treeshaking
treeshaking本质是去除多余代码算法。在前端的性能优化中,es6 推出了tree shaking机制,tree shaking就是当我们在项目中引入其他模块时,他会自动将我们用不到的代码,或者永远不会执行的代码摇掉,在Uglify阶段查出,不打包到bundle中。
学习treeshaking的目的也是是为了后面学习rollup打包原理做铺垫。在 rollup 中,一个文件就是一个模块。每一个模块都会根据文件的代码生成一个 AST 语法抽象树,rollup 需要对每一个 AST 节点进行分析。分析 AST 节点,就是看看这个节点有没有调用函数或方法。如果有,就查看所调用的函数或方法是否在当前作用域,如果不在就往上找,直到找到模块顶级作用域为止。如果本模块都没找到,说明这个函数、方法依赖于其他模块,需要从其他模块引入。rollup只处理函数和顶层的import/export变量。
0前置知识-安装相关依赖
安装webpack
npm install webpack webpack-cli --save-dev
初始化项目
npm init -y
查看webpack打包后的内容
npx webpack ./test1.js
安装nodemon
nodemon 一个辅助node.js开发的工具,当目录中的文件更改时,会自动重启node应用程序
npm i nodemon -g
测试代码命令:nodemon ./index.js
参数:watch
安装acorn
npm i acorn -d -s
const acorn = require('acorn');acorn的默认用法非常简单,直接来段代码字符串parse一下就出来AST结构了:
let acorn = require("acorn");
console.log(acorn.parse("for(let i=0;i<10;i+=1){console.log(i);}", {ecmaVersion: 2020}));解析后的AST语法树
Node {
type: 'Program',
start: 0,
end: 39,
body: [
Node {
type: 'ForStatement',
start: 0,
end: 39,
init: [Node],
test: [Node],
update: [Node],
body: [Node]
}
],
sourceType: 'script'
}
可以看到这个 AST 的类型为 program,表明这是一个程序。body 则包含了这个程序下面所有语句对应的 AST 子节点。每个节点都有一个 type 类型,例如 Identifier,说明这个节点是一个标识符;
安装magic-string
magic-string是一个操作字符串和生成source-map的工具。magic-string 是 rollup 作者写的一个关于字符串操作的库。
安装命令:
npm i magic-string -D -S
下面是 github 上的示例:
var MagicString = require('magic-string');
var magicString = new MagicString('export var name = "beijing"');
//类似于截取字符串
console.log(magicString.snip(0,6).toString()); // export
//从开始到结束删除字符串(索引永远是基于原始的字符串,而非改变后的)
console.log(magicString.remove(0,7).toString()); // var name = "beijing"
//很多模块,把它们打包在一个文件里,需要把很多文件的源代码合并在一起
let bundleString = new MagicString.Bundle();
bundleString.addSource({
content:'var a = 1;',
separator:'\n'
});
bundleString.addSource({
content:'var b = 2;',
separator:'\n'
});
/* let str = '';
str += 'var a = 1;\n'
str += 'var b = 2;\n'
console.log(str); */
console.log(bundleString.toString());
// var a = 1;
//var b = 2;其中引入方法
const MagicString = require('magic-string');magic-string的好处是会生成sourcemap
一、初识AST语法解析
抽象语法树(Abstract Syntax Tree,AST),或简称语法树(Syntax tree),是源代码语法结构的一种抽象表示。它以树状的形式表现编程语言的语法结构,树上的每个节点都表示源代码中的一种结构。通过操纵这颗树,我们可以精准的定位到声明语句、赋值语句、运算语句等等,实现对代码的分析、优化、变更等操作。
你可以简单理解为 它就是你所写代码的的树状结构化表现形式。webpack、UglifyJs、lint等工具的核心都是通过ast抽象语法书实现的,实现对代码的检查、分析。底层是调用的js parser 来生成抽象语法树。
AST工作流
- Parse(解析) 将源代码转换成抽象语法树,树上有很多的estree节点
- Transform(转换) 对抽象语法树进行转换
- Generate(代码生成) 将上一步经过转换过的抽象语法树生成新的代码

新建文件source.js
const a = ()=>'a888888'
const b = ()=>'b'
a()
在AST生成树网站预览结果
AST explorer
可以根据AST生成的数据逐层分析出变量信息
{
"type": "Program",
"start": 0,
"end": 46,
"body": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"start": 0,
"end": 23,
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"start": 6,
"end": 23,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 6,
"end": 7,
"name": "a"
},
"init": {
"type": "ArrowFunctionExpression",
"start": 10,
"end": 23,
"id": null,
"expression": true,
"generator": false,
"async": false,
"params": [],
"body": {
"type": "Literal",
"start": 14,
"end": 23,
"value": "a888888",
"raw": "'a888888'"
}
}
}
],
"kind": "const"
},
{
"type": "VariableDeclaration",
"start": 24,
"end": 41,
"declarations": [
{
"type": "VariableDeclarator",
"start": 30,
"end": 41,
"id": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 30,
"end": 31,
"name": "b"
},
"init": {
"type": "ArrowFunctionExpression",
"start": 34,
"end": 41,
"id": null,
"expression": true,
"generator": false,
"async": false,
"params": [],
"body": {
"type": "Literal",
"start": 38,
"end": 41,
"value": "b",
"raw": "'b'"
}
}
}
],
"kind": "const"
},
{
"type": "ExpressionStatement",
"start": 42,
"end": 45,
"expression": {
"type": "CallExpression",
"start": 42,
"end": 45,
"callee": {
"type": "Identifier",
"start": 42,
"end": 43,
"name": "a"
},
"arguments": [],
"optional": false
}
}
],
"sourceType": "module"
}
可以看到上面的拆解中,每一个块都有 type、start、end、body 这几个字段。其中 type 表达当前块的类型。比如 FunctionDeclaration 表示函数定义,Identifier 表示标识符、BlockStatement 表示块语句、ReturnStatement 表示返回语句等。start 表示该块开始的位置,end 表示该块结束的位置,body 表示子块。其他的字段根据块的性质不同有所不同。
新增index.js文件
//文件形式读取source.js
//fs模块 node.js中文件处理工具
const fs = require('fs');//引入
//读文件 readFileSync方法是同步读取文件,第一个参数表示文件路径,第二个参数表示读文件的编码方式(可省略)
const code = fs.readFileSync('./source.js').toString();
console.log('-------------source code----------------')
console.log(code);
//acorn 一个将代码解析为AST语法树的工具
const acorn = require('acorn');
const ast = acorn.parse(code,{ecmaVersion:'7'});//指定解析的js ECMAScript版本
console.log('--------------parsed as AST-------------')
ast.body.map(node=>{
console.log(node)
})
//MagicString 一个处理字符串的工具
const MagicString = require('magic-string');
const m = new MagicString(code);
console.log('--------------output node-------------')
console.log('index info')
ast.body.map((node,index)=>{
console.log(index+' ',m.snip(node.start,node.end).toString())//打印每个节点的信息
})
//分离声明和调用类型
const VariableDeclaration = []
const ExpressionStatement =[]
//对象当做map用 key是变量名,value是变量对应的节点
const VariableObj ={}
//statement数组 存放变量的声明和使用
const statementArr = []
ast.body.map(node=>{
if(node.type == 'VariableDeclaration') {
VariableDeclaration.push(node);//声明节点数组
//取声明数组的变量名key和节点value
const key = node.declarations[0].id.name
VariableObj[key] = node
} else if (node.type == 'ExpressionStatement') {
//对于引用的数组
ExpressionStatement.push(node);//引用节点数组
}
})
//取变量名
console.log('---------variableDeclaration name--------------')
VariableDeclaration.map(node=>{
console.log(node.declarations[0].id.name)
})
console.log('----------expressionStatement --------------')
ExpressionStatement.map(node=>{
// console.log(node.expression.callee.name)
console.log(node)
})
ExpressionStatement.map(node=>{
statementArr.push(VariableObj[node.expression.callee.name])//把表达式中使用的变量名的定义语句push到数组中
statementArr.push(node)//将表达式也push到数组中,未在表达式中调用的变量将不会遍历其VariableObj数组,也即过滤掉
})
console.log('------------treeshaking result----------')
// console.log(statementArr)
statementArr.map((node,index)=>{
console.log(index,m.snip(node.start,node.end).toString())
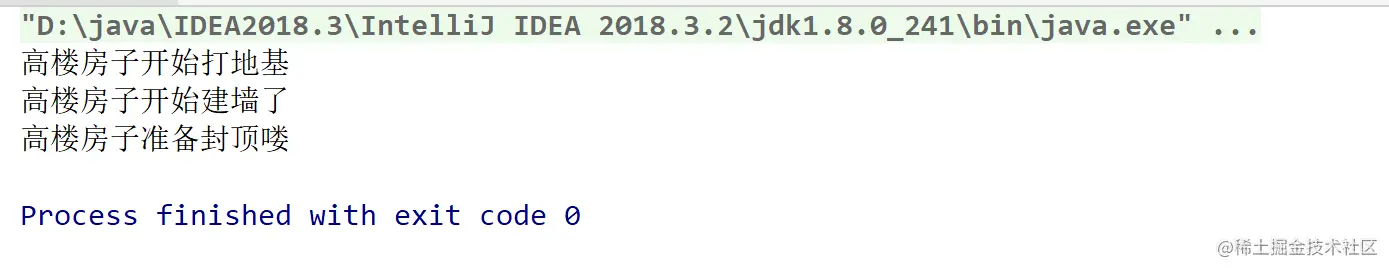
})执行语句nodemon ./index.js
输出
-------------source code----------------
const a = ()=>'a888888'
const b = ()=>'b'
a()
--------------parsed as AST-------------
Node {
type: 'VariableDeclaration',
start: 0,
end: 23,
declarations: [
Node {
type: 'VariableDeclarator',
start: 6,
end: 23,
id: [Node],
init: [Node]
}
],
kind: 'const'
}
Node {
type: 'VariableDeclaration',
start: 25,
end: 42,
declarations: [
Node {
type: 'VariableDeclarator',
start: 31,
end: 42,
id: [Node],
init: [Node]
}
],
kind: 'const'
}
Node {
type: 'ExpressionStatement',
start: 44,
end: 47,
expression: Node {
type: 'CallExpression',
start: 44,
end: 47,
callee: Node { type: 'Identifier', start: 44, end: 45, name: 'a' },
arguments: []
}
}
--------------output node-------------
index info
0 const a = ()=>'a888888'
1 const b = ()=>'b'
2 a()
---------variableDeclaration name--------------
a
b
----------expressionStatement --------------
Node {
type: 'ExpressionStatement',
start: 44,
end: 47,
expression: Node {
type: 'CallExpression',
start: 44,
end: 47,
callee: Node { type: 'Identifier', start: 44, end: 45, name: 'a' },
arguments: []
}
}
------------treeshaking result----------
0 const a = ()=>'a888888'
1 a()二、treeShaking节点遍历方法
采用TDD测试驱动开发方式
新增walk.js函数
首先,测试一下进入与退出函数
const walk = (ast, callObj)=>{
callObj.enter(ast)
callObj.leave(ast)
}
module.exports = walk编写walk.spec.js函数
测试ast是对象的情况
//walk.spec.js
//测试walk函数
describe('walk函数',()=>{
test('单个节点',()=>{
const ast = {
a:1,
// child:[{b:2}]
}
const walk = require('../walk')
const mockEnter = jest.fn()//fn方法是jest工厂方法
const mockLeave = jest.fn()
//walk函数遍历ast对象,对于单个节点,进入时调用enter函数,退出时调用leave函数
walk(ast,{
enter:mockEnter,
leave:mockLeave
})
//判断mockEnter是否被调用
let calls = mockEnter.mock.calls //calls是数组,每调用一次增加一项
expect(calls.length).toBe(1)//断言,ast={a:1}
expect(calls[0][0]).toEqual({a:1})
calls = mockLeave.mock.calls //在对leave是否调用进行判断
expect(calls.length).toBe(1)//断言,ast={a:1}
expect(calls[0][0]).toEqual({a:1})
})
})测试

由测试结果可以看出walk函数可以对{a:1}进行测试
使用--watchAll实时监听jest
jest --watchAll实现打印所有变量的变量名
实现过程:调用walk节点变量方法,自定义walk中的入参enter函数:根据node中ast语法树变量名type属性为VariableDeclaration取出所有的变量

新建test.js
//文件形式读取source.js
//fs模块 node.js中文件处理工具
const fs = require('fs');//引入
//读文件 readFileSync方法是同步读取文件,第一个参数表示文件路径,第二个参数表示读文件的编码方式(可省略)
const code = fs.readFileSync('./source.js').toString();
console.log('-------------source code----------------')
console.log(code);
//引入walk函数
const walk = require('./src/walk')
//acorn 一个将代码解析为AST语法树的工具
const acorn = require('acorn');
const ast = acorn.parse(code,{ecmaVersion:'7'});//指定解析的js ECMAScript版本
console.log('--------------walk ast-------------')
ast.body.map(node=>{
walk(node,{
enter:(node)=>{
// console.log('enter---------------lalala')
if(node && typeof node === 'object') {
if(node.type === 'VariableDeclaration'){
console.log(node.declarations[0].id.name)
// console.log(JSON.stringify(node.declarations[0].id.name,'\t','\t'))
}
}
},
leave:(node) =>{
// console.log('leave----------------lalala')
}
})
})
ast.body才是节点,打印结果如下

提升:找出任意层级的变量名
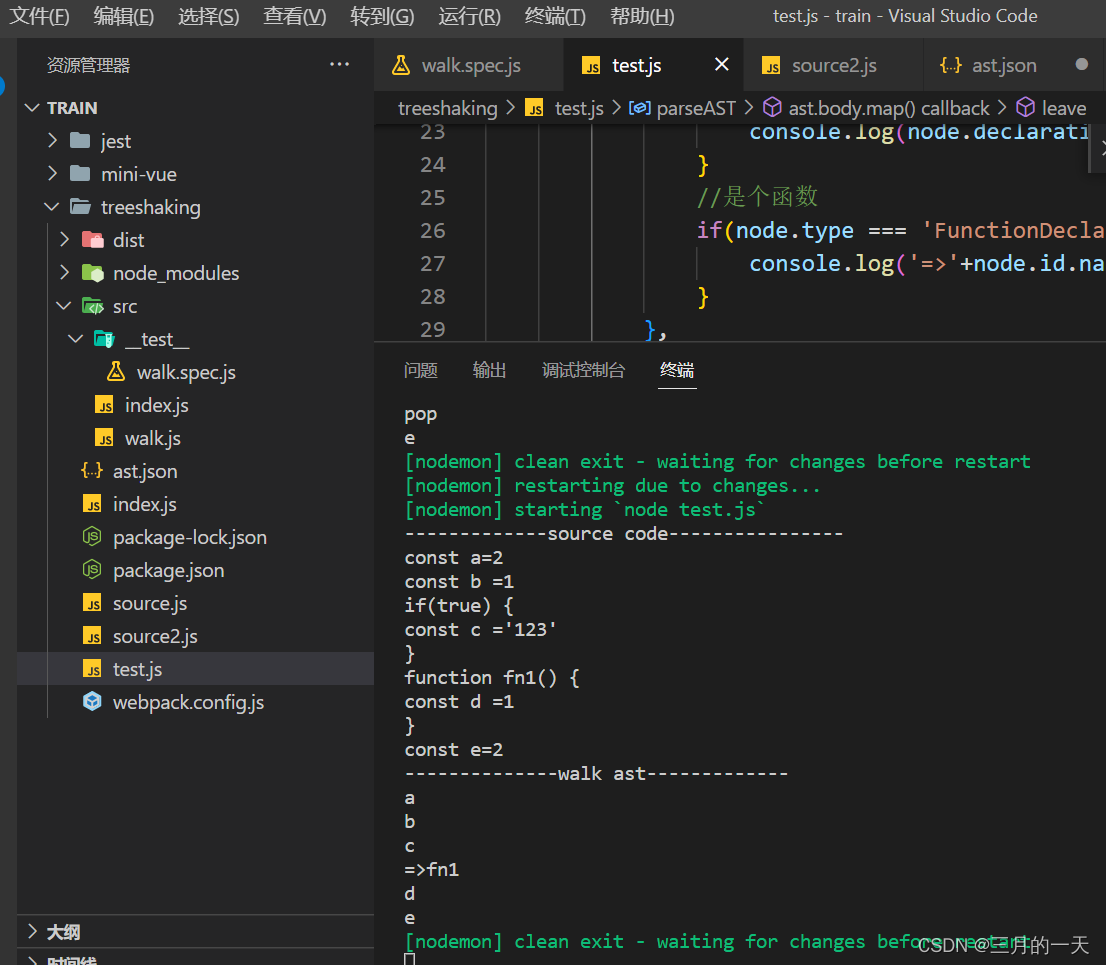
示例:
输入
const a,b =1
if(true) {
const c ='123'
}
function fn1() {
const d =1
}
const e =3
-----------------------------------
输出
a
b
c
fn1 =>d
e
-------------------------------------新增source2.js
存放原程序
const a=2
const b =1
if(true) {
const c ='123'
}
function fn1() {
const d =1
}新增test.js
//test.js
//文件形式读取source2.js
//fs模块 node.js中文件处理工具
const fs = require('fs');//引入
//读文件 readFileSync方法是同步读取文件,第一个参数表示文件路径,第二个参数表示读文件的编码方式(可省略)
const code = fs.readFileSync('./source2.js').toString();
console.log('-------------source code----------------')
console.log(code);
//引入walk函数
const walk = require('./src/walk')
//acorn 一个将代码解析为AST语法树的工具
const acorn = require('acorn');
const ast = acorn.parse(code,{ecmaVersion:'7'});//指定解析的js ECMAScript版本
console.log('--------------walk ast-------------')
const statements = []
const parseAST = (ast)=>{
ast.body.map(node=>{
// console.log(node)
walk(node,{
enter:(node)=>{
if(node.type === 'VariableDeclaration'){
console.log(node.declarations[0].id.name)
}
//是个函数
if(node.type === 'FunctionDeclaration'){
console.log('=>'+node.id.name)
}
},
leave:(node) =>{
}
})
})
}
parseAST(ast)
测试结果
nodemon test.js
三、作用域模拟
新建一个scope作用域实现类似于下面的结果
const a = '1'
function(){
const b = 2
}新增src/scope.js文件
module.exports = class Scope{
//定义构造方法
constructor(option){
//初始化names
this.names=[]
if(option){
this.parent = option.parent
}
}
//新增方法,每次添加一个变量名到作用域中
add(name){
this.names.push(name)
}
//判断对象中是否包含某个变量名,谁调用,this指向谁
contains(name){
return this.names.includes(name) || this.parent && this.parent.contains(name)
}
findDefiningScope(name){
//如果调用方的names中包含name,返回调用方本身,否则沿着调用方的作用域链逐层向上寻找
if(this.names.includes(name)){
return this
} else if(this.parent){//如果存在父作用域,递归寻找父作用域中是否含有该方法
return this.parent.findDefiningScope(name)
} else {
return null
}
}
}
升级contains(name)方法
findDefiningScope方法可以获取调用对象,如果找到一个对象即该对象包含name属性
module.exports = class Scope{
//定义构造方法
constructor(option){
//初始化names
this.names=[]
if(option){
this.parent = option.parent
}
}
//新增方法,每次添加一个变量名到作用域中
add(name){
this.names.push(name)
}
//判断对象中是否包含某个变量名,谁调用,this指向谁
contains(name){
// return this.names.includes(name) || this.parent && this.parent.contains(name)
//等价与下面 其中!!表示取字符串的布尔类型表示
return !! this.findDefiningScope(name)
}
//返回实际的作用域对象
findDefiningScope(name){
//如果调用方的names中包含name,返回调用方本身,否则沿着调用方的作用域链逐层向上寻找
if(this.names.includes(name)){
return this
} else if(this.parent){//如果存在父作用域,递归寻找父作用域中是否含有该方法
return this.parent.findDefiningScope(name)
} else {
return null
}
}
}新增src/__test__/scope.spec.js文件
describe('scope',()=>{
test('scope',()=>{
const Scope = require('../scope')
//实例化Scope,命名为route
const root = new Scope()
root.add('a')
//定义一个child子作用域,嵌套在Parent父作用域
const child = new Scope({'parent':root})
child.add('b')
//编写断言
expect(child.findDefiningScope('a')).toBe(root)//'child中是否有a',a在父作用域链上,按作用域规则可以找到
expect(child.contains('a')).toEqual(true)//toEqual比较每项每个的值
expect(child.findDefiningScope('b')).toBe(child)//toBe比较的是地址
expect(child.contains('b')).toBe(true)
// expect(child.findDefiningScope('c')).toBe(null)
// expect(child.contains('c')).toEqual(false)
})
})增加三级作用域,测试
describe('scope',()=>{
test('scope',()=>{
const Scope = require('../scope')
//实例化Scope,命名为route
const root = new Scope()
root.add('a')
//定义一个child子作用域,嵌套在Parent父作用域
const child = new Scope({'parent':root})
child.add('b')
//定义一个三级作用域,孙子节点
const childChild = new Scope({'parent':child})
childChild.add('c')
//编写断言
expect(child.findDefiningScope('a')).toBe(root)//'child中是否有a',a在父作用域链上,按作用域规则可以找到
expect(child.contains('a')).toEqual(true)//toEqual比较每项每个的值
expect(child.findDefiningScope('b')).toBe(child)//toBe比较的是地址
expect(child.contains('b')).toBe(true)
expect(child.findDefiningScope('c')).toBe(null)
expect(child.contains('c')).toEqual(false)
expect(childChild.findDefiningScope('b')).toBe(child)
expect(childChild.contains('b')).toEqual(true)
})
})四、整合节点遍历和作用域函数
新建analyze.js文件
//analyze.js
//输入是一个ast 输出是已经分析好的scope
const acorn = require('acorn')
const fs = require('fs')
const { node } = require('webpack')
const {walk} = require('../walk')
const code = fs.readFileSync('../source.js').toString()
const ast = acorn.parse(code,{ecmaVersion:7})
const Scope = require('./scope')
module.exports = function analyze(ast) {
const root = new Scope()
ast.body.map(node=>{
walk(node,{
enter:(node)=>{
if(node.type === 'Identifier'){
root.add(node.name)
// console.log(node.Identifier.name)
}
//是个函数 如果存在函数,函数在子作用域里
if(node.type === 'FunctionDeclaration'){
// console.log('=>'+node.id.name)
}
},
leave:(node) =>{
}
})
})
return new Scope()
}新增analyze.spec.js文件
describe('analyze',()=>{
test('analyze 1',()=>{
const analyze = require('../analyze')
//测试ast到scope
const acorn = require('acorn')
const fs = require('fs')
const {walk} = require('../walk')
const code = `
const a =1`
const ast = acorn.parse(code,{ecmaVersion:7})
const root = analyze(ast)
expect(root.findDefiningScope('a')).toBe(root)
expect(root.contains('a')).toEqual(true)
})
})