你是用的是服务器或者虚拟机的方式构建gem5,建议不要通过在windows下载gem5包然后copy到服务器或者虚拟机的方式获得gem5源代码,可能会遇到权限错误如下:
util/cpt_upgrader.py: Permission denied
如果使用的是个人设备,可以给予sudo权限并继续构建gem5模拟器(直接在linux系统中clone则不会遇到这个问题)。
sudo chmod 777 ./util/cpt_upgrader.py参考链接:Gem5 学习指南——基本配置_iTsta_zx的博客-CSDN博客
编译完成长这样:
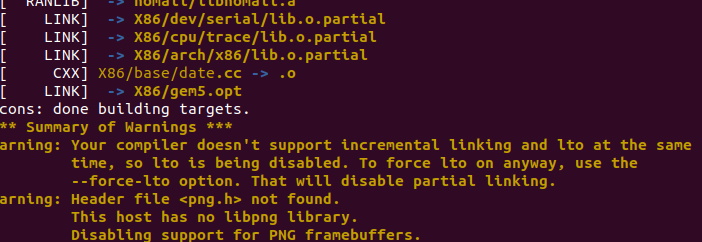
创建img镜像文件,具体步骤参看这篇博客:
(24条消息) Gem5模拟器,FS模式运行自定义程序(九)_好啊啊啊啊的博客-CSDN博客
三、popnet运行
(1)下载popnet源码
git clone https://gitee.com/hic_0757/popnet_modified.git(2)编译与依赖
该软件依赖 Boost 库和 cmake,假设源码目录为$ROOT,将当前目录切换为$ROOT:
cd $ROOT运行安装依赖库的命令:
sudo apt install libboost-all-dev
sudo apt install cmake运行编译命令:
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make注意gem5运行得到的communication是不能直接输入到popnet当中的,需要用以下代码(convertPop.cpp)进行转换,具体的实现思路我还在领会当中,后面我补一下:
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
class CommunicationRecord;
class Chiplet {
public:
void setTime(unsigned long long time) {
this->chipletStartCycle = time;
}
Chiplet() :chipletStartCycle(0), chipletNumber(-1) {
//do nothing
}
int chipletNumber;
unsigned long long chipletStartCycle;
std::vector<CommunicationRecord*> relatedRecord;
// if the srcCore number is the ChipletNumber, the record will be put here
};
class CommunicationRecord {
public:
CommunicationRecord()
:cycle(0), srcCore(0), targetCore(0) {
}
CommunicationRecord(unsigned long long _cycle, int _srcCore, int _targetCore) {
this->cycle = _cycle;
this->srcCore = _srcCore;
this->targetCore = _targetCore;
}
unsigned long long cycle;
int srcCore;
int targetCore;
};
/*
* this Program is aimed to generate the popnet trace file from the communication record
这段代码主要是用来生成一个名为bench.0.x的文件,其中x表示芯片的编号。这个文件包含了该芯片发送的所有消息的记录。
首先,对于每个芯片,都会创建一个输出文件,以"bench.0."+x的形式命名。然后,会在所有芯片的通信记录中找出所有源芯片编号为x的记录,并存入一个临时的记录数组中。这些记录会根据时间进行排序,然后写入文件中。每行记录的格式如下:
cycle 0 srcCore 0 targetCore 5
*/
std::string communicationBaseFileName = "communication";
int TotalChipletNumber = 0;
unsigned long long chipletNumberZeroStartCycle;
void sortTheChipletRecord(unsigned long long* cycle, int* sequency, int length);
// 输出bench0.0 bench0.1 等文件
void outputSenderFile(Chiplet* ChipletSet) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < ::TotalChipletNumber; j++) {
std::ofstream file;
int chipletNumber = j;
std::string baseName = "bench.0.";
baseName += char(chipletNumber + '0');
file.open(baseName.c_str(), std::ios::out);
// look for the record whose srcCore is j
std::vector<CommunicationRecord*> tmpRecordSet;
for (size_t i = 0; i < ::TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
for (size_t k = 0; k < ChipletSet[i].relatedRecord.size(); k++) {
CommunicationRecord* tmp = ChipletSet[i].relatedRecord[k];
if (tmp->srcCore == chipletNumber) {
tmpRecordSet.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
// sort the record
CommunicationRecord* record2sort = new CommunicationRecord[tmpRecordSet.size()]();
int* sequency = new int[tmpRecordSet.size()]();
unsigned long long* cycle = new unsigned long long[tmpRecordSet.size()];
for (size_t j = 0; j < tmpRecordSet.size(); j++) {
record2sort[j] = *tmpRecordSet[j];
sequency[j] = j;
cycle[j] = tmpRecordSet[j]->cycle;
}
sortTheChipletRecord(cycle, sequency, tmpRecordSet.size());
for (int i = 0; i < tmpRecordSet.size(); i++) {
record2sort[i] = *tmpRecordSet[sequency[i]];
}
// write to the sender file
for (int i = 0; i < tmpRecordSet.size(); i++) {
unsigned long long cycle = unsigned long long(((record2sort[i]).cycle -
chipletNumberZeroStartCycle) / 1000);
int targetCore = record2sort[i].targetCore;
file << cycle << " 0 " << j << " 0 " << targetCore
<< " 5" << std::endl;
}
file.close();
}
}
// 输出bench文件
void outputTheFile(CommunicationRecord* Record, int length) {
std::ofstream file;
file.open("bench", std::ios::out);
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; i++) {
unsigned long long cycle = unsigned long long((Record[i].cycle -
chipletNumberZeroStartCycle) / 1000);
int srcCore = Record[i].srcCore;
int targetCore = Record[i].targetCore;
file << cycle << " 0 " << srcCore << " 0 " << targetCore
<< " 5" << std::endl;
}
file.close();
}
// 用于生成全部trace文件
void generatePopnetTraceFile(Chiplet* chipletSet) {
int recordSize = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < ::TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
recordSize += chipletSet[i].relatedRecord.size();
}
//bool* recordComplete = new bool[::TotalChipletNumber]();
int* ptr2ChipletRecord = new int[::TotalChipletNumber]();
CommunicationRecord* TotalRecord = new CommunicationRecord[recordSize]();
for (size_t i = 0; i < recordSize; i++) {
bool init = false;
CommunicationRecord tmpRecord = CommunicationRecord(0, 0, 0);
int targetChipletNumber = -1;
for (size_t j = 0; j < ::TotalChipletNumber; j++) {
if (ptr2ChipletRecord[j] >= chipletSet[j].relatedRecord.size()) {
continue;
}
if (!init) {
tmpRecord = *chipletSet[j].relatedRecord[ptr2ChipletRecord[j]];
init = true;
targetChipletNumber = j;
}
// compare the time and decide the min
if ((chipletSet[j].relatedRecord[ptr2ChipletRecord[j]])->cycle < tmpRecord.cycle) {
tmpRecord = *chipletSet[j].relatedRecord[ptr2ChipletRecord[j]];
targetChipletNumber = j;
}
}
TotalRecord[i] = tmpRecord;
ptr2ChipletRecord[targetChipletNumber]++;
}
outputTheFile(TotalRecord, recordSize);
outputSenderFile(&chipletSet[0]);
}
void swap(int* first, int* second) {
int* tmp = first;
second = tmp;
first = second;
}
void swap(unsigned long long* first, unsigned long long* second) {
unsigned long long* tmp = first;
second = tmp;
first = second;
}
void sortTheChipletRecord(unsigned long long* cycle, int* sequency, int length) {
//buble sort because not requring high performance
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < length - 1; j++)
{
if (cycle[j] > cycle[j + 1]) {
swap(&cycle[j], &cycle[j + 1]);
swap(&sequency[j], &sequency[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
// 排序时间,防止出现cycle无法对齐的情况
void sortChipletTime(Chiplet* chipletSet) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < ::TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
// for each chiplet
Chiplet* currentChiplet = &chipletSet[i];
int size = currentChiplet->relatedRecord.size();
CommunicationRecord* tmp = new CommunicationRecord[size];
int* sequency = new int[size]();
unsigned long long* cycle = new unsigned long long[size];
for (size_t j = 0; j < size; j++) {
tmp[j] = *currentChiplet->relatedRecord[j];
sequency[j] = j;
cycle[j] = currentChiplet->relatedRecord[j]->cycle;
}
sortTheChipletRecord(cycle, sequency, (chipletSet[i]).relatedRecord.size());
currentChiplet->relatedRecord.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
currentChiplet->relatedRecord.push_back(&tmp[sequency[i]]);
}
}
}
// 查找chiplet的开始时间,因为gem5启动操作系统一般需要几十万cycle的开销。
void initChipletStartPoint(Chiplet* chiplet, bool isMainChiplet = false, unsigned long long
mainChipletCycle = 0) {
// here is some stuff that something must be fixed in the future
chiplet->setTime(chiplet->relatedRecord[0]->cycle);
if (!isMainChiplet) {
unsigned long long base = chiplet->relatedRecord[0]->cycle;
chiplet->relatedRecord[0]->cycle = chiplet->relatedRecord[0]->cycle - base +
mainChipletCycle + (rand() % 20) * 1000;
for (size_t i = 1; i < chiplet->relatedRecord.size(); i++) {
chiplet->relatedRecord[i]->cycle = chiplet->relatedRecord[i]->cycle - base +
mainChipletCycle;
}
}
else {
}
}
void processOneFile(Chiplet* chipletSet, int currentChipletNumber) {
std::ifstream myFile;
std::string realFile = communicationBaseFileName + (char)(currentChipletNumber + '0');
myFile.open(realFile.c_str(), std::ios::in);
std::stringstream ss;
std::string line = "";
while (std::getline(myFile, line)) {
ss.clear();
ss.str(line);
unsigned long long cycle;
int srcCoreNumber;
int targetCoreNumber;
int data;// we don't need it but for skipping
ss >> cycle >> srcCoreNumber >> targetCoreNumber >> data;
if (targetCoreNumber == -1) {// the message is for all
CommunicationRecord* tmp = new CommunicationRecord(cycle, srcCoreNumber,
currentChipletNumber);
for (size_t i = 0; i < ::TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
chipletSet[i].relatedRecord.push_back(tmp);
}
}
else {
chipletSet[targetCoreNumber].relatedRecord.push_back(new
CommunicationRecord(cycle, srcCoreNumber, currentChipletNumber));
}
}
myFile.close();
}
int main() {
std::cout << "Enter the TotalChipletNumber" << std::endl;
std::cin >> ::TotalChipletNumber;
//bool* chipletInit = new bool[TotalChipletNumber]();
Chiplet* myChipletSet = new Chiplet[::TotalChipletNumber]();
for (int i = 0; i < TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
myChipletSet[i].chipletNumber = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ::TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
processOneFile(myChipletSet, i);
}
sortChipletTime(myChipletSet);
initChipletStartPoint(&myChipletSet[0], true);
for (size_t i = 1; i < ::TotalChipletNumber; i++) {
initChipletStartPoint(&myChipletSet[i], false, myChipletSet[0].chipletStartCycle);
}
chipletNumberZeroStartCycle = myChipletSet[0].relatedRecord[0]->cycle;
generatePopnetTraceFile(myChipletSet);
return 0;
}四、benchmark和测试文件
我是天使,贴一下几个benchmark和测试文件,有的文件加了注释和输出测试:
(1)测试gadia_receive和gadia_call函数: test.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include "../gem5/m5ops.h"
/*
本示例test.cpp, 用于测试gadia_receive和gadia_call函数
*/
extern "C"
{
const int N = 500;
int main() {
cout << "let's test call function" << endl;
m5_gadia_call(0, 0, 0, 0);
m5_gadia_call(1, 0, 1, 0);
m5_gadia_call(2, 1, 0, 0);
m5_gadia_call(3, 1, 1, 0);
cout << "let's test receive function" << endl;
uint64_t a = m5_gadia_receive(0);
cout << " m5_gadia_receive(0) return " << a << endl;
a = m5_gadia_receive(0);
cout << "once again! m5_gadia_receive(0) return " << a << endl;
a = m5_gadia_receive(1);
cout << " m5_gadia_receive(1) return " << a << endl;
a = m5_gadia_receive(2);
cout << " m5_gadia_receive(2) return " << a << endl;
cout << (uint64_t)-4 << " " << (uint64_t)-3 << " " << (uint64_t)-2 << " " << (uint64_t)-1 <<endl;
cout << "finished " << (a==(uint64_t)-4) << (a==(uint64_t)-3) << (a==(uint64_t)-2) << (a==(uint64_t)-1) << endl;
return 0;
}
}(2)进一步测试: test.cpp
这个是基于2个Chiplet的矩阵乘法,我看完代码之后,我觉得应该先输入1再输入0,然后再通过convertPop.cpp将communication输出转化为bench文件输出计算正确的时间性能。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//#include "gem5/m5ops.h"
/*
本示例示范 2 个 chiplet 做 500*500 的矩阵乘工作,假设结果为 C,则 C 的大小为
500*500,用一维矩阵储存,则 chiplet0 计算矩阵乘 C 索引从 0 到 500*249 的结果,而
chiplet1 计算剩下的结果。
*/
extern "C"
{
const int N = 500;
int main() {
// 程序初始化开始
long long *martrix = (long long *)malloc(N * N * sizeof(long long));
for (int i = 0; i < N * N; i++) {
srand(i);
martrix[i] = rand() % 10;
}
cout << "init martrix" << endl;
long long *martrix2 = (long long *)malloc(N * N * sizeof(long long));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
srand(i + j);
martrix2[i * N + j] = rand() % 10;
}
}
cout << "init martrix2" << endl;
long long *martrix3 = (long long *)malloc(N * N * sizeof(long long));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
martrix3[i * N + j] = 0;
}
}
cout << "init martrix3" << endl;
// 初始化结束
// 初始化 gem5 的相关信息
int chipletNumber = -1;
cout << "enter the ChipletNumber" << endl;
std::cin >> chipletNumber;
// 完成 gem5 的相关信息初始化
m5_gadia_call(chipletNumber, chipletNumber, 0, 0); // 记录启始 cycle
// 示例的 totalChipletNumber 为 2,故不显式的写出来。
if (chipletNumber == 0) {
for (int i = N / 2; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
martrix3[i * N + j] = martrix3[i * N + j] + martrix[i * N + k] * martrix2[k * N + j];
}
}
m5_gadia_call(chipletNumber, 1, -2, 0);
int position = 0;
cout << " coming 0" << "coming while" << endl;
while (true) {
int result = (int)m5_gadia_receive(chipletNumber);
// 检测 chiplet1 是否完成了矩阵乘的工作
if(result == -1)
continue;
else if (result == -2) //代表等待的Chiplet已经完成读写
break;
else {
martrix3[position] = result;
position++;
}
}
m5_gadia_call(chipletNumber, chipletNumber, 0, 0); // 记录结束 cycle
return 0;
}// the following is responsible for collect
else if (chipletNumber == 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < N / 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < N; k++)
martrix3[i * N + j] = martrix3[i * N + j] + martrix[i * N + k] * martrix2[k * N + j];
// chiplet 1 把结果写入到共享储存中。
m5_gadia_call(chipletNumber, 0, (int)martrix3[i * N + j], 0);
}
}
cout << "coming 1" << endl;
// 告诉 chiplet0, chiplet1 已经完成矩阵乘法
m5_gadia_call(chipletNumber, 0, -2, 0);
return 0;
}
}
}(3)benchmark test01.cpp:矩阵乘法,
经我推敲,id输入0,theChipletScale输入9,N输入100应该可以,但是我还在测试,说实话我感觉这个theChipletScale没啥太大作用(可能我还没有领会到,因为thread_num=4已经写死了),代码思路我领会了并标注在了源代码上。
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstring>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "../gem5/m5ops.h"
using namespace std;
int* matrix1;
int* matrix2;
int* matrix3;
int N = 300;
int theChipletScale;
const int thread_num = 4;
int coreNum;
extern "C"{
void init(int id){
// 使用 sysconf 函数获取当前系统的 CPU 核心数,并将结果保存在 coreNum 变量中。
coreNum = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN);
// initialize matrix
matrix1 = (int*)malloc(N*N*sizeof(int));
matrix2 = (int*)malloc(N*N*sizeof(int));
matrix3 = (int*)malloc(N*N*sizeof(int));
for(int i = 0;i < N*N;i++){
matrix1[i] = 1;
matrix2[i] = 2;
}
memset(matrix3, 0, N*N*sizeof(int));
// initialize the info about the gem5
m5_gadia_call(id, 1, 0, 0);
cout << "init finished" << endl;
}
}
struct Args{
int offset;
int length;
pthread_barrier_t *barrier;
// Variables needed for timing
int num_threads;
int *counter;
pthread_mutex_t *mtx;
pthread_cond_t *cond;
// timeb *start;
// timeb *end;
clock_t *start;
clock_t *end;
int processID;
};
//用于同步线程和测量线程的运行时间
void perf_cycle(int num_threads, int *counter, pthread_mutex_t *mtx, pthread_cond_t *cond, clock_t *time, int id){
// Get the lock
pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
// Atomically decrement number of outstanding threads
*counter -= 1;
// Check if we are the last thread
// If not, wait to be signaled
if(*counter == 0){
// Update a timing variable
if(id == 0){
//m5_gadia_call(id, 0, 0, 2);
}else{
cout << " counter == 0, start call/receive" << endl;
m5_gadia_call(id, 0, 0, 2);
uint64_t a;
while(1){
a = m5_gadia_receive(theChipletScale);
if(a == (uint64_t)-4){
break;
}
}
}
// ftime(time);
*time = clock();
// Reset the counter
*counter = num_threads;
// Signal everyone to continue,唤醒等待该条件满足的所有线程
pthread_cond_broadcast(cond);
}else{
// Wait for the last thread before continuing
// pthread_cond_wait 函数用于将当前线程挂起,直到接收到一个条件变量的信号,然后继续执行。
// 可以被pthread_cond_signal()或者是pthread_cond_broadcast()函数唤醒
pthread_cond_wait(cond, mtx);
cout << " id: " << id << "counter: " << *counter << "is waiting ……" << endl;
}
// Everyone unlocks
pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
}
void caculate(int offset, int length){
for(int i = 0;i< length;i++){
int current_x = (i + offset) / N; // 第x行
int current_y = (i + offset) % N; //第y列
for(int k = 0;k < N;k++)
matrix3[i + offset] = matrix3[i + offset] + matrix1[current_y*N + k] * matrix2[k * N + current_x];
// matrix1对应行,matrix2对应列
}
}
void toWrite(int offset, int length, pthread_mutex_t *mtx){
pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
for(int i = 0;i< length;i++){
m5_gadia_call(0, 0, matrix3[i + offset], 0);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
}
int core_counter = 0;
// Pthread function for computing
// Takes a pointer to a struct of args as an argument
void *matrix_parallel(void *args){
// Cast void pointer to struct pointer
Args *local_args = (Args*)args;
// cpu_set_t 是一种数据类型,表示一个集合,用于存储 CPU 编号。
// 可以使用 CPU_SET 函数将一个 CPU 编号添加到 cpu_set_t 类型的变量中,使用 CPU_ZERO 函数将其清空。
cpu_set_t mask;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
// Unpack the arguments
pthread_barrier_t *barrier = local_args->barrier;
int length = local_args->length;
int offset = local_args->offset;
int num_threads = local_args->num_threads;
int *counter = local_args->counter;
pthread_mutex_t *mtx = local_args->mtx;
pthread_cond_t *cond = local_args->cond;
clock_t *start = local_args->start;
clock_t *end = local_args->end;
int id = local_args->processID;
// 使用 pthread_mutex_lock 和 pthread_mutex_unlock 函数加锁和解锁互斥量,防止多个线程同时修改 core_counter 变量
pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
if(core_counter >= coreNum){
core_counter = 0;
}
// 将当前线程绑定到一个特定的 CPU 上
CPU_SET(core_counter, &mask);
int a = sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask);
std::cout <<"counter is: " << core_counter << " and affinity is: " << a << std::endl;
core_counter++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
cout << "执行perf_cycle: " << offset << "--" << length << endl;
// Wait for all threads to be created before profiling
perf_cycle(num_threads, counter, mtx, cond, start, id);
cout << "执行caculate: " << offset << "--" << length << endl;
caculate(offset, length);
cout << "执行toWrite: " << offset << "--" << length << endl;
toWrite(offset, length, mtx);
// Stop monitoring when last thread exits
cout << "执行perf_cycle2: " << offset << "--" << length << endl;
perf_cycle(num_threads, counter, mtx, cond, end, id);
// Write the data
//toWrite(offset, length, mtx);
cout << "完成perf_cycle: " << offset << "--" << length << endl;
return 0;
}
// Helper function create thread
void launch_threads(int num_threads, int id){
// Create array of thread objects we will launch
pthread_t threads[num_threads];
// Create a barrier and initialize it
// 线程屏障可以用来实现线程同步,可以在多个线程之间共享数据时使用
pthread_barrier_t barrier;
pthread_barrier_init(&barrier, NULL, num_threads);
cout << "线程屏障创建完毕" << endl;
// Create an array of structs to pass to the threads
Args thread_args[num_threads];
// Create variables for performance monitoring
int counter = num_threads;
// 初始化一个互斥量和一个条件变量
pthread_mutex_t mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
clock_t start;
clock_t end;
m5_gadia_call(0, 1, 0, -1);
while(1){
cout << "陷入m5_gadia_receive(theChipletScale)" << theChipletScale << endl;
uint64_t a = m5_gadia_receive(theChipletScale);
if(a == (uint64_t)-4)
break;
}
// Launch threads
for(int i = 0; i < num_threads; i++){
// Pack struct with its arguments
thread_args[i].barrier = &barrier;
thread_args[i].offset = i*N*N/thread_num/2 + id*N*N/2;
thread_args[i].length = N*N/thread_num/2;
thread_args[i].num_threads = num_threads;
thread_args[i].counter = &counter;
thread_args[i].mtx = &mtx;
thread_args[i].cond = &cond;
thread_args[i].start = &start;
thread_args[i].end = &end;
thread_args[i].processID = id;
// Launch the thread
cout << "创建线程: " << id << "--" << thread_args[i].offset << "--" << thread_args[i].length << endl;
pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, matrix_parallel, (void*)&thread_args[i]);
}
cout << "所有线程创建完毕" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < num_threads; i++){
// pthread_join 阻塞当前线程,直到指定的线程终止。在等待过程中,当前线程会被挂起,不会执行其他任务;
// 常用于在主线程中等待其他线程的终止,以确保所有线程都已经完成了任务
pthread_join(threads[i], NULL);
}
cout << "所有线程执行完毕" << endl;
// long long timeCost = (long long)end.time*1000+end.millitm - (long long)start.time*1000+start.millitm;
long long timeCost = (long long)end - (long long)start;
// Print out the time
cout << " time parallel = " << timeCost << " millionseconds" << endl;
}
void print(){
for(int i = 0;i < N*N;i++)
std::cout << matrix3[i] << " ";
}
// 300*300
// A chiplet scale is sql(N*N/chipletNum)
int main(){
int id;
std::cout << "enter the id" << std::endl;
std::cin >> id;
std::cout << "enter chiplet number" << std::endl;
std::cin >> theChipletScale;
std::cout << " the scale N is: " << std::endl;
std::cin >> N;
//N = (int)sqrt(300*300/theChipletScale);
init(id);
launch_threads(thread_num, id);
std::cout << "current thread_num is: " << thread_num << std::endl;
std::cout << "scale is: " << N << std::endl;
std::cout << "finished " << std::endl;
return 0;
}(3)benchmark test02.cpp:BFS
先来的友友先将就看,我还没有研究这个代码,我过几天领悟了再来补坑。
// C++ implementation of the approach
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/timeb.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include "../gem5/m5ops.h"
const int thread_Num = 3;
const int totalFileLine = 27807;
int totalVertex = 7624;
pthread_mutex_t *mtx;
pthread_cond_t *cond;
pthread_mutex_t *data_mtx;
pthread_t threads[thread_Num + 1];
pthread_barrier_t _barrier;
class Node;
int *totalNode;
int *resultNode;
int *processNode;
int *bfsQueue;
int bfsQueue_length= 0;
int bfsQueue_counter = 0;
bool *visited;
bool mainThread;
bool subThread;
bool SomebodyWaiting;
int coreNum;
int *thread_counter;
int initValue;
int theChipletScale;
int processID;
using namespace std;
timeb myStart;
timeb myEnd;
// every node has a number
struct myArgs
{
pthread_barrier_t *_barrier;
int thread_id;
};
// it indicates node number1 has an undirected edge
// to node number2
void connectNode(int number1, int number2, int *num)
{
// from number1 -> number2
int postion1 = number1 * totalVertex + number2;
// from number2 -> number1
int position2 = number2 * totalVertex + number1;
num[position2] = 1;
num[postion1] = 1;
}
void initVetex()
{
totalNode = (int *)malloc(totalVertex * totalVertex * sizeof(int));
memset(totalNode, 0, totalVertex * totalVertex * sizeof(int));
resultNode = (int *)malloc(totalVertex * totalVertex * sizeof(int));
memset(resultNode, 0, totalVertex * totalVertex * sizeof(int));
}
void initGraph()
{
initVetex();
// build the graph
FILE *file = fopen("./data.csv", "r");
fseek(file, 13L, 0);
for (int i = 0; i < totalFileLine; i++)
{
int a;
int b;
if (fscanf(file, "%d,%d", &a, &b) == EOF)
break;
connectNode(a, b, totalNode);
}
fclose(file);
}
int unsafeGetData(bool isMain)
{
int tmp = -1;
if(!isMain && bfsQueue_length - bfsQueue_counter <= 2)
return tmp;
if (bfsQueue[bfsQueue_counter] == -1 || bfsQueue_counter == totalVertex)
return tmp;
pthread_mutex_lock(data_mtx);
if (bfsQueue_counter == bfsQueue_length)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(data_mtx);
return tmp;
}
tmp = bfsQueue[bfsQueue_counter];
bfsQueue_counter += 1;
pthread_mutex_unlock(data_mtx);
if ( isMain &&bfsQueue_length - bfsQueue_counter >= 5)
{
//pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
//std::cout << k++ << std::endl;
if (*thread_counter != thread_Num)
{
//std::cout << "let it go !" << std::endl;
pthread_cond_broadcast(::cond);
//SomebodyWaiting = false;
}
//pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
}
return tmp;
}
void init()
{
//std::cout << "enter id" << std::endl;
//std::cin >> processID;
/*
if(processID == 0)
initValue = 0;
else
initValue = 6666;
*/
initGraph();
//threadLib = (bool*)malloc((thread_Num + 1)*sizeof(bool));
visited = (bool *)malloc(totalVertex * sizeof(bool));
memset(visited, 0, totalVertex * sizeof(bool));
//memset(threadLib, 0, (thread_Num + 1)*sizeof(bool));
mainThread = false;
subThread = false;
SomebodyWaiting = false;
coreNum = sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN);
}
void printGraph()
{
for (int i = 0; i < totalVertex; i++)
{
std::cout << i << "-> ";
for (int j = 0; j < totalVertex; j++)
{
if (totalNode[i * totalVertex + j] == 1)
std::cout << j << ",";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
void printResult()
{
for (int i = 0; i < totalVertex; i++)
{
std::cout << i << "-> ";
for (int j = 0; j < totalVertex; j++)
{
if (resultNode[i * totalVertex + j] == 1)
std::cout << j << ",";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
bool whertherInLine(int id, int *myStack, int _counter)
{
int counter = _counter;
// from counter 2 the end of stack
while (1)
{
if (counter == totalVertex)
{
return false;
}
if (myStack[counter] == -1)
return false;
if (myStack[counter] == id)
return true;
counter++;
}
}
void processCurrentNode(int id, int *length, int *myStack)
{
if (visited[id])
return;
else{
// some collision will occur if the call is executed
//m5_gadia_call(processID, 0, id, 0);
}
visited[id] = true;
//std::cout << id << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < totalVertex; i++)
{
if (totalNode[id * totalVertex + i] == 1 && visited[i] == false)
{
if (!whertherInLine(i, myStack, 0))
{
//std::cout << i << " ";
myStack[*length] = i;
*length += 1;
m5_gadia_call(0, 0, i, 0);
}
}
}
//std::cout << *length << std::endl;
}
void* normalBFS_for_test(void* args)
{
// We define the totalNode[0] as the root which we will start our work
int previous = initValue;
// stack initialization
bfsQueue = (int *)malloc(totalVertex * sizeof(int));
// -1 indicates the value is not initialized
for (int i = 0; i < totalVertex; i++)
{
bfsQueue[i] = -1;
}
pthread_barrier_wait(&::_barrier);
//myStack[0] = previous;
while (1)
{
processCurrentNode(previous, &::bfsQueue_length, ::bfsQueue);
if (bfsQueue[bfsQueue_counter] == -1 || bfsQueue_counter == totalVertex)
break;
int current = unsafeGetData(true);
if(current == -1)
break;
connectNode(previous, current, resultNode);
previous = current;
}
mainThread = true;
std::cout << "mainThread is over" << std::endl;
while(!subThread){
std::cout << *thread_counter << std::endl;
//busy waitting
}
ftime(&::myEnd);
//normalBFS_for_test();
//printGraph();
//printResult();
long long timeCost = (long long)::myEnd.time*1000+::myEnd.millitm - (long long)::myStart.time*1000+::myStart.millitm;
// Print out the time
cout << "Thread Number is: " << thread_Num << std::endl;
cout << " time parallel = " << timeCost << " millionseconds" << endl;
return NULL;
}
void stackPush(int* singleStack, int* counter, int value){
*counter += 1;
singleStack[*counter] = value;
}
void my_DFS(int id)
{
int* singleStack = (int*)malloc(totalVertex*sizeof(int));
int* counter;
int a = -1;
counter = &a;
// init the stack
for(int i = 0;i < totalVertex;i++){
singleStack[i] = -1;
}
stackPush(singleStack, counter, id);
int previous = id;
while (1)
{
//std::cout << previous << " ";
for (int i = 0; i < totalVertex; i++)
{
int current_vertex = i;
if (visited[current_vertex])
continue;
// first we check the node
if (whertherInLine(current_vertex, bfsQueue, 0))
{
continue;
}
// then we let it be visited
visited[current_vertex] = true;
m5_gadia_call(0, 0, current_vertex, 0);
// finally we add it to the thread_stack
stackPush(singleStack, counter, current_vertex);
}
if (*counter == -1)
break;
int current = singleStack[*counter];
singleStack[*counter] = -1;
*counter -= 1;
//thread_stack.pop();
connectNode(previous, current, resultNode);
previous = current;
}
}
bool anotherChipletCmplt = false;
void* checkThread(void* args){
while(1){
if(mainThread && subThread)
break;
uint64_t result = m5_gadia_receive(-1);
if(result == (uint64_t)-2 || result == (uint64_t)-1 ||result == (uint64_t)-4 || result == (uint64_t)-6)
continue;
int tmp = (int)result;
//std::cout << tmp << std::endl;
visited[tmp] = true;
}
//m5_gadia_call(processID, 0, 0, 1);
return NULL;
}
// -1 means the function should quit
int Idon_tKnowHow2Quit()
{
int tmp = -1;
pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
tmp = unsafeGetData(false);
if (tmp == -1)
{
SomebodyWaiting = true;
//std::cout << "Before thread_counter is: " << *thread_counter << std::endl;
*thread_counter -= 1;
if (*thread_counter == 0){
subThread = true;
std::cout << "subThread is true" << std::endl;
}
//std::cout << "one to sleep" << std::endl;
//pthread_cond_wait(cond, mtx);
while(1){
pthread_cond_wait(cond, mtx);
tmp = unsafeGetData(false);
if(tmp != -1)
break;
}
subThread = false;
*thread_counter += 1;
//std::cout << " Afer thread_counter is: " << *thread_counter << std::endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
return tmp;
}else{
pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
return tmp;
}
//std::cout << "one go ahead" << std::endl;
//subThread = false;
//*thread_counter += 1;
//std::cout << " Afer thread_counter is: " << *thread_counter << std::endl;
pthread_mutex_unlock(mtx);
return tmp;
}
int core_counter = 0;
void *pthread2DFS(void *args)
{
cpu_set_t mask;
CPU_ZERO(&mask);
pthread_mutex_lock(mtx);
if (core_counter >= coreNum)
{
core_counter = 0;
}
CPU_SET(core_counter, &mask);
int a = sched_setaffinity(0, sizeof(mask), &mask);
std::cout << "counter is: " << core_counter << " and affinity is: " << a << std::endl;
core_counter++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(::mtx);
pthread_barrier_wait(&::_barrier);
// here we should wait the other thread enter the area
// create a stack with a list which we can check the element
while (1)
{
int tmp = Idon_tKnowHow2Quit();
if (tmp == -1)
continue;
//std::cout << tmp << " " ;
my_DFS(tmp);
}
//std::cout << "one thread complt" << std::endl;
return NULL;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
std::cout << "enter the root(initValue)" << std::endl;
std::cin >> initValue;
std::cout << "enter chiplet number" << std::endl;
std::cin >> theChipletScale;
init();
std::cout << "init done !" << std::endl;
m5_gadia_call(0, 0, 0, 1);
while(1){
uint64_t a = m5_gadia_receive(theChipletScale);
if(a == (uint64_t)-4)
break;
}
std::cout << "start!" << std::endl;
//initPthread
pthread_mutex_t _mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_cond_t _cond = PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;
::mtx = &_mtx;
::cond = &_cond;
pthread_barrier_init(&::_barrier, NULL, thread_Num + 1);
pthread_mutex_t _data_mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
::data_mtx = &_data_mtx;
int a = thread_Num;
::thread_counter = &a;
//m5_gadia_call(processID, 1, 0, 0);
for(int i = 0;i < thread_Num;i++){
pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL, pthread2DFS, NULL);
}
pthread_t check;
pthread_create(&check, NULL, checkThread, NULL);
pthread_detach(check);
pthread_create(&threads[thread_Num], NULL, normalBFS_for_test, NULL);
ftime(&::myStart);
ftime(&::myEnd);
// initPthread
// let threads go
for(int i = 0;i <= thread_Num;i++){
pthread_detach(threads[i]);
}
while(!subThread || !mainThread){
// busy waiting
}
ftime(&::myEnd);
//normalBFS_for_test();
//printGraph();
//printResult();
long long timeCost = (long long)::myEnd.time*1000+myEnd.millitm - (long long)::myStart.time*1000+myStart.millitm;
// Print out the time
cout << "Thread Number is: " << thread_Num << std::endl;
cout << " time parallel = " << timeCost << " millionseconds" << endl;
}



![[UE笔记]延迟与延迟补偿](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2420d56cf00f4ab8a6365f289187145a.png)