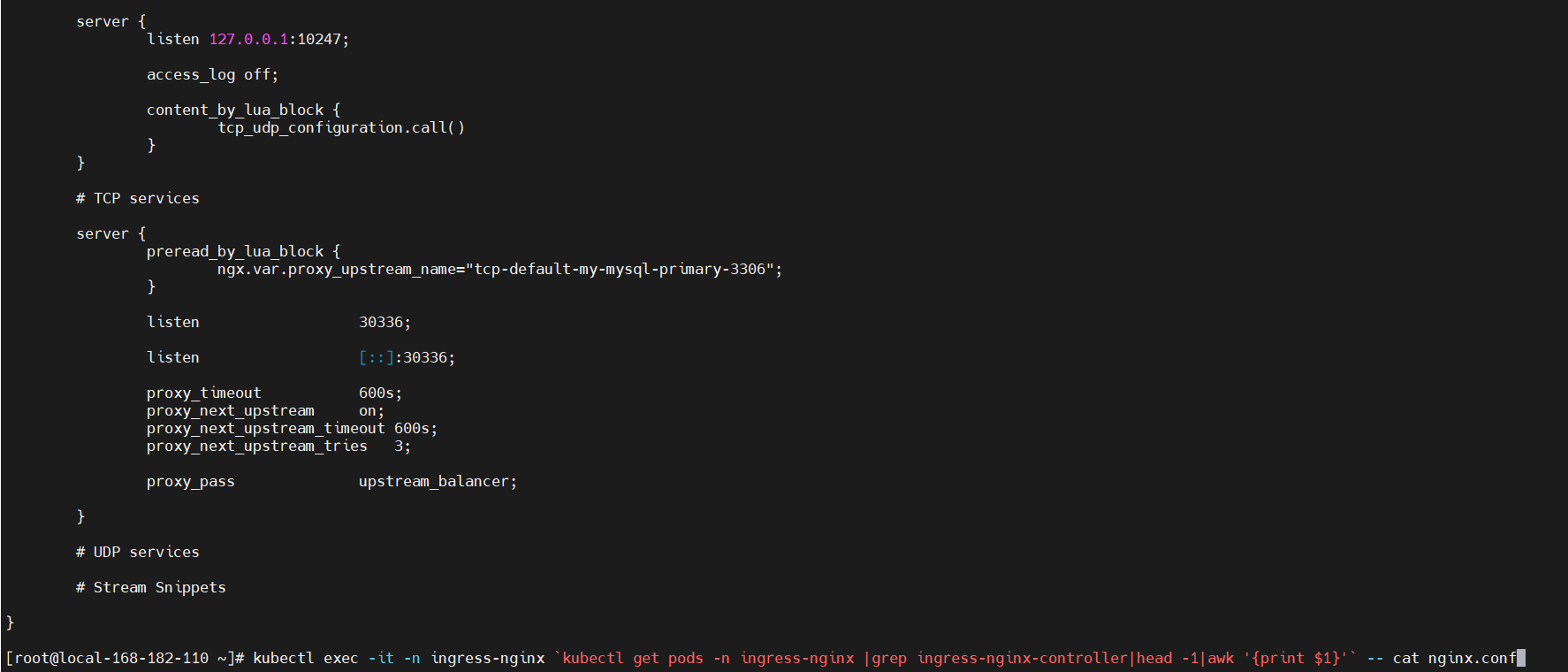
文章目录
- 一、PyTorch环境检查
- 二、查看张量类型
- 三、查看张量尺寸和所占内存大小
- 四、创建张量
- 4.1 创建值全为1的张量
- 4.2 创建值全为0的张量
- 4.3 创建值全为指定值的张量
- 4.4 通过 list 创建张量
- 4.5 通过 ndarray 创建张量
- 4.6 创建指定范围和间距的有序张量
- 4.7 创建单位矩阵(对角线为1)
- 五、生成随机张量
- 5.1 按均匀分布生成
- 5.2 按标准正态分布生成
- 5.3 生成指定区间的整型随机张量
- 5.4 获取随机序列
- 六、张量的索引与切片
- 6.1 索引
- 6.2 切片
- 6.2.1 获取张量的前/后N个元素
- 6.2.2 根据指定步长获取张量的前/后N个元素
- 6.2.3 根据特殊索引获取张量值
- 6.2.4 根据 mask 选取张量值
- 6.2.5 根据展平的索引获取张量值
- 七、张量的维度变换
- 7.1 view 和 reshape 尺寸变换
- 7.2 unsqueeze 升维
- 7.3 squeeze 降维
- 7.4 expand 扩展
- 7.5 repeat 复制
- 7.6 .t() 转置
- 7.7 transpose 维度变换
- 7.8 permute 维度变换
- 八、张量的拼接和拆分
- 8.1 cat
- 8.2 stack
- 8.3 split
- 8.4 chunk
- 九、基本运算
- 9.1 广播机制
- 9.2 matmul 矩阵/张量乘法
- 9.3 pow 次方运算
- 9.4 sqrt 平方根运算
- 9.5 exp 指数幂运算
- 9.6 log 对数运算(相当于 ln)
- 9.7 取整
- 9.8 clamp 控制张量的取值范围
- 十、统计属性
- 10.1 norm 求范数
- 10.2 mean、median、sum、min、max、prod、argmax、argmin
- 10.3 topk 获取最大的k个值
- 10.4 kthvalue 获取第k大的值
- 10.5 比较运算函数
- 十一、高级操作
- 11.1 where
- 11.2 gather
一、PyTorch环境检查
import torch
# 输出PyTorch版本
print(torch.__version__)
# 检查PyTorch是否支持GPU加速
print("cuda:", torch.cuda.is_available())
输出:
1.8.0+cu101
cuda: True
二、查看张量类型
import torch
a = torch.randn(2, 3)
b = torch.randint(0, 1, (2, 3))
print(a.type())
print(b.type())
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
print(isinstance(a, torch.FloatTensor))
print(isinstance(b, torch.FloatTensor))
输出:
torch.FloatTensor
torch.LongTensor
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
True
False
三、查看张量尺寸和所占内存大小
import torch
a = torch.randn(2, 3)
print(a.size(), type(a.size()))
print(a.shape, type(a.shape))
print("维度数:", a.dim())
print("所占内存大小:", a.numel())
输出:
torch.Size([2, 3]) <class 'torch.Size'>
torch.Size([2, 3]) <class 'torch.Size'>
维度数: 2
所占内存大小: 6
四、创建张量
4.1 创建值全为1的张量
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 3)
print(a)
输出:
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
4.2 创建值全为0的张量
import torch
a = torch.zeros(2, 3)
print(a)
输出:
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
4.3 创建值全为指定值的张量
import torch
a = torch.full([2, 3], 6.6)
print(a)
print(a.shape)
a = torch.full([], 6.6)
print(a)
print(a.shape)
输出:
tensor([[6.6000, 6.6000, 6.6000],
[6.6000, 6.6000, 6.6000]])
torch.Size([2, 3])
tensor(6.6000)
torch.Size([])
4.4 通过 list 创建张量
import torch
print(torch.LongTensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]))
print(torch.Tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]))
print(torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]))
输出:
tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]])
tensor([[1., 2.],
[3., 4.]])
4.5 通过 ndarray 创建张量
import torch
import numpy as np
a = np.array([2, 3.3])
print(type(a))
print(torch.from_numpy(a))
输出:
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
tensor([2.0000, 3.3000], dtype=torch.float64)
4.6 创建指定范围和间距的有序张量
import torch
print("torch.arange(0,10):", torch.arange(0, 10))
print("torch.arange(0,10,2):", torch.arange(0, 10, 2))
print("torch.linspace(0,10,steps = 4):", torch.linspace(0, 10, steps=4))
print("torch.linspace(0,10,steps = 10):", torch.linspace(0, 10, steps=10))
print("torch.linspace(0,10,steps = 11):", torch.linspace(0, 10, steps=11))
print("torch.logspace(0,-1,steps = 10):", torch.logspace(0, -1, steps=10))
print("torch.logspace(0,1,steps = 10):", torch.logspace(0, 1, steps=10))
输出:
torch.arange(0,10): tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
torch.arange(0,10,2): tensor([0, 2, 4, 6, 8])
torch.linspace(0,10,steps = 4): tensor([ 0.0000, 3.3333, 6.6667, 10.0000])
torch.linspace(0,10,steps = 10): tensor([ 0.0000, 1.1111, 2.2222, 3.3333, 4.4444, 5.5556, 6.6667, 7.7778,
8.8889, 10.0000])
torch.linspace(0,10,steps = 11): tensor([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10.])
torch.logspace(0,-1,steps = 10): tensor([1.0000, 0.7743, 0.5995, 0.4642, 0.3594, 0.2783, 0.2154, 0.1668, 0.1292,
0.1000])
torch.logspace(0,1,steps = 10): tensor([ 1.0000, 1.2915, 1.6681, 2.1544, 2.7826, 3.5938, 4.6416, 5.9948,
7.7426, 10.0000])
4.7 创建单位矩阵(对角线为1)
import torch
# n * n
print(torch.eye(3))
print(torch.eye(4, 4))
# 非 n * n
print(torch.eye(2, 3))
输出:
tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1.]])
tensor([[1., 0., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]])
tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 0.]])
五、生成随机张量
5.1 按均匀分布生成
均匀分布:0-1之间
import torch
# 生成shape为(2,3,2)的Tensor
random_tensor = torch.rand(2, 3, 2)
print(random_tensor)
print(type(random_tensor))
print(random_tensor.shape)
输出:
tensor([[[0.3321, 0.7077],
[0.8372, 0.2545],
[0.5849, 0.0312]],
[[0.6792, 0.8339],
[0.9689, 0.5579],
[0.2843, 0.6578]]])
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
5.2 按标准正态分布生成
标准正态分布:均值为0,方差为1
import torch
# 生成shape为(2,3,2)的Tensor
random_tensor = torch.randn(2, 3, 2)
print(random_tensor)
print(type(random_tensor))
print(random_tensor.shape)
输出:
tensor([[[ 1.6622, 1.4002],
[ 1.5145, -0.0427],
[ 0.4082, -0.3527]],
[[ 1.2381, -0.2409],
[-1.0770, -1.1289],
[-1.5798, 0.3093]]])
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
5.3 生成指定区间的整型随机张量
import torch
# 生成shape为(2,3,2)的Tensor
# 整数范围[1,4)
random_tensor = torch.randint(1, 4, (2, 3, 2))
print(random_tensor)
print(type(random_tensor))
print(random_tensor.shape)
输出:
tensor([[[3, 2],
[2, 2],
[3, 3]],
[[2, 1],
[2, 1],
[1, 1]]])
<class 'torch.Tensor'>
torch.Size([2, 3, 2])
5.4 获取随机序列
import torch
# torch中没有random.shuffle
# y = torch.randperm(n) y是把0到n-1这些数随机打乱得到的一个数字序列
# randperm(n, out=None, dtype=torch.int64)-> LongTensor
idx = torch.randperm(3)
a = torch.Tensor(4, 2)
print(a)
print(idx, idx.type())
print(a[idx])
输出:
tensor([[0.0000e+00, 5.5491e-43],
[1.8754e+28, 8.0439e+20],
[4.2767e-05, 1.0413e-11],
[4.2002e-08, 6.5558e-10]])
tensor([0, 1, 2]) torch.LongTensor
tensor([[0.0000e+00, 5.5491e-43],
[1.8754e+28, 8.0439e+20],
[4.2767e-05, 1.0413e-11]])
六、张量的索引与切片
6.1 索引
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)
print("a[0].shape:", a[0].shape)
print("a[0,0].shape:", a[0, 0].shape)
print("a[0,0,2,4]:", a[0, 0, 2, 4])
输出:
a[0].shape: torch.Size([3, 28, 28])
a[0,0].shape: torch.Size([28, 28])
a[0,0,2,4]: tensor(0.2935)
6.2 切片
6.2.1 获取张量的前/后N个元素
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)
print("a.shape:", a.shape)
print("a[:2].shape:", a[:2].shape)
print("a[:2,:1,:,:].shape:", a[:2, :1, :, :].shape)
print("a[:2,1:,:,:].shape:", a[:2, 1:, :, :].shape)
print("a[:2,-1:,:,:].shape:", a[:2, -1:, :, :].shape)
输出:
a.shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
a[:2].shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 28, 28])
a[:2,:1,:,:].shape: torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28])
a[:2,1:,:,:].shape: torch.Size([2, 2, 28, 28])
a[:2,-1:,:,:].shape: torch.Size([2, 1, 28, 28])
6.2.2 根据指定步长获取张量的前/后N个元素
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)
print("a.shape:", a.shape)
print("a[:,:,0:28:2,0:28:2].shape:", a[:, :, 0:28:2, 0:28:2].shape)
print("a[:,:,::2,::2].shape:", a[:, :, ::2, ::2].shape)
输出:
a.shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
a[:,:,0:28:2,0:28:2].shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14])
a[:,:,::2,::2].shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 14, 14])
6.2.3 根据特殊索引获取张量值
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)
print("a.shape:", a.shape)
print("a.index_select(0,torch.tensor([0,2])).shape:", a.index_select(0, torch.tensor([0, 2])).shape)
print("a.index_select(1,torch.tensor([1,2])).shape:", a.index_select(1, torch.tensor([1, 2])).shape)
print("a.index_select(2,torch.arange(28)).shape:", a.index_select(2, torch.arange(28)).shape)
print("a.index_select(2,torch.arange(8)).shape:", a.index_select(2, torch.arange(8)).shape)
print("a[...].shape:", a[...].shape)
print("a[0,...].shape:", a[0, ...].shape)
print("a[:,1,...].shape:", a[:, 1, ...].shape)
print("a[...,:2].shape:", a[..., :2].shape)
输出:
a.shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
a.index_select(0,torch.tensor([0,2])).shape: torch.Size([2, 3, 28, 28])
a.index_select(1,torch.tensor([1,2])).shape: torch.Size([4, 2, 28, 28])
a.index_select(2,torch.arange(28)).shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
a.index_select(2,torch.arange(8)).shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 8, 28])
a[...].shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
a[0,...].shape: torch.Size([3, 28, 28])
a[:,1,...].shape: torch.Size([4, 28, 28])
a[...,:2].shape: torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 2])
6.2.4 根据 mask 选取张量值
import torch
a = torch.rand(3,4)
print(a)
mask = a.ge(0.5)
print(mask)
b = torch.masked_select(a, mask)
print(b)
print(b.shape)
输出:
tensor([[0.6119, 0.3231, 0.8763, 0.6680],
[0.5421, 0.0359, 0.2040, 0.2894],
[0.5961, 0.7953, 0.2759, 0.7808]])
tensor([[ True, False, True, True],
[ True, False, False, False],
[ True, True, False, True]])
tensor([0.6119, 0.8763, 0.6680, 0.5421, 0.5961, 0.7953, 0.7808])
torch.Size([7])
6.2.5 根据展平的索引获取张量值
import torch
a = torch.Tensor([[4, 3, 5], [6, 7, 8]])
print(a)
print(torch.take(a, torch.tensor([0, 2, -1])))
输出:
tensor([[4., 3., 5.],
[6., 7., 8.]])
tensor([4., 5., 8.])
七、张量的维度变换
7.1 view 和 reshape 尺寸变换
view 和 reshape 的用法一致
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 1, 28, 28)
print(a.shape)
print(a.view(4, 28 * 28).shape)
print(a.view(4 * 28, 28).shape)
print(a.view(4, 28, 28, 1).shape)
输出:
torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 784])
torch.Size([112, 28])
torch.Size([4, 28, 28, 1])
7.2 unsqueeze 升维
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 1, 28, 28)
print("a.shape:", a.shape)
print("a.unsqueeze(0).shape:", a.unsqueeze(0).shape)
print("a.unsqueeze(-1).shape:", a.unsqueeze(-1).shape)
b = torch.rand(32)
print("b.shape:", b.shape)
print("b.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0).shape:", b.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0).shape)
输出:
a.shape: torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
a.unsqueeze(0).shape: torch.Size([1, 4, 1, 28, 28])
a.unsqueeze(-1).shape: torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28, 1])
b.shape: torch.Size([32])
b.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(0).shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
7.3 squeeze 降维
import torch
b = torch.rand(4, 1, 28, 28)
print("b.shape:", b.shape)
print("b.squeeze().shape:", b.squeeze().shape)
print("b.squeeze(0).shape:", b.squeeze(0).shape)
print("b.squeeze(-1).shape:", b.squeeze(-1).shape)
输出:
b.shape: torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
b.squeeze().shape: torch.Size([4, 28, 28])
b.squeeze(0).shape: torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
b.squeeze(-1).shape: torch.Size([4, 1, 28, 28])
7.4 expand 扩展
import torch
b = torch.rand(1, 32, 1, 1)
print("b.shape:", b.shape)
print("b.expand(4,32,14,14).shape:", b.expand(4, 32, 14, 14).shape)
print("b.expand(-1,32,-1,-1).shape:", b.expand(-1, 32, -1, -1).shape)
print("b.expand(-1,32,-1,4).shape:", b.expand(-1, 32, -1, 4).shape)
输出:
b.shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
b.expand(4,32,14,14).shape: torch.Size([4, 32, 14, 14])
b.expand(-1,32,-1,-1).shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
b.expand(-1,32,-1,4).shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 4])
7.5 repeat 复制
import torch
b = torch.rand(1, 32, 1, 1)
print("b.shape:", b.shape)
print("b.repeat(4,32,1,1).shape:", b.repeat(4, 32, 1, 1).shape)
print("b.repeat(4,1,1,1).shape:", b.repeat(4, 1, 1, 1).shape)
print("b.repeat(4,1,32,32).shape:", b.repeat(4, 1, 32, 32).shape)
输出:
b.shape: torch.Size([1, 32, 1, 1])
b.repeat(4,32,1,1).shape: torch.Size([4, 1024, 1, 1])
b.repeat(4,1,1,1).shape: torch.Size([4, 32, 1, 1])
b.repeat(4,1,32,32).shape: torch.Size([4, 32, 32, 32])
7.6 .t() 转置
import torch
b = torch.rand(3, 4)
print(b)
print(b.t())
输出:
tensor([[0.3598, 0.3820, 0.9488, 0.2987],
[0.7339, 0.2339, 0.5251, 0.2017],
[0.8442, 0.6528, 0.2914, 0.5034]])
tensor([[0.3598, 0.7339, 0.8442],
[0.3820, 0.2339, 0.6528],
[0.9488, 0.5251, 0.2914],
[0.2987, 0.2017, 0.5034]])
7.7 transpose 维度变换
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)
print(a.shape)
print(a.transpose(1, 3).shape)
输出:
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 28, 28, 3])
7.8 permute 维度变换
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 3, 28, 28)
print(a.shape)
print(a.permute(0,2,3,1).shape)
输出:
torch.Size([4, 3, 28, 28])
torch.Size([4, 28, 28, 3])
八、张量的拼接和拆分
8.1 cat
import torch
a = torch.rand(4, 32, 8)
b = torch.rand(5, 32, 8)
c = torch.cat([a, b], dim=0)
print(c.shape) # torch.Size([9, 32, 8])
8.2 stack
import torch
a1 = torch.rand(4,3,16,32)
a2 = torch.rand(4,3,16,32)
c = torch.stack([a1,a2],dim = 2)
print(c.shape) # torch.Size([4, 3, 2, 16, 32])
8.3 split
import torch
a = torch.rand(32, 8)
b = torch.rand(32, 8)
c = torch.stack([a, b], dim=0)
print(c.shape) # torch.Size([2, 32, 8])
aa, bb = c.split([1, 1], dim=0)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape) # torch.Size([1, 32, 8]) torch.Size([1, 32, 8])
aa, bb = c.split([20, 12], dim=1)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape) # torch.Size([2, 20, 8]) torch.Size([2, 12, 8])
8.4 chunk
import torch
a = torch.rand(32, 8)
b = torch.rand(32, 8)
c = torch.stack([a, b], dim=0)
print(c.shape) # torch.Size([2, 32, 8])
aa, bb = c.chunk(2, dim=0)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape) # torch.Size([1, 32, 8]) torch.Size([1, 32, 8])
aa, bb = c.chunk(2, dim=1)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape) # torch.Size([2, 16, 8]) torch.Size([2, 16, 8])
aa, bb, cc, dd = c.chunk(4, dim=1)
print(aa.shape, bb.shape, cc.shape,
dd.shape) #torch.Size([2, 8, 8]) torch.Size([2, 8, 8]) torch.Size([2, 8, 8]) torch.Size([2, 8, 8])
九、基本运算
9.1 广播机制
import torch
a = torch.rand(2,2)
print(a)
b = torch.rand(2)
print(b)
print(a+b)
输出:
tensor([[0.4668, 0.6053],
[0.5321, 0.8734]])
tensor([0.7595, 0.6517])
tensor([[1.2263, 1.2570],
[1.2916, 1.5251]])
9.2 matmul 矩阵/张量乘法
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 2) * 3
b = torch.ones(2, 2)
print(a)
print(b)
print(torch.matmul(a, b))
输出:
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
tensor([[6., 6.],
[6., 6.]])
9.3 pow 次方运算
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 2) * 3
print(a)
print(torch.pow(a, 3))
输出:
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
tensor([[27., 27.],
[27., 27.]])
9.4 sqrt 平方根运算
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 2) * 9
print(a)
print(torch.pow(a, 0.5))
print(torch.sqrt(a))
输出:
tensor([[9., 9.],
[9., 9.]])
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
9.5 exp 指数幂运算
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 2)
print(a)
print(torch.exp(a))
输出:
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
tensor([[2.7183, 2.7183],
[2.7183, 2.7183]])
9.6 log 对数运算(相当于 ln)
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 2) * 3
print(a)
print(torch.log(a))
输出:
tensor([[3., 3.],
[3., 3.]])
tensor([[1.0986, 1.0986],
[1.0986, 1.0986]])
9.7 取整
- floor():向下取整
- ceil():向上取整
- round():四舍五入
- trunc():截取整数部分
- frac():截取小数部分
import torch
a = torch.tensor(3.14)
print(a) # tensor(3.1400)
print(torch.floor(a)) #tensor(3.)
print(torch.ceil(a)) #tensor(4.)
print(torch.round(a)) #tensor(3.)
print(torch.trunc(a)) #tensor(3.)
print(torch.frac(a)) #tensor(0.1400)
9.8 clamp 控制张量的取值范围
import torch
a = torch.rand(2, 3) * 15
print(a)
# 将大于8的值设置为8;小于4的值设置为4
print(torch.clamp(a, 4, 8))
输出:
tensor([[ 8.8872, 5.6534, 14.3027],
[ 0.8305, 12.6266, 13.9683]])
tensor([[8.0000, 5.6534, 8.0000],
[4.0000, 8.0000, 8.0000]])
十、统计属性
10.1 norm 求范数
import torch
a = torch.ones(2, 3)
b = torch.norm(a) # 默认求2范数
c = torch.norm(a, p=1) # 指定求1范数
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
输出:
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
tensor(2.4495)
tensor(6.)
10.2 mean、median、sum、min、max、prod、argmax、argmin
- prod():返回张量里所有元素的乘积
- armax():返回张量中最大元素的展平索引
- argmin():返回张量中最小元素的展平索引
import torch
a = torch.arange(8).view(2, 4).float()
print(a)
'''
tensor([[0., 1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6., 7.]])
'''
print(a.mean()) #tensor(3.5000)
print(a.median()) #tensor(3.)
print(a.sum()) #tensor(28.)
print(a.min()) #tensor(0.)
print(a.max()) #tensor(7.)
print(a.prod()) #tensor(0.)
print(a.argmax()) #tensor(7)
print(a.argmin()) #tensor(0)
import torch
a = torch.rand(2,4)
print(a)
print(a.max(dim = 1))
print(a.max(dim = 1,keepdim = True))
输出:
tensor([[0.7239, 0.9412, 0.7602, 0.2131],
[0.6277, 0.1033, 0.8300, 0.9909]])
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([0.9412, 0.9909]),
indices=tensor([1, 3]))
torch.return_types.max(
values=tensor([[0.9412],
[0.9909]]),
indices=tensor([[1],
[3]]))
10.3 topk 获取最大的k个值
import torch
a = torch.rand(2,4)
print(a)
print(a.topk(2,dim=1))
'''
tensor([[0.3247, 0.9220, 0.4314, 0.8123],
[0.7133, 0.2471, 0.0281, 0.3595]])
torch.return_types.topk(
values=tensor([[0.9220, 0.8123],
[0.7133, 0.3595]]),
indices=tensor([[1, 3],
[0, 3]]))
'''
10.4 kthvalue 获取第k大的值
import torch
a = torch.rand(2, 4)
print(a)
print(a.kthvalue(3,dim=1))
'''
tensor([[0.0980, 0.0479, 0.9298, 0.5638],
[0.9095, 0.9071, 0.4913, 0.6144]])
torch.return_types.kthvalue(
values=tensor([0.5638, 0.9071]),
indices=tensor([3, 1]))
'''
10.5 比较运算函数
import torch
a = torch.rand(2, 3)
print(a)
'''
tensor([[0.1196, 0.5068, 0.9272],
[0.6395, 0.2433, 0.9702]])
'''
# a >= 0.5
print(a.ge(0.5))
'''
tensor([[False, True, True],
[ True, False, True]])
'''
# a > 0.5
print(a.gt(0.5))
'''
tensor([[False, True, True],
[ True, False, True]])
'''
# a <= 0.5
print(a.le(0.5))
'''
tensor([[ True, False, False],
[False, True, False]])
'''
# a < 0.5
print(a.lt(0.5))
'''
tensor([[ True, False, False],
[False, True, False]])
'''
# a = 0.5
print(a.eq(0.5))
'''
tensor([[False, False, False],
[False, False, False]])
'''
十一、高级操作
11.1 where
import torch
cond = torch.rand(2, 2)
a = torch.zeros(2, 2)
b = torch.ones(2, 2)
print(cond)
'''
tensor([[0.3622, 0.9658],
[0.1774, 0.6670]])
'''
print(a)
'''
tensor([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]])
'''
print(b)
'''
tensor([[1., 1.],
[1., 1.]])
'''
# 满足条件cond.ge(0.5)的按照a的对应元素赋值,否则按照b的对应元素赋值
print(torch.where(cond.ge(0.5), a, b))
'''
tensor([[1., 0.],
[1., 0.]])
'''
11.2 gather
帮助我们从批量tensor中取出指定乱序索引下的数据
import torch
a = torch.arange(3, 12).view(3, 3)
print(a)
'''
tensor([[ 3, 4, 5],
[ 6, 7, 8],
[ 9, 10, 11]])
'''
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]])
print(a.gather(1, index)) # tensor([[5, 4, 3]])
index = torch.tensor([[2, 1, 0]]).t()
print(a.gather(1, index))
'''
tensor([[5],
[7],
[9]])
'''
index = torch.tensor([[0, 2],
[1, 2]])
print(a.gather(1, index))
'''
tensor([[3, 5],
[7, 8]])
'''
参考链接:图解PyTorch中的torch.gather函数
在强化学习DQN中的使用 gather() 函数




![[附源码]计算机毕业设计家庭整理服务管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/717d0ef431d74e06b24f75aa820b6b25.png)