一. 多级时间轮实现框架
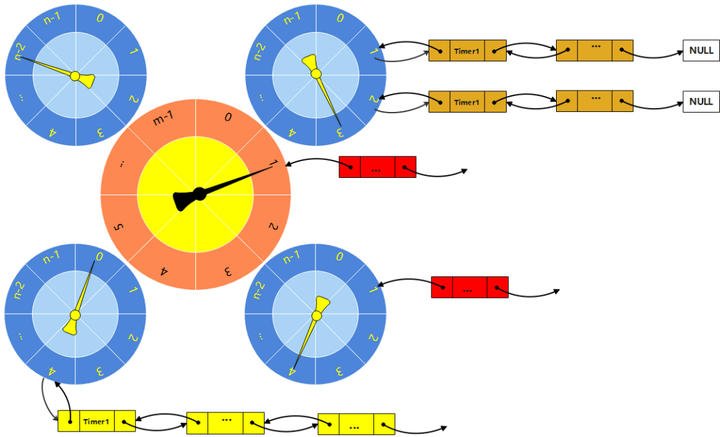
上图是5个时间轮级联的效果图。中间的大轮是工作轮,只有在它上的任务才会被执行;其他轮上的任务时间到后迁移到下一级轮上,他们最终都会迁移到工作轮上而被调度执行。
多级时间轮的原理也容易理解:就拿时钟做说明,秒针转动一圈分针转动一格;分针转动一圈时针转动一格;同理时间轮也是如此:当低级轮转动一圈时,高一级轮转动一格,同时会将高一级轮上的任务重新分配到低级轮上。从而实现了多级轮级联的效果。
1.1 多级时间轮对象
多级时间轮应该至少包括以下内容:
-
每一级时间轮对象
-
轮子上指针的位置 关于轮子上指针的位置有一个比较巧妙的办法:那就是位运算。比如定义一个无符号整型的数:
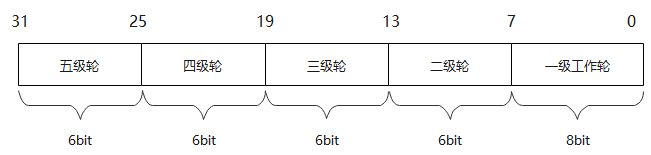
通过获取当前的系统时间便可以通过位操作转换为时间轮上的时间,通过与实际时间轮上的时间作比较,从而确定时间轮要前进调度的时间,进而操作对应时间轮槽位对应的任务。
为什么至少需要这两个成员呢?
-
定义多级时间轮,首先需要明确的便是级联的层数,也就是说需要确定有几个时间轮。
-
轮子上指针位置,就是当前时间轮运行到的位置,它与真实时间的差便是后续时间轮需要调度执行,它们的差值是时间轮运作起来的驱动力。
多级时间轮对象的定义
//实现5级时间轮 范围为0~ (2^8 * 2^6 * 2^6 * 2^6 *2^6)=2^32
struct tvec_base
{
unsigned long current_index;
pthread_t thincrejiffies;
pthread_t threadID;
struct tvec_root tv1; /*第一个轮*/
struct tvec tv2; /*第二个轮*/
struct tvec tv3; /*第三个轮*/
struct tvec tv4; /*第四个轮*/
struct tvec tv5; /*第五个轮*/
};1.2 时间轮对象
我们知道每一个轮子实际上都是一个哈希表,上面我们只是实例化了五个轮子的对象,但是五个轮子具体包含什么,有几个槽位等等没有明确(即struct tvec和struct tvec_root)。
#define TVN_BITS 6
#define TVR_BITS 8
#define TVN_SIZE (1<<TVN_BITS)
#define TVR_SIZE (1<<TVR_BITS)
struct tvec {
struct list_head vec[TVN_SIZE];/*64个格子*/
};
struct tvec_root{
struct list_head vec[TVR_SIZE];/*256个格子*/
};
此外,每一个时间轮都是哈希表,因此它的类型应该至少包含两个指针域来实现双向链表的功能。这里我们为了方便使用通用的struct list_head的双向链表结构。
1.3 定时任务对象

定时器的主要工作是为了在未来的特定时间完成某项任务,而这个任务经常包含以下内容:
-
任务的处理逻辑(回调函数)
-
任务的参数
-
双向链表节点
-
到时时间
定时任务对象的定义
typedef void (*timeouthandle)(unsigned long );
struct timer_list{
struct list_head entry; //将时间连接成链表
unsigned long expires; //超时时间
void (*function)(unsigned long); //超时后的处理函数
unsigned long data; //处理函数的参数
struct tvec_base *base; //指向时间轮
};在时间轮上的效果图:
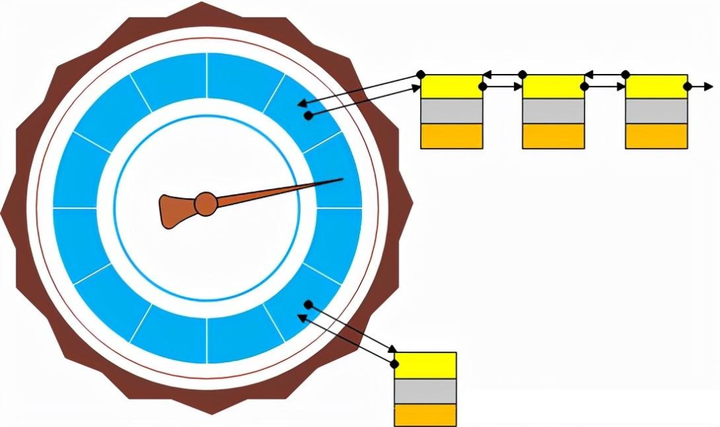
1.4 双向链表
在时间轮上我们采用双向链表的数据类型。采用双向链表的除了操作上比单链表复杂,多占一个指针域外没有其他不可接收的问题。而多占一个指针域在今天大内存的时代明显不是什么问题。至于双向链表操作的复杂性,我们可以通过使用通用的struct list结构来解决,因为双向链表有众多的标准操作函数,我们可以通过直接引用list.h头文件来使用他们提供的接口。
struct list可以说是一个万能的双向链表操作框架,我们只需要在自定义的结构中定义一个struct list对象即可使用它的标准操作接口。同时它还提供了一个类似container_of的接口,在应用层一般叫做list_entry,因此我们可以很方便的通过struct list成员找到自定义的结构体的起始地址。
关于应用层的log.h, 我将在下面的代码中附上该文件。如果需要内核层的实现,可以直接从linux源码中获取。
1.5 联结方式
多级时间轮效果图:
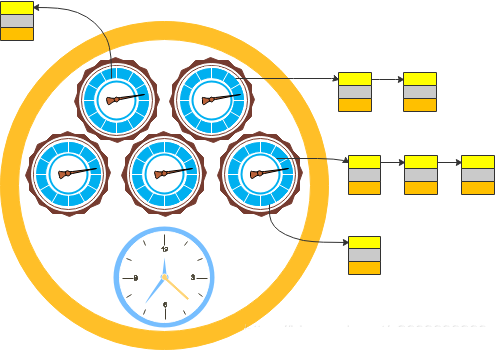
相关视频推荐
c++ 后端面试:现场手撕一个定时器
海量定时任务设计-时间轮
后端开发必学4种层式结构:B+/B-树、时间轮、跳表、LSM-Tree
免费学习地址:c/c++ linux服务器开发/后台架构师
需要C/C++ Linux服务器架构师学习资料加qun812855908获取(资料包括C/C++,Linux,golang技术,Nginx,ZeroMQ,MySQL,Redis,fastdfs,MongoDB,ZK,流媒体,CDN,P2P,K8S,Docker,TCP/IP,协程,DPDK,ffmpeg等),免费分享

二. 多级时间轮C语言实现
2.1 双向链表头文件: list.h
提到双向链表,很多的源码工程中都会实现一系列的统一的双向链表操作函数。它们为双向链表封装了统计的接口,使用者只需要在自定义的结构中添加一个struct list_head结构,然后调用它们提供的接口,便可以完成双向链表的所有操作。这些操作一般都在list.h的头文件中实现。
Linux源码中也有实现(内核态的实现)。他们实现的方式基本完全一样,只是实现的接口数量和功能上稍有差别。可以说这个list.h文件是学习操作双向链表的不二选择,它几乎实现了所有的操作:增、删、改、查、遍历、替换、清空等等。这里我拼凑了一个源码中的log.h函数,终于凑够了多级时间轮中使用到的接口。
#if !defined(_BLKID_LIST_H) && !defined(LIST_HEAD)
#define _BLKID_LIST_H
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Simple doubly linked list implementation.
*
* Some of the internal functions ("__xxx") are useful when
* manipulating whole lists rather than single entries, as
* sometimes we already know the next/prev entries and we can
* generate better code by using them directly rather than
* using the generic single-entry routines.
*/
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
#define INIT_LIST_HEAD(ptr) do { \
(ptr)->next = (ptr); (ptr)->prev = (ptr); \
} while (0)
static inline void
__list_add(struct list_head *entry,
struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = entry;
entry->next = next;
entry->prev = prev;
prev->next = entry;
}
/**
* Insert a new element after the given list head. The new element does not
* need to be initialised as empty list.
* The list changes from:
* head → some element → ...
* to
* head → new element → older element → ...
*
* Example:
* struct foo *newfoo = malloc(...);
* list_add(&newfoo->entry, &bar->list_of_foos);
*
* @param entry The new element to prepend to the list.
* @param head The existing list.
*/
static inline void
list_add(struct list_head *entry, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(entry, head, head->next);
}
/**
* Append a new element to the end of the list given with this list head.
*
* The list changes from:
* head → some element → ... → lastelement
* to
* head → some element → ... → lastelement → new element
*
* Example:
* struct foo *newfoo = malloc(...);
* list_add_tail(&newfoo->entry, &bar->list_of_foos);
*
* @param entry The new element to prepend to the list.
* @param head The existing list.
*/
static inline void
list_add_tail(struct list_head *entry, struct list_head *head)
{
__list_add(entry, head->prev, head);
}
static inline void
__list_del(struct list_head *prev, struct list_head *next)
{
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
}
/**
* Remove the element from the list it is in. Using this function will reset
* the pointers to/from this element so it is removed from the list. It does
* NOT free the element itself or manipulate it otherwise.
*
* Using list_del on a pure list head (like in the example at the top of
* this file) will NOT remove the first element from
* the list but rather reset the list as empty list.
*
* Example:
* list_del(&foo->entry);
*
* @param entry The element to remove.
*/
static inline void
list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
}
static inline void
list_del_init(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(entry);
}
static inline void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{
__list_del(list->prev, list->next);
list_add_tail(list, head);
}
/**
* Check if the list is empty.
*
* Example:
* list_empty(&bar->list_of_foos);
*
* @return True if the list contains one or more elements or False otherwise.
*/
static inline int
list_empty(struct list_head *head)
{
return head->next == head;
}
/**
* list_replace - replace old entry by new one
* @old : the element to be replaced
* @new : the new element to insert
*
* If @old was empty, it will be overwritten.
*/
static inline void list_replace(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
new->next = old->next;
new->next->prev = new;
new->prev = old->prev;
new->prev->next = new;
}
/**
* Retrieve the first list entry for the given list pointer.
*
* Example:
* struct foo *first;
* first = list_first_entry(&bar->list_of_foos, struct foo, list_of_foos);
*
* @param ptr The list head
* @param type Data type of the list element to retrieve
* @param member Member name of the struct list_head field in the list element.
* @return A pointer to the first list element.
*/
#define list_first_entry(ptr, type, member) \
list_entry((ptr)->next, type, member)
static inline void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,
struct list_head *new)
{
list_replace(old, new);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(old);
}
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
((type *)((char *)(ptr)-(unsigned long)(&((type *)0)->member)))
/**
* list_for_each - iterate over elements in a list
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop counter.
* @head: the head for your list.
*/
#define list_for_each(pos, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next; pos != (head); pos = pos->next)
/**
* list_for_each_safe - iterate over elements in a list, but don't dereference
* pos after the body is done (in case it is freed)
* @pos: the &struct list_head to use as a loop counter.
* @pnext: the &struct list_head to use as a pointer to the next item.
* @head: the head for your list (not included in iteration).
*/
#define list_for_each_safe(pos, pnext, head) \
for (pos = (head)->next, pnext = pos->next; pos != (head); \
pos = pnext, pnext = pos->next)
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif /* _BLKID_LIST_H */这里面一般会用到一个重要实现:container_of, 它的原理这里不叙述
2.2 调试信息头文件: log.h
这个头文件实际上不是必须的,我只是用它来添加调试信息(代码中的errlog(), log()都是log.h中的宏函数)。它的效果是给打印的信息加上颜色,效果如下:
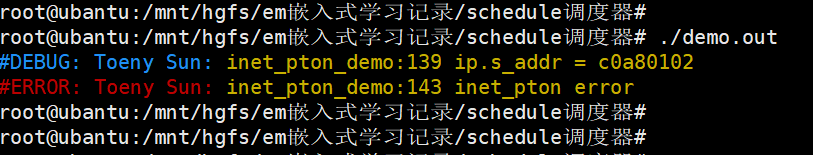
log.h的代码如下:
#ifndef _LOG_h_
#define _LOG_h_
#include <stdio.h>
#define COL(x) "\033[;" #x "m"
#define RED COL(31)
#define GREEN COL(32)
#define YELLOW COL(33)
#define BLUE COL(34)
#define MAGENTA COL(35)
#define CYAN COL(36)
#define WHITE COL(0)
#define GRAY "\033[0m"
#define errlog(fmt, arg...) do{ \
printf(RED"[#ERROR: Toeny Sun:"GRAY YELLOW" %s:%d]:"GRAY WHITE fmt GRAY, __func__, __LINE__, ##arg);\
}while(0)
#define log(fmt, arg...) do{ \
printf(WHITE"[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: "GRAY YELLOW"%s:%d]:"GRAY WHITE fmt GRAY, __func__, __LINE__, ##arg);\
}while(0)
#endif2.3 时间轮代码: timewheel.c
/*
*毫秒定时器 采用多级时间轮方式 借鉴linux内核中的实现
*支持的范围为1 ~ 2^32 毫秒(大约有49天)
*若设置的定时器超过最大值 则按最大值设置定时器
**/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include "list.h"
#include "log.h"
#define TVN_BITS 6
#define TVR_BITS 8
#define TVN_SIZE (1<<TVN_BITS)
#define TVR_SIZE (1<<TVR_BITS)
#define TVN_MASK (TVN_SIZE - 1)
#define TVR_MASK (TVR_SIZE - 1)
#define SEC_VALUE 0
#define USEC_VALUE 2000
struct tvec_base;
#define INDEX(N) ((ba->current_index >> (TVR_BITS + (N) * TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK)
typedef void (*timeouthandle)(unsigned long );
struct timer_list{
struct list_head entry; //将时间连接成链表
unsigned long expires; //超时时间
void (*function)(unsigned long); //超时后的处理函数
unsigned long data; //处理函数的参数
struct tvec_base *base; //指向时间轮
};
struct tvec {
struct list_head vec[TVN_SIZE];
};
struct tvec_root{
struct list_head vec[TVR_SIZE];
};
//实现5级时间轮 范围为0~ (2^8 * 2^6 * 2^6 * 2^6 *2^6)=2^32
struct tvec_base
{
unsigned long current_index;
pthread_t thincrejiffies;
pthread_t threadID;
struct tvec_root tv1; /*第一个轮*/
struct tvec tv2; /*第二个轮*/
struct tvec tv3; /*第三个轮*/
struct tvec tv4; /*第四个轮*/
struct tvec tv5; /*第五个轮*/
};
static void internal_add_timer(struct tvec_base *base, struct timer_list *timer)
{
struct list_head *vec;
unsigned long expires = timer->expires;
unsigned long idx = expires - base->current_index;
#if 1
if( (signed long)idx < 0 ) /*这里是没有办法区分出是过时还是超长定时的吧?*/
{
vec = base->tv1.vec + (base->current_index & TVR_MASK);/*放到第一个轮的当前槽*/
}
else if ( idx < TVR_SIZE ) /*第一个轮*/
{
int i = expires & TVR_MASK;
vec = base->tv1.vec + i;
}
else if( idx < 1 << (TVR_BITS + TVN_BITS) )/*第二个轮*/
{
int i = (expires >> TVR_BITS) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv2.vec + i;
}
else if( idx < 1 << (TVR_BITS + 2 * TVN_BITS) )/*第三个轮*/
{
int i = (expires >> (TVR_BITS + TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv3.vec + i;
}
else if( idx < 1 << (TVR_BITS + 3 * TVN_BITS) )/*第四个轮*/
{
int i = (expires >> (TVR_BITS + 2 * TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv4.vec + i;
}
else /*第五个轮*/
{
int i;
if (idx > 0xffffffffUL)
{
idx = 0xffffffffUL;
expires = idx + base->current_index;
}
i = (expires >> (TVR_BITS + 3 * TVN_BITS)) & TVN_MASK;
vec = base->tv5.vec + i;
}
#else
/*上面可以优化吧*/;
#endif
list_add_tail(&timer->entry, vec);
}
static inline void detach_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
{
struct list_head *entry = &timer->entry;
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = NULL;
entry->prev = NULL;
}
static int __mod_timer(struct timer_list *timer, unsigned long expires)
{
if(NULL != timer->entry.next)
detach_timer(timer);
internal_add_timer(timer->base, timer);
return 0;
}
//修改定时器的超时时间外部接口
int mod_timer(void *ptimer, unsigned long expires)
{
struct timer_list *timer = (struct timer_list *)ptimer;
struct tvec_base *base;
base = timer->base;
if(NULL == base)
return -1;
expires = expires + base->current_index;
if(timer->entry.next != NULL && timer->expires == expires)
return 0;
if( NULL == timer->function )
{
errlog("timer's timeout function is null\n");
return -1;
}
timer->expires = expires;
return __mod_timer(timer,expires);
}
//添加一个定时器
static void __ti_add_timer(struct timer_list *timer)
{
if( NULL != timer->entry.next )
{
errlog("timer is already exist\n");
return;
}
mod_timer(timer, timer->expires);
}
/*添加一个定时器 外部接口
*返回定时器
*/
void* ti_add_timer(void *ptimewheel, unsigned long expires,timeouthandle phandle, unsigned long arg)
{
struct timer_list *ptimer;
ptimer = (struct timer_list *)malloc( sizeof(struct timer_list) );
if(NULL == ptimer)
return NULL;
bzero( ptimer,sizeof(struct timer_list) );
ptimer->entry.next = NULL;
ptimer->base = (struct tvec_base *)ptimewheel;
ptimer->expires = expires;
ptimer->function = phandle;
ptimer->data = arg;
__ti_add_timer(ptimer);
return ptimer;
}
/*
*删除一个定时器 外部接口
*
* */
void ti_del_timer(void *p)
{
struct timer_list *ptimer =(struct timer_list*)p;
if(NULL == ptimer)
return;
if(NULL != ptimer->entry.next)
detach_timer(ptimer);
free(ptimer);
}
/*时间轮级联*/
static int cascade(struct tvec_base *base, struct tvec *tv, int index)
{
struct list_head *pos,*tmp;
struct timer_list *timer;
struct list_head tv_list;
/*将tv[index]槽位上的所有任务转移给tv_list,然后清空tv[index]*/
list_replace_init(tv->vec + index, &tv_list);/*用tv_list替换tv->vec + index*/
list_for_each_safe(pos, tmp, &tv_list)/*遍历tv_list双向链表,将任务重新添加到时间轮*/
{
timer = list_entry(pos,struct timer_list,entry);/*struct timer_list中成员entry的地址是pos, 获取struct timer_list的首地址*/
internal_add_timer(base, timer);
}
return index;
}
static void *deal_function_timeout(void *base)
{
struct timer_list *timer;
int ret;
struct timeval tv;
struct tvec_base *ba = (struct tvec_base *)base;
for(;;)
{
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
while( ba->current_index <= (tv.tv_sec*1000 + tv.tv_usec/1000) )/*单位:ms*/
{
struct list_head work_list;
int index = ba->current_index & TVR_MASK;/*获取第一个轮上的指针位置*/
struct list_head *head = &work_list;
/*指针指向0槽时,级联轮需要更新任务列表*/
if(!index && (!cascade(ba, &ba->tv2, INDEX(0))) &&( !cascade(ba, &ba->tv3, INDEX(1))) && (!cascade(ba, &ba->tv4, INDEX(2))) )
cascade(ba, &ba->tv5, INDEX(3));
ba->current_index ++;
list_replace_init(ba->tv1.vec + index, &work_list);
while(!list_empty(head))
{
void (*fn)(unsigned long);
unsigned long data;
timer = list_first_entry(head, struct timer_list, entry);
fn = timer->function;
data = timer->data;
detach_timer(timer);
(*fn)(data);
}
}
}
}
static void init_tvr_list(struct tvec_root * tvr)
{
int i;
for( i = 0; i<TVR_SIZE; i++ )
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tvr->vec[i]);
}
static void init_tvn_list(struct tvec * tvn)
{
int i;
for( i = 0; i<TVN_SIZE; i++ )
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&tvn->vec[i]);
}
//创建时间轮 外部接口
void *ti_timewheel_create(void )
{
struct tvec_base *base;
int ret = 0;
struct timeval tv;
base = (struct tvec_base *) malloc( sizeof(struct tvec_base) );
if( NULL==base )
return NULL;
bzero( base,sizeof(struct tvec_base) );
init_tvr_list(&base->tv1);
init_tvn_list(&base->tv2);
init_tvn_list(&base->tv3);
init_tvn_list(&base->tv4);
init_tvn_list(&base->tv5);
gettimeofday(&tv, NULL);
base->current_index = tv.tv_sec*1000 + tv.tv_usec/1000;/*当前时间毫秒数*/
if( 0 != pthread_create(&base->threadID,NULL,deal_function_timeout,base) )
{
free(base);
return NULL;
}
return base;
}
static void ti_release_tvr(struct tvec_root *pvr)
{
int i;
struct list_head *pos,*tmp;
struct timer_list *pen;
for(i = 0; i < TVR_SIZE; i++)
{
list_for_each_safe(pos,tmp,&pvr->vec[i])
{
pen = list_entry(pos,struct timer_list, entry);
list_del(pos);
free(pen);
}
}
}
static void ti_release_tvn(struct tvec *pvn)
{
int i;
struct list_head *pos,*tmp;
struct timer_list *pen;
for(i = 0; i < TVN_SIZE; i++)
{
list_for_each_safe(pos,tmp,&pvn->vec[i])
{
pen = list_entry(pos,struct timer_list, entry);
list_del(pos);
free(pen);
}
}
}
/*
*释放时间轮 外部接口
* */
void ti_timewheel_release(void * pwheel)
{
struct tvec_base *base = (struct tvec_base *)pwheel;
if(NULL == base)
return;
ti_release_tvr(&base->tv1);
ti_release_tvn(&base->tv2);
ti_release_tvn(&base->tv3);
ti_release_tvn(&base->tv4);
ti_release_tvn(&base->tv5);
free(pwheel);
}
/************demo****************/
struct request_para{
void *timer;
int val;
};
void mytimer(unsigned long arg)
{
struct request_para *para = (struct request_para *)arg;
log("%d\n",para->val);
mod_timer(para->timer,3000); //进行再次启动定时器
sleep(10);/*定时器依然被阻塞*/
//定时器资源的释放是在这里完成的
//ti_del_timer(para->timer);
}
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
void *pwheel = NULL;
void *timer = NULL;
struct request_para *para;
para = (struct request_para *)malloc( sizeof(struct request_para) );
if(NULL == para)
return 0;
bzero(para,sizeof(struct request_para));
//创建一个时间轮
pwheel = ti_timewheel_create();
if(NULL == pwheel)
return -1;
//添加一个定时器
para->val = 100;
para->timer = ti_add_timer(pwheel, 3000, &mytimer, (unsigned long)para);
while(1)
{
sleep(2);
}
//释放时间轮
ti_timewheel_release(pwheel);
return 0;
}2.4 编译运行
peng@ubuntu:/mnt/hgfs/timer/4. timerwheel/2. 多级时间轮$ ls
a.out list.h log.h mutiTimeWheel.c
toney@ubantu:/mnt/hgfs/timer录/4. timerwheel/2. 多级时间轮$ gcc mutiTimeWheel.c -lpthread
toney@ubantu:/mnt/hgfs/timer/4. timerwheel/2. 多级时间轮$ ./a.out
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100
[#DEBUG: Toeny Sun: mytimer:370]:100从结果可以看出:如果添加的定时任务是比较耗时的操作,那么后续的任务也会被阻塞,可能一直到超时,甚至一直阻塞下去,这个取决于当前任务是否耗时。
这个理论上是绝不能接受的:一个任务不应该也不能去影响其他的任务吧。但是目前没有对此问题进行改进和完善,以后有机会再继续完善吧。