文章目录
- 1.条件查询 where
- 2. 通配符与模糊查询
- 3. 映射
- 4. 排序 order_by
- 5. 取部分 limit 和offset
- 6. 分组 group by
- 7.左右连表 left outer join ... on
- 8. 联合查询 union
1.条件查询 where
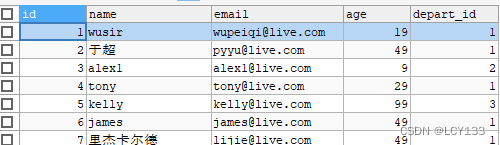
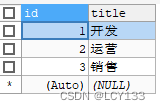
表内容:
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='root',passwd='root',charset='utf8',db='db26')
cursor = conn.cursor()
# sql2 = """
# create table info(
# id int not null auto_increment primary key,
# name varchar(16) not null,
# email varchar(32) not null,
# age int,
# depart_id int
# )default charset=utf8;
# """
# cursor.execute(sql2)
#conn.commit()
#sql = "select * from info where age>30"
# sql = "select * from info where id!=3"
#sql = "select * from info where id between 2 and 4"
#sql = "select * from info where (id between 2 and 4) and age>10"
#sql = "select * from info where id in (1,2,4)"
#sql = "select * from info where id not in (1,2,4)"
# sql = "select * from info where id in (select id from depart)"
# sql = "select * from info where not exists (select * from depart where id=5)"
#sql = "select * from info where exists (select * from depart where id=2)"
#sql = "select * from (select * from info where id>2)as T where age>10"
#sql = "select * from (select * from info where id>2) as T where age>10"
#sql = "select * from info where name like '%wu%'"
#sql = "select * from info where email like '%@live.com'"
sql = "select * from info where email like '__peiqi@live.co_'"
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
#print(result)
for i in result:
print(i)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
2. 通配符与模糊查询
% 代表任意个任意字符
_ 代表单个任意字符
select * from info where name like "%沛%";
select * from info where name like "%沛";
select * from info where email like "%@live.com";
select * from info where name like "武%齐";
select * from info where name like "k%y";
select * from info where email like "wupeiqi%";
select * from info where email like "_@live.com";
select * from info where email like "_upeiqi@live.com";
select * from info where email like "__peiqi@live.com";
select * from info where email like "__peiqi_live.co_";
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1',port=3306,user='root',passwd='root',charset='utf8',db='db26')
cursor = conn.cursor()
#sql = "select * from info where name like '%wu%'"
#sql = "select * from info where email like '%@live.com'"
sql = "select * from info where email like '__peiqi@live.co_'"
cursor.execute(sql)
result = cursor.fetchall()
#print(result)
for i in result:
print(i)
cursor.close()
conn.close()
3. 映射
- 映射是指什么?查找的内容单独建一列,
select * from info;
select id, name from info;
select id, name as NM from info;
select id, name as NM, 123 from info;
注意:少些select * ,自己需求。
select
id,
name,
666 as num,
( select max(id) from depart ) as mid, -- max/min/sum 只能返回一个值,max(id)是一个值
( select min(id) from depart) as nid, -- max/min/sum
age
from info;
select
id,
name,
( select title from depart where depart.id=info.depart_id) as x1
from info;
# 注意:效率很低
select
id,
name,
( select title from depart where depart.id=info.depart_id) as x1,
-- 顺序:先查表info,取出id,name列,再查当列的depart_id是否等于depart.id,AS后是重命名
( select title from depart where depart.id=info.id) as x2
from info;
select
id,
name,
case depart_id when 1 then "第1部门" end v1
from info;
select
id,
name,
case depart_id when 1 then "第1部门" else "其他" end v2
-- case语句 如果depart_id为1,就写为第一部门,否则就其他 该列为v2
from info;
select
id,
name,
case depart_id when 1 then "第1部门" end v1,
case depart_id when 1 then "第1部门" else "其他" end v2,
case depart_id when 1 then "第1部门" when 2 then "第2部门" else "其他" end v3,
-- case语句 如果depart_id为1,就写为第一部门,如果是2 就是第2部门 否则就其他 该列为v2
case when age<18 then "少年" end v4,
case when age<18 then "少年" else "油腻男" end v5,
case when age<18 then "少年" when age<30 then "青年" else "油腻男" end v6
-- case语句 如果age<18就是少年,age<30就是青年,否则就其他 就是油腻, 该列为v6
from info;
4. 排序 order_by
select * from info order by age desc; -- 倒序
select * from info order by age asc; -- 顺序
select * from info order by id desc;
select * from info order by id asc;
select * from info order by age asc,id desc; -- 优先按照age从小到大;如果age相同则按照id从大到小。
select * from info where id>10 order by age asc,id desc;
select * from info where id>6 or name like "%y" order by age asc,id desc;
5. 取部分 limit 和offset
select * from info limit 5; -- 获取前5条数据
select * from info order by id desc limit 3; -- 先排序,再获取前3条数据
select * from info where id > 4 order by id desc limit 3; -- 先排序,再获取前3条数据
select * from info limit 3 offset 2; -- 从位置2开始,向后获取前3数据
limit 配合offset可以用于分页操作,比如在数据表内有1000条数据,每页显示10个,可以分为100页
- 第一页:`select * from info limit 10 offset 0;`
- 第二页:`select * from info limit 10 offset 10;`
- 第三页:`select * from info limit 10 offset 20;`
- 第四页:`select * from info limit 10 offset 30;
6. 分组 group by
sql = "select depart_id,max(age),min(age),avg(age),count(id),sum(age) from info group by depart_id"
-- 查询 按照depart_id分组后 按照分组后的每组找出聚合函数后的内容,
sql = "select depart_id,count(id) from info group by depart_id having count(id) > 2;"
-- 先分组 后having子查询
sql = "select count(id) from info"
sql = "select min(id) from info"
select * from info where id in (select max(id) from info group by age);
-- 先查找每个年龄的最大ID,后查询这些ID的信息
select age,count(id) from info group by age having count(id) > 2;
--
select age,count(id) from info where id > 4 group by age having count(id) > 2;
-- 聚合条件放在having后面
-- 一个最复杂的例子
select age,count(id) from info where id > 2 group by age having count(id) > 1 order by age desc limit 1;
- 要查询的表info
- 条件 id>2
- 根据age分组
- 对分组后的数据再根据聚合条件过滤 count(id)>1
- 根据age从大到小排序
- 获取第1条
7.左右连表 left outer join … on
主表 left outer join 从表 on 主表.x = 从表.id
-- 左外连接时左边的表是主表,根据某个条件进行连表,利用了一个主表和一个从表
select * from info left outer join depart on info.depart_id = depart.id;
sql = "select info.id,info.name,info.email,info.age,info.depart_id,depart.title from info left outer join depart on info.depart_id=depart.id"
-- 左连接并显示指定字段
sql = "select * from info right outer join depart on info.depart_id=depart.id"
-- 右连接 右边是主表 左边是从表
sql = "select * from info right join depart on info.depart_id=depart.id"
-- 谁是主表 就要展示谁为主,没有对应的展示那些元素为null,主要使用的是左外连接
select * from info left outer join depart on ....
select * from depart left outer join info on ....
简写 可以去掉outer 默认是外连接
内连接:表 inner join 表 on 条件
互相匹配,只有两者能关联上的数据才会显示,没有关联的数据就不会显示
select * from info inner join depart on info.depart_id=depart.id;
8. 联合查询 union
- 又称为上下连表 很少用到,可以用于多张表联合去重
select id,title from depart
union
select id,name from info;
select id,title from depart
union
select email,name from info;
-- 列数需相同
-- 数据类型不一致没问题
select id from depart
union all
select id from info;
-- 保留所有,查询时不会自动去重
到目前为止SQL执行顺序:
join/union
on
where
group by
having
order by
limit