使用openmv,通过阈值颜色和形状来去真假宝藏。调试过程发现颜色的阈值比较重要,因为不准的话,它会把一些颜色相近的物体也识别了。识别的精度有待提高,可以使用YOLOV5来精确识别,奈何本人没精力来弄这个。
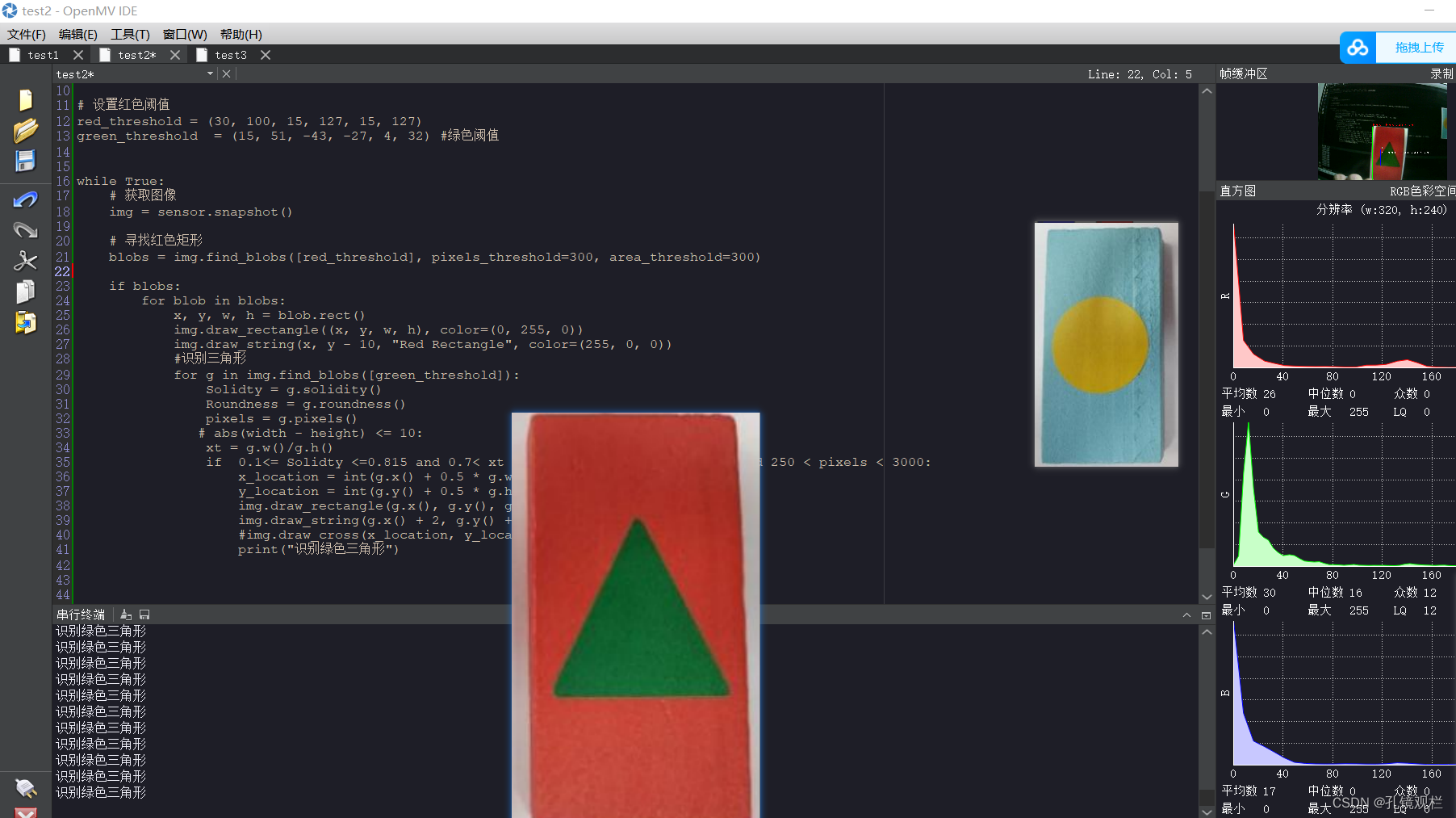
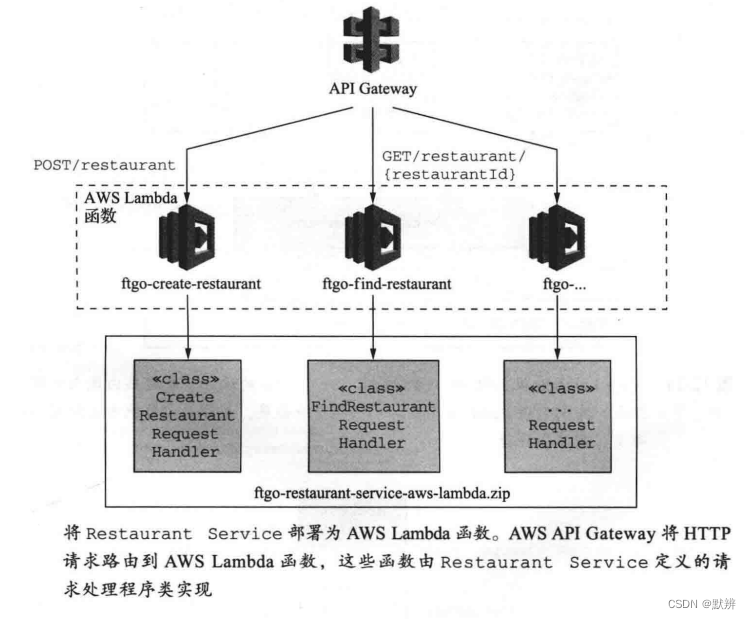
打开机器视觉的阈值调节器
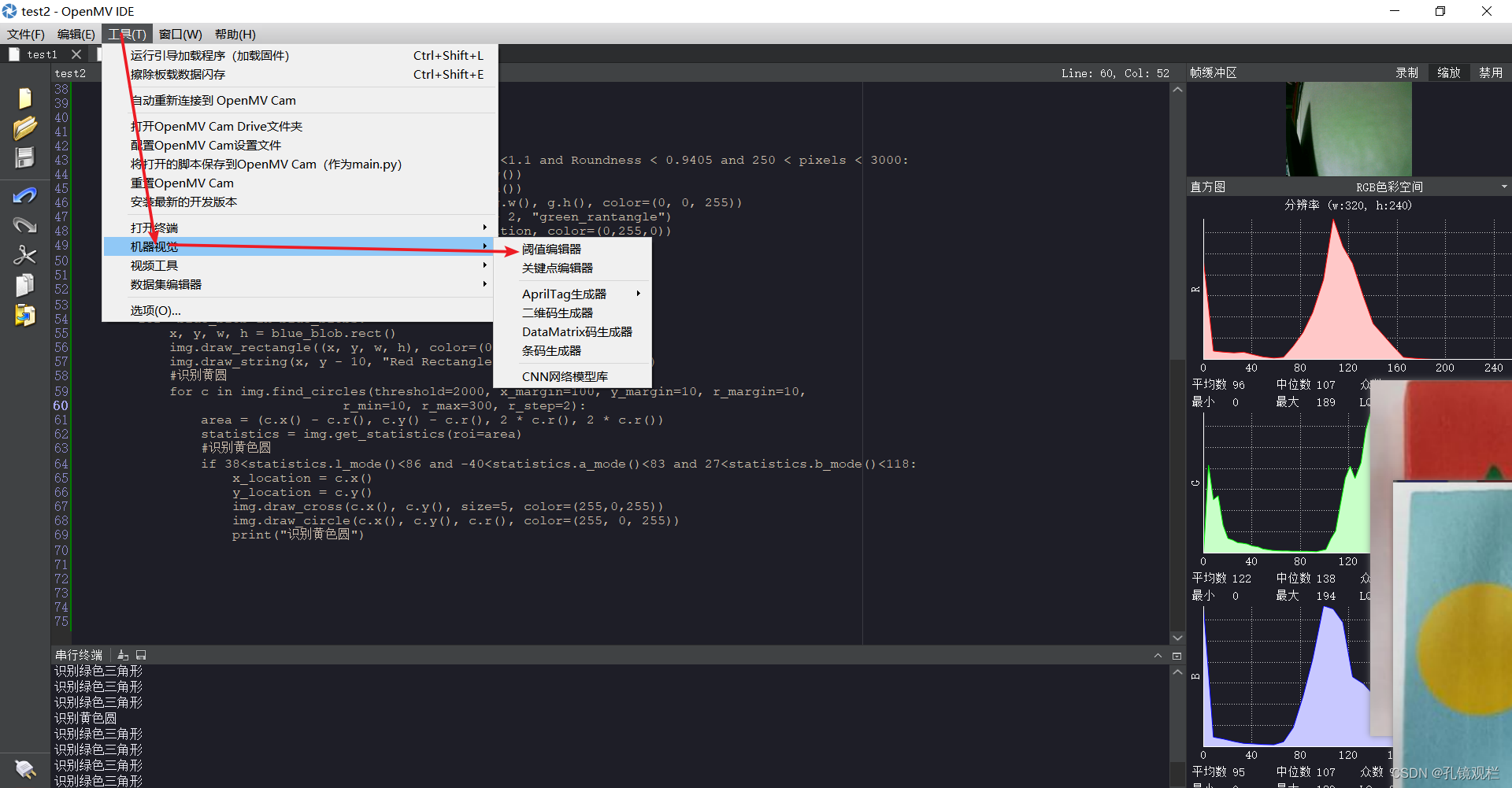
使用方法: 阈值调节主要是把你想要的颜色调为白色,其它颜色为黑色。将调节好的六个参数复制至代码那里。
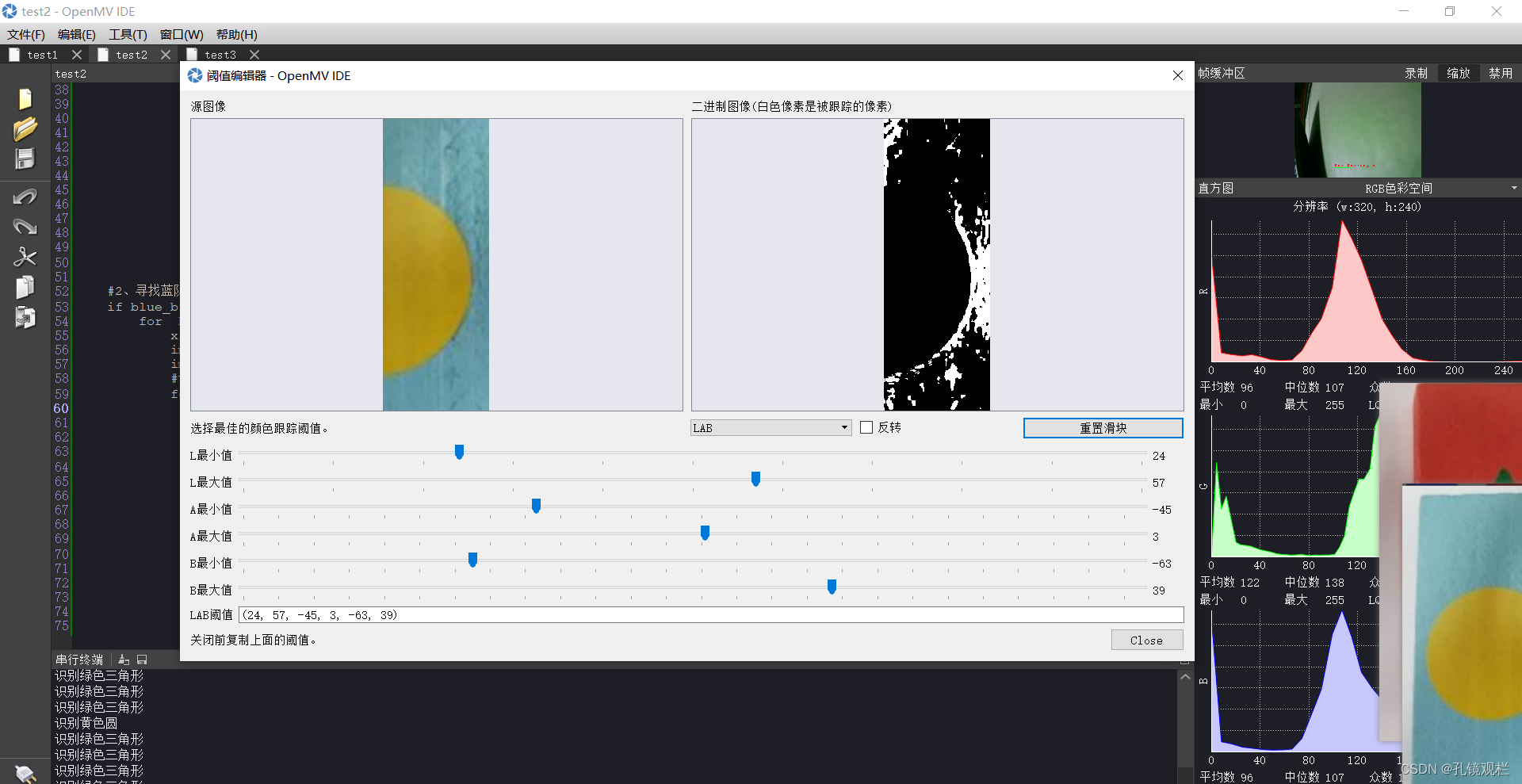
共六个参数,从上到下按顺序,L、A、B的最小值不超过其最大值,但也看情况。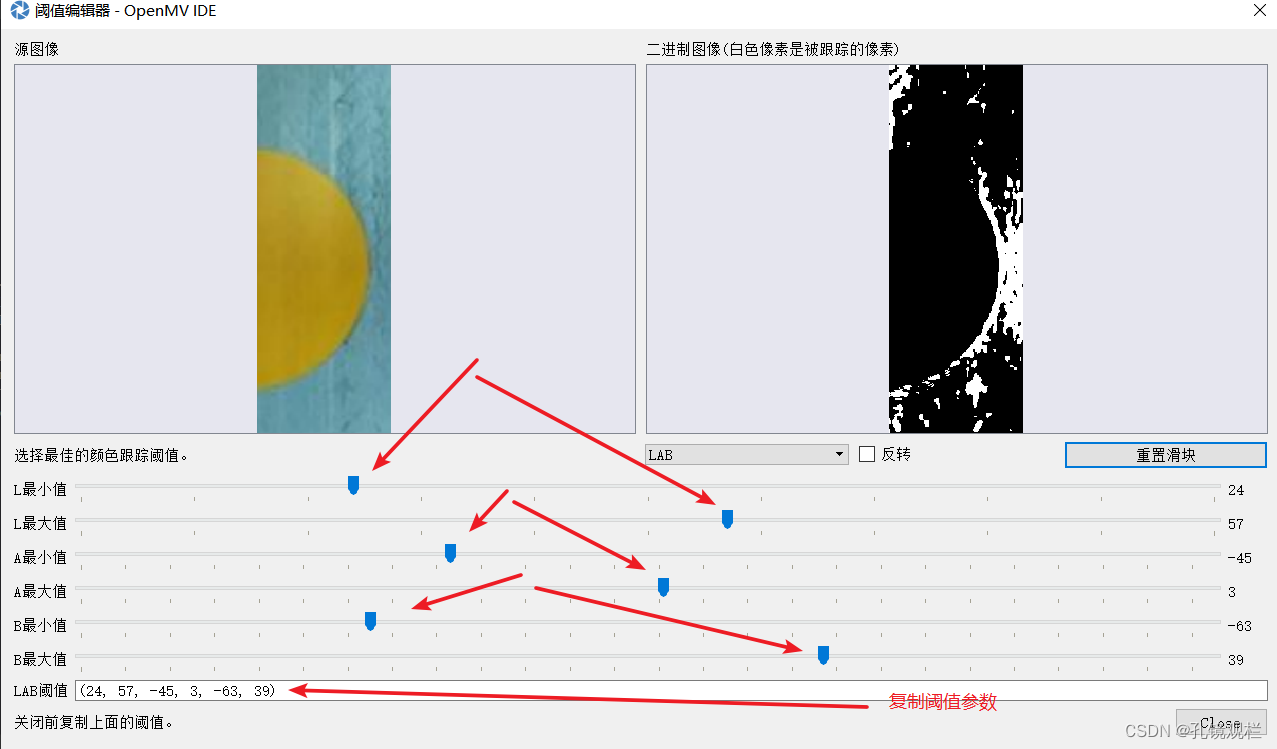
阈值没调好的效果。
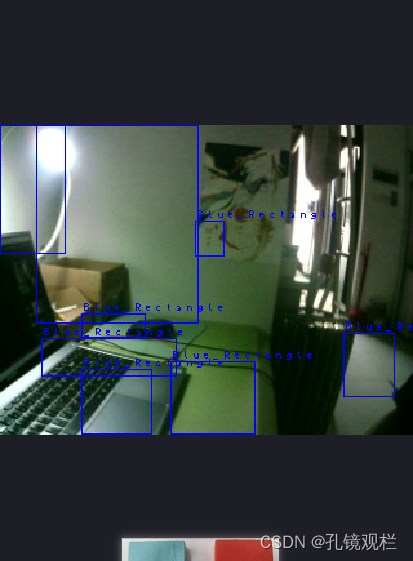
(openmv拍宿舍,是谁放假了还在学校参加比赛 ^@^ ,大冤种就是我)

附一段杂的代码,仅供参考:
import sensor, image, time
sensor.reset() # Reset and initialize the sensor.
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565) # Set pixel format to RGB565 (or GRAYSCALE)
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQVGA) # Set frame size to QVGA (320x240)
sensor.skip_frames(time = 2000) # Wait for settings take effect.
sensor.set_auto_gain(False) # 关闭自动增益
sensor.set_auto_whitebal(False) # 关闭自动白平衡
clock = time.clock()
fs_cnt = 0
x_list = []
y_list = []
len_list = []
area_list = []
color_list = []
x_location = 0
y_location = 0
shape = 0 # 0没检测到1圆形2长方形3三角形
color = 0 # 0没检测到1圆形2长方形3三角形
sidelen = 0 # 单位cm
area = 0
xt = 0
red_threshold = [(27,54,-35,59,3,68)] #红色阈值
blue_threshold = [(37, 74, -80, 6, -100, -5)] #浅蓝色阈值
yellow_threshold = [(38, 86, -40, 83, 27, 118)] #黄色阈值
green_threshold = [(15, 52, -88, -12, -122, 44)] #绿色阈值
while True:
clock.tick()
fs_cnt = fs_cnt + 1
img = sensor.snapshot().lens_corr(1.8)
#img.bilateral(1)
#矩形识别
for d in img.find_rects(threshold=10000):
area = (d[0], d[1], d[2], d[3])
statistics1 = img.get_statistics(roi=area) # 像素颜色统计
xq = 0
xq = d[2] / d[3]
coners = d.corners()
sb = ((abs(coners[0][0] - coners[1][0]))**2 + (abs(coners[0][1]-coners[1][1])**2))**0.5
#识别红色矩形(3, 59, -82, 108, -122, 44)
if 3<statistics1.l_mode()<59 and -82<statistics1.a_mode()<108 and -122<statistics1.b_mode()<44 and 0.8<xq<1.2:
#color = 1
x_location = int(d[0] + d[2] / 2)
y_location = int(d[1] + d[3] / 2)
img.draw_rectangle(d.rect(), color=(0, 255, 0))
img.draw_cross(x_location, y_location, color=(0,255,0)) #绿色标识
print("识别红色矩形")
#识别三角形
for g in img.find_blobs(green_threshold):
Solidty = g.solidity()
Roundness = g.roundness()
pixels = g.pixels()
# abs(width - height) <= 10:
xt = g.w()/g.h()
if 0.1<= Solidty <=0.815 and 0.9< xt <1.1 and Roundness < 0.9405 and 250 < pixels < 3000:
x_location = int(g.x() + 0.5 * g.w())
y_location = int(g.y() + 0.5 * g.h())
img.draw_rectangle(g.x(), g.y(), g.w(), g.h(), color=(255, 0, 0))
img.draw_string(g.x() + 2, g.y() + 2, "green_rantangle")
#img.draw_cross(x_location, y_location, color=(0,255,0))
print("识别绿色三角形")
#识别蓝色矩形(35, 73, -49, -9, -34, 62)
#if 35<statistics1.l_mode()<73 and -49<statistics1.a_mode()<-9 and -34<statistics1.b_mode()<62 and 0.8<xq<1.2:
# x_location = int(d[0] + d[2] / 2)
# y_location = int(d[1] + d[3] / 2)
# img.draw_rectangle(d.rect(), color=(255, 255, 0))
# img.draw_cross(x_location, y_location, color=(255,255,0)) #黄色标识
# print("识别蓝色矩形")
#识别圆形
for c in img.find_circles(threshold=2000, x_margin=100, y_margin=10, r_margin=10,
r_min=10, r_max=200, r_step=2):
area = (c.x() - c.r(), c.y() - c.r(), 2 * c.r(), 2 * c.r())
statistics = img.get_statistics(roi=area)
#识别黄色圆
if 38<statistics.l_mode()<86 and -40<statistics.a_mode()<83 and 27<statistics.b_mode()<118:
x_location = c.x()
y_location = c.y()
img.draw_cross(c.x(), c.y(), size=5, color=(255,0,255))
img.draw_circle(c.x(), c.y(), c.r(), color=(255, 0, 255))
print("识别黄色圆")