目录链接:
力扣编程题-解法汇总_分享+记录-CSDN博客
GitHub同步刷题项目:
https://github.com/September26/java-algorithms
原题链接:力扣
描述:
在 n*m 大小的棋盘中,有黑白两种棋子,黑棋记作字母 "X", 白棋记作字母 "O",空余位置记作 "."。当落下的棋子与其他相同颜色的棋子在行、列或对角线完全包围(中间不存在空白位置)另一种颜色的棋子,则可以翻转这些棋子的颜色。
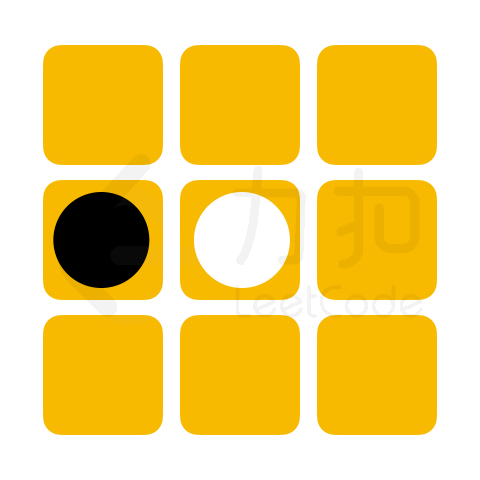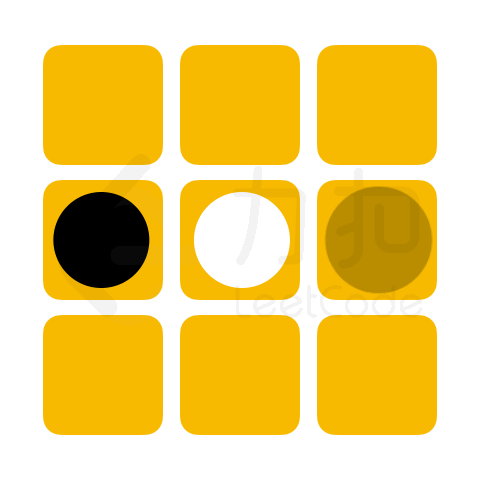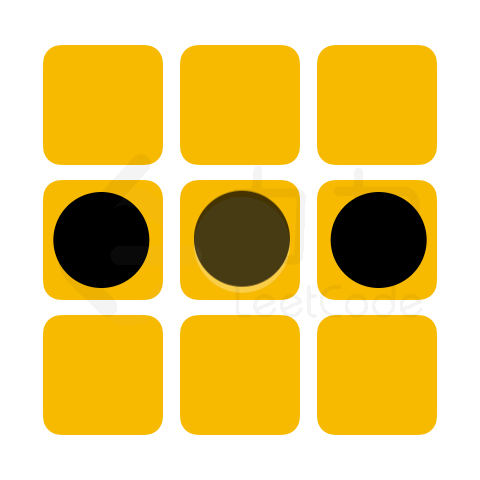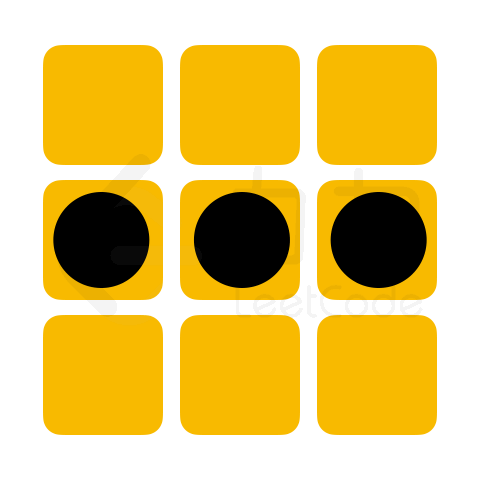
「力扣挑战赛」黑白翻转棋项目中,将提供给选手一个未形成可翻转棋子的棋盘残局,其状态记作 chessboard。若下一步可放置一枚黑棋,请问选手最多能翻转多少枚白棋。
注意:
- 若翻转白棋成黑棋后,棋盘上仍存在可以翻转的白棋,将可以 继续 翻转白棋
- 输入数据保证初始棋盘状态无可以翻转的棋子且存在空余位置
示例 1:
输入:
chessboard = ["....X.","....X.","XOOO..","......","......"]输出:
3解释: 可以选择下在
[2,4]处,能够翻转白方三枚棋子。
示例 2:
输入:
chessboard = [".X.",".O.","XO."]输出:
2解释: 可以选择下在
[2,2]处,能够翻转白方两枚棋子。
示例 3:
输入:
chessboard = [".......",".......",".......","X......",".O.....","..O....","....OOX"]输出:
4解释: 可以选择下在
[6,3]处,能够翻转白方四枚棋子。
提示:
1 <= chessboard.length, chessboard[i].length <= 8chessboard[i]仅包含"."、"O"和"X"
解题思路:
/**
* LCP 41. 黑白翻转棋
* 解题思路:
* 有可能没有太好的思路,这题的限制是8*8的棋盘,所以可以使用穷举的策略。
* 每个位置,都计算出放入黑子之后的所有影响到的白棋。
* 首先把chessboard转换为二位int类型的数组board,每个位置上,0代表是空的,1代表放的是白棋,2代表放的是黑棋。
* 所以searchDirection方法中,输入值为x,y坐标,以及二维数组board。
* 然后使用广度优先搜索,构建一个队列,队列中的初始值就是x,y,因为后面遍历中的过程中可能会添加新的。
* 然后分别向8个方向生成新的位置newX,newY,然后查看是否满足,如果满足,则一条路径上所有的点都加入到队列中。
* 然后继续下一轮的循环,知道队列为空。
*
*/
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
/**
* LCP 41. 黑白翻转棋
* 解题思路:
* 有可能没有太好的思路,这题的限制是8*8的棋盘,所以可以使用穷举的策略。
*
*/
class Solution_LCP41
{
public:
static constexpr int directions[8][2] = {{1, 0}, {1, 1}, {0, 1}, {-1, 1}, {-1, 0}, {-1, -1}, {0, -1}, {1, -1}};
const int CHESS_NULL = 0; // 没有放置
const int CHESS_WHITE = 1; // 白棋
const int CHESS_BLACK = 2; // 黑棋
int searchDirection(vector<vector<int>> board, int x, int y)
{
queue<pair<int, int>> qu;
int sum = 0;
qu.emplace(make_pair(x, y));
while (!qu.empty())
{
auto [nx, ny] = qu.front();
qu.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
int newX = nx;
int newY = ny;
vector<pair<int, int>> record;
bool flag = true;
int step = 0;
while (true)
{
newY = newY + directions[i][1];
newX = newX + directions[i][0];
if (newX < 0 || newY < 0 || newX >= board[0].size() || newY >= board.size())
{
flag = false;
break;
}
if (board[newY][newX] == CHESS_NULL)
{
flag = false;
break;
}
else if (board[newY][newX] == CHESS_BLACK)
{
break;
}
record.push_back(make_pair(newX, newY));
step++;
}
if (flag)
{
for (int j = 0; j < record.size(); j++)
{
board[record[j].second][record[j].first] = CHESS_BLACK;
qu.emplace(record[j].first, record[j].second);
}
sum += step;
}
}
}
return sum;
}
int flipChess(vector<string> &chessboard)
{
vector<vector<int>> board;
for (const string &str : chessboard)
{
vector<int> line;
for (char c : str)
{
if (c == 'X')
{
line.push_back(2);
}
else if (c == 'O')
{
line.push_back(1);
}
else
{
line.push_back(0);
}
}
board.push_back(line);
}
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < board[0].size(); j++)
{
if (board[i][j] != 0)
{
continue;
}
if (i == 6 && j == 3)
{
std::cout << "1:" << std::endl;
}
int step = searchDirection(board, j, i);
max = max > step ? max : step;
}
}
return max;
}
};