一、数据集介绍

Data Set Information:
These data are the results of a chemical analysis of wines grown in the same region in Italy but derived from three different cultivars. The analysis determined the quantities of 13 constituents found in each of the three types of wines.
I think that the initial data set had around 30 variables, but for some reason I only have the 13 dimensional version. I had a list of what the 30 or so variables were, but a.) I lost it, and b.), I would not know which 13 variables are included in the set.
The attributes are (dontated by Riccardo Leardi, riclea ‘@’ anchem.unige.it )
- Alcohol
- Malic acid
- Ash
- Alcalinity of ash
- Magnesium
- Total phenols
- Flavanoids
- Nonflavanoid phenols
- Proanthocyanins
- Color intensity
- Hue
- OD280/OD315 of diluted wines
- Proline
In a classification context, this is a well posed problem with “well behaved” class structures. A good data set for first testing of a new classifier, but not very challenging.
Attribute Information:
All attributes are continuous
No statistics available, but suggest to standardise variables for certain uses (e.g. for us with classifiers which are NOT scale invariant)
NOTE: 1st attribute is class identifier (1-3)
二、使用贝叶斯分类
代码首先加载WINE数据集,并对数据进行预处理,然后划分训练集和测试集,并将它们转换为PyTorch张量。接着计算每个类别的先验概率、均值和标准差,然后定义了一个朴素贝叶斯分类器。最后在测试集上进行预测并计算准确率。需要注意的是,在这个示例中,我们使用了PyTorch的正态分布概率密度函数来计算每个特征的似然概率,这是因为WINE数据集的特征是连续值。如果特征是离散值,我们需要使用多项式分布概率质量函数来计算似然概率。
import torch
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# 加载WINE数据集
data = load_wine()
# 数据预处理
X = data.data
y = data.target
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 转换为PyTorch张量
X_train = torch.from_numpy(X_train).float()
y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train).long()
X_test = torch.from_numpy(X_test).float()
y_test = torch.from_numpy(y_test).long()
# 计算每个类别的先验概率
priors = []
for c in range(3):
priors.append((y_train == c).sum().item() / len(y_train))
# 计算每个类别的均值和标准差
means = []
stds = []
for c in range(3):
X_c = X_train[y_train == c]
mean_c = X_c.mean(dim=0)
std_c = X_c.std(dim=0)
means.append(mean_c)
stds.append(std_c)
# 定义朴素贝叶斯分类器
def predict(X):
scores = []
for c in range(3):
log_prior = np.log(priors[c])
log_likelihood = torch.distributions.Normal(means[c], stds[c]).log_prob(X).sum(dim=1)
score_c = log_prior + log_likelihood
scores.append(score_c)
scores = torch.stack(scores, dim=1)
_, predicted = torch.max(scores, 1)
return predicted
# 在测试集上进行预测
y_pred = predict(X_test)
accuracy = (y_pred == y_test).sum().item() / len(y_test)
print('Accuracy on test set: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100))

三、使用支持向量机分类
代码首先加载WINE数据集,并对数据进行预处理,然后划分训练集和测试集,并将它们转换为PyTorch张量。接着训练一个支持向量机分类器,这里我们选择线性核函数并设置参数C为1.0。最后在测试集上进行预测并计算准确率。
PyTorch本身并不提供SVM分类器的实现,我们使用了scikit-learn库的SVC类来训练SVM分类器。在训练SVM分类器之前,我们将PyTorch张量转换为NumPy数组,这是因为scikit-learn库的SVC类需要接受NumPy数组作为输入。同样,在预测时,我们也需要将测试集的PyTorch张量转换为NumPy数组。
import torch
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.svm import SVC
# 加载WINE数据集
data = load_wine()
# 数据预处理
X = data.data
y = data.target
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 转换为PyTorch张量
X_train = torch.from_numpy(X_train).float()
y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train).long()
X_test = torch.from_numpy(X_test).float()
# 训练SVM分类器
clf = SVC(kernel='linear', C=1.0)
clf.fit(X_train.numpy(), y_train.numpy())
# 在测试集上进行预测
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test.numpy())
accuracy = (y_pred == y_test).sum().item() / len(y_test)
print('Accuracy on test set: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100))

四、使用神经网络分类
代码首先加载WINE数据集,并对数据进行预处理,然后划分训练集和测试集,并将它们转换为PyTorch张量。接着定义了一个具有三个全连接层的神经网络,使用交叉熵损失函数和Adam优化器进行训练,最后在测试集上进行预测并计算准确率。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
# 加载WINE数据集
data = load_wine()
# 数据预处理
X = data.data
y = data.target
scaler = StandardScaler()
X = scaler.fit_transform(X)
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
# 转换为PyTorch张量
X_train = torch.from_numpy(X_train).float()
y_train = torch.from_numpy(y_train).long()
X_test = torch.from_numpy(X_test).float()
y_test = torch.from_numpy(y_test).long()
# 定义神经网络
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
torch.manual_seed(2)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(13, 64)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(64, 32)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(32, 3)
def forward(self, x):
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
net = Net()
# 定义损失函数和优化器
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.001)
# 训练神经网络
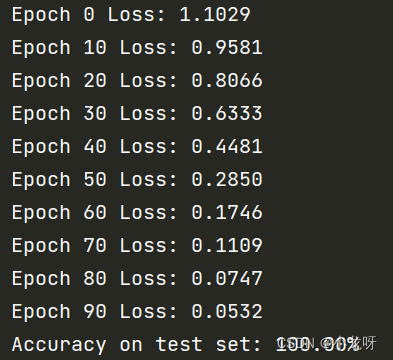
for epoch in range(100):
optimizer.zero_grad()
output = net(X_train)
loss = criterion(output, y_train)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch % 10 == 0:
print('Epoch %d Loss: %.4f' % (epoch, loss.item()))
# 在测试集上进行预测
with torch.no_grad():
output = net(X_test)
_, predicted = torch.max(output, 1)
total = y_test.size(0)
correct = (predicted == y_test).sum().item()
accuracy = correct / total
print('Accuracy on test set: %.2f%%' % (accuracy * 100))



![有序表的应用:[Leetcode 327] 区间和的个数](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/c7eaf13dc11348c49d7c610f3ececa9d.jpeg)