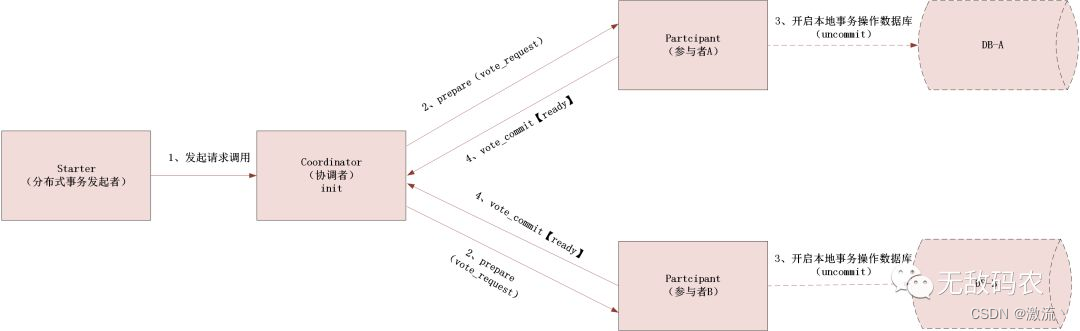
1、目的
在大型数据集上训练class-conditional GAN,并探索相关的trick
2、贡献
1)数据集的扩大使得GAN的表现也随之提升。文章的网络参数量是之前工作的2~4倍,batch size是之前的8倍。文章分别从两方面对performance进行提升:scalability - architectural change;conditioning - regularization scheme
2)发现了truncation trick,通过sampling technique来平衡variaty和fidelity的trade-off
3)要想实现完全的训练stability,就必须大幅度牺牲performance
3、网络结构
1)SA-GAN
2)class information
G:class-conditional BatchNorm(所有BatchNorm层使用shared embedding,linearly projected to each layer's gains and biases,以节省computation和memory损耗)
D:projection
3)2 steps D, 1 step G
4)evaluation时,对G的weights moving average
5)增加depth和width可以显著提升实验结果
6)skip-z将noise向量z添加到网络多层中。BigGAN通过将z分为chunks,然后和conditional vector c并联;BigGAN-deep则直接将z和conditional vector c并联
4、创新性
1)truncated normal
z sampling: values fall outside a range are resampled to fall inside that range
trade-off: threshold ↑,sample variety ↑,quality ↓
2)Orthogonal Initialization
truncated normal在一些模型下性能不好(这里我没看懂为啥不好,文章说会导致训练和测试的distribution shift?),可以通过让G smooth来中和该问题
![]()
最终文章采用了改良版
![]()
5、局限性
1)会出现training collapse。训练不稳定的来源是G和D共同作用的结果。为了使得训练稳定,就需要牺牲最终的performance,因此不如直接用early stopping

-> Generator
每个weight matrix的top three singular values 对mode collapse是最informative的
![]()
spectral normalization可以防止或者
逐步增加和爆发,并且在一些情况下还能略微提升实验结果,但仍然无法完全制止training collapse
-> Discriminator
G会周期性的产生会严重干扰D的batches
![]()
以0为中心的梯度惩罚使得训练更加stable,但是最终的performance严重下降
D的loss逐渐接近0,但是在collapse时会迅速增加。因为D在训练集上过拟合了
2)出现了新的failure类型。以往的生成模型的failure主要包括local artifacts、images consisting of texture blobs instead of objects、canonical mode collapse。文章发现了class leakage