- mongodb入门
- mongodb-java api的使用
- springboot整合mongodb
- 评论
一 MongoDB
1.1 MongoDB简介
MongoDB是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库。由C++语言编写。旨在为WEB应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。
MongoDB是一个介于关系数据库和非关系数据库之间的产品,是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的,它支持的数据结构非常松散,是类似json的bson格式,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。
MongoDB最大的特点是它支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系数据库单表查询的绝大部分功能,而且还支持对数据建立索引。
官网:https://www.mongodb.com
1.2 MongoDB安装
1.2.1 windows安装mongodb
官网下载mongodb安装包
https://www.mongodb.com/try/download/community
1 将mongodb压缩包解压到指定目录即可
2 配置环境变量 将mongodb/bin目录配置到path中

3 启动 ,双击bin/mongod.exe
如果启动时,报错
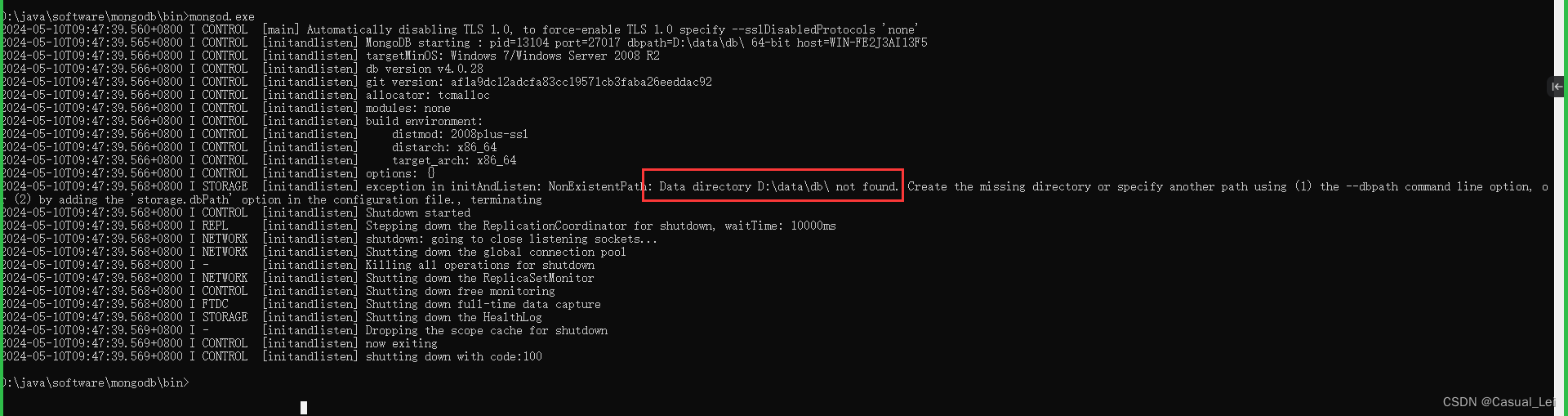
说明是mongodb启动时会默认加载这个路径作为存储数据的地方,而当前路径没有,就需要手动新建一个目录
4 启动完成以后,可以双击mongo.exe,打开命令行连接本机mongodb,测试本机mongodb是否启动成功

1.2.2 docker安装mongodb
# 安装mongodb容器
docker run -id --name=mongodb --hostname=mongodb -p 27017:27017 mongo
# 进入mongodb容器
docker exec -it mongodb /bin/bash
# 进入mongodb命令行
mongo
# 查看当前mongodb中所有的数据库
show dbs
# 安装mongodb容器并设置用户名,密码
docker run -id --name=mongodb --hostname=mongodb -p 27017:27017 -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=root -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 mongo
# mongodb设置了密码以后,怎么连接?
docker exec -it mongodb /bin/bash # 进入mongodb容器
mongo # 进入mongodb命令行
use admin # 切换到admin数据库
db.auth("用户名","密码") # 输入用户名和密码,如果返回1就说明登录成功
1.3 MongoDB基本使用
1.3.1 基本概念
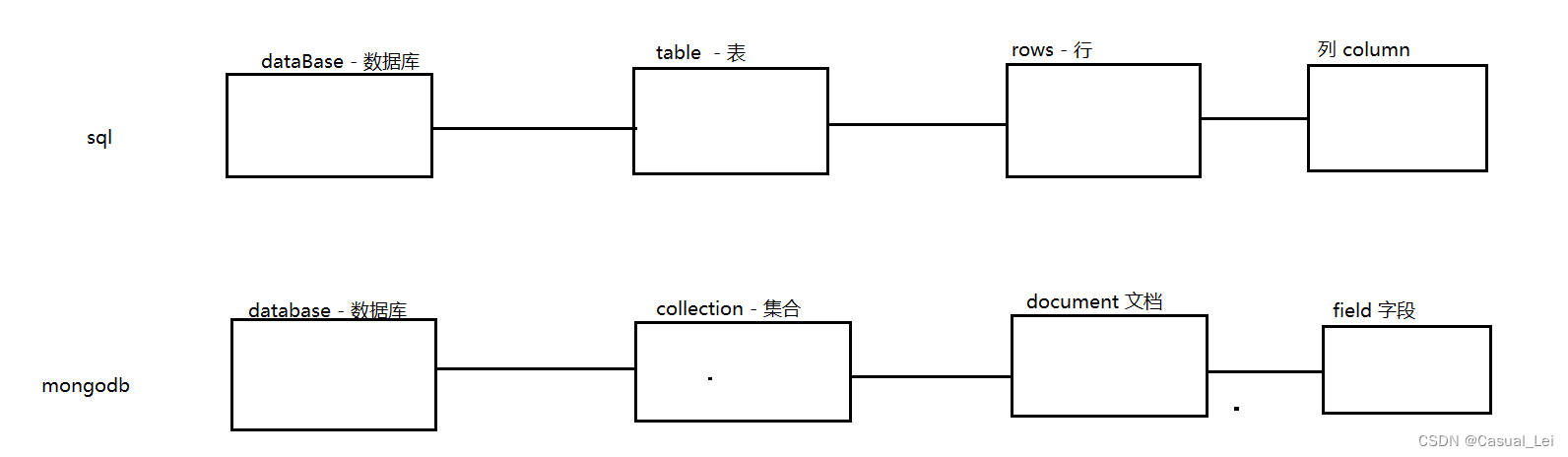
在使用Mongodb以前,为了方便理解,先对应关系型数据库了解下相关概念
| sql概念 | mongodb概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| database | database | 数据库 |
| table | collection | 数据库表/集合 |
| row | document | 数据行/文档 |
| column | field | 列/字段 |
| index | index | 索引 |
| table joins | 表关联,mongodb不支持 | |
| primary key | primary key | 主键,MongoDB自动将_id字段设置为主键 |
1.3.2 数据库和表操作
查看所有数据库 show dbs
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
切换数据库 use 数据库名
> use admin
switched to db admin
创建数据库和表
在MongoDB中,数据库是自动创建的,通过use切换到新数据库中,进行插入数据即可自动创建数据库和表
# 查看所有的数据库,当前没有test数据库
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
# 切换到test数据库
> use test
switched to db test
# 再次查看所有数据库,还是没有test,说明use只是切换数据库,不会创建数据库
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
# 直接向test数据库中的user表插入数据
> db.user.insert({id:1,name:"zhangsan"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
# 查看所有数据库,当前有了test数据库
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
test 0.000GB
删除数据库
> db.dropDatabase()
{ "dropped" : "test", "ok" : 1 }
> show dbs
admin 0.000GB
local 0.000GB
查看所有的表 show tables/collections
> show tables
user
> show collections
user
删除表 drop
> db.user.drop()
true
> show tables
1.3.3 文档操作
1.3.3.1 新增数据
insert/save 如果当前没有这个表,那么当第一次新增数据时,会自动新建表
> db.user.insert({id:1,name:"zhangsan"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.save({id:2,name:"lisi"})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98397dbe43ebeabeadf"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zhangsan" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98f97dbe43ebeabeae0"), "id" : 2, "name" : "lisi" }
1.3.3.2 更新数据
db.表名.update({query},{set})
query: 就相当于sql中写在where条件后面
set : 就是修改后的字段值,相当于Sql中set
# 更新数据,更新id=1的name为zs
> db.user.update({id:1},{$set:{name:"zs"}})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98397dbe43ebeabeadf"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98f97dbe43ebeabeae0"), "id" : 2, "name" : "lisi" }
# 更新id=2的数据,年龄为30,但是其他字段都会删除掉
> db.user.update({id:2},{age:30})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98397dbe43ebeabeadf"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98f97dbe43ebeabeae0"), "age" : 30 }
# 更新id=1的数据,age=35,如果age字段不存在,会默认新增该字段
> db.user.update({id:1},{$set:{age:35}})
WriteResult({ "nMatched" : 1, "nUpserted" : 0, "nModified" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98397dbe43ebeabeadf"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs", "age" : 35 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98f97dbe43ebeabeae0"), "age" : 30 }
1.3.3.3 删除数据
# 删除id=1
> db.user.remove({id:1})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638c98f97dbe43ebeabeae0"), "age" : 30 }
# 删除所有
> db.user.remove({})
WriteResult({ "nRemoved" : 1 })
> db.user.find()
1.3.3.4 查询数据
#查询语句结构
db.user.find([query],[fields])
query 是查询的条件
fields 是查询的字段
# 造数据
> db.user.insert({id:1,name:"zs",age:20})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.insert({id:2,name:"ls",age:35})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.insert({id:3,name:"ww",age:28})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
> db.user.insert({id:4,name:"zl",age:32})
WriteResult({ "nInserted" : 1 })
# 查询所有
> db.user.find()
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3497dbe43ebeabeae5"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs", "age" : 20 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3d97dbe43ebeabeae6"), "id" : 2, "name" : "ls", "age" : 35 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc4897dbe43ebeabeae7"), "id" : 3, "name" : "ww", "age" : 28 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc5797dbe43ebeabeae8"), "id" : 4, "name" : "zl", "age" : 32 }
# 只查询id,name字段
> db.user.find({},{id:1,name:1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3497dbe43ebeabeae5"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3d97dbe43ebeabeae6"), "id" : 2, "name" : "ls" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc4897dbe43ebeabeae7"), "id" : 3, "name" : "ww" }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc5797dbe43ebeabeae8"), "id" : 4, "name" : "zl" }
# 查询条数
> db.user.find().count()
4
# 查询ID=1的数据
> db.user.find({id:1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3497dbe43ebeabeae5"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs", "age" : 20 }
# 查询年龄在25-35之间的数据
> db.user.find({age:{$lte:35,$gte:25}})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3d97dbe43ebeabeae6"), "id" : 2, "name" : "ls", "age" : 35 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc4897dbe43ebeabeae7"), "id" : 3, "name" : "ww", "age" : 28 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc5797dbe43ebeabeae8"), "id" : 4, "name" : "zl", "age" : 32 }
# 查询年龄<=35,且id>=3的
> db.user.find({age:{$lte:35},id:{$gte:3}})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc4897dbe43ebeabeae7"), "id" : 3, "name" : "ww", "age" : 28 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc5797dbe43ebeabeae8"), "id" : 4, "name" : "zl", "age" : 32 }
# 查询id=1 or id=2的数据
> db.user.find({$or:[{id:1},{id:2}]})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3497dbe43ebeabeae5"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs", "age" : 20 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3d97dbe43ebeabeae6"), "id" : 2, "name" : "ls", "age" : 35 }
# 分页查询 skip()跳过几条数据,可以理解为从第几条开始查询 limit()查询的条数
> db.user.find().skip(2).limit(2)
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc4897dbe43ebeabeae7"), "id" : 3, "name" : "ww", "age" : 28 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc5797dbe43ebeabeae8"), "id" : 4, "name" : "zl", "age" : 32 }
# 按照年龄倒序排 -1倒序排列 1 正序排列
> db.user.find().sort({age:-1})
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3d97dbe43ebeabeae6"), "id" : 2, "name" : "ls", "age" : 35 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc5797dbe43ebeabeae8"), "id" : 4, "name" : "zl", "age" : 32 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc4897dbe43ebeabeae7"), "id" : 3, "name" : "ww", "age" : 28 }
{ "_id" : ObjectId("6638cc3497dbe43ebeabeae5"), "id" : 1, "name" : "zs", "age" : 20 }
1.3.4 索引操作
索引通常能够极大的提高查询的效率,如果没有索引,MongoDB在读取数据时必须扫描集合中的每个文件并选取
那些符合查询条件的记录。
这种扫描全集合的查询效率是非常低的,特别在处理大量的数据时,查询可以要花费几十秒甚至几分钟,这对网站
的性能是非常致命的。
索引是特殊的数据结构,索引存储在一个易于遍历读取的数据集合中,索引是对数据库表中一列或多列的值进行排
序的一种结构
# 查看索引 说明:1表示升序创建索引,-1表示降序创建索引。
> db.user.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "test.user"
}
]
# 创建索引 按照年龄升序创建索引
> db.user.createIndex({age:1})
{
"createdCollectionAutomatically" : false,
"numIndexesBefore" : 1,
"numIndexesAfter" : 2,
"ok" : 1
}
> db.user.getIndexes()
[
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"_id" : 1
},
"name" : "_id_",
"ns" : "test.user"
},
{
"v" : 2,
"key" : {
"age" : 1
},
"name" : "age_1",
"ns" : "test.user"
}
]
#删除索引
db.user.dropIndex("age_1")
#或者,删除除了_id之外的索引
db.user.dropIndexes()
#创建联合索引
db.user.createIndex({'age':1, 'id':-1})
#查看索引大小,单位:字节
db.user.totalIndexSize()
1.4 Mongodb图形客户端的使用
1.4.1 安装mongoDB客户端
Robo 3T是MongoDB的客户端工具,我们可以使用它来操作MongoDB。

注意:如果连接的是远程云服务器的话,一定要在安全组中放行mongodb的端口27017
1.4.2 客户端基本使用


二 java操作MongoDB
1 javaApi操作MongoDB
导依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongodb-driver-sync</artifactId>
<version>3.9.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.1 文档操作
连接MongoDB
@Test
public void test() throws Exception{
// 创建MongoDb客户端
MongoClient mongoClient = MongoClients.create("mongodb://root:123456@116.205.236.142:27017");
// 选择要操作的数据库
MongoDatabase database = mongoClient.getDatabase("test");
// 选择要操作的表
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("user");
System.out.println(collection);
// 关闭客户端连接
mongoClient.close();
}
文档crud
public class MongodbTest {
private static MongoClient mongoClient = null;
public MongoCollection<Document> getCollection() throws Exception{
// 创建MongoDb客户端
mongoClient = MongoClients.create("mongodb://116.205.236.142:27017");
// 选择要操作的数据库
MongoDatabase database = mongoClient.getDatabase("test");
// 选择要操作的表
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection("user");
System.out.println(collection);
return collection;
}
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception{
// 连接mongodb,获取要操作的表
MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection();
// 构造要新增的数据
Document document = new Document("id", 5).append("name", "tq").append("age", 24);
// 插入数据
collection.insertOne(document);
// 关闭客户端连接
mongoClient.close();
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception{
// 连接mongodb,获取要操作的表
MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection();
// 构建修改的条件
Bson bson = Filters.eq("id", 5);
// 构建修改后的对象
Bson bson1 = Updates.set("age", 26);
// 修改数据
collection.updateOne(bson,bson1 );
// 关闭客户端
mongoClient.close();
}
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception{
// 连接mongodb,获取要操作的表
MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection();
// 删除id=5的数据
collection.deleteOne(Filters.eq("id", 5));
// 关闭客户端
mongoClient.close();
}
@Test
public void testQuery() throws Exception{
// 连接mongodb,获取要操作的表
MongoCollection<Document> collection = getCollection();
// 查询所有数据
FindIterable<Document> documents = collection.find();
for (Document document : documents) {
System.out.println(document);
}
System.out.println("==============================================");
// 查询age在25-35之间的,按照年龄倒序排列,且分页查询
FindIterable<Document> documents1 = collection.find(
Filters.and(
Filters.lte("age", 35),
Filters.gte("age", 25)
)
).sort(Sorts.descending("age")).skip(0).limit(2);
for (Document document : documents1) {
System.out.println(document);
}
// 关闭客户端
mongoClient.close();
}
}
1.2 操作对象
定义要操作的员工类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Employee {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String intro;
private Integer sex;
}
crud操作
public class EmployeeTest {
private static MongoClient mongoClient = null;
public MongoCollection<Employee> getCollection() throws Exception{
//定义对象的解码注册器
CodecRegistry pojoCodecRegistry = CodecRegistries.
fromRegistries(MongoClientSettings.getDefaultCodecRegistry(),
CodecRegistries.fromProviders(PojoCodecProvider.builder().automatic(true).build())
);
// 创建MongoDb客户端
mongoClient = MongoClients.create("mongodb://116.205.236.142:27017");
// 选择要操作的数据库
MongoDatabase database = mongoClient.getDatabase("test").withCodecRegistry(pojoCodecRegistry);;
// 选择要操作的表
MongoCollection<Employee> collection = database.getCollection("employee", Employee.class);
System.out.println(collection);
return collection;
}
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception{
Employee employee = new Employee(1L, "zhangsan", 30, "张三是一个好员工", 1);
MongoCollection<Employee> collection = getCollection();
collection.insertOne(employee);
mongoClient.close();
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception{
MongoCollection<Employee> collection = getCollection();
collection.updateOne(Filters.eq("_id", 1), Updates.set("name", "张三"));
mongoClient.close();
}
@Test
public void testFind() throws Exception{
MongoCollection<Employee> collection = getCollection();
for (Employee employee : collection.find(Filters.eq("age", 30))) {
System.out.println(employee);
}
mongoClient.close();
}
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception{
MongoCollection<Employee> collection = getCollection();
collection.deleteOne(Filters.eq("_id",1));
mongoClient.close();
}
}
2 spring-data-mongodb
spring-data对MongoDB做了支持,使用spring-data-mongodb可以简化MongoDB的操作。
springboot spring data mongodb 就是在springboot项目中使用spring data mongodb
导入依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置application.yml配置文件
spring:
application:
name: springboot-mongodb-demo
data:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/test1
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
测试类测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(classes = App.class)
public class MongodbTest {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Test
public void testAdd() throws Exception{
Employee employee = new Employee(1L, "张三", 30, "张三是个好员工", 1);
mongoTemplate.save(employee);
}
@Test
public void testGetAll() throws Exception{
List<Employee> employees = mongoTemplate.findAll(Employee.class);
System.out.println(employees);
}
@Test
public void testUpdate() throws Exception{
Employee employee = new Employee(1L, "张三1", 28, "张三1是个好员工", 1);
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("id").is(employee.getId()));
Update update = new Update().set("name", employee.getName())
.set("age", employee.getAge())
.set("intro", employee.getIntro())
.set("sex", employee.getSex());
mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,Employee.class);
}
@Test
public void testDelete() throws Exception{
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("id").is(1));
mongoTemplate.remove(query,Employee.class);
}
}
评论功能
用户可以对看上的车辆提问,别的用户或者销售人员可以针对用户的提问进行回复。
需要实现的功能:
发表评价
回复评论
展示该商品的评论
删除评论/回复
-
基于mongodb 将评论数据存放在mongodb中
- 模式自由:MongoDB是一个面向文档的数据库,这意味着它不使用固定的表结构,而是使用灵活的文档模型来存储数据。在商品评论场景中,评论的字段可能会随着业务的发展而发生变化,使用MongoDB可以更加灵活地应对这种变化,而无需修改整个数据库结构。
- 高性能:MongoDB的查询性能通常优于传统关系型数据库,尤其是在处理大量数据时。对于商品评论系统来说,可能需要存储和检索大量的评论数据,MongoDB的高性能可以确保系统的响应速度和稳定性。
- 可扩展性:MongoDB支持分布式存储和自动分片,可以轻松实现横向扩展。这意味着当评论数据量增长时,可以通过添加更多的服务器来扩展存储容量和查询性能,而无需停机或中断服务。
- 易用性:MongoDB使用BSON(二进制JSON)格式存储数据,数据以文档的形式组织,类似于JSON对象。这使得数据的存储和检索更加直观和易于理解,降低了开发难度。
- 数据一致性:MongoDB支持数据复制和冗余存储,以提供高可用性和数据备份。这意味着即使发生硬件故障或网络问题,也可以保证数据的完整性和一致性,从而确保商品评论系统的稳定性和可靠性。
MongoDB的模式自由、高性能、可扩展性、易用性和数据一致性等特点使其成为商品评论功能中存储数据的理想选择。然而,具体是否使用MongoDB还需要根据项目的实际需求和技术栈来决定
2 后端实现
domain
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Comment {
private String id;
private Long userId;
private String username;
private Long carId;
private String content;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date commentTime;
private List<CommentReplies> replies;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class CommentReplies {
private String id;
private Long userId;
private String username;
private String content;
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss",timezone = "GMT+8")
private Date repliesTime;
}
dto
@Data
public class AddRepliesDTO {
private String commentId;
private Long userId;
private String username;
private String content;
}
controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/comment")
public class CommentController {
@Autowired
private ICommentService commentService;
@PutMapping
public AjaxResult addOrUpdate(@RequestBody Comment comment){
if(Objects.nonNull(comment.getId())){
commentService.update(comment);
}else{
commentService.add(comment);
}
return AjaxResult.me();
}
@DeleteMapping
public AjaxResult deleteById(String id){
commentService.deleteById(id);
return AjaxResult.me();
}
@GetMapping("/carId/{carId}")
public AjaxResult getByCarId(@PathVariable("carId")Long carId){
List<Comment> list = commentService.getByCarId(carId);
return AjaxResult.me().setData(list);
}
@PutMapping("/addReplies")
public AjaxResult addReplies(@RequestBody AddRepliesDTO dto){
commentService.addReplies(dto);
return AjaxResult.me();
}
}
service
@Service
public class CommentServiceImpl implements ICommentService {
@Autowired
private MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Override
public void add(Comment comment) {
comment.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""));
comment.setCommentTime(new Date());
mongoTemplate.save(comment);
}
@Override
public void update(Comment comment) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("id").is(comment.getId()));
Update update = new Update().set("content", comment.getContent())
.set("commentTime", new Date());
mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,Comment.class);
}
@Override
public void deleteById(String id) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("id").is(id));
mongoTemplate.remove(query,Comment.class);
}
@Override
public List<Comment> getByCarId(Long carId) {
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("carId").is(carId));
query.with(Sort.by(Sort.Direction.DESC, "commentTime"));
List<Comment> list = mongoTemplate.find(query, Comment.class);
return list;
}
@Override
public void addReplies(AddRepliesDTO dto) {
Comment comment = mongoTemplate.findById(dto.getCommentId(), Comment.class);
CommentReplies commentReplies = new CommentReplies();
BeanUtils.copyProperties(dto, commentReplies);
commentReplies.setRepliesTime(new Date());
commentReplies.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString().replaceAll("-", ""));
List<CommentReplies> replies = comment.getReplies();
if(replies == null){
replies = new ArrayList<>();
}
replies.add(commentReplies);
Query query = Query.query(Criteria.where("id").is(comment.getId()));
Update update = new Update().set("replies", replies);
mongoTemplate.updateFirst(query,update,Comment.class);
}
}