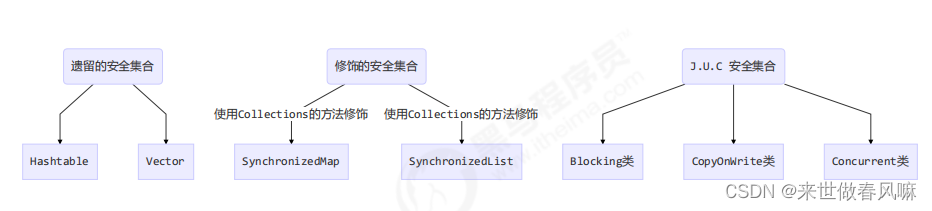
一、线程安全集合类概述
线程安全集合类可以分为三大类:(1)遗留的线程安全集合如 Hashtable , Vector(2)使用 Collections 装饰的线程安全集合,如:
1️⃣Collections.synchronizedCollection
2️⃣Collections.synchronizedList
3️⃣Collections.synchronizedMap
4️⃣Collections.synchronizedSet
5️⃣Collections.synchronizedNavigableMap
6️⃣Collections.synchronizedNavigableSet
7️⃣Collections.synchronizedSortedMap
8️⃣Collections.synchronizedSortedSet
(3)java.util.concurrent.*(J.U.C 安全集合)
重点介绍java.util.concurrent.* 下的线程安全集合类,可以发现它们有规律,里面包含三类关键词:Blocking、CopyOnWrite、Concurrent
1️⃣Blocking 大部分实现基于锁,并提供用来阻塞的方法
2️⃣CopyOnWrite 之类容器修改开销相对较重
3️⃣Concurrent 类型的容器
Concurrent 类型的容器:
(1)内部很多操作使用 cas 优化,一般可以提供较高吞吐量
(2)弱一致性
1️⃣遍历时弱一致性,例如,当利用迭代器遍历时,如果容器发生修改,迭代器仍然可以继续进行遍历,这时内容是旧的
2️⃣求大小弱一致性, size 操作未必是 100% 准确3️⃣读取弱一致性
遍历时如果发生了修改,对于非安全容器来讲,使用 fail-fast 机制也就是让遍历立刻失败,抛出 ConcurrentModifificationException ,不再继续遍历
二、ConcurrentHashMap
1. 练习:单词计数
public class TestWordCount { public static void main(String[] args) { demo( // 创建 map 集合 // 创建 ConcurrentHashMap 对不对? () -> new ConcurrentHashMap<String, LongAdder>(8,0.75f,8), (map, words) -> { for (String word : words) { // 如果缺少一个 key,则计算生成一个 value , 然后将 key value 放入 map // a 0 LongAdder value = map.computeIfAbsent(word, (key) -> new LongAdder()); // 执行累加 value.increment(); // 2 /*// 检查 key 有没有 Integer counter = map.get(word); int newValue = counter == null ? 1 : counter + 1; // 没有 则 put map.put(word, newValue);*/ } } ); } private static void demo2() { Map<String, Integer> collect = IntStream.range(1, 27).parallel() .mapToObj(idx -> readFromFile(idx)) .flatMap(list -> list.stream()) .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Function.identity(), Collectors.summingInt(w -> 1))); System.out.println(collect); } private static <V> void demo(Supplier<Map<String, V>> supplier, BiConsumer<Map<String, V>, List<String>> consumer) { Map<String, V> counterMap = supplier.get(); // key value // a 200 // b 200 List<Thread> ts = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) { int idx = i; Thread thread = new Thread(() -> { List<String> words = readFromFile(idx); consumer.accept(counterMap, words); }); ts.add(thread); } ts.forEach(t -> t.start()); ts.forEach(t -> { try { t.join(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }); System.out.println(counterMap); } public static List<String> readFromFile(int i) { ArrayList<String> words = new ArrayList<>(); try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream("tmp/" + i + ".txt")))) { while (true) { String word = in.readLine(); if (word == null) { break; } words.add(word); } return words; } catch (IOException e) { throw new RuntimeException(e); } } }
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA游戏账号交易平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d02a035704774e2e90828338e2a92f01.png)







![[开发浏览器实战]关于Firefox火狐浏览器的说明一二(国内版 国际版区别 账号切换 插件-恢复关闭的标签页 插件-tempermonkey油猴)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5bc2170155fe4727aec041d9a9b7ab58.png)