Faiss是Facebook AI Research开发的快速相似性搜索(similarity search)计算库,为稠密向量提供高效相似度搜索和聚类,支持十亿级别向量的搜索。
Faiss 的核心原理是基于向量索引和近似最近邻搜索。它通过构建索引结构来加速相似性搜索,以在大规模数据集中快速找到最相似的向量。
本节不介绍Faiss的原理,只介绍使用方法。
1. 安装
# Faiss分为cpu和gpu两个版本,按需进行安装
#cpu版,faiss-cpu仅支持cpu
conda install -c pytorch faiss-cpu
#gpu版,faiss-gpu支持cpu和gpu
conda install -c pytorch faiss-gpu
2. Faiss使用
Faiss使用较为简单,主要分为三部分,构建数据集、建立索引并添加向量、检索。
2.1 构建数据集
首先拥有数据集,然后转化为向量。文本向量化可以使用向量模型,比如m3e,ernie-base,text2vec等等。
注意,在 Python 中,矩阵始终表示为 numpy 数组。数据类型dtype必须是float32.
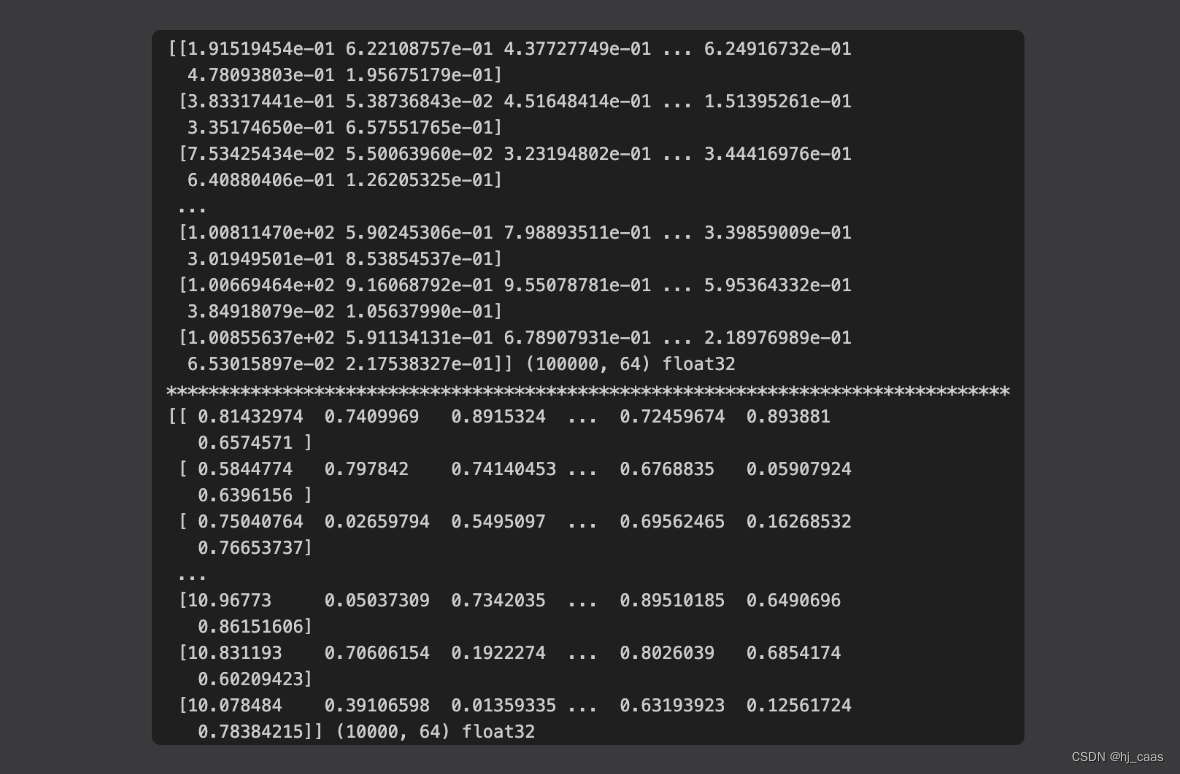
#例一,官方代码
import numpy as np
d = 64 # dimension
nb = 100000 # database size
nq = 10000 # nb of queries
np.random.seed(1234) # make reproducible
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype('float32')
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000.
xq = np.random.random((nq, d)).astype('float32')
xq[:, 0] += np.arange(nq) / 1000.
print(xb,xb.shape,xb.dtype)
print("*"*80)
print(xq,xq.shape,xq.dtype)
# 例二,使用text2vec-large-chinese模型演示
from text2vec import SentenceModel
sentences = ['如何更换花呗绑定银行卡', '花呗更改绑定银行卡','怎么换银行卡', '银行卡毁坏如何补办', '花呗如何打开']
model = SentenceModel('GanymedeNil/text2vec-large-chinese')
embeddings = model.encode(sentences)
if embeddings.dtype!='float32':
embeddings = embeddings.astype('float32')
else:
pass
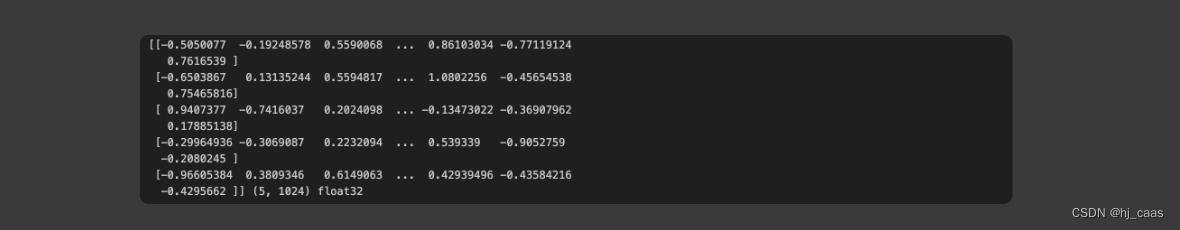
print(embeddings,embeddings.shape,embeddings.dtype)
2.2 构建索引并添加向量
Faiss的核心是索引,建立索引可以提高搜索效率。Faiss含有多种索引,如IndexFlatL2,IndexFlatIP,IndexIVFFlat等。建立索引之前需要明确向量的维数。大多数索引需要进行训练,以分析向量的分布。
当索引建立并训练后,可以对索引执行两个操作:add和search。
#例一,跟2.1例一承接
import faiss # make faiss available
index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d) # build the index,d is dimension
print(index.is_trained) # 指示索引是否需要训练,输出为True,代表该类index不需要训练,只需要add向量进去即可
index.add(xb) # add vectors to the index
print(index.ntotal) # 索引向量的数量

#例二,跟2.1例二承接
import faiss
num,d = embeddings.shape
index = faiss.IndexFlatL2(d)
print(index.is_trained)
index.add(embeddings)
print(index.ntotal)

2.3 检索
Faiss在索引上进行的基本搜索操作是k-近邻搜索,即对于每个查询向量,在数据库中找到其k个近邻。
k = 4 # we want to see 4 nearest neighbors
D, I = index.search(xb[:5], k) # sanity check
print(I) # I是每个待检索query最相似TopK的索引列表
print(D) # D是每个待检索query最相似TopK的索引对应的距离
D, I = index.search(xq, k) # actual search
print(I[:5]) # neighbors of the 5 first queries
print(I[-5:]) # neighbors of the 5 last queries

k = 4
query = ['花呗如何更换银行卡呢']
query_embedding = model.encode(query)
if query_embedding.dtype!='float32':
query_embedding = query_embedding.astype('float32')
else:
pass
D, I = index.search(query_embedding, k)
print(I)
print(D)
#结果解读:I是检索返回结果排序,相对来说检索结果还算准确,但是分数有点大,说明文本向量化不够准确。

2.4 总结
在本节中使用的索引类型不需要训练,大家可以使用IndexIVFFlat(倒排索引)试试,倒排索引需要进行索引训练,而且检索效率更高。
3. 小结
Faiss检索使用简单,主要在于如何进行准确的文本向量化,才能确保返回正确的检索结果。目前大模型外接知识库中,其中一步就是文本检索,文本检索不准确就会导致“garbage in, garbage out“。
参考
-
https://www.writebug.com/article/1c571b48-1b41-11ee-8711-0242ac14000f
-
https://github.com/facebookresearch/faiss
-
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/357414033
-
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/133210698
-
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43791511/article/details/122513786




![[小尘送书-第二期]《从零开始读懂量子力学》由浅入深,解释科学原理;从手机到超导,量子无处不在;从微观到宏观,遐想人生的意义!](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8db00f7e59664a5fa80e4db1934c5666.png#pic_center)

![[c++实验] 快读快写,O123优化,原版用时对比](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/79f8c3b9b73046e5a9379585b2bc180f.png)