作业:补充网络定义部分,使用卷积神经网络实现宝石分类
要求:1.补充完成CNN的网络结构定义方法实现宝石识别 2.可尝试不同网络结构、参数等力求达到更好的效果

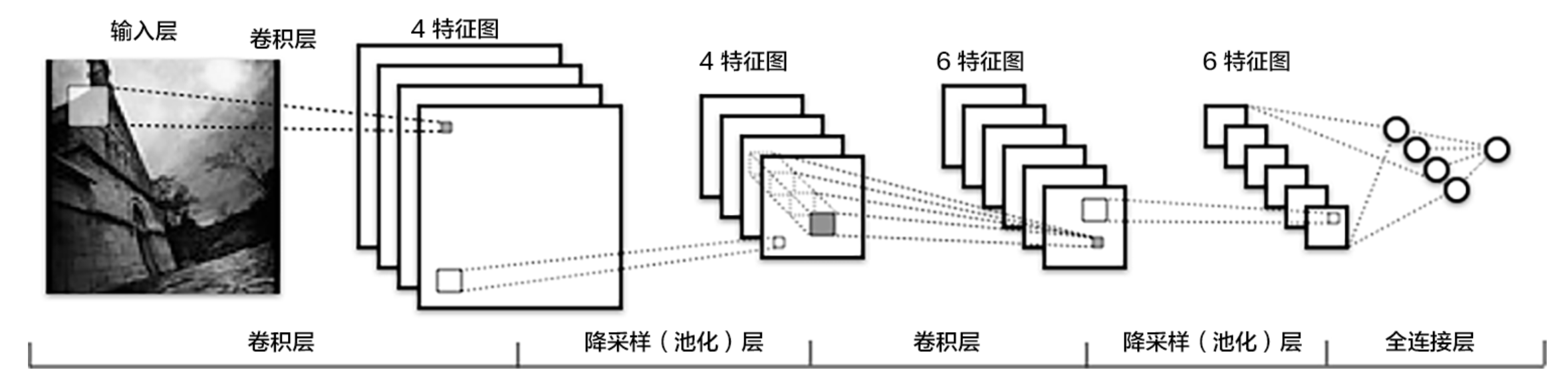
卷积神经网络
卷积神经网络是提取图像特征的经典网络,其结构一般包含多个卷积层与池化层的交替组合。
数据集介绍
数据集地址:宝石分类数据集地址
文件夹目录结构为:data/data218356/,后面的218356这个编号在paddle中启动不同的环境时会发生改变。
-
数据集文件名为archive_train.zip,archive_test.zip。
-
该数据集包含25个类别不同宝石的图像。
-
这些类别已经分为训练和测试数据。
-
图像大小不一,格式为.jpeg。**

# 查看当前挂载的数据集目录, 该目录下的变更重启环境后会自动还原
# View dataset directory.
# This directory will be recovered automatically after resetting environment.
!ls /home/aistudio/data
加粗样式
#导入需要的包
from __future__ import print_function
import os
import zipfile
import random
import json
import cv2
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import paddle
from paddle.io import Dataset
import paddle.nn as nn
1、数据准备
'''
参数配置
'''
train_parameters = {
"input_size": [3, 224, 224], # 输入图片的shape
"class_dim": 25, # 分类数
"src_path":"data/data218356/archive_train.zip", # 原始数据集路径
"target_path":"/home/aistudio/data/dataset", # 要解压的路径
"train_list_path": "./train.txt", # train_data.txt路径
"eval_list_path": "./eval.txt", # eval_data.txt路径
"label_dict":{}, # 标签字典
"readme_path": "/home/aistudio/data/readme.json",# readme.json路径
"num_epochs":120, # 训练轮数
"train_batch_size": 25, # 批次的大小
"learning_strategy": { # 优化函数相关的配置
"lr": 0.0005 # 超参数学习率
}
}
print(type(train_parameters))
<class 'dict'>
def unzip_data(src_path,target_path):
'''
解压原始数据集,将src_path路径下的zip包解压至data/dataset目录下
'''
if(not os.path.isdir(target_path)):
z = zipfile.ZipFile(src_path, 'r')
z.extractall(path=target_path)
z.close()
else:
print("文件已解压")
def get_data_list(target_path,train_list_path,eval_list_path):
'''
生成数据列表
'''
# 获取所有类别保存的文件夹名称
data_list_path = target_path
class_dirs = os.listdir(data_list_path)
if '__MACOSX' in class_dirs:
class_dirs.remove('__MACOSX')
# 存储要写进eval.txt和train.txt中的内容
trainer_list=[]
eval_list=[]
class_label=0
i = 0
for class_dir in class_dirs:
path = os.path.join(data_list_path,class_dir)
# 获取所有图片
img_paths = os.listdir(path)
for img_path in img_paths: # 遍历文件夹下的每个图片
i += 1
name_path = os.path.join(path,img_path) # 每张图片的路径
if i % 10 == 0:
eval_list.append(name_path + "\t%d" % class_label + "\n")
else:
trainer_list.append(name_path + "\t%d" % class_label + "\n")
train_parameters['label_dict'][str(class_label)]=class_dir
class_label += 1
#乱序
random.shuffle(eval_list)
with open(eval_list_path, 'a') as f:
for eval_image in eval_list:
f.write(eval_image)
#乱序
random.shuffle(trainer_list)
with open(train_list_path, 'a') as f2:
for train_image in trainer_list:
f2.write(train_image)
print ('生成数据列表完成!')
# 参数初始化
src_path=train_parameters['src_path']
target_path=train_parameters['target_path']
train_list_path=train_parameters['train_list_path']
eval_list_path=train_parameters['eval_list_path']
batch_size=train_parameters['train_batch_size']
# 解压原始数据到指定路径
unzip_data(src_path,target_path)
#每次生成数据列表前,首先清空train.txt和eval.txt
with open(train_list_path, 'w') as f:
f.seek(0)
f.truncate()
with open(eval_list_path, 'w') as f:
f.seek(0)
f.truncate()
#生成数据列表
get_data_list(target_path,train_list_path,eval_list_path)
生成数据列表完成!
class Reader(Dataset):
def __init__(self, data_path, mode='train'):
"""
数据读取器
:param data_path: 数据集所在路径
:param mode: train or eval
"""
super().__init__()
self.data_path = data_path
self.img_paths = []
self.labels = []
if mode == 'train':
with open(os.path.join(self.data_path, "train.txt"), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
self.info = f.readlines()
for img_info in self.info:
img_path, label = img_info.strip().split('\t')
self.img_paths.append(img_path)
self.labels.append(int(label))
else:
with open(os.path.join(self.data_path, "eval.txt"), "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
self.info = f.readlines()
for img_info in self.info:
img_path, label = img_info.strip().split('\t')
self.img_paths.append(img_path)
self.labels.append(int(label))
def __getitem__(self, index):
"""
获取一组数据
:param index: 文件索引号
:return:
"""
# 第一步打开图像文件并获取label值
img_path = self.img_paths[index]
img = Image.open(img_path)
if img.mode != 'RGB':
img = img.convert('RGB')
img = img.resize((224, 224), Image.BILINEAR)
img = np.array(img).astype('float32')
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1)) / 255
label = self.labels[index]
label = np.array([label], dtype="int64")
return img, label
def print_sample(self, index: int = 0):
print("文件名", self.img_paths[index], "\t标签值", self.labels[index])
def __len__(self):
return len(self.img_paths)
#训练数据加载
train_dataset = Reader('/home/aistudio/',mode='train')
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
#测试数据加载
eval_dataset = Reader('/home/aistudio/',mode='eval')
eval_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(eval_dataset, batch_size = 8, shuffle=False)
train_dataset.print_sample(200)
print(train_dataset.__len__())
eval_dataset.print_sample(0)
print(eval_dataset.__len__())
print(type(eval_dataset.__getitem__(10)))
print(len(eval_dataset.__getitem__(10)))
print(eval_dataset.__getitem__(10)[0].shape)
print(eval_dataset.__getitem__(10)[1].shape)
文件名 /home/aistudio/data/dataset/Variscite/variscite_19.jpg 标签值 9
730
文件名 /home/aistudio/data/dataset/Carnelian/carnelian_6.jpg 标签值 13
81
<class 'tuple'>
2
(3, 224, 224)
(1,)
Batch=0
Batchs=[]
all_train_accs=[]
def draw_train_acc(Batchs, train_accs):
title="training accs"
plt.title(title, fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("batch", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("acc", fontsize=14)
plt.plot(Batchs, train_accs, color='green', label='training accs')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
all_train_loss=[]
def draw_train_loss(Batchs, train_loss):
title="training loss"
plt.title(title, fontsize=24)
plt.xlabel("batch", fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel("loss", fontsize=14)
plt.plot(Batchs, train_loss, color='red', label='training loss')
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()
2、定义模型
# 定义卷积神经网络实现宝石识别
# --------------------------------------------------------补充完成网络结构定义部分,实现宝石分类------------------------------------------------------------
# 定义网络块
class ConvPool(paddle.nn.Layer):
'''卷积+池化'''
def __init__(self,
num_channels,#1
num_filters, #2
filter_size,#3
pool_size,#4
pool_stride,#5
groups,#6
conv_stride=1,
conv_padding=1,
):
super(ConvPool, self).__init__()
self._conv2d_list = []
for i in range(groups):
conv2d = self.add_sublayer( #添加子层实例
'bb_%d' % i,
paddle.nn.Conv2D( # layer
in_channels=num_channels, #通道数
out_channels=num_filters, #卷积核个数
kernel_size=filter_size, #卷积核大小
stride=conv_stride, #步长
padding = conv_padding, #padding
)
)
num_channels = num_filters
self._conv2d_list.append(conv2d)
self._pool2d = paddle.nn.MaxPool2D(
kernel_size=pool_size, #池化核大小
stride=pool_stride #池化步长
)
# print(self._conv2d_list)
def forward(self, inputs):
x = inputs
for conv in self._conv2d_list:
x = conv(x)
x = paddle.nn.functional.relu(x)
x = self._pool2d(x)
return x
# 定义VGG网络结构
class VGGNet(paddle.nn.Layer):
def __init__(self):
super(VGGNet, self).__init__()
self.convpool01 = ConvPool(3,64,3,2,2,1)
self.convpool02 = ConvPool(64,128,3,2,2,2)
self.convpool03 = ConvPool(128,256,3,2,2,4)
self.convpool04 = ConvPool(256,512,3,2,2,3)
self.convpool05 = ConvPool(512,512,3,2,2,3)
self.pool_5_shape = 512*7*7
self.fc01 = paddle.nn.Linear(self.pool_5_shape,4096)
self.fc02 = paddle.nn.Linear(4096,4096)
# self.fc03 = paddle.nn.Linear(4096,train_parameters['class_dim'])
self.fc03 = paddle.nn.Linear(4096,25) #25为类别通道
def forward(self, inputs, label=None):
out = self.convpool01(inputs)
out = self.convpool02(out)
out = self.convpool03(out)
out = self.convpool04(out)
out = self.convpool05(out)
out = paddle.reshape(out,shape=[-1,512*7*7])
out = self.fc01(out)
out = self.fc02(out)
out = self.fc03(out)
if label is not None:
acc = paddle.metric.accuracy(input=out,label=label)
return out,acc
else:
return out
# class MyCNN():
# def __init__(self):
# self = VGGNet
# def train():
3、训练模型-CNN
model=VGGNet() # 模型实例化
model.train() # 训练模式
# model = paddle.Model(VGGNet())
# model.summary((1, 3, 224, 224))
cross_entropy = paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
opt=paddle.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=train_parameters['learning_strategy']['lr'],\
parameters=model.parameters())
epochs_num=train_parameters['num_epochs'] #迭代次数
for pass_num in range(train_parameters['num_epochs']):
for batch_id,data in enumerate(train_loader()):
image = data[0]
label = data[1]
predict=model(image) #数据传入model
loss=cross_entropy(predict,label)
acc=paddle.metric.accuracy(predict,label)#计算精度
if batch_id!=0 and batch_id%5==0:
Batch = Batch+5
Batchs.append(Batch)
all_train_loss.append(loss.numpy()[0])
all_train_accs.append(acc.numpy()[0])
print("epoch:{},step:{},train_loss:{},train_acc:{}".format(pass_num,batch_id,loss.numpy(),acc.numpy()))
loss.backward()
opt.step()
opt.clear_grad() #opt.clear_grad()来重置梯度
paddle.save(model.state_dict(),'MyCNN')#保存模型->MyCNN,后续模型评估用到此变量
draw_train_acc(Batchs,all_train_accs)
draw_train_loss(Batchs,all_train_loss)
W0531 15:51:36.444547 99 gpu_resources.cc:61] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 11.2, Runtime API Version: 11.2
W0531 15:51:36.449091 99 gpu_resources.cc:91] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 8.2.
epoch:119,step:45,train_loss:[0.00298419],train_acc:[1.]
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2349: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
if isinstance(obj, collections.Iterator):
/opt/conda/envs/python35-paddle120-env/lib/python3.7/site-packages/matplotlib/cbook/__init__.py:2366: DeprecationWarning: Using or importing the ABCs from 'collections' instead of from 'collections.abc' is deprecated, and in 3.8 it will stop working
return list(data) if isinstance(data, collections.MappingView) else data
4、模型评估-CNN
#模型评估
para_state_dict = paddle.load("MyCNN")
#model = MyCNN()
model = VGGNet()
model.set_state_dict(para_state_dict) #加载模型参数
model.eval() #验证模式
accs = []
for batch_id,data in enumerate(eval_loader()):#测试集
image=data[0]
label=data[1]
predict=model(image)
acc=paddle.metric.accuracy(predict,label)
accs.append(acc.numpy()[0])
avg_acc = np.mean(accs)
print("当前模型在验证集上的准确率为:",avg_acc)
当前模型在验证集上的准确率为: 0.84090906
5、模型预测-CNN
def unzip_infer_data(src_path,target_path):
'''
解压预测数据集
'''
if(not os.path.isdir(target_path)):
z = zipfile.ZipFile(src_path, 'r')
z.extractall(path=target_path)
z.close()
def load_image(img_path):
'''
预测图片预处理
'''
img = Image.open(img_path)
if img.mode != 'RGB':
img = img.convert('RGB')
img = img.resize((224, 224), Image.BILINEAR)
img = np.array(img).astype('float32')
img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # HWC to CHW
img = img/255 # 像素值归一化
return img
infer_src_path = '/home/aistudio/data/data218356/archive_test.zip'
infer_dst_path = '/home/aistudio/data/archive_test'
unzip_infer_data(infer_src_path,infer_dst_path)
para_state_dict = paddle.load("MyCNN")
model = VGGNet()
model.set_state_dict(para_state_dict) #加载模型参数
model.eval() #验证模式
#展示预测图片
infer_path='data/archive_test/alexandrite_3.jpg'
img = Image.open(infer_path)
plt.imshow(img) #根据数组绘制图像
plt.show() #显示图像
#对预测图片进行预处理
infer_imgs = []
infer_imgs.append(load_image(infer_path))
infer_imgs = np.array(infer_imgs)
label_dic = train_parameters['label_dict']
for i in range(len(infer_imgs)):
data = infer_imgs[i]
dy_x_data = np.array(data).astype('float32')
dy_x_data=dy_x_data[np.newaxis,:, : ,:]
img = paddle.to_tensor (dy_x_data)
out = model(img)
lab = np.argmax(out.numpy()) #argmax():返回最大数的索引
print("第{}个样本,被预测为:{},真实标签为:{}".format(i+1,label_dic[str(lab)],infer_path.split('/')[-1].split("_")[0]))
print("结束")
总结
在实验过程中,发现学习率,batch_size,epoch等超参数对模型的性能影响较大。在图像任务上,使用GPU训练的速度远远高于CPU,但在下一个任务“使用RNN实现英文电影评论的情感分析”中,好像CPU训练的速度更快(CPU 是paddle提供的base version,为GPU V100)。
在脚手架的支持下,实现结构复杂的模型好像并不是很困难。模型的调优以及如何把握调优的方向成为了难题。