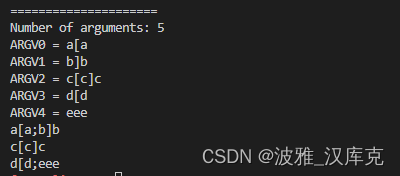
A 特殊元素平方和

模拟
class Solution {
public:
int sumOfSquares(vector<int> &nums) {
int res = 0;
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (n % (i + 1) == 0)
res += nums[i] * nums[i];
return res;
}
};
B 数组的最大美丽值
](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cccac309b3a248ab9f421af8e7d2b614.png)

差分数组: n u m s [ i ] nums[i] nums[i]可以变为 [ n u m s [ i ] − k , n u m s [ i ] + k ] [nums[i] - k, nums[i] + k] [nums[i]−k,nums[i]+k]内的数, 所有可以用差分数组将这段区间+1, 遍历数组执行区间加之后求差分数组前缀和的最大值, 注意为避免下标为负数可以将下标添加一个偏移量.
class Solution {
public:
int maximumBeauty(vector<int> &nums, int k) {
int mx = 0, mn = INT32_MAX;//nums中的最小值和最大值
for (auto x: nums) {
mx = max(mx, x);
mn = min(mn, x);
}
int c = mn - k;//下标偏移量
int N = mx + k + 1 - (mn - k) + 2;
int d[N];
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));
for (auto x: nums) {
d[x - k - c]++;
d[x + k - c + 1]--;
}
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0, cur = 0; i < N; i++) {
cur += d[i];
res = max(res, cur);
}
return res;
}
};
C 合法分割的最小下标


模拟: 一个合法分割两边的支配元素必等于原数组的支配元素, 所有升序枚举 i i i, 记录两边支配元素的计数, 判断是否满足条件
class Solution {
public:
int minimumIndex(vector<int> &nums) {
map<int, int> cnt;
for (auto x: nums)
cnt[x]++;
int val, mx = 0;//支配元素为val, 其出现次数为mx
for (auto &[k, v]: cnt)
if (v > mx) {
val = k;
mx = v;
}
for (int i = 0, cur = 0, n = nums.size(); i < n - 1; i++) {
if (nums[i] == val)
cur++;
if (cur * 2 > i + 1 && (mx - cur) * 2 > n - i - 1)//是一个合法分割
return i;
}
return -1;
}
};
D 最长合法子字符串的长度

线段树: 定义 r [ i ] r[i] r[i]表示以 w o r d [ i ] word[i] word[i]为左端点的没有出现在 f o r b i d d e n forbidden forbidden中的最长字符串长度为 r [ i ] − i + 1 r[i]-i+1 r[i]−i+1. 因为 f o r b i d d e n forbidden forbidden中字符串长度不超过10, 所有可以先用集合存一下 f o r b i d d e n forbidden forbidden的串, 然后遍历 i i i计算出 r [ i ] r[i] r[i]. 考虑以 i i i为左端点的字串, 其最长的合法子字符串长度为 m i n { r [ k ] ∣ i ≤ k ≤ r [ i ] } − i + 1 min\{r[k] \; |\; i\le k \le r[i] \}-i+1 min{r[k]∣i≤k≤r[i]}−i+1, 用线段树求区间最小值.
typedef long long ll;
//线段树模板
struct SegmentTree {
ll tl;
ll tr;
ll s;
ll mark;
int lazy;
};
vector<SegmentTree> st;
inline void push_down(ll index) {
st[index << 1].lazy = 1;
st[index << 1 | 1].lazy = 1;
st[index << 1].mark += st[index].mark;
st[index << 1 | 1].mark += st[index].mark;
st[index << 1].s += st[index].mark;
st[index << 1 | 1].s += st[index].mark;
st[index].lazy = 0;
st[index].mark = 0;
}
inline void push_up(ll index) {
st[index].s = min(st[index << 1].s, st[index << 1 | 1].s);
}
void build(ll l, ll r, vector<int> &li, ll index = 1) {//初始化
st[index].tl = l;
st[index].tr = r;
st[index].lazy = 0;
st[index].mark = 0;
if (l == r) {
st[index].s = li[l - 1];
} else {
ll mid = (l + r) >> 1;
build(l, mid, li, index << 1);
build(mid + 1, r, li, index << 1 | 1);
push_up(index);
}
}
ll query(ll l, ll r, ll index = 1) {//查询区间[l,r]上的最小值
if (l <= st[index].tl and st[index].tr <= r) {
return st[index].s;
} else {
if (st[index].lazy)
push_down(index);
if (r <= st[index << 1].tr)
return query(l, r, index << 1);
else if (l > st[index << 1].tr)
return query(l, r, index << 1 | 1);
return min(query(l, r, index << 1), query(l, r, index << 1 | 1));
}
}
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidSubstring(string word, vector<string> &forbidden) {
set<string> vis[11];
for (auto &si: forbidden)//按串的长度分组
vis[si.size()].insert(si);
int n = word.size();
vector<int> r(n, n - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {//计算r[i]
string t;
for (int j = i; j < n && t.size() < 10; j++) {
t.push_back(word[j]);
if (vis[t.size()].count(t)) {
r[i] = j - 1;//
break;
}
}
}
st = vector<SegmentTree>(4 * n + 5);
build(1, n, r);// 建树, 树中下标从1开始
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)//枚举左端点
if (i <= r[i])
res = max(res, (int) query(i + 1, r[i] + 1) - i + 1);
return res;
}
};