前言:
基于Boost库的搜索引擎
为何基于Boost库?
- 从技术上说:这个项目用了很多Boost库的接口
- 从搜索引擎存储内说:存储的内容是Boost库的内容预期效果
预期效果:用户在浏览器输入关键词,浏览器显示相关结果
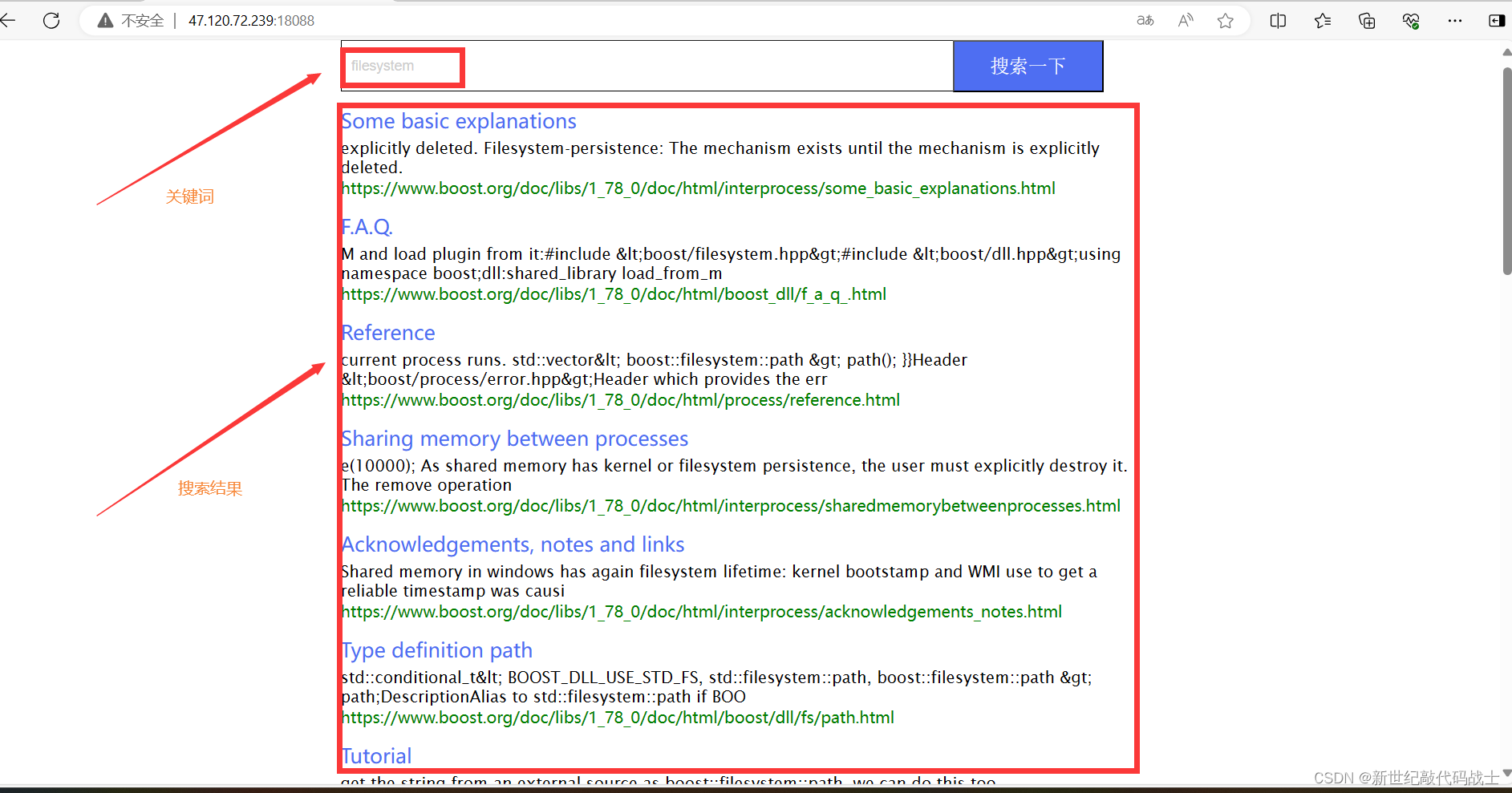
STEP1:导入Boos库数据到服务器
由于我们是将Boost库中的数据作为服务器的数据源,所以我们要把Boost库相关数据拉取到服务器上。
1.导入数据源到服务器
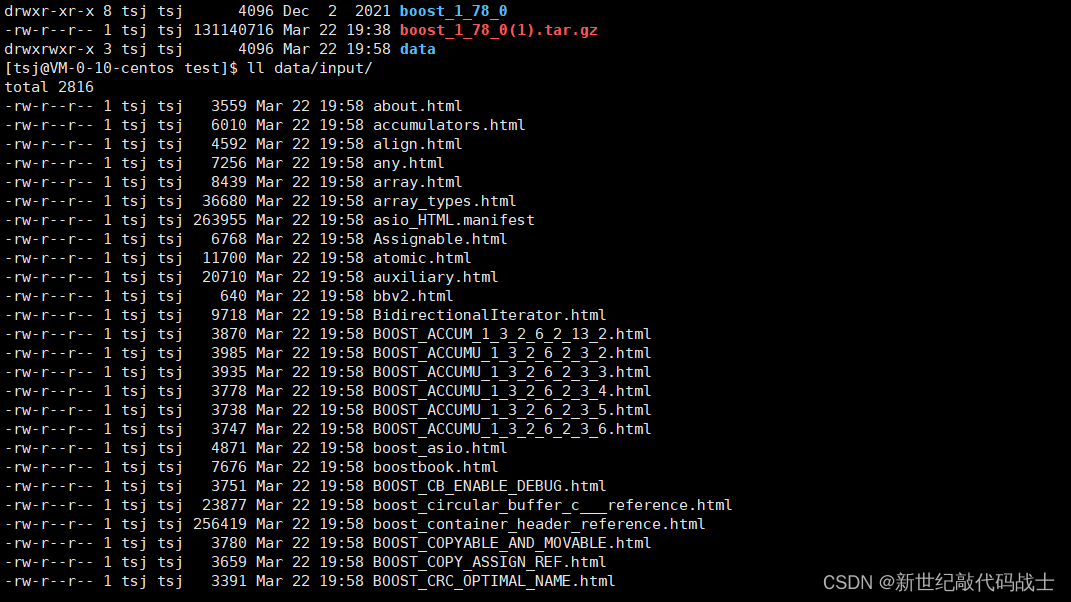
我们选择的是Boost 库中html文件作为数据源
数据源url:Index of main/release/1.78.0/source
boost官网下载文件,导入文件数据到Linux中,使用rz指令

2.解压文件
使用指令 tar xzf 压缩包名称,得到解压后的文件夹

但这个文件夹内,有非常多的内容
我们选择doc路径下html文件夹中的内容作为数据源(里面存放的都是html文件)

建立文件夹data/input,用于存放doc/html下的文件内容
mkdir data/input
cp -r boost_1_78_0/doc/html/* data/input/
数据源准备工作完毕
STEP2:处理数据模块
在处理数据之前,需要明确,我们的数据源现在是存储在文件上的,我们想要使用它,必须把它加载到内存中,所以第一步,我们需要存放他们的文件路径
1.存放文件路径
//src_path="data/input" --存放html文件的路径
//files_list --用于保存文件路径的容器
bool enumfile(const std::string &src_path, std::vector<std::string> *files_list)
{
// 引入boost开发库 因为c++对文件系统的支持不是很好
// 展开boost的命名空间
namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
//path是一个用于处理文件操作的类
fs::path root_path(src_path);
// 判断路径是否存在
if (!fs::exists(root_path))
{
std::cerr << "file not exists" << std::endl;
return false;
}
// 存在 递归遍历 recursive_directory_iterator end == nullptr
fs::recursive_directory_iterator end;
// 筛选文件
for (fs::recursive_directory_iterator iter(root_path); iter != end; iter++)
{
// is_regular_file是否为普通文件 eg:png false
if (!fs::is_regular_file(*iter))
continue;//跳过本次循环,筛选下一个文件
// 是否为html文件 path.extension()
if (iter->path().extension() != ".html")
continue;//跳过本次循环,筛选下一个文件
// html文件,将文件路径导入到容器中
files_list->push_back(iter->path().string());
}
return true;
}tips:
boost::filesystem::path
filesystem是一个模块,提供了许多与文件处理相关的组件
path是一个类,包含了许多与文件处理相关的接口,
例如,获取文件扩展名-->path::extension()
2.处理文件内容
我们已经获取到了想要的文件路径了,接下来就可以使用文件操作的相关接口,打开文件内容,并对文件内容做相关的处理——提取标题、内容、url
//files_list --存放文件路径的容器
//results --用于存放提取出来的文件内容的容器
//ns_util::fileutil::readfile --读取文件内容的接口
//docinfo_t 定义如下:
typedef struct docinfo
{
std::string title;
std::string content;
std::string url;
} docinfo_t;
static bool parsehtml(const std::vector< std::string> &files_list,std::vector<docinfo_t> *results)
{
// 解析文件
// file--本地文件路径
for (const std::string &file : files_list)
{
std::string result;
// 1.读取文件信息
ns_util::fileutil::readfile(file, &result);
docinfo_t doc;
// 2.解析文件的title
if (!parsertitle(result, &doc.title))
{
continue;
}
// 3.解析文件的content
if (!parsercontent(result, &doc.content))
{
continue;
}
// 4.解析文件的url
if (!parserurl(file, &doc.url))
{
continue;
}
//解析好的内容存入容器,使用移动构造提高效率
results->push_back(std::move(doc));
}
return true;
}提取标题
在html文件中,标题是以<title>出现</title>结尾的
举个例子:
以下html代码中,<title></title>间的白字部分就是标题

可以根据上述特性编写代码:
//file --文件内容
//title --提取的标题存放进的容器
static bool parsertitle(const std::string &file, std::string *title)
{
size_t begin = file.find("<title>");//寻找title出现的位置
if (begin == std::string::npos)
{
return false;
}
size_t end = file.find("</title>");//寻找</title>出现的位置
if (end == std::string::npos)
{
return false;
}
if (begin > end)
{
return false;
}
begin += std::string("<title>").size();
*title = file.substr(begin, end - begin);//截取标题内容
return true;
}
提取content
content是以'>'开始标志的,是以'<'为结尾标志的,<>xxxx<> xxxx就是content
举个例子:下面HTML代码中标出来的白字部分就是content内容

但请注意:不是说只要出现'>',后面就是content,例如
<a name="xpressive.legal"></a><p>'>'后出现的是'<',这是HTML语言的标签
只要'>'出现的不是'<',那就是content
根据上述规则,可以编写代码
//file --存放文件内容的容器
//content --存放提取内容(content)的容器
static bool parsercontent(const std::string &file, std::string *content)
{
// 去标签
enum status
{
Lable,
Content
};
enum status s = Lable;
for (const char c : file)//按字符读取文件内容
{
switch (s)
{
case Lable://是标签
if (c == '>')//内容开始的标志
s = Content;//切换状态
break;
case Content:
if (c == '<')//不是内容
s = Lable;
else//是内容
{
if (c == '\n')//将\n置为空字符,原因后文会提到
c == ' ';
content->push_back(c);
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return true;
}提取url
这里更准确的说法,应该是拼接url,按照我们预期的效果,页面应该要显示搜索内容所在的url
我们的数据源皆来自https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_78_0/doc/html/
我们的容器中存放的文件路径是data/input/具体的文件名
所以我们要如此拼接:https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_78_0/doc/html/+具体的文件名
//file_path --文件路径
//url --用于存放拼接好的url的容器
//src_path --data/input
static bool parserurl(const std::string &file_path, std::string *url)
{
std::string url_head = "https://www.boost.org/doc/libs/1_78_0/doc/html";
std::string url_tail = file_path.substr(src_path.size());
*url = url_head + url_tail;
return true;
}3.保存处理好的文件内容
我们已经将每一个文件所对应的内容存放在vector<docinfo_t>中了,接下来需要对一个个的docinfo_t进行格式化处理,并将其写入磁盘,以待使用
为什么要进行格式化处理?方便内容提取,在后文中会有具体体现
如何格式化?以特定字符作为内容内title content url的分隔符,以特定字符作为内容与内容之间的分隔符
将vector<docinfo_t>中的内容作格式化处理
title\3content\3url\n-->一个完整的内容
写到data/raw_html/raw.txt
//results --存放结构体数据的容器
//output --写入磁盘的文件路径
bool savehtml(const std::vector<docinfo_t> &results, const std::string &output)
{
#define sep '\3' // title\3content\3url\n
// 按照二进制方式写入
std::ofstream out(output, std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);
if (!out.is_open())
{
std::cerr << "open " << output << "failed!" << std::endl;
return false;
}
for (const docinfo_t &item : results)//读取每一个结构体信息
{
std::string out_string;
out_string = item.title;
out_string += sep; //title\3
out_string += item.content; //title\3content
out_string += sep; //title\3content\3
out_string += item.url; //title\3content\3url
out_string += '\n'; //title\3content\3url\n
out.write(out_string.c_str(), out_string.size());
}
out.close();
return true;
}STEP3:构建索引模块
何为索引?即搜索引擎的查找规则
举个例子:当我们在浏览器输入“hello world”时,浏览器会显示大量页面,从hello world 到 页面,使这一过程发生的就是索引
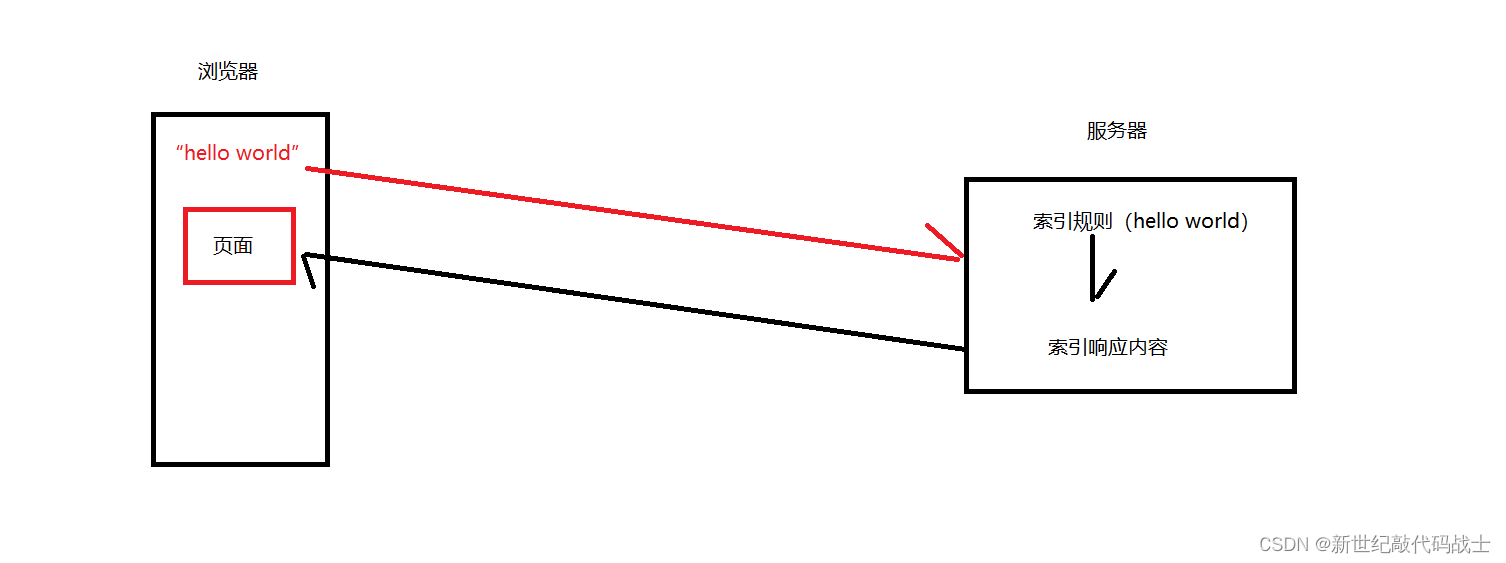
索引规则有如下2种:
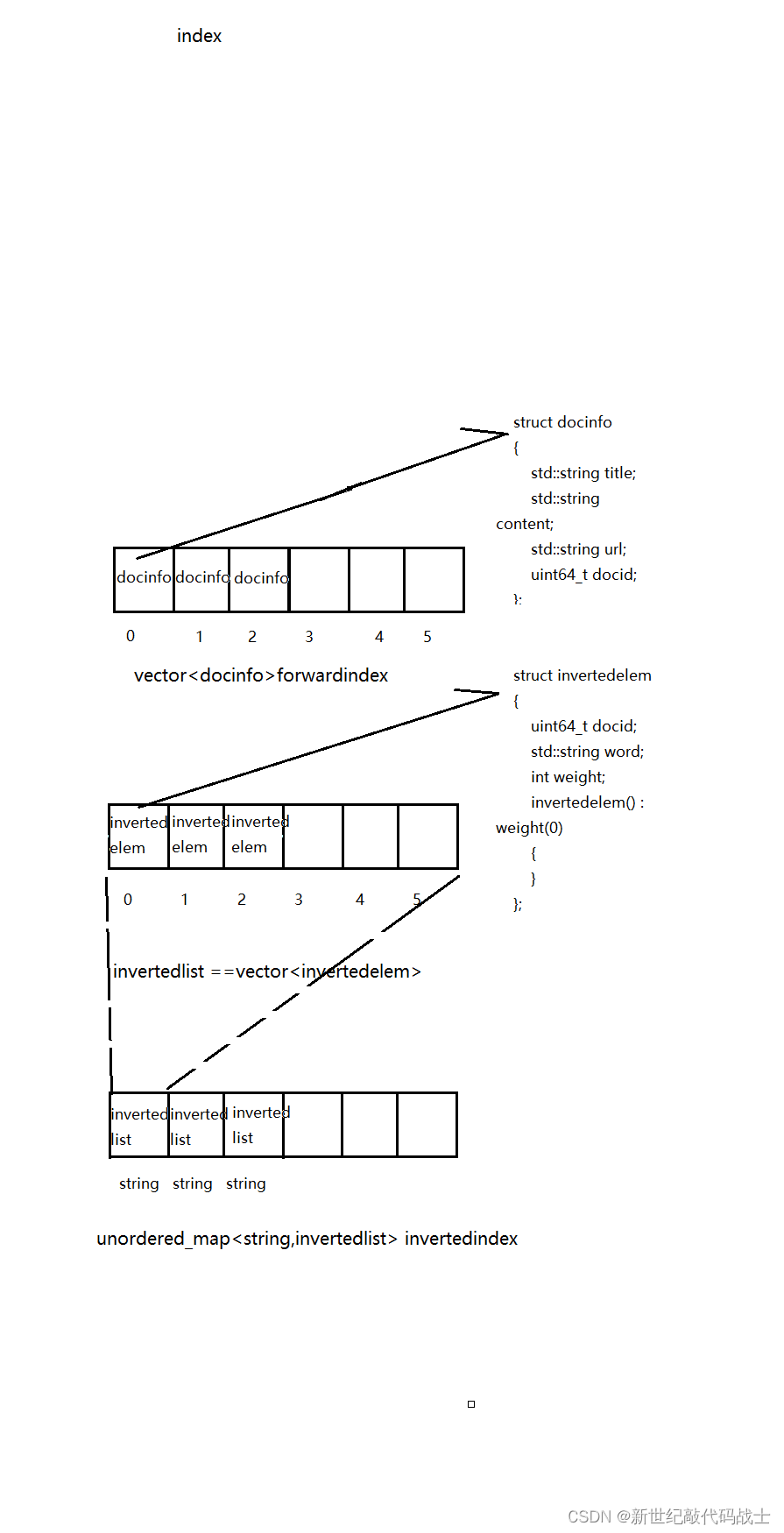
- 正排索引:根据文档id找到文档内容,所以它的底层是vector<docinfo_t>,下标就是文档id,里面存的就是文档内容
- 倒排索引:根据关键词找到文档id 并通过文档id找到文档内容,他是根据关键词在文章中出现的权重为基础,构建索引的
我们要对谁构建索引?存在磁盘上的格式化的数据源
构建正排索引
//line --存放文件内容的容器
//out --存放切分结果的容器
//forwardindex --正排索引 类型vector<docinfo>
struct docinfo
{
std::string title;
std::string content;
std::string url;
uint64_t docid;
};
//...文件读取操作
docinfo *bulidforwardindex(const std::string &line)
{
// 对line进行 title content url 的分词
std::vector<std::string> out;
const std::string sep = "\3"; //以'\3'为分割标志
ns_util::stringutil::split(line, &out, sep); //调用切分字符的接口
if(out.size()!=3){
return nullptr;
}
docinfo doc;
doc.title = out[0];
doc.content = out[1];
doc.url = out[2];
doc.docid = forwardindex.size();
forwardindex.push_back(std::move(doc));
//std::cout<<(forwardindex[forwardindex.size()-1].url)<<std::endl;//表明正派建立成功
return &forwardindex.back(); //返回构建好的一组数据,供建立倒排索引使用
}构建倒排索引
//wordmap --unordered_map<string,wordcnt>类型 用于存储被划分词在标题与内容中出现的次数
//invertedindex --unordered_map<string,invertedlist>类型 用于表示关键词与网页间的对应关系
//ilist --invertedlist类型,typedef vector<invertedelem> invertedlist
//item --invertedelem类型
struct invertedelem
{
uint64_t docid;
std::string word;
int weight;
invertedelem() : weight(0)
{
}
};
bool buildinvertedindex(const docinfo &doc)
{
struct wordcnt //用于计算被划分的词在标题/内容出现的次数
{
int titlecnt; //用于计算被划分的标题词在标题中出现的次数
int contentcnt; //用于计算被划分的内容词在内容中出现的次数
wordcnt() : titlecnt(0), contentcnt(0)
{
}
};
std::string title = doc.title; //取出完整的标题
std::string content = doc.content; //取出完整的内容
// jieba分词--title
std::vector<std::string> titlecut;
ns_util::jiebautil::cutstring(title, &titlecut);
// 拿到了jieba为我们分好的词 --title
std::unordered_map<std::string, wordcnt> wordmap;
for (auto &s : titlecut) //遍历被划分的标题词
{
boost::to_lower(s); //不区分大小写
wordmap[s].titlecnt++; //记录标题词在标题出现次数
}
// jieba分词--content
std::vector<std::string> contentcut;
ns_util::jiebautil::cutstring(content, &contentcut);
for (auto &s : contentcut) //遍历被划分的内容词
{
boost::to_lower(s);
wordmap[s].contentcnt++; //记录内容词在内容出现次数
}
// word -> id word weight
#define X 10
#define Y 1
//构建倒排索引 被划分的词才是主角
for (auto &wmap : wordmap)
{
invertedelem item;
item.docid = doc.docid;
item.word = wmap.first;
//构建各个词在此"网页"中的权重 --标题:10/次 内容:1/次
item.weight = X * wmap.second.titlecnt + Y * wmap.second.contentcnt;
//构建被划分的词与"网页"的关系
invertedlist &ilist = invertedindex[wmap.first];
// std::cout<<"invert success"<<std::endl;//表明创建倒排成功
ilist.push_back(std::move(item));
}
return true;
}现在,forwardindex 与invertedlist都已经按照各自的索引规则存储好了数据,上层想要调用使用这里面的数据,还需要我们提供两个接口
//正排索引的调用接口
//docid --想要查找的内容对应的id
docinfo *getforwardindex(uint64_t docid)
{
if (docid >= forwardindex.size())
{
std::cerr << "no expected doc" << std::endl;
return nullptr;
}
return &forwardindex[docid];
}
//倒排索引的调用接口
//word: 以word关键字为key值对相应内容做检索
invertedlist *getinvertedlist(const std::string &word)
{
auto iter = invertedindex.find(word);
if (invertedindex.end() == iter)
{
return nullptr;
}
return &(iter->second);
}
STEP4:编写服务端模块
服务端的作用是:接受客户端传过来的关键词,并对关键词进行分词,利用构建好的索引,并返回相关页面
工作流程:
InitSearcher --初始化工作
创建单例,构建索引(文件-->内存)
//Index --Index对象
void initsearcher()
{
Index = ns_index::index::getinstance(); //获取单例
if(Index==nullptr)
{
std::cerr<<"getinstance fail"<<std::endl;
exit(1);
}
std::cout<<"get instance success"<<std::endl;
Index->buildindex(input); //创建索引
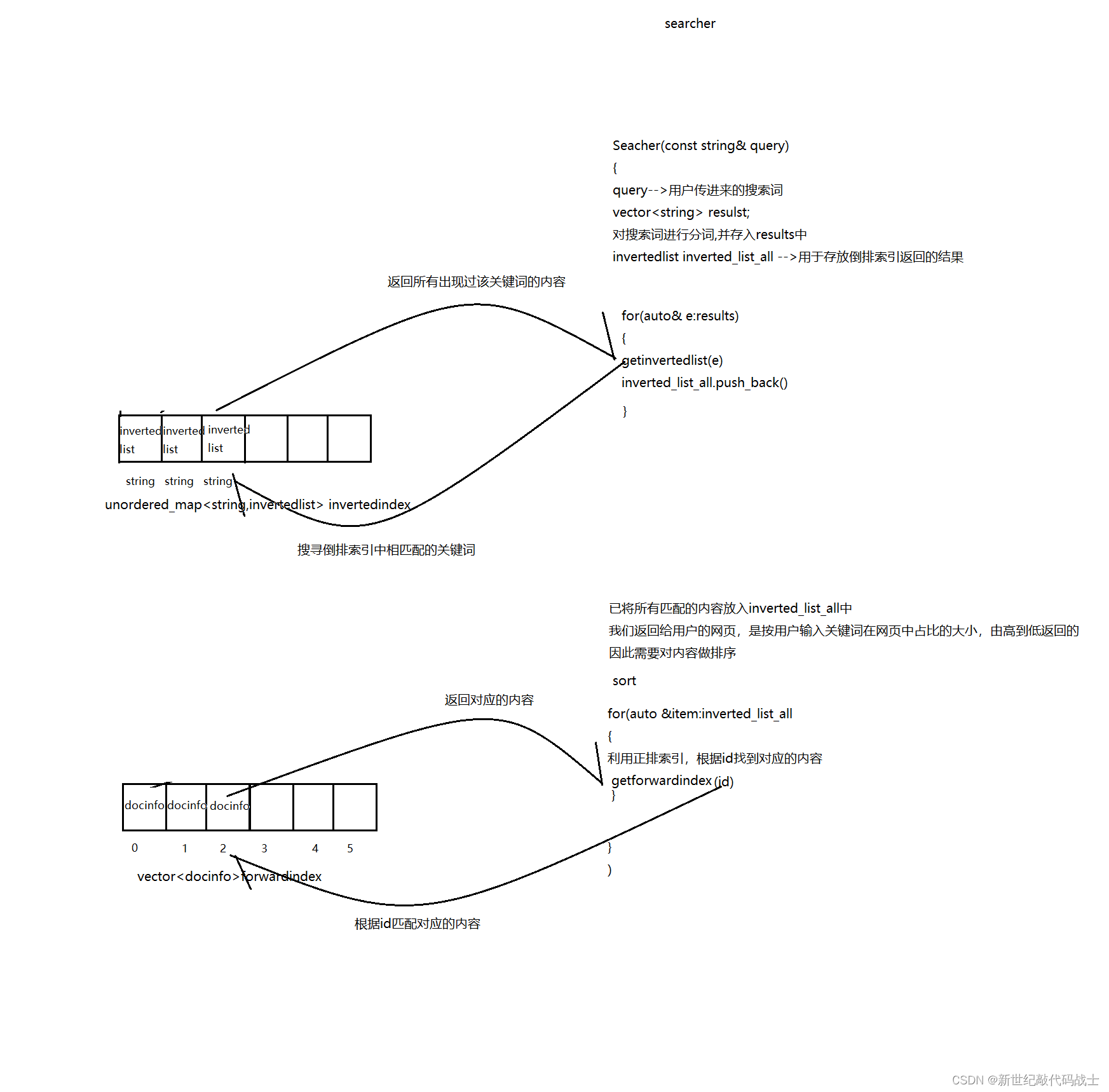
}Search --搜索工作
对用户的关键词进行分词,然后查倒排,将结果存放到inverted_list_all当中去
对查找结果按照权重进行排序
根据文档id,查询相关结果
为了达到像真实网页一般显示,我们要对内容做摘要
利用 Json对结果进行序列化,返回给客户端
//query --用户传进来的关键词
//jsonstring --要返回的结果
void search(const std::string &query, std::string *jsonstring)
{
// 对query进行分词
std::vector< std::string> cutwords;
ns_util::jiebautil::cutstring(query, &cutwords);
ns_index::invertedlist inverted_list_all;
for (auto word : cutwords)
{
boost::to_lower(word);
ns_index::invertedlist *inverted_list;
inverted_list = Index->getinvertedlist(word);
if (inverted_list == nullptr)
{
std::cerr<<"get inverted_list err"<<std::endl;
continue;
}
inverted_list_all.insert(inverted_list_all.end(), inverted_list->begin(), inverted_list->end());
}
// 按照相关性对内容进行排序
std::sort(inverted_list_all.begin(), inverted_list_all.end(), [](const ns_index::invertedelem &e1, const ns_index::invertedelem &e2)
{ return e1.weight > e2.weight; });
//利用Json对结果进行反序列化,并将结果返回给上层
Json::Value root;
for (auto &item : inverted_list_all)
{
ns_index::docinfo *doc = Index->getforwardindex(item.docid);
if (nullptr == doc)
{
std::cerr<<"get doc fail"<<std::endl;
continue;
}
Json::Value elem;
elem["title"] = doc->title;
elem["desc"] = getdesc(doc->content, item.word); //对内容做摘要
elem["url"] = doc->url;
//here~~!!
//for debug
elem["weight"]=item.weight;
elem["docid"]=(int)doc->docid;
root.append(elem);
}
Json::StyledWriter writer;
*jsonstring = writer.write(root);
}
std:: string getdesc(const std:: string &content, const std::string &word)
{
int prev_step = 50;
int next_step = 100;
//int pos = content.find(word);//大小写问题 split->Split
auto iter=std::search(content.begin(),content.end(),word.begin(),word.end(),[](int x,int y){return std::tolower(x)==std::tolower(y);});
if(iter==content.end())
{
return "none1";
}
int pos=std::distance(content.begin(),iter);
int start = 0;
int end = content.size() - 1;
if (pos - prev_step > start)
{
start = pos - prev_step;
}
if (pos + next_step < end)
{
end = pos + next_step;
}
if (start > end)
return "none2";
std:: string desc = content.substr(start, end - start);
return desc;
}
这里的服务端模块,其实就是大量的在调用索引模块的接口,服务端是上层,索引模块是下层
为方便理解,下图简单勾勒出了二者关系
server-index关系图:
STEP5:编写http服务模块
http服务模块,位于应用层,是整个服务器的最上层,具体工作是:启动服务器,完成socket编程(创建套接字、绑定套接字、监听套接字、等待连接),接受客户端请求,返回服务器结果。
#include "searcher.hpp"
#include "cpphttplib/httplib.h"
const std::string root_path = "./wwwroot";
int main()
{
ns_searcher::searcher sear;
sear.initsearcher();
httplib::Server svr;
svr.set_base_dir(root_path.c_str());
svr.Get("/s", [&sear](const httplib::Request &req, httplib::Response &rsp)
{
if (!req.has_param("word"))
{
rsp.set_content("必须要有搜索关键字!", "text/plain; charset=utf-8");
return;
}
std::string word = req.get_param_value("word");
std::string json_string;
sear.search(word, &json_string);
rsp.set_content(json_string, "application/json");
});
svr.listen("0.0.0.0", 18088);
return 0;
}STEP6:部署日志到服务器中
部署日志信息是为了监控服务器状态,方便对服务端的管理。




![[flask]cookie的基本使用/](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/53d9e47e4b91420187a59faa2ba89a8d.png)