883. 高斯消元解线性方程组 - AcWing题库
输入一个包含 n 个方程 n 个未知数的线性方程组。
方程组中的系数为实数。
求解这个方程组。
下图为一个包含 m 个方程 n 个未知数的线性方程组示例:
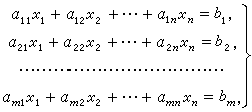
输入格式
第一行包含整数 n。
接下来 n 行,每行包含 n+1 个实数,表示一个方程的 n 个系数以及等号右侧的常数。
输出格式
如果给定线性方程组存在唯一解,则输出共 n 行,其中第 i 行输出第 i 个未知数的解,结果保留两位小数。
注意:本题有 SPJ,当输出结果为 0.00 时,输出 -0.00 也会判对。在数学中,一般没有正零或负零的概念,所以严格来说应当输出 0.00,但是考虑到本题作为一道模板题,考察点并不在于此,在此处卡住大多同学的代码没有太大意义,故增加 SPJ,对输出 -0.00 的代码也予以判对。
如果给定线性方程组存在无数解,则输出 Infinite group solutions。
如果给定线性方程组无解,则输出 No solution。
数据范围
1≤n≤100
所有输入系数以及常数均保留两位小数,绝对值均不超过 100
输入样例:
3
1.00 2.00 -1.00 -6.00
2.00 1.00 -3.00 -9.00
-1.00 -1.00 2.00 7.00
输出样例:
1.00
-2.00
3.00解析:高斯消元
枚举每一列c
1.找到绝对值最大的一行
2.将该行放到最上面
3.将该行第一个数变成1
4.将下面所有行的第c列的数变成0
5.最后从下往上操作使得每一行只保留一个系数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<algorithm>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<set>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100 + 5;
const double eps = 1e-6;
int n;
double a[N][N];
void out() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++) {
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
int gauss() {
int r, c;
for (r = 1, c = 1; c <= n ; c++) {
int t = r;
//找到当前c列位置的最大值的哪一行
for (int i = r; i <= n; i++) {
if (fabs(a[i][c]) > fabs(a[t][c]))
t = i;
}
//特判,如果当前最大值是零,则跳过这一列
if (fabs(a[t][c]) < eps)continue;
//将当前这行放到上面
for (int i = c; i <= n + 1; i++)swap(a[r][i], a[t][i]);
//将这一行除以一个数使得第c列的数为1
for (int i = n+1; i >= c; i--)a[r][i] /= a[r][c];
//将这一行以下的每一行的第c列的数全部变为0
for (int i = r + 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (fabs(a[i][c]) > eps) {
for (int j = n + 1; j >= c; j--)
a[i][j] -= a[r][j] * a[i][c];
}
}
r++;
//out();
}
//如果行数小于方程组的未知数的个数
if (r < n-1) {
//判断是否有0!=0的情况
for (int i = r; i <= n; i++) {
if (fabs(a[i][n+1]) > eps)
return 2;//无解
}
return 1;//无穷多解
}
//操作使得每一行只有一个未知数
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++)
a[i][n+1] -= a[i][j] * a[j][n+1];
}
return 0;//有解
}
int main() {
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n + 1; j++) {
cin >> a[i][j];
}
}
int t = gauss();
if (t == 0) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
printf("%.2lf\n", a[i][n + 1]);
}
else if (t == 1)cout << "Infinite group solutions" << endl;
else cout << "No solution" << endl;
return 0;
}






![[NISACTF 2022]babyserialize - 反序列化+waf绕过【*】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6583643d70204090b8f9f879548075b5.png)