以下是本人学习笔记
原视频:最新QT从入门到实战完整版|传智教育
qt开发从入门到实战1
练习示例
设计一个按钮,点击时弹出新窗口,再次点击时新窗口关闭
// exercise
QWidget* second_window = new QWidget();
QPushButton* btn3 = new QPushButton("open", this);
btn3->move(0, 100);
connect(btn3, &QPushButton::clicked, second_window, [=](){
if(btn3->text() == "open"){
second_window->show();
second_window->resize(100, 100);
btn3->setText("close");
}else if(btn3->text() == "close"){
second_window->close();
btn3->setText("open");
}
});
注意:加入窗口和加入对象树是两个不同的概念
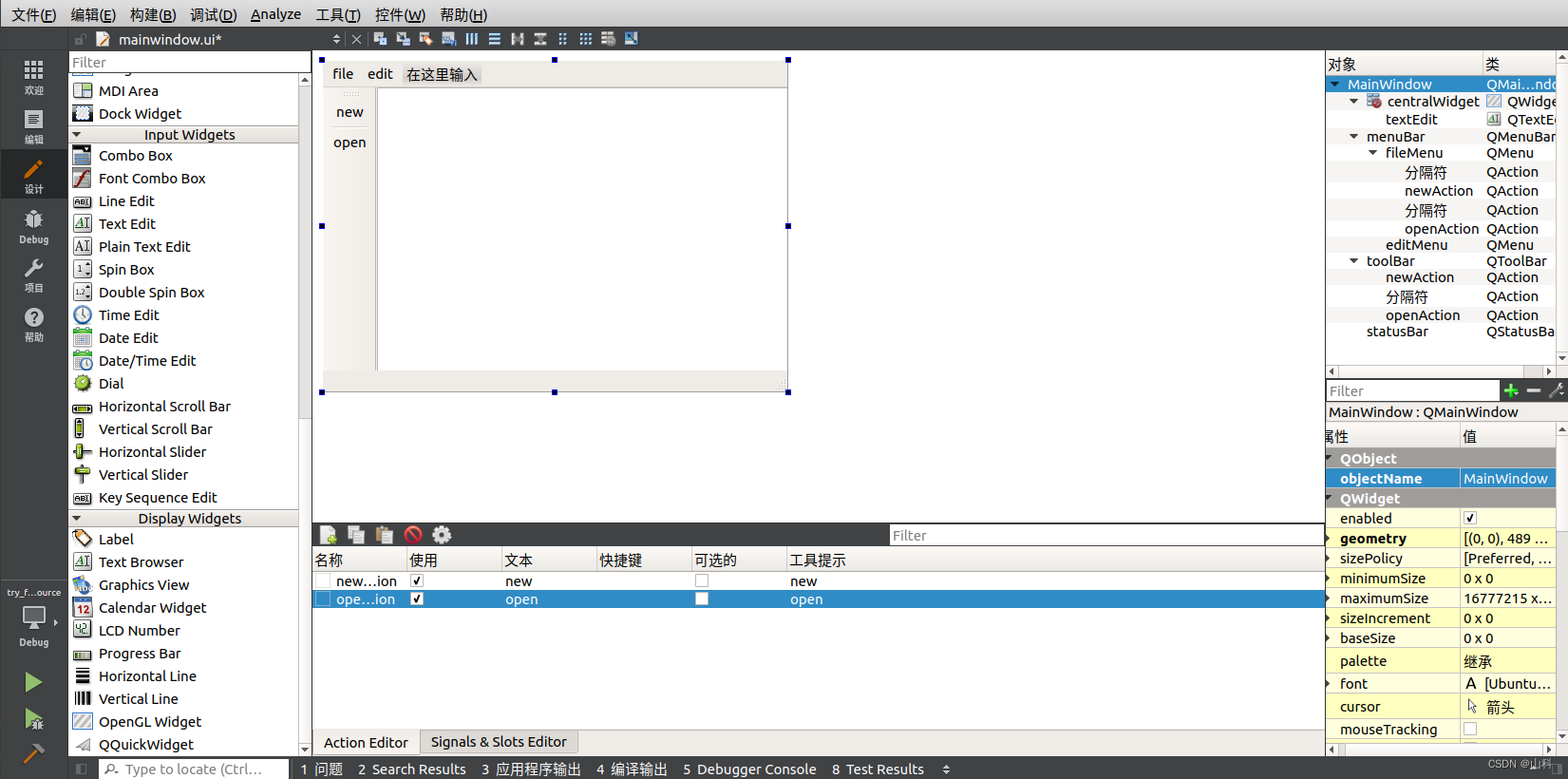
一、窗口中的基础部件
1.创建菜单栏
讲解见注释
// 创建菜单栏
// 菜单栏最多只有一个
// menuBar构造函数已经把自身加入对象树了
QMenuBar* bar = menuBar();
// 将菜单栏放入窗口
setMenuBar(bar);
// 创建菜单
QMenu* fileMenu = bar->addMenu("file");
QMenu* editMenu = bar->addMenu("edit");
// 创建菜单项
QAction* newAction = fileMenu->addAction("new");
// 添加分隔线
fileMenu->addSeparator();
QAction* openAction = fileMenu->addAction("open");
2.创建工具栏
// 工具栏可以有多个
QToolBar* toolBar = new QToolBar(this); // 加入对象树
// 加入窗口和加入对象树是两个不同的概念
addToolBar(Qt::LeftToolBarArea ,toolBar); // 加入窗口
// 设置工具栏是否可以移动(相当于总开关)
toolBar->setMovable(false);
// 设置工具栏只可以左右停靠
toolBar->setAllowedAreas(Qt::LeftToolBarArea | Qt::RightToolBarArea);
toolBar->setFloatable(false);
// 设置工具栏内容
// 相当于工具栏和菜单栏公用的功能
toolBar->addAction(newAction);
toolBar->addAction(openAction);
// 工具栏中添加控件
QPushButton* btn = new QPushButton("aa", this);
toolBar->addWidget(btn);
3.创建状态栏
// 状态栏最多只有一个
QStatusBar* stBar = statusBar();
// 将状态栏放入窗口
setStatusBar(stBar);
// 放标签控件
QLabel* label1 = new QLabel("tips", this);
stBar->addWidget(label1);
QLabel* label2 = new QLabel("right tips", this);
// right labels
stBar->addPermanentWidget(label2);
4.创建铆接部件(浮动窗口)+中心部件
// 创建铆接部件(浮动窗口):可以有多个
QDockWidget* dockWidget = new QDockWidget("float", this);
// 浮动窗口的位置是相对于核心部件的位置而言的(在核心部件的上/下/左/右)
addDockWidget(Qt::TopDockWidgetArea, dockWidget);
// 设置后期停靠区域:只允许上下
dockWidget->setAllowedAreas(Qt::TopDockWidgetArea | Qt::BottomDockWidgetArea);
5.创建中心部件
// 设置中心部件:只有一个
QTextEdit* edit = new QTextEdit(this);
setCentralWidget(edit);
0.无代码版
创建项目时勾选创建ui界面,之后在ui中手动拖拽部件(手动狗头)
二、资源文件的添加
利用无代码方式进行控件的布局后,添加的部件在源文件中可以通过ui找到
- 寻找到项目文件位置,将需要用的资源放在项目文件夹中,代码里使用相对路径
- 在Qt项目中,右击项目->添加新文件
- 选择qt->qt resource file(最终生成.qrc文件)
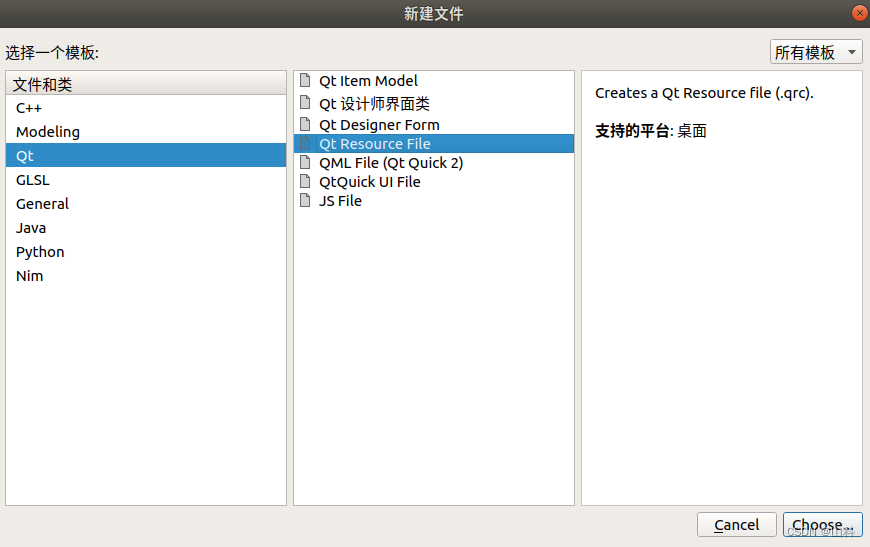
- 命名后默认选项即可
- 添加前缀(仅作区分用)
- 添加文件:全选之前加入项目文件夹的图片即可
注意:
- 从res.qrc切出后,双击文件无法唤起页面,需要右击res.qrc->open in editor
- 图片资源必须得是png格式,不然会不显示图片
三、对话框
1.模态/非模态对话框
// 点击新建按钮,弹出一个对话框
connect(ui->newAction, &QAction::triggered, [=](){
// 对话框分类
// 1.模态对话框:不可以对其他窗口进行操作
// 2.非模态对话框:可以对其他窗口进行操作
// 模态创建(阻塞)
QDialog dlg1(this);
dlg1.resize(200, 100);
// 在模态对话框关闭之前,程序会一直在此阻塞
dlg1.exec();
qDebug() << "模态创建";
});
connect(ui->openAction, &QAction::triggered, [=](){
// 非模态对话框创建
// 以下方式创建会让对话框在离开匿名函数时就被销毁
// QDialog dlg2(this);
// dlg2.show();
// 将对话框创建在堆上即可
QDialog* dlg2 = new QDialog(this);
dlg2->resize(200, 100);
dlg2->show();
// 使其在关闭时删除对象(因为默认只有在主窗口关闭时,所有对象才会被销毁)
dlg2->setAttribute(Qt::WA_DeleteOnClose);
qDebug() << "非模态对话框创建";
});
2.标准对话框
标准对话框是Qt内置的用于简化开发的一系列对话框
消息对话框
// 错误对话框
QMessageBox::critical(this, "critical", "error");
// 信息对话框
QMessageBox::information(this, "information", "some info");
// 提问对话框(父亲, 标题, 内容, 按钮类型, 与回车关联的按钮)
// 返回值是standarButton类型
if(QMessageBox::Save == QMessageBox::question(this, "question", "Q?", QMessageBox::Cancel | QMessageBox::Save, QMessageBox::Save))
{
qDebug() << "save something";
}else
{
qDebug() << "cancel";
}
// 警告对话框
QMessageBox::warning(this, "warning", "stop!");
tips:静态对象可以通过①创建对象访问②直接通过类名访问
其他对话框
// 其他对话框
// 文件对话框(parent, title, default path, filter file)
QString filePath = QFileDialog::getOpenFileName(this, "open files", "/home", "*.txt");
qDebug() << filePath;
// 字体对话框
bool flag;
QFont font = QFontDialog::getFont(&flag, QFont("console", 36));
qDebug() << font;
// 颜色对话框(上面两种有warning)
// QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(QColor(255, 255, 255));
// QColor color = QColorDialog::getColor(Qt::red, this);
QColor color(0, 0, 0);
QColorDialog colorDialog(color, this);
colorDialog.setOption(QColorDialog::DontUseNativeDialog);
if( colorDialog.exec() == QDialog::Accepted )
{
// 获取当前选中的颜色
color = colorDialog.currentColor();
qDebug() << color;
}
3.未完待续
p23

![[NISACTF 2022]babyserialize - 反序列化+waf绕过【*】](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6583643d70204090b8f9f879548075b5.png)




![[PyTorch][chapter 56][GAN 代码实现]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a8e80cba4242487786a8fc9cd7479f1c.png)