前言:在很多情况下,需要根据点云来拟合球体,本博文主要介绍各种方法的拟合情况及优缺点,希望对各位小伙伴有所帮助!
目录
1. vtkFitImplicitFunction进行球拟合
2. 四点求解球
1. vtkFitImplicitFunction进行球拟合
缺点:需要输入待拟合球的半径和结构,即在已知最优解的情况下求解。
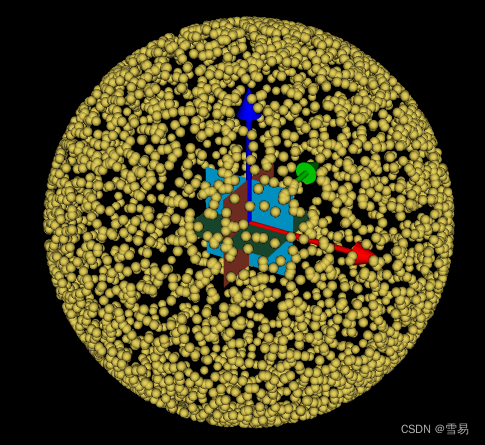
vtkMath::RandomSeed(4355412); // for test result consistency
double radius = 1.0;
vtkSmartPointer<vtkBoundedPointSource> points =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkBoundedPointSource>::New();
points->SetNumberOfPoints(1000000);
points->SetBounds(-2.0, 2.0, -2.0, 2.0, -2.0, 2.0);
points->Update();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphere> sphere =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphere>::New();
sphere->SetRadius(radius*2);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkFitImplicitFunction> fit =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkFitImplicitFunction>::New();
fit->SetInputConnection(points->GetOutputPort());
fit->SetImplicitFunction(sphere);
fit->SetThreshold(.01);
fit->Update();
std::cout << fit->GetOutput()->GetNumberOfPoints() << " out of "
<< points->GetNumberOfPoints() << " points are within "
<< fit->GetThreshold() << " of the implicit function" << std::endl;
vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource> sphereSource =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkSphereSource>::New();
sphereSource->SetRadius(radius * .05);
vtkSmartPointer<vtkGlyph3D> glyph3D =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkGlyph3D>::New();
glyph3D->SetInputConnection(fit->GetOutputPort());
glyph3D->SetSourceConnection(sphereSource->GetOutputPort());
glyph3D->ScalingOff();
glyph3D->Update();
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper> glyph3DMapper =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkPolyDataMapper>::New();
glyph3DMapper->SetInputConnection(glyph3D->GetOutputPort());
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor> glyph3DActor =
vtkSmartPointer<vtkActor>::New();
glyph3DActor->SetMapper(glyph3DMapper);
glyph3DActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(0.8900, 0.8100, 0.3400);
m_viewer->renderWindow()->GetRenderers()->GetFirstRenderer()->AddActor(glyph3DActor);
m_viewer->renderWindow()->Render();
2. 四点求解球
缺点:要求输入的四点为精确球上的点;否则计算错误。
void fitSphere(vtkPoints* points, double center[3], double& radius) {
double p1[3];
double p2[3];
double p3[3];
double p4[3];
points->GetPoint(0, p1);
points->GetPoint(1, p2);
points->GetPoint(2, p3);
points->GetPoint(3, p4);
double a = p1[0] - p2[0], b = p1[1] - p2[1], c = p1[2] - p2[2];
double a1 = p3[0] - p4[0], b1 = p3[1] - p4[1], c1 = p3[2] - p3[2];
double a2 = p2[0] - p3[0], b2 = p2[1] - p3[1], c2 = p2[2] - p3[2];
double D = a * b1 * c2 + a2 * b * c1 + c * a1 * b2 - (a2 * b1 * c + a1 * b * c2 + a * b2 * c1);
if (D == 0)
{
return;
}
double A = p1[0] * p1[0] - p2[0] * p2[0];
double B = p1[1] * p1[1] - p2[1] * p2[1];
double C = p1[2] * p1[2] - p2[2] * p2[2];
double A1 = p3[0] * p3[0] - p4[0] * p4[0];
double B1 = p3[1] * p3[1] - p4[1] * p4[1];
double C1 = p3[2] * p3[2] - p4[2] * p4[2];
double A2 = p2[0] * p2[0] - p3[0] * p3[0];
double B2 = p2[1] * p2[1] - p3[1] * p3[1];
double C2 = p2[2] * p2[2] - p3[2] * p3[2];
double P = (A + B + C) / 2;
double Q = (A1 + B1 + C1) / 2;
double R = (A2 + B2 + C2) / 2;
double Dx = P * b1 * c2 + b * c1 * R + c * Q * b2 - (c * b1 * R + P * c1 * b2 + Q * b * c2);
double Dy = a * Q * c2 + P * c1 * a2 + c * a1 * R - (c * Q * a2 + a * c1 * R + c2 * P * a1);
double Dz = a * b1 * R + b * Q * a2 + P * a1 * b2 - (a2 * b1 * P + a * Q * b2 + R * b * a1);
center[0] = Dx / D;
center[1] = Dy / D;
center[2] = Dz / D;
radius = sqrt((p1[0] - center[0]) * (p1[0] - center[0]) +
(p1[1] - center[1]) * (p1[1] - center[1]) +
(p1[2] - center[2]) * (p1[2] - center[2]));
}