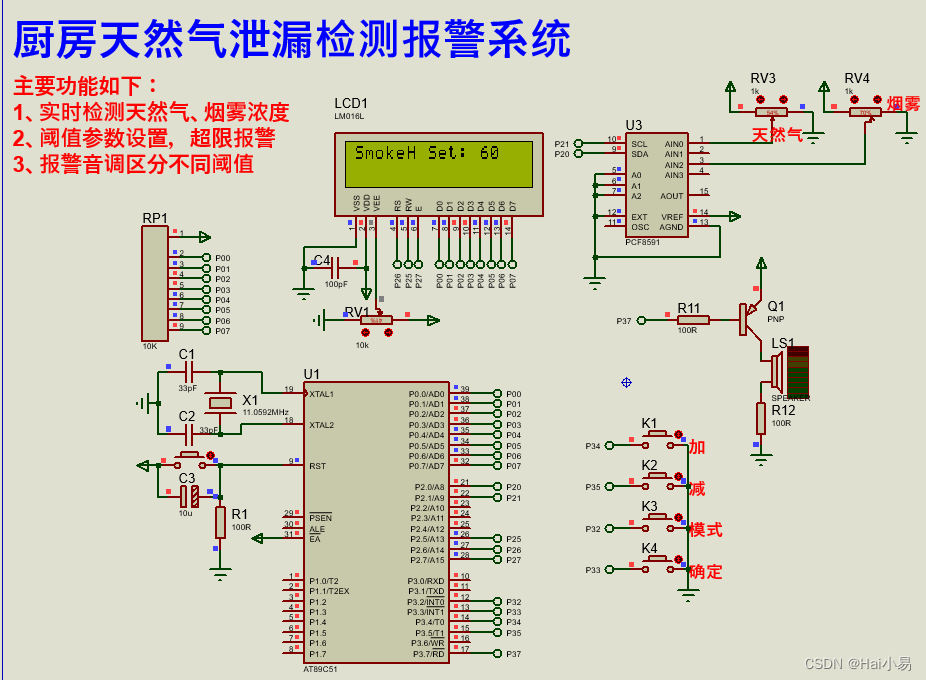
监控糖果机
假设现在需要一台监视器去生成报告,报告中包括糖果机的位置、库存等信息
// 糖果机 public class GumballMachine{ String loc; public GumballMachine(String loc, int count){ this.loc = loc; } public String getLoc(){ return loc; } // 其他方法省略 } // 监视器 public class GumballMonitor{ GumballMachine gumballMachine; public GumballMonitor(GumballMachine gumballMachine){ this.gumballMachine = gumballMachine; } public void report(){ System.out.println(gumballMachine,getLoc()); // 打印其余数据 } } // 开始测试 public class GumballMachineTest{ public static void main(String[] agrs){ GumballMachine gumballMachine = new GumballMachine(args[0], Integer.parseInt(args[1])); GumballMonitor gumballMonitor = new GumballMonitor(gumballMachine); gumballMonitor.report(); } }此时客户想要远程监控糖果机,意味着无法直接将糖果机对象直接传给监视器对象,该怎么办?不如创建一个代理对象,通过该对象实现远程调用。对于客户而言,看起来在做远程调用,实际是调用本地的代理对象,代理对象通过网络去调用真正的糖果机
代理模式
- 为另一个对象提供一个替身或占位符以控制对该对象的访问
- 被代理的对象可以是远程的对象、创建开销大的对象或需要安全控制的对象
- 代理模式有多种实现,如糖果机监视器属于远程代理
- 代理模式类图如下所示,其中:
远程监控糖果机-远程代理
书中涉及到
Java RMI,这里不再叙述,大致过程如下图所示:
显示CD封面-虚拟代理
当创建一个对象开销较大时就可以使用虚拟代理,该代理在真正需要一个对象的时候会被创建。真正的对象在创建前和创建中时,虚拟代理作为对象的替身;对象创建好后,代理就会把请求委托给对象
现在想要从网站上获取CD封面,但是加载图像需要一定时间,在等待时间中应该显示一些其他内容,等下载完成后就显示下载好的封面
class ImageProxy implements Icon{ // Icon接口定义了获取Icon属性、打印Icon等方法
ImageIcon imageIcon; // 真正对象,也实现了Icon接口
URL imageURL;
public ImageProxy(URL url){
imageURL = url; // 图像的下载网址
}
public int geyIconWidth(){
// 真正Icon已经下载完成,就去获取真实数值
if(imageIcon != null){
return imageIcon.getIconWidth();
}else{
return 100; // 还没下载完成就返回一个自定义数值
}
}
// 其余方法类似,对于下载完成和为完成采用两种方式
}
动态代理
在完成下面的配对服务前,需要先了解什么是动态代理
- Java可用
java.lang.reflect包在运行时动态地创建代理类,实现一或多个接口,并将方法的调用转发到指定的类,因为实际的代理类是在运行时创建的,称该技术为动态代理- 因为此时
Proxy类不是自己实现的,所以不能将代码放在Proxy类中,而是将代码放在InvacationHandler中,它响应代理的任何调用
配对服务-保护代理
保护代理可以根据访问权限决定客户能否访问对象
现在想要完成一项配对服务,别人可以约会对象进行打分
// 每个参与配对用户需要实现的接口 public interface PersonBean{ String getName(); int getHotOrNotRating(); void setName(); void setHotOrNotRating(int rating); // 其他属性的getter和setter省略 } // 某个参与配对的用户 public class PersonBeanImpl implements PersonBean{ String name; int rating; int ratingCount = 0; // 计算当前用户收到评分的平均值 public int getHotOrNotRating(){ if(ratingCount == 0){ return 0; } return (rating / ratingCount); } // 统计当前用户收到评分的总值和给其评分的人数 public void setHotOrNotRating(int rating){ this.rating += rating; ratingCount++; } }但是该系统需要满足当前用户可以修改个人信息,但是不能修改别人给自己的评分,其他用户可以给当前用户评分,但是不能修改当前用户的个人信息,该如何实现?需要创建两个代理,一个访问自己的
PersonBean对象,另一个访问其他客户的PersonBean对象
- 创建两个
InvocationHandler:InvocationHandler实现代理的行为,Java负责创建真实的代理类和对象,自己提供handler(在方法调用时知道该做什么):

// 客户看自己bean时(也就是查看自己信息)
public class OwnerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
PersonBean personBean;
public OwnerInvocationHandler(PersonBean person){
this.person = person;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throw IllegalAccessException{
try{
// 客户可以获取自己所有信息
if(method.getName().startWith("get")){
return method.invoke(person, agrs);
// 客户不允许修改自己评分
}else if(method.getName().startWith("setHotOrNotRating")){
throw new IllegalAccessException();
// 允许设置其他个人信息,比如年龄等
}else if(method.getName().startWith("set")){
return method.invoke(person, agrs);
}
}catch(InvocationTargetException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
- 创建动态
Proxy类:该方法定义在测试类中
// 创建客户自己的代理
PersonBean getOwnerPorxy(PersonBean person){
return (PersonBean)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new OwnerInvocationHandler(person)
);
}
// 创建其他人的代理
PersonBean getNonOwnerPorxy(PersonBean person){
return (PersonBean)Proxy.newProxyInstance(
person.getClass().getClassLoader(),
person.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new NonOwnerInvocationHandler(person)
);
}
- 开始测试:
public class MatchMakingTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
MatchMakingTest test = new MatchMakingTest();
test.drive();
}
public void drive(){
PersonBean psj = getPersonFromDatabase("psj"); // 从数据库中获取psj信息
// 下面两个代理的realSubject都是psj对象
PersonBean ownerProxy = getOwnerPorxy(psj); // 创建客户自己的代理
ownerProxy.setHotOrNotRating(10); // 报错
PersonBean nonOwnerProxy = getNonOwnerPorxy(psj); // 创建其他人的代理
ownerProxy.setName("xxx"); // 报错
}
}
参考
Head First 设计模式-代理模式
设计模式-代理模式






![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计校园失物招领管理系统(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/263507da4c1f42d9929222d1dda90125.png)