OpenCV除了使用光流算法与普通插值实现图像视频超分,还提供AI深度学习实现视频超分。算法模型包括:edsr、espcn、fsrcnn、lapsrn,实现超分的倍数有2、3、4、8。通过AI实现的视频超分比传统算法的效果更好,图像更清晰。
1、超分算法对比
在opencv_contrib外置库的dnn_superres模块,就是用AI实现的图像/视频超分。接下来,我们对比AI算法、双三次插值、最近邻插值、Lanczos插值的超分效果。通过计算图像的PSNR、SSIM来评估超分质量。
#include <iostream>
#include <opencv2/opencv_modules.hpp>
#include <opencv2/dnn_superres.hpp>
#include <opencv2/quality.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace dnn_superres;
static Vec2d getQualityValues(Mat orig, Mat upsampled)
{
double psnr = PSNR(upsampled, orig);
Scalar q = quality::QualitySSIM::compute(upsampled, orig, noArray());
double ssim = mean(Vec3d((q[0]), q[1], q[2]))[0];
return Vec2d(psnr, ssim);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 4) {
cout << "usage:";
cout << "Arg 1: image path | Path to image\n";
cout << "Arg 2: algorithm | edsr, espcn, fsrcnn or lapsrn\n";
cout << "Arg 3: path to model file \n";
cout << "Arg 4: scale | 2, 3, 4 or 8 \n";
cout << "-----------------------------------------------" << endl;
return -1;
}
string path = string(argv[1]);
string algorithm = string(argv[2]);
string model = string(argv[3]);
int scale = atoi(argv[4]);
Mat img = imread(path);
if (img.empty()) {
cerr << "Couldn't load image: " << img << "\n";
return -2;
}
// 裁剪图像
int width = img.cols - (img.cols % scale);
int height = img.rows - (img.rows % scale);
Mat cropped = img(Rect(0, 0, width, height));
Mat img_downscaled;
resize(cropped, img_downscaled, Size(), 1.0 / scale, 1.0 / scale);
Mat img_new;
DnnSuperResImpl sr;
vector <Mat> allImages;
// 读取模型:以ESPCN为例,"models/ESPCN_x2.pb"
sr.readModel(model);
// 设置超分算法、超分倍数
sr.setModel(algorithm, scale);
sr.upsample(img_downscaled, img_new);
vector<double> psnrValues = vector<double>();
vector<double> ssimValues = vector<double>();
// 1、深度学习模型
Vec2f quality = getQualityValues(cropped, img_new);
psnrValues.push_back(quality[0]);
ssimValues.push_back(quality[1]);
cout << sr.getAlgorithm() << ":" << endl;
cout << "PSNR: " << quality[0] << " SSIM: " << quality[1] << endl;
// 2、双三次插值
Mat bicubic;
resize(img_downscaled, bicubic, Size(), scale, scale, INTER_CUBIC);
quality = getQualityValues(cropped, bicubic);
psnrValues.push_back(quality[0]);
ssimValues.push_back(quality[1]);
cout << "Bicubic " << endl;
cout << "PSNR: " << quality[0] << " SSIM: " << quality[1] << endl;
// 3、最近邻插值
Mat nearest;
resize(img_downscaled, nearest, Size(), scale, scale, INTER_NEAREST);
quality = getQualityValues(cropped, nearest);
psnrValues.push_back(quality[0]);
ssimValues.push_back(quality[1]);
cout << "Nearest neighbor" << endl;
cout << "PSNR: " << quality[0] << " SSIM: " << quality[1] << endl;
// 4、LANCZOS插值
Mat lanczos;
resize(img_downscaled, lanczos, Size(), scale, scale, INTER_LANCZOS4);
quality = getQualityValues(cropped, lanczos);
psnrValues.push_back(quality[0]);
ssimValues.push_back(quality[1]);
cout << "Lanczos" << endl;
cout << "PSNR: " << quality[0] << " SSIM: " << quality[1] << endl;
return 0;
}2、超分效果对比
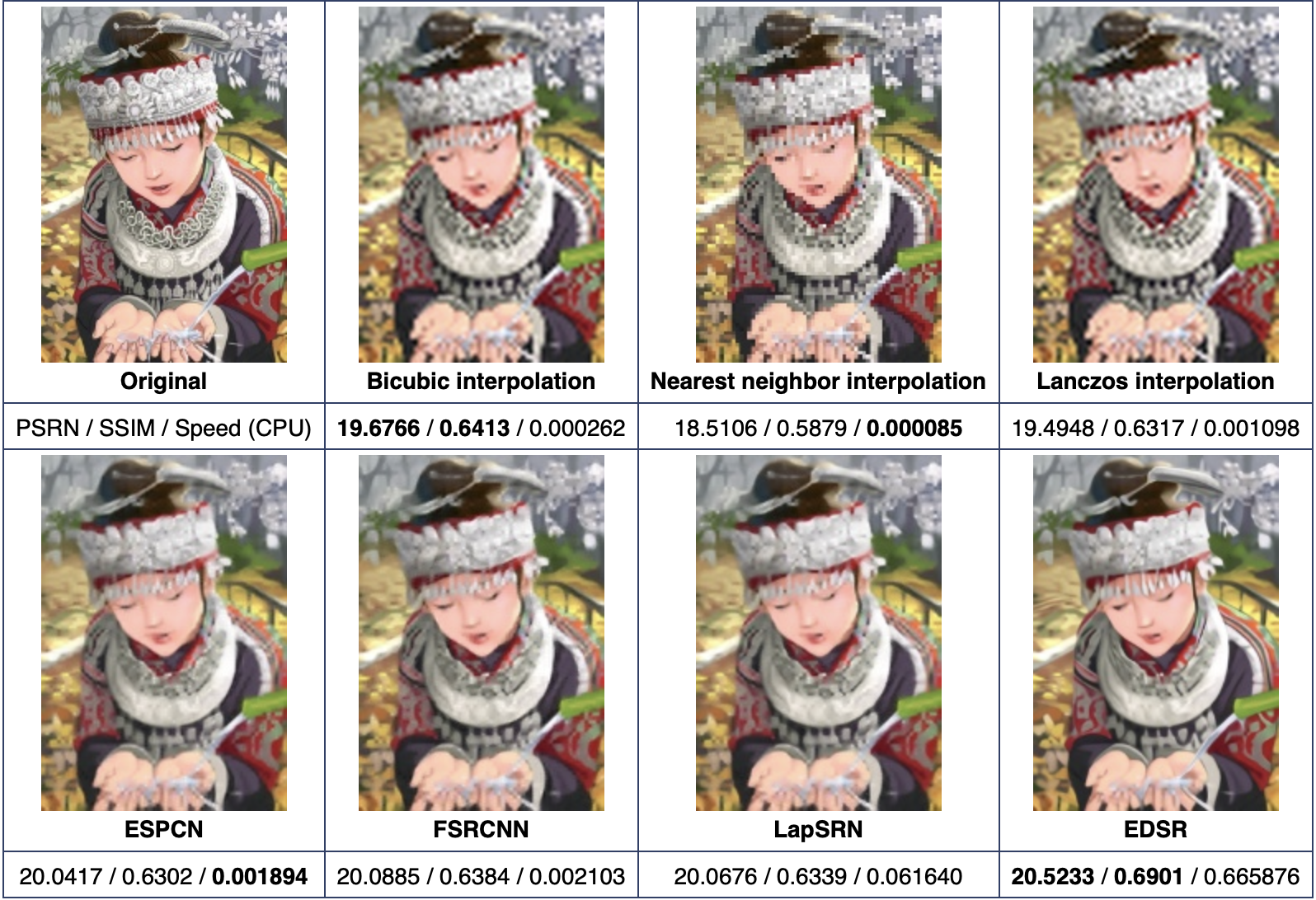
以4倍超分为例,各个算法实现超分的效果如下图所示。可以看到双三次插值、最近邻插值、Lanczos插值的图像有马赛克方块,而通过AI实现超分的图像比较清晰。

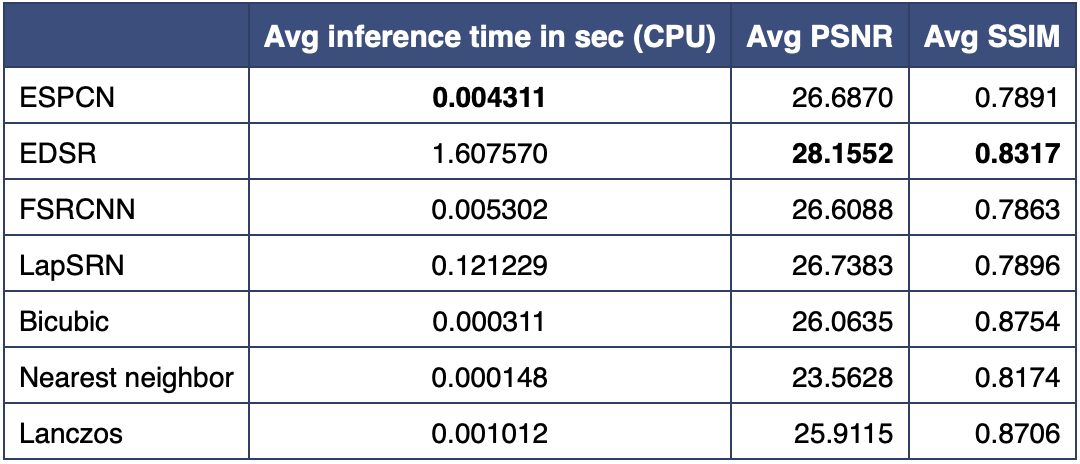
具体的耗时、PSNR、SSIM数据,如下表所示。可以看到,传统算法的耗时很少,PSNR值在26左右。而AI算法的耗时比较高,其中EDSR模型的耗时有1.6s,PSNR值最高(超过28)。
3、AI视频超分
通过VideoCapture来读取视频帧,然后使用DnnSuperResImpl实现逐帧超分,接着用VideoWriter写视频文件。完整的示例代码如下:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 4) {
cout << "usage: Arg 1: input video path" << endl;
cout << "\t Arg 2: output video path" << endl;
cout << "\t Arg 3: algorithm | edsr, espcn, fsrcnn or lapsrn" << endl;
cout << "\t Arg 4: scale | 2, 3, 4 or 8 \n";
cout << "\t Arg 5: path to model file \n";
return -1;
}
string input_path = string(argv[1]);
string output_path = string(argv[2]);
string algorithm = string(argv[3]);
int scale = atoi(argv[4]);
string path = string(argv[5]);
VideoCapture input_video(input_path);
int ex = static_cast<int>(input_video.get(CAP_PROP_FOURCC));
Size S = Size((int) input_video.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH) * scale,
(int) input_video.get(CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT) * scale);
VideoWriter output_video;
output_video.open(output_path, ex, input_video.get(CAP_PROP_FPS), S, true);
if (!input_video.isOpened())
{
std::cerr << "Could not open the video." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// 读取超分模型、设置超分倍数
DnnSuperResImpl sr;
sr.readModel(path);
sr.setModel(algorithm, scale);
for(;;)
{
Mat frame, output_frame;
// 读取视频帧
input_video >> frame;
if ( frame.empty() )
break;
// 执行超分
sr.upsample(frame, output_frame);
// 写入超分后的视频帧
output_video << output_frame;
char c=(char)waitKey(25);
if(c==27)
break;
}
input_video.release();
output_video.release();
return 0;
}4、AI超分源码
首先把图像转换为浮点格式,然后拆分YCbCr通道,传入深度学习网络进行超分,最后重建图像。源码如下:
void DnnSuperResImpl::upsample(InputArray img, OutputArray result)
{
if (net.empty())
CV_Error(Error::StsError, "Model not specified. Please set model via setModel().");
if (this->alg == "espcn" || this->alg == "lapsrn" || this->alg == "fsrcnn")
{
// 预处理: 转成浮点格式
Mat preproc_img;
preprocess_YCrCb(img, preproc_img);
// 拆分通道,仅用Y通道进行推理
Mat ycbcr_channels[3];
split(preproc_img, ycbcr_channels);
Mat Y = ycbcr_channels[0];
// 创建blob
cv::Mat blob;
dnn::blobFromImage(Y, blob, 1.0);
// 使用神经网络进行超分
this->net.setInput(blob);
Mat blob_output = this->net.forward();
// 从blob转换回image
std::vector <Mat> model_outs;
dnn::imagesFromBlob(blob_output, model_outs);
Mat out_img = model_outs[0];
// 重建图像: 对Cr、Cb进行超分,融合第三层网络
reconstruct_YCrCb(out_img, preproc_img, result, this->sc);
}
else if (this->alg == "edsr")
{
// Div2K数据集的平均值
Scalar mean = Scalar(103.1545782, 111.561547, 114.35629928);
// 转成浮点格式
Mat float_img;
img.getMat().convertTo(float_img, CV_32F, 1.0);
// 创建blob、抽取数据集的平均值
cv::Mat blob;
dnn::blobFromImage(float_img, blob, 1.0, Size(), mean);
// 使用神经网络进行超分
this->net.setInput(blob);
Mat blob_output = this->net.forward();
// 从blob转换回image
std::vector <Mat> model_outs;
dnn::imagesFromBlob(blob_output, model_outs);
// 后处理: 添加平均值
Mat(model_outs[0] + mean).convertTo(result, CV_8U);
}
else
{
CV_Error(cv::Error::StsNotImplemented, String("Unknown/unsupported superres algorithm: ") + this->alg);
}
}






![[算法前沿]--028-基于Hugging Face -Transformers的预训练模型微调](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/3ba51fe4f21d4d528ca7b0f2fd78aee4.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZHJvaWRzYW5zZmFsbGJhY2s,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA56We5rSb5Y2O,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16#pic_center)