缓存是分布式系统中的重要组件,主要解决数据库数据的高并发访问问题。在实际开发中,尤其是用户 访问量较大的网站,为了提高服务器访问性能、减少数据库的访问压力、提高用户体验,使用缓存显得 尤为重要。Spring Boot对缓存提供了良好的支持
默认缓存管理
Spring框架支持透明地向应用程序添加缓存并对缓存进行管理,其管理缓存的核心是将缓存应用于操作 数据的方法中,从而减少操作数据的次数,同时不会对程序本身造成任何干扰。Spring Boot继承了Spring框架的缓存管理功能,通过使用@EnableCaching注解开启基于注解的缓存支持,Spring Boot可以启动缓存管理的自动化配置
Spring Boot默认缓存体验
1.使用@EnableCaching注解开启基于注解的缓存支持,该注解通常会添加在项目启动类上
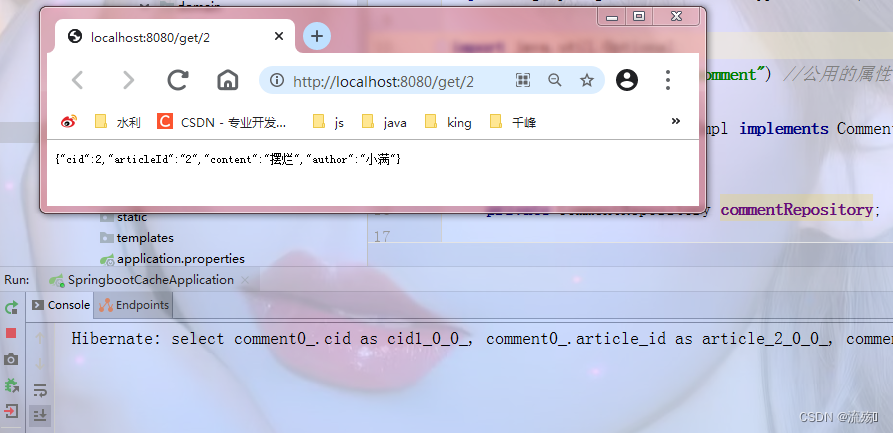
2.使用@Cacheable注解对数据操作方法进行缓存管理。将@Cacheable注解标注在CommentService类 的查询方法上,对查询结果进行缓存
这样我们就不会每次访问的时候都去数据库进行查询,大大节省了效率,只要查的数据一致,无论查多少次都只会进行一次查询,然后保存到缓存区,之后每次查询的数据都是从缓存中获取的
Spring Boot缓存注解介绍
1.@EnableCaching注解:@EnableCaching是由Spring框架提供的,Spring Boot框架对该注解进行了继承,该注解需要配置在类上(在Spring Boot中,通常配置在项目启动类上),用于开启基于注解的缓存支持。
2.@Cacheable注解:@Cacheable注解也是由Spring框架提供的,可以作用于类或方法(通常用在数据查询方法上),用于 对方法的查询结果进行缓存存储。@Cacheable注解的执行顺序是,先进行缓存查询,如果为空则进行 方法查询,并将结果进行缓存;如果缓存中有数据,不进行方法查询,而是直接使用缓存数据
cacheNames 缓存空间名 unless 条件成立则不缓存 key 指定id,默认为形参的具体指
#result 获取结果
3.@CachePut注解:@CachePut注解是由Spring框架提供的,可以作用于类或方法(通常用在数据更新方法上),该注解的 作用是更新缓存数据。@CachePut注解的执行顺序是,先进行方法调用,然后将方法结果更新到缓存 中
4.@CacheEvict注解;
@CacheEvict注解是由Spring框架提供的,可以作用于类或方法(通常用在数据删除方法上),该注解 的作用是删除缓存数据。@CacheEvict注解的默认执行顺序是,先进行方法调用,然后清除缓存。 @CacheEvict注解提供了多个属性,这些属性与@Cacheable注解的属性基本相同。 除此之外,@CacheEvict注解额外提供了两个特殊属性allEntries和beforeInvocation,其说明如下
1)allEntries属性:allEntries属性表示是否清除指定缓存空间中的所有缓存数据,默认值为false(即默认只删除指定key对应的缓存数据)。例如@CacheEvict(cacheNames="comment",allEntries= true)表示方法执行后会删除 缓存空间comment中所有的数据
2)beforeInvocation属性:beforeInvocation属性表示是否在方法执行之前进行缓存清除,默认值为false(即默认在执行方法后再 进行领存清除)例如@CacheEvict(cacheNames="comment",beforeInvocation=true)表示会在方法执 行之前进行缓存清除。
需要注意的是,如果将@CacheEvict注解的beforeInvocation属性设置为true,会存在一定的弊端。例 如在进行数据删除的方法中发生了异常,这会导致实际数据并没有被删除,但是缓存数据却被提前清除了
5.@Caching注解:如果处理复杂规则的数据缓存可以使用@Caching注解,该注解作用于类或者方法上。@Caching注解包 含三个属性cacheable、put和evict,它们的作用等同于@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict。
例子:@Caching(cacheable = {@Cacheable(cacheNames = "comment", key = "#comment_id")},put = {@CachePut(cacheNames = "comment", key = "#result.author")})
6.@CacheConfig注解:@CacheConfig注解作用于类,主要用于统筹管理类中所有使用@Cacheable、@CachePut和@CacheEvict注解标注的方法中的公共属性,这些公共属性包括 cacheNames,keyGenerator,cacheManager和cacheResolver。
基于注解的Redis缓存实现
1.添加pom文件
<!-- 引入整合Redis缓存的依赖启动器 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> </dependency>
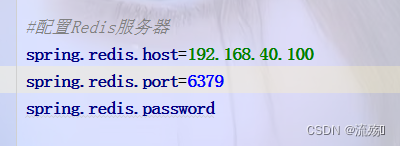
2. 在核心配置文件application.properties中添加Redis服务的连接配置
# Redis服务器地址 spring.redis.host=192.168.40.100 # Redis服务器连接端口 spring.redis.port=6379 # Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空) spring.redis.password=
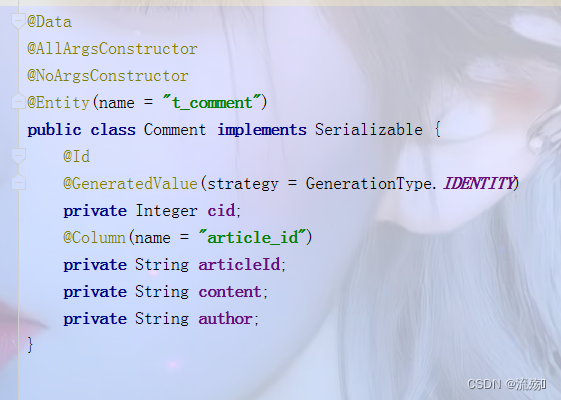
3.在对实体类对象进行缓存存储时必须先实现 序列化,让实体类实现Serializable接口,否则会出现缓存异 常,导致程序无法正常执行
4.编写实体类CommentServiceImpl
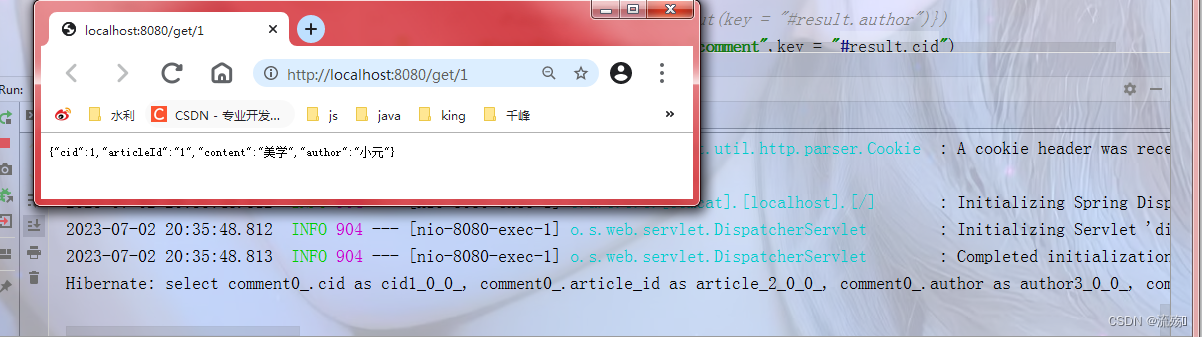
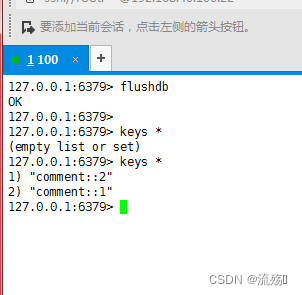
import com.example.springboot_cache.domain.Comment; import com.example.springboot_cache.repository.CommentRepository; import com.example.springboot_cache.service.CommentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.Optional; @CacheConfig(cacheNames = "comment") //公用的属性可以在这个注解里面指定 @Service public class CommentServiceImpl implements CommentService { @Autowired private CommentRepository commentRepository; @Override @Cacheable(unless = "#result==null") public Comment findById(int comment_id) { Optional<Comment> optional = commentRepository.findById(comment_id); if(optional.isPresent()){ return optional.get();//获取optional中的comment对象 } return null; } @Override @CachePut(key = "#result.cid") public Comment updateComment(Comment c) { int i = commentRepository.updateComment(c.getAuthor(), c.getCid()); Optional<Comment> cc = commentRepository.findById(c.getCid()); if(cc.isPresent()){ return cc.get(); } return null; } @Override @CacheEvict() public void deleteComment(Integer cid) { Comment comment = new Comment(); comment.setCid(cid); commentRepository.delete(comment); } }5.编写完成后重启项目,然后访问刚刚的接口,可以看到也实现了缓存,数据存储在Redis中
基于API的Redis缓存实现
1.编写实体类 APICommentServiceImpl
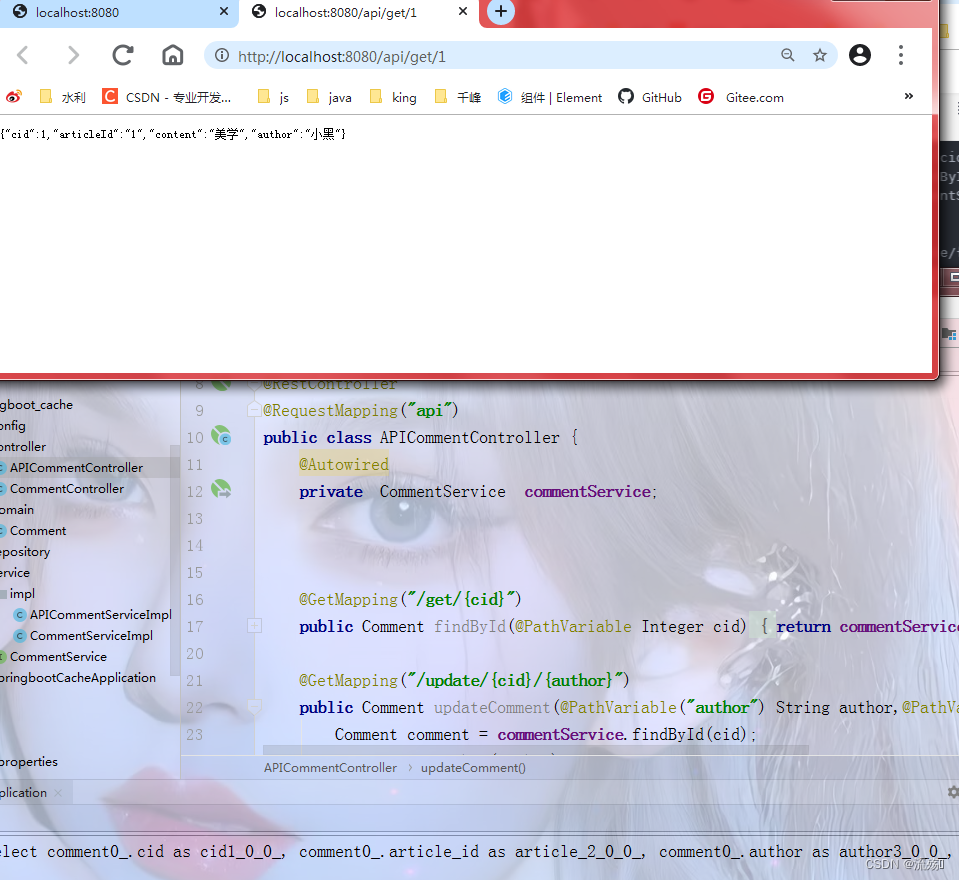
import com.example.springboot_cache.domain.Comment; import com.example.springboot_cache.repository.CommentRepository; import com.example.springboot_cache.service.CommentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import java.util.Optional; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; @Service public class APICommentServiceImpl implements CommentService { @Autowired private CommentRepository commentRepository; @Autowired //简化了Redis操作的模板类,底层封装了Jedis private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; @Override//将数据存到redis中,如果存在则直接返回 public Comment findById(int comment_id) { Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("comment_" + comment_id); if(o==null){ Optional<Comment> optional = commentRepository.findById(comment_id); if(optional.isPresent()){ Comment comment = optional.get();//获取optional中的comment对象 // redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment_id,comment); redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+comment_id,comment,1, TimeUnit.DAYS); return comment; }else { return null; } }else { return (Comment) o; } } @Override public Comment updateComment(Comment c) { int i = commentRepository.updateComment(c.getAuthor(), c.getCid()); Optional<Comment> cc = commentRepository.findById(c.getCid()); if(cc.isPresent()){ return cc.get(); } redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("comment_"+c.getCid(),cc.get()); return null; } @Override public void deleteComment(Integer cid) { Comment comment = new Comment(); comment.setCid(cid); commentRepository.delete(comment); redisTemplate.delete("comment_"+cid); } }2.编写控制层类APICommentController
import com.example.springboot_cache.domain.Comment; import com.example.springboot_cache.service.CommentService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; @RestController @RequestMapping("api") public class APICommentController { @Autowired private CommentService commentService; @GetMapping("/get/{cid}") public Comment findById(@PathVariable Integer cid){ return commentService.findById(cid); } @GetMapping("/update/{cid}/{author}") public Comment updateComment(@PathVariable("author") String author,@PathVariable("cid") int cid){ Comment comment = commentService.findById(cid); comment.setAuthor(author); Comment c = commentService.updateComment(comment); return c; } @DeleteMapping("/delete/{cid}") public void deleteComment(@PathVariable Integer cid){ commentService.deleteComment( cid); } }3.编写完成后重启之间要先把CommentServiceImpl的@Service注释掉
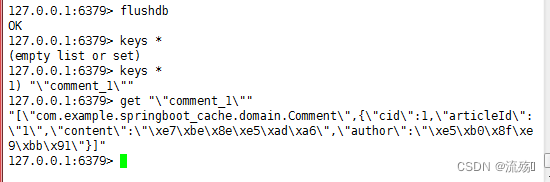
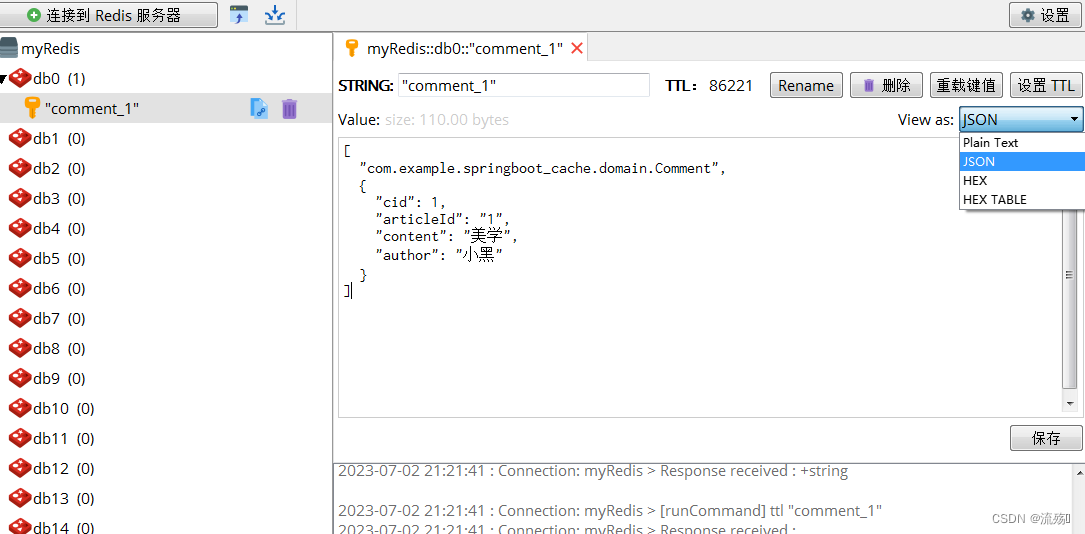
也是只在数据库查询一次,之后就再Redis缓存中查询,但是我们看到的缓存数据是二进制的乱码,我们并看不到,所以就需要我们的配置类来把存储的数据转化JSON格式
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect; import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration; import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.*; import java.time.Duration; @Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Bean//api乱码解决 public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){ //Redis模板类的连接工厂 RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate =new RedisTemplate<>(); redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); //使用JSON格式序列化对象 将对象的数据缓存为ket,value的结构 Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2 = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class); //解决查询缓存转换异常的问题 ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); jackson2.setObjectMapper(om); //设置redisTemplate模板的序列化数据方式 redisTemplate.setDefaultSerializer(jackson2); return redisTemplate; } @Bean //注解乱码解决 返回值表示一个Redis缓存管理器对象,通过这对象来管理和配置基于注解式开发缓存的数据进行序列化转化 public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){ Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer json =new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);//设置value的序列化方式 RedisSerializer<String> strSerializer =new StringRedisSerializer();//设置key的序列化方式 //解决查询缓存转换异常的问题 ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper(); om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY); om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL); json.setObjectMapper(om); //创建 RedisCacheConfiguration 对象 RedisCacheConfiguration configuration =RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig() .entryTtl(Duration.ofDays(1))//设置存活时间为1天 .serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(strSerializer))//指定key进行序列化 .serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(json)) .disableCachingNullValues();//null值不允许参与序列化操作 //RedisCacheManager对象 设置默认的缓存 RedisCacheManager man = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(configuration).build(); return man; } }配置完成后重新查询,然后在官网下载Redis的软件工具,将查看的格式改为JSON我们就可以查询到不是二进制乱码的数据