文章目录
- 区间问题
- 905. 区间选点(排序 + 贪心)
- 908. 最大不相交区间数量(排序 + 贪心)
- 906. 区间分组(排序 + 优先队列 + 贪心)⭐
- 907. 区间覆盖(排序 + 贪心)
- Huffman树
- 148. 合并果子(优先队列 + 贪心)
- 排序不等式
- 913. 排队打水
- 绝对值不等式
- 104. 货仓选址(选中点位置)
- 推公式
- 125. 耍杂技的牛⭐⭐⭐
区间问题
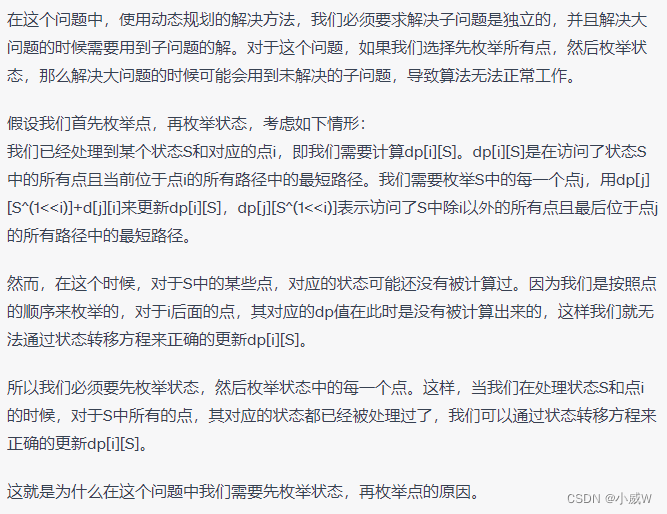
对于区间问题,通常需要先排序,(一般情况下都是左端点排序)。
相关链接:【算法】区间合并类题目总结
905. 区间选点(排序 + 贪心)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1111/
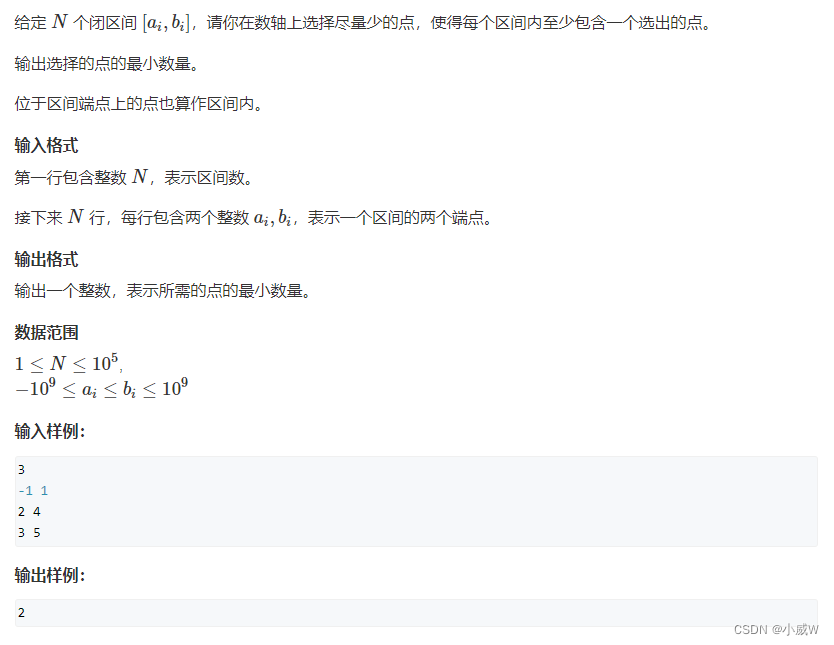
解法可见:【算法】区间合并类题目总结 的问题 —— 452. 用最少数量的箭引爆气球
可以左边界排序 或 右边界排序。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[][] r = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
r[i][0] = sc.nextInt();
r[i][1] = sc.nextInt();
}
// 按起点升序排序
Arrays.sort(r, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int ans = 0, last = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int[] cur: r) {
if (cur[0] <= last) last = Math.min(last, cur[1]);
else {
++ans;
last = cur[1];
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
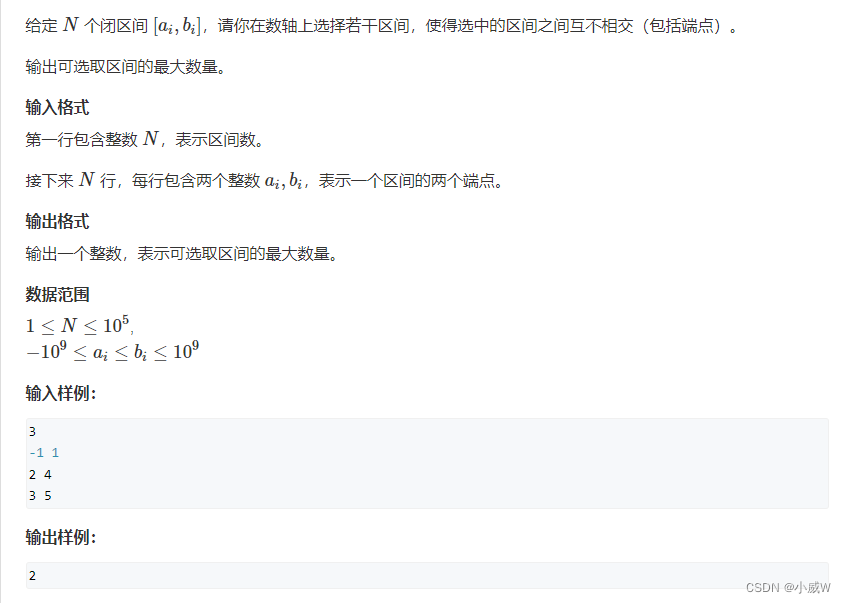
908. 最大不相交区间数量(排序 + 贪心)
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1112/
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int n = sin.nextInt();
int[][] r = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
r[i][0] = sin.nextInt();
r[i][1] = sin.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(r, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]); // 左端点排序
int ans = 0, last = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int[] x: r) {
if (x[0] > last) {
++ans;
last = x[1];
} else {
last = Math.min(last, x[1]);
}
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
906. 区间分组(排序 + 优先队列 + 贪心)⭐
https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/problem/content/1113/

贪心思路:

使用优先队列来维护所有组的结束端点位置,这样就可以快速找到当前结束位置最靠前的组。
最后优先队列中有多少元素就表示需要多少组。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = sin.nextInt();
int[][] r = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
r[i][0] = sin.nextInt();
r[i][1] = sin.nextInt();
}
Arrays.sort(r, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]); // 左端点排序
// pq 里存储了各个组的结束位置(从小到大排列)
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int[] x: r) {
if (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek() < x[0]) pq.poll(); // 如果可以加入当前存在的组
pq.offer(x[1]);
}
System.out.println(pq.size());
}
}
907. 区间覆盖(排序 + 贪心)
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/909/

每次贪心地找出符合左端点 <= start 的区间中右端点最远的那个。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int s = sin.nextInt(), t = sin.nextInt();
int n = sin.nextInt();
int[][] r = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
r[i][0] = sin.nextInt();
r[i][1] = sin.nextInt();
}
// 左端点升序排序
Arrays.sort(r, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int ans = 0, last = s - 1;
for (int i = 0, j; i < n && last < t; ++i) {
j = i; // j 从 i 开始枚举
// 找到左端点<= s的区间中,右端点最大的那个
while (j < n && r[j][0] <= s) {
last = Math.max(last, r[j][1]);
++j;
}
++ans;
s = last + 1; // 更新当前需要的开始端点
i = Math.max(i, j - 1);
}
System.out.println(last >= t? ans: -1);
}
}
Huffman树
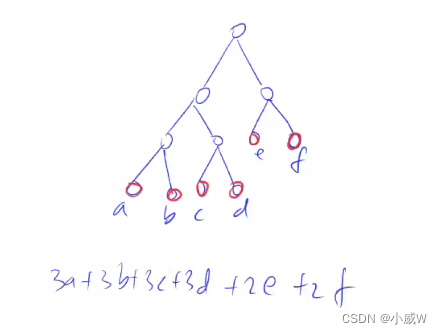
148. 合并果子(优先队列 + 贪心)
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/150/

贪心得想,每次先合并体力耗费小的。(因为先合并的对答案的贡献次数多)。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = sin.nextInt();
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) pq.offer(sin.nextInt());
int ans = 0;
while (pq.size() > 1) {
int c = pq.poll() + pq.poll();
pq.offer(c);
ans += c;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
排序不等式
913. 排队打水
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/915/

先让接的快的人接水。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = sin.nextInt();
long[] times = new long[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) times[i] = sin.nextInt();
Arrays.sort(times);
long ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans += times[i] * (n - i - 1);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
绝对值不等式
104. 货仓选址(选中点位置)
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/106/
选择中点位置即可。
具体的操作是找中位数。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = sin.nextInt();
long[] a = new long[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) a[i] = sin.nextLong();
Arrays.sort(a);
long pos = a[n / 2], ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans += Math.abs(pos - a[i]);
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}
推公式
125. 耍杂技的牛⭐⭐⭐
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/127/

结论:按照 wi + si 从小到大的顺序排,最大的危险系数一定是最优的。
如何证明?—— 反证法
 看 i 和 i + 1 交换位置之后会发生什么。
看 i 和 i + 1 交换位置之后会发生什么。
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
int n = sin.nextInt();
int[][] cows = new int[n][2];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int w = sin.nextInt(), s = sin.nextInt();
cows[i][0] = w + s;
cows[i][1] = w;
}
Arrays.sort(cows, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int ans = 0, sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
int s = cows[i][0] - cows[i][1], w = cows[i][1];
ans = Math.max(ans, sum - s);
sum += w;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
}