1.stack / queue(栈,队列)
stack
构造函数 stack<int> v;
入栈 v.push(i);
出栈 v.pop();
是否为空 v.empty()
queue
构造函数 queue<int> v;
入队 v.push(i);
出队 v.pop();
是否为空 v.empty();
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <stack> /*引入栈容器*/
#include <queue> /*引入队列容器*/
using namespace std; /*引入标准命名空间*/
void test0()
{
/**** 创建栈容器对象 *****/
stack<int> v;
/**** 入栈数据:1,2,3,4,5,6 ***/
for(int i = 1; i < 7;i++)
{
v.push(i);
cout << "入栈栈顶数据:" << v.top() << endl;
}
cout <<"—————————— 出栈 ——————————" << endl;
/**** 出栈数据:6,5,4,3,2,1 ***/
while(v.size() != 0)
{
cout << "出栈栈顶数据:" << v.top() << endl;
v.pop();
}
/**** 判断栈是否为空 *****/
cout << "栈是否为空:" << (v.empty() == true ? "为空" : "非空") << endl;
}
void test1()
{
/*** 1.创建队列容器对象 ***/
queue<int> v;
/*** 2.入队数据: 1,2,3,4,5,6 ****/
for(int i = 1; i < 7;i++)
{
v.push(i);/*入队*/
cout << "入队队头元素:" << v.front() << "\t入队队尾元素:" << v.back() << endl;
}
cout << "———————— 出队元素 ——————————" << endl;
/*** 3.出队数据:1,2,3,4,5,6 *****/
while(v.size() != 0)
{
cout << "出队队头元素:" << v.front() << "\t出队队尾元素:" << v.back() << endl;
v.pop(); /*出队*/
}
/*** 4.判断队列是否为空 ****/
cout << "队列是否为空:" << (v.empty() == true ? "为空" : "非空") << endl;
}
int main()
{
test0();
test1();
return 0;
}
2.pair (键值对 iostream 里面自带的)
构造函数: pair<int,string> v(10000, "aaaaaa");
输出模式: v.first, v.second
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/********** pair 键值对 ***********
* <key主键 , value值>
* 类使用: pair
* 成员:
template<class _T1, class _T2>
struct pair
{
pair(_T1 key,_T2 value):first(key),second(value){} //构造函数
typedef _T1 first_type; /// @c 第一个元素的类型:主键
typedef _T2 second_type; /// @c 第二个元素的类型:数值
_T1 first; /// @c 第一个元素的值:主键值
_T2 second; /// @c 第二个元素的值:value值
};
********************************/
//模仿 pair 类
template<class _T1, class _T2>
struct my_pair
{
/** 默认权限是 公有权限 **/
my_pair(_T1 key,_T2 value):first(key),second(value){} //构造函数
typedef _T1 first_type; // @c 第一个元素的类型:主键
typedef _T2 second_type; // @c 第二个元素的类型:数值
/*** 主要学习: first , second ***/
_T1 first; // @c 第一个元素的值:主键值
_T2 second; // @c 第二个元素的值:value值
};
int main()
{
/***** 案例: 主键:学号, 值:学生姓名 *******/
my_pair<int,string> v(1000,"张三");
cout << "主键:" << v.first << "\t值:" << v.second << endl;
/***** 标准的键值对 ****/
pair<int,string> v1(1001,"李四");
cout << "主键:" << v1.first << "\t值:" << v1.second << endl;
/***** 主要解决 一个参数无法操作的内容,例如 返回值类型只允许一个返回值,但是项目需要返回两个甚至
* 多个,所以可以使用键值对实现方案 ****************/
return 0;
}
3.set (集合 不可重复) /multiset(数据可重复存储)
/************* set 容器 ******************
* 特点:
* 1.去除重复值
* 2.插入时自动排序
* 3.容器内部元素插入时为常对象 - 只能访问常函数
* (自身就是key主键,主键不能修改)
* 4. set容器无法修改内部元素值
* **************************************/
构造函数: set<int > v;
增加数据: v.insert(111);
查询数据: v.find(111);
统计set 容器元素个数 : v.count();
容器是否为空 : v.empty();
clear(); //清除所有元素
erase(pos); //删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器
erase(beg, end); //删除区间(beg, end)的所有元素,返回下元素的迭代器
erase(elem); //删除容器中值为elem的元素。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <set> /*set集合容器*/
#include <vector> /*单端数组容器*/
using namespace std;/*标准命名空间*/
#define ADDR_SIZE(x) (sizeof(x)/sizeof(x[0])) //求取元素个数
/************* set 容器 ******************
* 特点:
* 1.去除重复值
* 2.插入时自动排序
* 3.容器内部元素插入时为常对象 - 只能访问常函数
* (自身就是key主键,主键不能修改)
* **************************************/
void test0()
{
set<int> v;
int addr[] = {1,6,78,23,5,45,2,5}; /*无序数组*/
cout << "***** 插入数据 **** " << endl;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> pair_set;
for(size_t i = 0; i < ADDR_SIZE(addr);i++)
{
pair_set = v.insert(addr[i]); /*插入数据*/
if(pair_set.second == true)
{
cout << "插入成功:" << *pair_set.first << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "插入失败:" << addr[i] << endl;
}
}
cout << "***** 打印set数据 ********" << endl;
set<int>::iterator it;
for(it = v.begin(); it != v.end() ; it++)
{
cout << *it << ",";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "***** 试图去修改set容器元素值 ******" << endl;
it = v.begin(); /*第一元素*/
cout << "第一个元素:" << *it << endl;
// *it = 500; set容器无法修改内部元素值
cout << "***** 容器大小和判断是否为空 *****" << endl;
cout << "当前元素个数:" << v.size() << endl;
cout << "当前容器是否为空:" << (v.empty() == true ? "为空" : "非空") << endl;
cout << "***** 容器查找和统计元素 ******" << endl;
it = v.find(7);
if(it != v.end())
{
cout << "找到了元素为:" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "容器内没有找到为7的元素" << endl;
}
int num = v.count(5);
cout << "统计容器内元素为5的个数:" << num << endl;
}
/************* multiset 容器 ******************
* 特点:
* 1.插入时自动排序
* 2.容器内部元素插入时为常对象 - 只能访问常函数
* (自身就是key主键,主键不能修改)
* **************************************/
void test1()
{
multiset<int> v;
int addr[] = {1,6,78,23,5,45,2,5}; /*无序数组*/
cout << "***** 插入数据 **** " << endl;
multiset<int>::iterator it;
#if 0 //插入
for(size_t i = 0; i < ADDR_SIZE(addr);i++)
{
it = v.insert(addr[i]); /*插入数据*/
}
#else
vector<int> v_vector;
for(size_t i = 0; i < ADDR_SIZE(addr);i++)
{
v_vector.push_back(addr[i]);
}
cout << "vector的数据:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i< v_vector.size() ;i++)
{
cout << v_vector[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
v.insert(v_vector.begin(),v_vector.end());
#endif
cout << "***** 打印set元素 ****" << endl;
for(it = v.begin() ; it != v.end() ;it++)
{
cout << *it << ",";
}
cout << endl;
#if 1
v_vector.assign(v.begin(),v.end());
cout << "vector的数据:" << endl;
for(int i = 0; i< v_vector.size() ;i++)
{
cout << v_vector[i] << ",";
}
cout << endl;
#endif
cout << "***** 试图去修改set容器元素值 ******" << endl;
it = v.begin(); /*第一元素*/
cout << "第一个元素:" << *it << endl;
// *it = 500; set容器无法修改内部元素值
cout << "***** 容器大小和判断是否为空 *****" << endl;
cout << "当前元素个数:" << v.size() << endl;
cout << "当前容器是否为空:" << (v.empty() == true ? "为空" : "非空") << endl;
cout << "***** 容器查找和统计元素 ******" << endl;
it = v.find(7);
if(it != v.end())
{
cout << "找到了元素为:" << *it << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "容器内没有找到为7的元素" << endl;
}
int num = v.count(5);
cout << "统计容器内元素为5的个数:" << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test1();
return 0;
}
4.map(地图) /multimap(可重复 地图)
/*********** map容器 ************
* 特点:
* 1.去除重复的主键
* ****************************/
构造函数 ; map <int,string> v;
增加数据 : v.insert(pair<int,string>(1,"aaaa"));
v[键值]= value; ==> v[1]="aaaa" (修改,可以通过主键修改value值(①存在则修改②不存在则插入)
删除数据:
clear(); //清除所有元素
erase(pos); //删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器
erase(beg, end); //删除区间(beg, end)的所有元素,返回下元素的迭代器
erase(键值); //删除容器中值为 键值 的元素。
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <map> /*引入 map 容器*/
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;/*引入标准命名空间*/
/*********** map容器 ************
* 特点:
* 1.去除重复的主键
* ****************************/
void test0()
{
/*** 1.实例化map对象 map<key,value>***/
map<int,string> v;
/*** 2.插入数据 *****/
string names[] = {"张三","李四","王五","赵六","蕾蕾","李丽"};
for(int i = 5; i >= 0;i--)
{
//int id = rand() % 5 + 10000;
int id = 10000 + i;
pair< map<int,string>::iterator , bool> pair_map;
pair_map = v.insert(pair<int,string>(id,names[i]));
cout << "插入:" << (pair_map.second == true ? "成功" : "失败") << endl;
cout << "学号:" << id << "\t姓名:" << names[i] << endl;
}
cout << "****打印map容器数据****" << endl;
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for(it = v.begin() ; it != v.end() ; it++) // *t <==> pair<int,string>
{
cout << "主键:" << (*it).first <<"\tvalue值:" << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout << "****访问,可以通过主键访问value值****" << endl;
cout << v[10000] << endl;
cout << v[10004] << endl;
cout << "****修改,可以通过主键修改value值(①存在则修改②不存在则插入)" << endl;
v[10000] = "王";
v[10100] = "蒋";
cout << "****打印map容器数据****" << endl;
for(it = v.begin() ; it != v.end() ; it++) // *t <==> pair<int,string>
{
cout << "主键:" << (*it).first <<"\tvalue值:" << (*it).second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL)); /*制种*/
test0();
return 0;
}
5.set 和 map
代码:
#include <iostream>
/***** 这两个容器底层都是使用 二叉树实现 *****
* 1.自动排序
* 2.使用二分法方式
* 3.是数组和链表的折中方案
* *************************************/
#include <set> /*集合容器*/
#include <map> /*图容器*/
using namespace std;
/****** 自定义一个类 *****/
class People
{
public:
People(string ID = "0",string name = "",string sex = "女",int age = 0,int height = 0)
:m_ID(ID),m_name(name),m_sex(sex),m_age(age),m_height(height)
{
/*构造函数*/
}
/********* 只读的函数,就一定要制作成const常函数,否则 set 容器使用不了 *******/
bool operator <(/*this*/const People &people) const
{
return this->m_ID < people.m_ID;
}
friend ostream &operator <<(ostream &out,const People &people)
{
out << "\t" << people.m_ID
<< "\t" << people.m_name
<< "\t" << people.m_sex
<< "\t" << people.m_age
<< "\t" << people.m_height;
return out;
}
string ID() const;
string name() const;
void setName(const string &name);
string sex() const;
void setSex(const string &sex);
int age() const;
void setAge(int age);
int height() const;
void setHeight(int height);
protected:
string m_ID; /*身份证号*/ //一般唯一的就是身份证号
string m_name; /*姓名*/
string m_sex; /*性别*/
int m_age; /*年龄*/
int m_height; /*身高*/
};
void test_set()
{
#if 0
/* 1.实例化 set 容器装载 People 对象 */
set<People> v;
#else
/* 1.实例化 set 容器装载 People 对象,自定义规则set<People,仿函数类名> */
class Cmp_People
{
public:
bool operator ()(const People &people,const People &people2)
{
return people.height() < people2.height();
}
};
set<People,Cmp_People> v;
#endif
/* 2.插入信息到容器 :默认使用运算符重载 < 比较运算符*/
v.insert(People("522724193561231651","王廷胡","男",18,160));
v.insert(People("522724193561231652","望提升","女",16,165));
v.insert(People("522724193852231652","马旭升","男",19,185));
v.insert(People("522624193852231653","马云","男",45,165));
/* 3.遍历打印数据 */
set<People>::iterator it;
for(it = v.begin() ; it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
void test_map()
{
#if 1
/******** 1.实例化map容器装载People **********/
//map<string,People> v;
class Cmp_string
{
public:
bool operator()(const string &str1,const string &str2)
{
return str1 < str2;
}
};
map<string,People,Cmp_string> v;
/******** 2.装载数据到map中 ******************/
v.insert(pair<string,People>("522724193561231651",People("522724193561231651","王廷胡","男",18,160)));
v.insert(pair<string,People>("522624193852231653",People("532624193852231653","马云","男",45,165)));
v["522724193561231652"] = People("522724193561231652","望提升","女",16,165);
/******** 3.遍历打印数据 **********************/
map<string,People>::iterator it;
for(it = v.begin();it != v.end() ; it++)
{
cout << (*it).second << endl;
}
cout << "————————————————————————————————————" << endl;
/******** 4.中括号访问 ********/
cout << v["522724193561231652"] << endl;
#else
/******** 1.实例化multimap容器装载People **********/
multimap<string,People> v;
/******** 2.装载数据到map中 ******************/
v.insert(pair<string,People>("522724193561231651",People("522724193561231651","王廷胡","男",18,160)));
v.insert(pair<string,People>("522724193561231651",People("522724193561231651","李白","男",18,160)));
/******** 3.遍历打印数据 **********************/
multimap<string,People>::iterator it;
for(it = v.begin();it != v.end() ; it++)
{
cout << (*it).second << endl;
}
#endif
}
int main()
{
//test_set();
test_map();
return 0;
}
string People::ID() const
{
return m_ID;
}
string People::name() const
{
return m_name;
}
void People::setName(const string &name)
{
m_name = name;
}
string People::sex() const
{
return m_sex;
}
void People::setSex(const string &sex)
{
m_sex = sex;
}
int People::age() const
{
return m_age;
}
void People::setAge(int age)
{
m_age = age;
}
int People::height() const
{
return m_height;
}
void People::setHeight(int height)
{
m_height = height;
}
6. 新学的内容 (json )(它的作用还不知道)
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation, JS对象简谱)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于 ECMAScript(European Computer Manufacturers Association, 欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范)的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
了解连接 : JSON_百度百科 (baidu.com)
在线格式JSON:Json在线格式化工具-Json解析视图查看器-Json在线解析格式化工具 (jsons.cn)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
#include "json/json.h" /* 引入json 头文件 */
using namespace Json;
int main()
{
/*** 定义一个 json 对象 ****/
Json::Value value;
/*** 没有则增加,有则修改 ****/
value["姓名"] = "王廷胡";
value["年龄"] = 18;
value["性别"] = "男";
value["身高"] = 165;
value["家庭"] = "和睦";
/***** value 转 基础类型 *****/
cout << "姓名:" << value["姓名"].asString() << endl;
cout << "年龄:" << value["年龄"].asInt() << endl;
cout << "家庭:" << value["家庭"].asCString() << endl;
/**** value 输出 *****/
cout << value << endl;
/**** value 转格式化 C 或 C++ *******/
string str_json = value.toStyledString();
cout << str_json << endl;
const char *C_json = str_json.data();
cout << str_json << endl;
#if 0
fstream fp;
fp.open("test.json",ios_base::trunc | ios_base::out | ios_base::in);
if(fp.is_open() == false) return -1;
fp.write(C_json,strlen(C_json));
fp.close();
#else
fstream fp;
fp.open("test.json",ios_base::out | ios_base::in);
if(fp.is_open() == false) return -1;
string str;
char ch;
while(fp.eof() != true)
{
ch = fp.get();
str += ch;
}
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
/***** 将string 或 char * 转为 JSON的Value ******/
Reader json_Read;
Value json_value;
#if 1 /* C++的string 风格 */
json_Read.parse(str,json_value);
#else /* C语言的char *风格 */
json_Read.parse("{\"姓名\":\"李白\"\"}",json_value);
#endif
cout << "姓名:" << json_value["字符集"]["GBK"] << endl;
#endif
return 0;
}
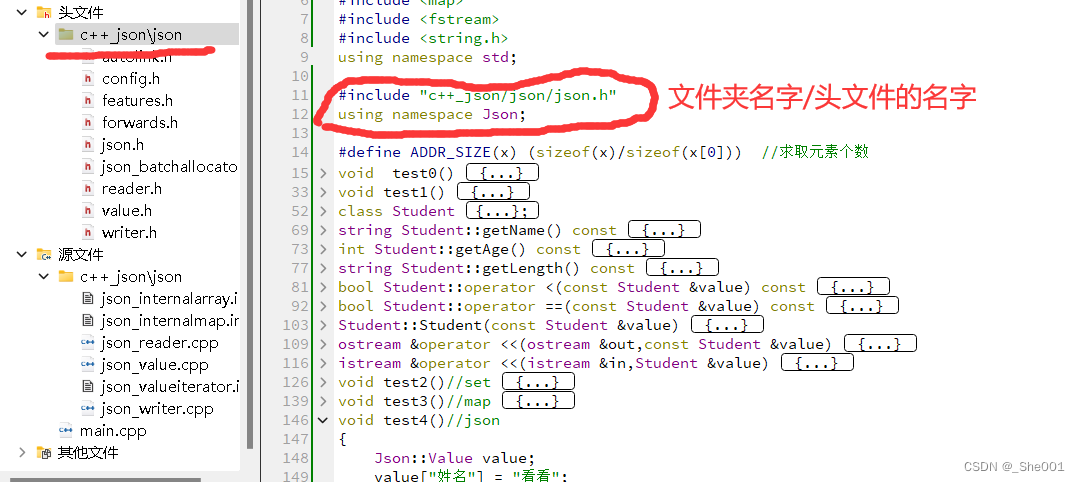
资源里面有 json 资源
linux 视屏监控
代码:
main.cpp
// #include "cv.h"
// #include "highgui.h"
#include "opencv2/core/core.hpp" /* 引入opencv核心库 -lopencv_core */
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" /*图像处理库 -lopencv_highgui */
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" /*摄像头库 -lopencv_imgproc */
using namespace cv; /*引入 OPencv 命名空间 */
int main(int, char**)
{
VideoCapture cap(0); /*实例化摄像头 对象 依赖于 0号摄像头 */
if(!cap.isOpened()) return -1;/*打开0号摄像头*/
Mat frame, edges; /*实例化两个图片对象 frame , edges */
namedWindow("edges",1);/*创建窗体 名称为 edges */
for(;;)
{
cap >> frame; /*摄像头拍照 结果写入 frame 图片对象 */
edges = frame;
// cvtColor(frame, edges, CV_BGR2GRAY); /*灰度处理*/
// GaussianBlur(edges, edges, Size(7,7), 1.5, 1.5);/*高斯模糊*/
// Canny(edges, edges, 0, 30, 3);/*边缘检测*/
imshow("edges", edges);
if(waitKey(30) >= 0) break;
}
return 0;
}
makefile
#源文件
SOURCES += main.cpp
#编译标志
CONFIG += -std=c++11
CONFIG += -g
#链接库
CONFIG += -lopencv_core -lopencv_highgui -lopencv_imgproc
#编译器
CC = g++
#应用名称
APP = a.out
#编译
${APP}:${SOURCES}
${CC} $^ ${CONFIG} -o $@
clean:
rm -rf ${APP}
在相对应的目录下,输入命令:
1. makefile
2. ./a.out
就可以了

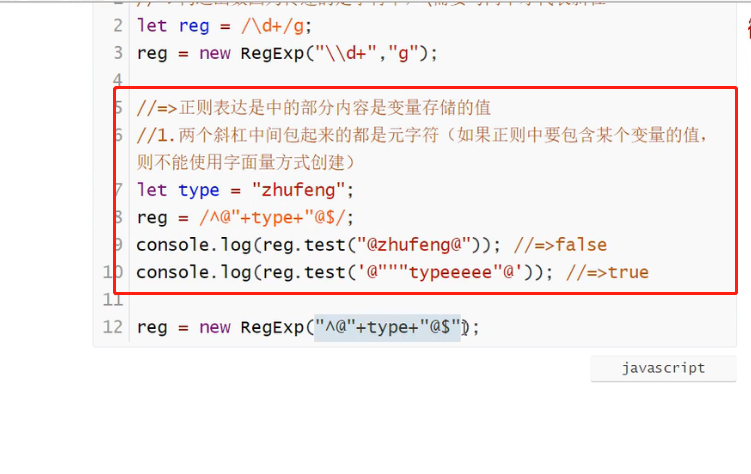
有些地方要注意:
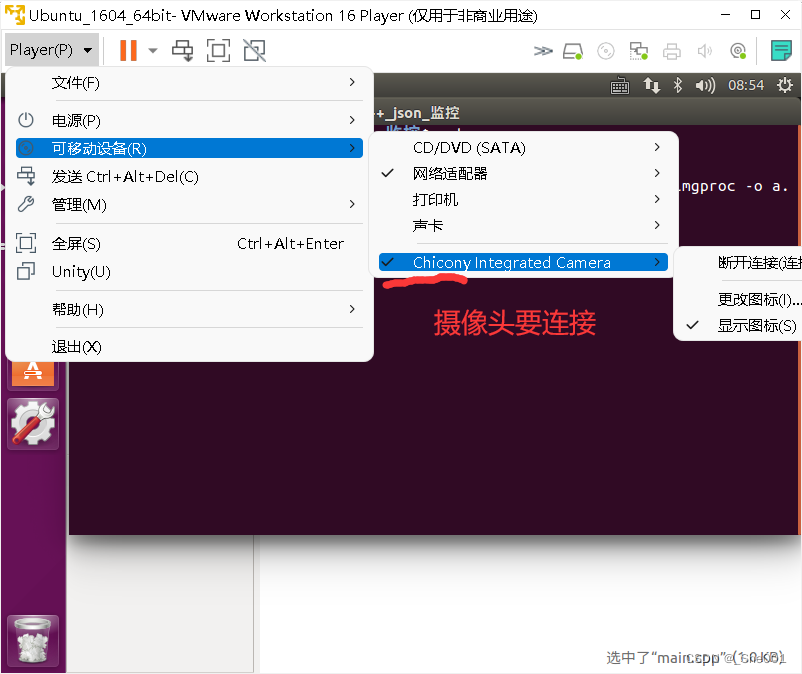





![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django儿童早教课程管理系统论文2022](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c0d3f0d9586e4a1682b774ff1c1b1709.png)


![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计SSM科技项目在线评审系统(程序+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/14622f3e321642e4b8b4875bbb810cdf.png)

![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计疫情防控期间人员档案追寻系统设计与实现论文JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/69bb747af3064bb5b9be90331bb3c4f3.png)
