目录
1. platform平台简介
1.1 platform总线
1.2 platform 驱动
1.3 platform设备
2.platform平台总线初始化
3. platform驱动框架
4.实验
4.1 无设备树的platform设备注册
4.2 无设备树的platform驱动
4.3 有设备树的platform驱动
1. platform平台简介

当我们向系统注册一个驱动的时候,总线就会在设备列表中查找,看看有没有与之匹配的设备,如果有的话就将两者联系起来。同样的,当向系统中注册一个设备的时候,总线就会在驱动列表中查找看有没有与之匹配的设备,有的话也联系起来。驱动和设备之间的匹配就是依靠总线bus的match函数进行匹配的。
但是在 SOC 中有些外设是没有总线这个概念的,但是又要使用总线、驱动和设备模型该怎么办呢?为了解决此问题, Linux 提出了 platform 这个虚拟总线,相应的就有 platform_driver 和 platform_device。
1.1 platform总线
Linux系统内核使用bus_type结构体表示总线,此结构体定义在文件include/linux/device.h, bus_type 结构体内容如下:
struct bus_type {
const char *name;//总线类型名称
const char *dev_name;//该总线下的设备节点名称
struct device *dev_root;//该总线下的根设备节点
struct device_attribute *dev_attrs; /* use dev_groups instead *///该总线下所有设备的属性组
const struct attribute_group **bus_groups;//该总线的属性组
const struct attribute_group **dev_groups;//该总线下所有设备的属性组
const struct attribute_group **drv_groups;//该总线下所有设备驱动程序的属性组
int (*match)(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv);//用于检查设备是否匹配总线类型的函数
int (*uevent)(struct device *dev, struct kobj_uevent_env *env);//发送uevent消息的函数
int (*probe)(struct device *dev);//在设备被添加到总线上时调用的函数
int (*remove)(struct device *dev);//当设备被移除时调用的函数
void (*shutdown)(struct device *dev);//在系统关机时调用的函数
int (*online)(struct device *dev);//在设备被启用时调用的函数
int (*offline)(struct device *dev);//在设备被禁用时调用的函数
int (*suspend)(struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);//在设备被暂停时调用的函数
int (*resume)(struct device *dev);//在设备从暂停状态恢复时调用的函数
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;//设备的电源管理操作
const struct iommu_ops *iommu_ops;//用于执行输入/输出内存管理单元操作的指针
struct subsys_private *p; //用于保存总线私有数据的指针
struct lock_class_key lock_key;//用于调试锁问题的锁类别密钥
};match 函数,此函数很重要,单词 match 的意思就是“匹配、相配”,因此此函数就是完成设备和驱动之间匹配的,总线就是使用 match 函数来根据注册的设备来查找对应的驱动,或者根据注册的驱动来查找相应的设备,因此每一条总线都必须实现此函数。 match 函数有两个参数: dev 和 drv,这两个参数分别为 device 和 device_driver 类型,也就是设备和驱动。platform 总线是 bus_type 的一个具体实例,定义在文件 drivers/base/platform.c, platform 总线定义如下:
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",//设备名称
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,//设备属性、含获取sys文件名,该总线会放在/sys/bus下
.match = platform_match,//匹配设备和驱动,匹配成功就调用driver的.probe函数
.uevent = platform_uevent,//消息传递,比如热插拔操作
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};platform_bus_type 就是 platform 平台总线,其中 platform_match 就是匹配函数。我们来看一下驱动和设备是如何匹配的, platform_match 函数定义在文件 drivers/base/platform.c 中,函数内容如下所示:
static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev);
struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv);
/* When driver_override is set, only bind to the matching driver */
if (pdev->driver_override)
return !strcmp(pdev->driver_override, drv->name);
/* Attempt an OF style match first */
//设备树匹配方式
if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try ACPI style match */
//ACPI匹配方式
if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv))
return 1;
/* Then try to match against the id table */
//id_table匹配方式
if (pdrv->id_table)
return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL;
/* fall-back to driver name match */
//name匹配方式
return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);
}
1.2 platform 驱动
platform_driver结构体表示平台驱动:
struct platform_driver {
//当驱动和硬件信息匹配成功之后,就会调用probe函数,驱动所有的资源的注册和初始化全部放在probe函数中
int (*probe)(struct platform_device *);
//硬件信息被移除了,或者驱动被卸载了,全部要释放,释放资源的操作就放在该函数中
int (*remove)(struct platform_device *);
void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *);
int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume)(struct platform_device *);
//内核维护的所有的驱动必须包含该成员,通常driver->name用于和设备进行匹配
struct device_driver driver;
//往往一个驱动可能能同时支持多个硬件,这些硬件的名字都放在该结构体数组中
const struct platform_device_id *id_table;
bool prevent_deferred_probe;
};driver 成员,为 device_driver 结构体变量, Linux 内核里面大量使用到了面向对象的思维, device_driver 相当于基类,提供了最基础的驱动框架:
struct device_driver {
const char *name; //用于和硬件进行匹配。
struct bus_type *bus; //指向总线描述符的指针,总线连接所支持的设备。
struct module *owner;//设备驱动的owner,通常为THIS_MODULE
const char *mod_name; /* used for built-in modules */
// 通过sysfs操作设备驱动的bind/unbind,用来使能/关闭设备与驱动的自动匹配
bool suppress_bind_attrs; /* disables bind/unbind via sysfs */
enum probe_type probe_type;
const struct of_device_id *of_match_table;//device_tree中使用,用于匹配设备。
const struct acpi_device_id *acpi_match_table;
int (*probe) (struct device *dev);//当设备匹配/移除的时候,会调用设备驱动的probe/remove函数。
int (*remove) (struct device *dev);
void (*shutdown) (struct device *dev);//代表设备驱动在调用管理的时候的回调函数
int (*suspend) (struct device *dev, pm_message_t state);
int (*resume) (struct device *dev);
const struct attribute_group **groups;
const struct dev_pm_ops *pm;
struct driver_private *p;
};
of_match_table 就是采用设备树的时候驱动使用的匹配表,同样是数组,每个匹配项都为 of_device_id 结构体类型,此结构体定义在文件 include/linux/mod_devicetable.h 中,内容如下:
/*
* Struct used for matching a device
*/
struct of_device_id {
char name[32];
char type[32];
char compatible[128];
const void *data;
};
compatible 非常重要,因为对于设备树而言,就是通过设备节点的 compatible 属性值和 of_match_table 中每个项目的 compatible 成员变量进行比较,如果有相等的就表示设备和此驱动匹配成功。
在编写 platform 驱动的时候,首先定义一个 platform_driver 结构体变量,然后实现结构体中的各个成员变量,重点是实现匹配方法以及 probe 函数。当驱动和设备匹配成功以后 probe函数就会执行,具体的驱动程序在 probe 函数里面编写,比如字符设备驱动等等。
1.3 platform设备
platform 驱动已经准备好了,我们还需要 platform 设备,否则的话单单一个驱动也做不了什么。 platform_device 这个结构体表示 platform 设备,这里我们要注意,如果内核支持设备树的话就不要再使用 platform_device 来描述设备了,因为改用设备树去描述了。当然了,你如果一定要用 platform_device 来描述设备信息的话也是可以的。 platform_device 结构体定义在文件include/linux/platform_device.h 中,结构体内容如下:
struct platform_device {
const char *name;//设备的名称
int id; //用于标识该设备的ID
bool id_auto;
struct device dev;//内核中维护的所有的设备必须包含该成员,
u32 num_resources;//资源个数
struct resource *resource;//描述资源
const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;
char *driver_override; /* Driver name to force a match */
/* MFD cell pointer */
struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell;
/* arch specific additions */
struct pdev_archdata archdata;
};resource 表示资源,也就是设备信息,比如外设寄存器等。 Linux 内核使用 resource结构体表示资源, resource 结构体内容如下:
struct resource {
resource_size_t start;//表示资源的起始值,
resource_size_t end;//表示资源的最后一个字节的地址, 如果是中断,end和satrt相同
const char *name;// 可不写
unsigned long flags;//资源的类型
struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child;
};
start 和 end 分别表示资源的起始和终止信息,对于内存类的资源,就表示内存起始和终止地址, name 表示资源名字, flags 表示资源类型,可选的资源类型都定义在了文件include/linux/ioport.h 里面,如下所示:
/*
* IO resources have these defined flags.
*/
#define IORESOURCE_BITS 0x000000ff /* Bus-specific bits */
#define IORESOURCE_TYPE_BITS 0x00001f00 /* Resource type */
#define IORESOURCE_IO 0x00000100 /* PCI/ISA I/O ports */
#define IORESOURCE_MEM 0x00000200
#define IORESOURCE_REG 0x00000300 /* Register offsets */
#define IORESOURCE_IRQ 0x00000400
#define IORESOURCE_DMA 0x00000800
#define IORESOURCE_BUS 0x00001000在以前不支持设备树的Linux版本中,用户需要编写platform_device变量来描述设备信息,然后使用 platform_device_register 函数将设备信息注册到 Linux 内核中,此函数原型如下所示:
int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
device_initialize(&pdev->dev);
arch_setup_pdev_archdata(pdev);
return platform_device_add(pdev);
}
int platform_device_add(struct platform_device *pdev)
{
int i, ret;
if (!pdev)
return -EINVAL;
if (!pdev->dev.parent)
pdev->dev.parent = &platform_bus;;//父设备设置为platform_bus
pdev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;//设置挂在platform总线上
switch (pdev->id) {
default:
dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d", pdev->name, pdev->id);
break;
case PLATFORM_DEVID_NONE:
dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s", pdev->name);
break;
case PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO:
/*
* Automatically allocated device ID. We mark it as such so
* that we remember it must be freed, and we append a suffix
* to avoid namespace collision with explicit IDs.
*/
ret = ida_simple_get(&platform_devid_ida, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL);
if (ret < 0)
goto err_out;
pdev->id = ret;
pdev->id_auto = true;
dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d.auto", pdev->name, pdev->id);
break;
}
for (i = 0; i < pdev->num_resources; i++) {
struct resource *p, *r = &pdev->resource[i];
if (r->name == NULL)
r->name = dev_name(&pdev->dev);
p = r->parent;
if (!p) {
if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_MEM)
p = &iomem_resource;
else if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_IO)
p = &ioport_resource;
}
if (p && insert_resource(p, r)) {
dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to claim resource %d\n", i);
ret = -EBUSY;
goto failed;
}
}
pr_debug("Registering platform device '%s'. Parent at %s\n",
dev_name(&pdev->dev), dev_name(pdev->dev.parent));
ret = device_add(&pdev->dev); //向内核中sys/device中注册一个设备
if (ret == 0)
return ret;
failed:
if (pdev->id_auto) {
ida_simple_remove(&platform_devid_ida, pdev->id);
pdev->id = PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO;
}
while (--i >= 0) {
struct resource *r = &pdev->resource[i];
if (r->parent)
release_resource(r);
}
err_out:
return ret;
}2.platform平台总线初始化
初始化过程:
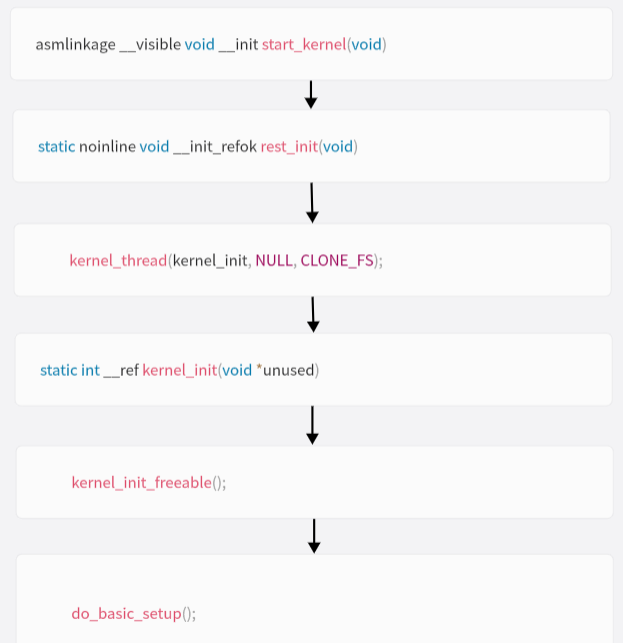
在do_basic_setup中会通过driver_init调用platform_bus_init()函数初始化platform总线:
void __init driver_init(void)
{
/* These are the core pieces */
devtmpfs_init();
devices_init();
buses_init();
classes_init();
firmware_init();
hypervisor_init();
/* These are also core pieces, but must come after the
* core core pieces.
*/
platform_bus_init();
cpu_dev_init();
memory_dev_init();
container_dev_init();
of_core_init();
}
struct device platform_bus = {
.init_name = "platform",
};
struct bus_type platform_bus_type = {
.name = "platform",//设备名称
.dev_groups = platform_dev_groups,//设备属性、含获取sys文件名,该总线会放在/sys/bus下
.match = platform_match,//匹配设备和驱动,匹配成功就调用driver的.probe函数
.uevent = platform_uevent,//消息传递,比如热插拔操作
.pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops,
};
int __init platform_bus_init(void)
{
int error;
early_platform_cleanup();
error = device_register(&platform_bus);
if (error)
return error;
error = bus_register(&platform_bus_type);
if (error)
device_unregister(&platform_bus);
of_platform_register_reconfig_notifier();
return error;
}
int device_register(struct device *dev)
{
device_initialize(dev);
return device_add(dev);
}
void device_initialize(struct device *dev)
{
//所有的dev都有公共的device_set,在系统初始化的时候动态分配
dev->kobj.kset = devices_kset;
kobject_init(&dev->kobj, &device_ktype); //初始化kobject
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->dma_pools);//初始化链表
mutex_init(&dev->mutex); //初始化锁
lockdep_set_novalidate_class(&dev->mutex);
spin_lock_init(&dev->devres_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->devres_head); //将此dev加入链表中
device_pm_init(dev); //电源管理的初始化
set_dev_node(dev, -1);
#ifdef CONFIG_GENERIC_MSI_IRQ
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->msi_list);
#endif
}通过函数device_add()把已经初始化完成的设备添加到相对应的总线下:
int device_add(struct device *dev)
{
struct device *parent = NULL;
struct kobject *kobj;
struct class_interface *class_intf;
int error = -EINVAL;
dev = get_device(dev); //增加设备的引用计数dev->kobj->kref
if (!dev)
goto done;
if (!dev->p) {
//私有数据没有的话,申请并初始化:是连接bus,parent,对应驱动等重要连接点
error = device_private_init(dev);
if (error)
goto done;
}
/*
* for statically allocated devices, which should all be converted
* some day, we need to initialize the name. We prevent reading back
* the name, and force the use of dev_name()
*/
if (dev->init_name) {
//用dev的init_name初始化dev->kobject->name,实际是目录名
dev_set_name(dev, "%s", dev->init_name);
dev->init_name = NULL;
}
/* subsystems can specify simple device enumeration */
//dev的init_name不存在且dev->kobject->name也不存在,则用bus的dev_name和dev_id来设置目录名
if (!dev_name(dev) && dev->bus && dev->bus->dev_name)
dev_set_name(dev, "%s%u", dev->bus->dev_name, dev->id);
if (!dev_name(dev)) { //如果上面几个步骤都还没找到可设的目录名,则失败返回,设备必须要放在某个目录下
error = -EINVAL;
goto name_error;
}
pr_debug("device: '%s': %s\n", dev_name(dev), __func__);
parent = get_device(dev->parent); //父节点引用计数加1
kobj = get_device_parent(dev, parent); //拿到父节点
//拿到父节点赋值给本dev->kobj.parent,确定设备父子关系,也确定了sysfs中的目录关系
if (kobj)
dev->kobj.parent = kobj;
/* use parent numa_node */
//设置该设备节点为-1
if (parent)
set_dev_node(dev, dev_to_node(parent));
/* first, register with generic layer. */
/* we require the name to be set before, and pass NULL */
//把内嵌的kobject注册到设备模型中,将设备加入到kobject模型中,创建sys项目目录,目录名字为kobj->name
error = kobject_add(&dev->kobj, dev->kobj.parent, NULL);
if (error)
goto Error;
/* notify platform of device entry */
if (platform_notify)
platform_notify(dev);
/*创建sys目录下设备的uevent属性文件,通过它可以查看设备的uevent事件,主要是在/sys/devices/.../中添加dev的uevent属性文件*/
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
if (error)
goto attrError;
/*实际创建的kobject都是在device下面,其他class,bus之类的里面的具体设备都是device目录下设备的符号链接,这里是在class下创建符号链接 */
error = device_add_class_symlinks(dev);
if (error)
goto SymlinkError;
error = device_add_attrs(dev);//创建sys目录下设备其他属性文件(添加设备属性文件)
if (error)
goto AttrsError;
error = bus_add_device(dev);//添加设备的总线属性,将设备加入到管理它的bus总线的设备连表上,创建subsystem链接文件,链接class下的具体的子系统文件夹 将设备添加到其总线的设备列表中。
if (error)
goto BusError;
error = dpm_sysfs_add(dev);//把设备增加到sysfs电源管理power目录(组)下,如果该设备设置电源管理相关的内容
if (error)
goto DPMError;
device_pm_add(dev);//设备添加到电源管理相关的设备列表中
//主设备号存在,则产生dev属性,在/dev目录下产生设备节点文件
if (MAJOR(dev->devt)) {
/*创建sys目录下设备的设备号属性,即major和minor /主要是在sys/devices/...中添加dev属性文件*/
error = device_create_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
if (error)
goto DevAttrError;
/*在/sys/dev/char/或者/sys/dev/block/创建devt的属性的连接文件,形如10:45,由主设备号和次设备号构成,指向/sys/devices/.../的具体设备目录*/
error = device_create_sys_dev_entry(dev);//该链接文件只具备读属性,显示主设备号:次设备号,如10:45,用户空间udev响应uevent事件时,将根据设备号在/dev下创建节点文件
if (error)
goto SysEntryError;
devtmpfs_create_node(dev);
}
/* Notify clients of device addition. This call must come
* after dpm_sysfs_add() and before kobject_uevent().
*/
if (dev->bus)//通知客户端,有新设备加入
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&dev->bus->p->bus_notifier,
BUS_NOTIFY_ADD_DEVICE, dev);
/*产生一个内核uevent事件(这里是有设备加入),可以是helper,也可是通过netlink机制和用户空间通信该事件可以被内核以及应用层捕获,属于linux设备模型中热插拔机制*/
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
//给设备探测寻找相对应的驱动,在bus上找dev对应的drv,主要执行__device_attach,主要进行match,sys_add,执行probe函数和绑定等操作
bus_probe_device(dev);
if (parent)
klist_add_tail(&dev->p->knode_parent,//添加新设备到父设备的子列表中
&parent->p->klist_children);
if (dev->class) {//如果改dev有所属类,则将dev的添加到类的设备列表里面
mutex_lock(&dev->class->p->mutex);//要使用class的互斥锁
/* tie the class to the device */
klist_add_tail(&dev->knode_class,//dev添加到class的klist_device链表(对driver也有klist_driver链表)
&dev->class->p->klist_devices);
/* notify any interfaces that the device is here */
/*通知有新设备加入,执行该dev的class_intf->add_dev(),好处是只有设备匹配注册成功了,才进行其它的注册工作(如字符设备的注册,生成/dev/***节点文件)以及部分初始化工作。*/
list_for_each_entry(class_intf,
&dev->class->p->interfaces, node)
if (class_intf->add_dev)
class_intf->add_dev(dev, class_intf);
mutex_unlock(&dev->class->p->mutex);
}
done:
put_device(dev);
return error;
SysEntryError:
if (MAJOR(dev->devt))
device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_dev);
DevAttrError:
device_pm_remove(dev);
dpm_sysfs_remove(dev);
DPMError:
bus_remove_device(dev);
BusError:
device_remove_attrs(dev);
AttrsError:
device_remove_class_symlinks(dev);
SymlinkError:
device_remove_file(dev, &dev_attr_uevent);
attrError:
kobject_uevent(&dev->kobj, KOBJ_REMOVE);
kobject_del(&dev->kobj);
Error:
cleanup_device_parent(dev);
put_device(parent);
name_error:
kfree(dev->p);
dev->p = NULL;
goto done;
}会通过bus_probe_device函数为设备探测驱动:
void bus_probe_device(struct device *dev)
{
struct bus_type *bus = dev->bus;
struct subsys_interface *sif;
if (!bus) //确定总线存在
return;
/*drivers_autoprobe是一个bit变量,为l则允许本条总线上的device注册时自动匹配driver,drivers_autoprobe默认总是为1,除非用户空间修改*/
if (bus->p->drivers_autoprobe)
device_initial_probe(dev);//匹配设备和驱动
mutex_lock(&bus->p->mutex);
list_for_each_entry(sif, &bus->p->interfaces, node)
if (sif->add_dev)
sif->add_dev(dev, sif);
mutex_unlock(&bus->p->mutex);
}
void device_initial_probe(struct device *dev)
{
__device_attach(dev, true);
}
static int __device_attach(struct device *dev, bool allow_async)
{
int ret = 0;
device_lock(dev);
if (dev->driver) {//driver已经放在device了(初始化device,时,手动添加的driver)
if (klist_node_attached(&dev->p->knode_driver)) {
ret = 1;
goto out_unlock;
}
ret = device_bind_driver(dev);//driver放在device里了,但还没真正的绑定 ,则执行这个函数绑定
if (ret == 0)
ret = 1;
else {
dev->driver = NULL;
ret = 0;
}
} else {//刚注册的device,没有添加对应的driver,需要查找匹配对应的驱动
struct device_attach_data data = {
.dev = dev,
.check_async = allow_async,
.want_async = false,
};
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);
//遍历总线上的driver链表,一个一个进行匹配
ret = bus_for_each_drv(dev->bus, NULL, &data,
__device_attach_driver);
if (!ret && allow_async && data.have_async) {
/*
* If we could not find appropriate driver
* synchronously and we are allowed to do
* async probes and there are drivers that
* want to probe asynchronously, we'll
* try them.
*/
dev_dbg(dev, "scheduling asynchronous probe\n");
get_device(dev);
async_schedule(__device_attach_async_helper, dev);
} else {
pm_request_idle(dev);
}
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_put(dev->parent);
}
out_unlock:
device_unlock(dev);
return ret;
}如果设备是第一次添加进来的话,会通过bus_for_each_drv函数来调用__device_attach_driver函数进行驱动的探测:
static int __device_attach_driver(struct device_driver *drv, void *_data)
{
struct device_attach_data *data = _data;
struct device *dev = data->dev;
bool async_allowed;
/*
* Check if device has already been claimed. This may
* happen with driver loading, device discovery/registration,
* and deferred probe processing happens all at once with
* multiple threads.
*/
if (dev->driver)
return -EBUSY;
if (!driver_match_device(drv, dev))
return 0;
async_allowed = driver_allows_async_probing(drv);
if (async_allowed)
data->have_async = true;
if (data->check_async && async_allowed != data->want_async)
return 0;
return driver_probe_device(drv, dev);
}
static inline int driver_match_device(struct device_driver *drv,
struct device *dev)
{
//调用总线下的match函数
return drv->bus->match ? drv->bus->match(dev, drv) : 1;
}然后通过调用bus总线下的match函数进行设备与驱动的匹配。
int driver_probe_device(struct device_driver *drv, struct device *dev)
{
int ret = 0;
if (!device_is_registered(dev))
return -ENODEV;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: matched device %s with driver %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_get_sync(dev->parent);
pm_runtime_barrier(dev);
ret = really_probe(dev, drv);//真正的probe函数
pm_request_idle(dev);
if (dev->parent)
pm_runtime_put(dev->parent);
return ret;
}当设备与驱动匹配完成后,在really_probe函数中执行我们在驱动中定义的probe函数:
static int really_probe(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
int ret = 0;
int local_trigger_count = atomic_read(&deferred_trigger_count);
atomic_inc(&probe_count);
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: probing driver %s with device %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, drv->name, dev_name(dev));
WARN_ON(!list_empty(&dev->devres_head));
dev->driver = drv;//匹配好后的驱动信息记录到设备内部
/* If using pinctrl, bind pins now before probing */
ret = pinctrl_bind_pins(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
if (driver_sysfs_add(dev)) {//driver加入sysfs(其实就是创建各种符号链接,前面device默认绑定有driver那里已经分析过了)
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: driver_sysfs_add(%s) failed\n",
__func__, dev_name(dev));
goto probe_failed;
}
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->activate) {
ret = dev->pm_domain->activate(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
/*
* Ensure devices are listed in devices_kset in correct order
* It's important to move Dev to the end of devices_kset before
* calling .probe, because it could be recursive and parent Dev
* should always go first
*/
devices_kset_move_last(dev);
if (dev->bus->probe) {//如果设备上定义probe函数则调用
ret = dev->bus->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
} else if (drv->probe) {//否则调用驱动上的probe函数
ret = drv->probe(dev);
if (ret)
goto probe_failed;
}
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->sync)
dev->pm_domain->sync(dev);
driver_bound(dev);//将设备加入到驱动支持的设备链表中,一个设备需要一个驱动,一个驱动支持多个设备,前面device默认绑定driver那里已经分析过了
ret = 1;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': %s: bound device %s to driver %s\n",
drv->bus->name, __func__, dev_name(dev), drv->name);
goto done;
probe_failed:
devres_release_all(dev);
driver_sysfs_remove(dev);
dev->driver = NULL;
dev_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
if (dev->pm_domain && dev->pm_domain->dismiss)
dev->pm_domain->dismiss(dev);
switch (ret) {
case -EPROBE_DEFER:
/* Driver requested deferred probing */
dev_dbg(dev, "Driver %s requests probe deferral\n", drv->name);
driver_deferred_probe_add(dev);
/* Did a trigger occur while probing? Need to re-trigger if yes */
if (local_trigger_count != atomic_read(&deferred_trigger_count))
driver_deferred_probe_trigger();
break;
case -ENODEV:
case -ENXIO:
pr_debug("%s: probe of %s rejects match %d\n",
drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
break;
default:
/* driver matched but the probe failed */
printk(KERN_WARNING
"%s: probe of %s failed with error %d\n",
drv->name, dev_name(dev), ret);
}
/*
* Ignore errors returned by ->probe so that the next driver can try
* its luck.
*/
ret = 0;
done:
atomic_dec(&probe_count);
wake_up(&probe_waitqueue);
return ret;
}以上是设备与驱动匹配的相关流程。
当完成了platform_bus设备的注册后,platform_bus_init()函数会执行bus_register()函数将platform总线注册到系统中:
/*bus_register:工作就是完成bus_type_private的初始化.创建 注册的这条总线需要的目录文件.
在这条总线目录下创建/device /driver 目录
初始化这条总线上的设备链表:struct klist klist_devices;
初始化这条总线上的驱动链表:struct klist klist_drivers;*/
int bus_register(struct bus_type *bus)
{
int retval;
struct subsys_private *priv;
struct lock_class_key *key = &bus->lock_key;
priv = kzalloc(sizeof(struct subsys_private), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!priv)
return -ENOMEM;
priv->bus = bus;//struct bus_type_private *p;所指向的内容动态分配.
bus->p = priv;//subsys_private
BLOCKING_INIT_NOTIFIER_HEAD(&priv->bus_notifier);
//kobject对应一个目录,这个目录就是我们看到的总线名字/bus/platform
retval = kobject_set_name(&priv->subsys.kobj, "%s", bus->name);
if (retval)
goto out;
//bus_kset = kset_create_and_add("bus", &bus_uevent_ops, NULL);
priv->subsys.kobj.kset = bus_kset;//platform目录在bus下,即/bus/platform:初始化kset的成员kobject,为kset_register()做准备.
priv->subsys.kobj.ktype = &bus_ktype;//static struct kobj_type bus_ktype = { .sysfs_ops = &bus_sysfs_ops, };
priv->drivers_autoprobe = 1;//设置该标志, 当有driver注册时,会自动匹配devices上的设备并用probe初始化,
//当有device注册时,也同样找到driver并会初始化
//int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
//if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) { error = driver_attach(drv); }
retval = kset_register(&priv->subsys);//注册kset,创建目录结构,以及层次关系 生成/bus/platform
if (retval)
goto out;
retval = bus_create_file(bus, &bus_attr_uevent);//platform目录下生成bus_attr_uevent属性文件
if (retval)
goto bus_uevent_fail;
priv->devices_kset = kset_create_and_add("devices", NULL,
&priv->subsys.kobj); //在platform下面创建一个platform/device,是platform这条总线的device的根目录.
if (!priv->devices_kset) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto bus_devices_fail;
}
priv->drivers_kset = kset_create_and_add("drivers", NULL,//在platform下面创建一个platform/driver,是platform这条总线的driver的根目录.
&priv->subsys.kobj);
if (!priv->drivers_kset) {
retval = -ENOMEM;
goto bus_drivers_fail;
}
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&priv->interfaces);
__mutex_init(&priv->mutex, "subsys mutex", key);
//初始化 platform_bus_type->p->klist_devices 就是初始化device的list_head
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, klist_devices_get, klist_devices_put);
klist_init(&priv->klist_drivers, NULL, NULL);//device,driver注册都挂在对应的链表上.
retval = add_probe_files(bus);//创建文件
if (retval)
goto bus_probe_files_fail;
retval = bus_add_groups(bus, bus->bus_groups);
if (retval)
goto bus_groups_fail;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': registered\n", bus->name);
return 0;
bus_groups_fail:
remove_probe_files(bus);
bus_probe_files_fail:
kset_unregister(bus->p->drivers_kset);
bus_drivers_fail:
kset_unregister(bus->p->devices_kset);
bus_devices_fail:
bus_remove_file(bus, &bus_attr_uevent);
bus_uevent_fail:
kset_unregister(&bus->p->subsys);
out:
kfree(bus->p);
bus->p = NULL;
return retval;
}其实就是创建platform目录下的一些目录和属性文件信息。
3. platform驱动框架
当我们定义并初始化好 platform_driver 结构体变量以后,需要在驱动入口函数里面调用platform_driver_register 函数向 Linux 内核注册一个 platform 驱动, platform_driver_register 函数
原型如下所示:
#define platform_driver_register(drv) \
__platform_driver_register(drv, THIS_MODULE)
extern int __platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *,
struct module *);
int __platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv,
struct module *owner)
{
drv->driver.owner = owner;
drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;
if (drv->probe)
drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe;
if (drv->remove)
drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove;
if (drv->shutdown)
drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown;
return driver_register(&drv->driver);
}
int driver_register(struct device_driver *drv)
{
int ret;
struct device_driver *other;
BUG_ON(!drv->bus->p);//driver的总线必须要有自己的subsys,因为这个才是整个bus连接device和driver的核心
/* driver和bus两种都实现了下面函数,而实际最只能执行一个,所以告警说重复 */
if ((drv->bus->probe && drv->probe) ||
(drv->bus->remove && drv->remove) ||
(drv->bus->shutdown && drv->shutdown))
printk(KERN_WARNING "Driver '%s' needs updating - please use "
"bus_type methods\n", drv->name);
/* 查找驱动是否已经装载注册,已经装载的则直接返回 */
other = driver_find(drv->name, drv->bus);
if (other) {
printk(KERN_ERR "Error: Driver '%s' is already registered, "
"aborting...\n", drv->name);
return -EBUSY;
}
/* 把驱动加入总线的驱动链表 */
ret = bus_add_driver(drv);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = driver_add_groups(drv, drv->groups);//把驱动加入驱动的group中
if (ret) {
bus_remove_driver(drv);
return ret;
}
//将事件发送到用户空间
kobject_uevent(&drv->p->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);
return ret;
}
int bus_add_driver(struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct bus_type *bus;
struct driver_private *priv;
int error = 0;
bus = bus_get(drv->bus);//拿到driver所属的总线
if (!bus)
return -EINVAL;
pr_debug("bus: '%s': add driver %s\n", bus->name, drv->name);
/* bus有自己的private,device有自己的private,driver也有,功能就是负责连接对方 */
priv = kzalloc(sizeof(*priv), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!priv) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto out_put_bus;
}
//初始化klist,以及填充driver的private里面的内容
klist_init(&priv->klist_devices, NULL, NULL);
priv->driver = drv;
drv->p = priv;
priv->kobj.kset = bus->p->drivers_kset;//driver绑定bus(通过各自里面的privte)
error = kobject_init_and_add(&priv->kobj, &driver_ktype, NULL,
"%s", drv->name);
if (error)
goto out_unregister;
/*把driver在bus的节点,加入到bus的driver链表的最后一个*/
klist_add_tail(&priv->knode_bus, &bus->p->klist_drivers);
if (drv->bus->p->drivers_autoprobe) {
if (driver_allows_async_probing(drv)) {
pr_debug("bus: '%s': probing driver %s asynchronously\n",
drv->bus->name, drv->name);
async_schedule(driver_attach_async, drv);
} else {
error = driver_attach(drv);//driver匹配device
if (error)
goto out_unregister;
}
}
module_add_driver(drv->owner, drv);
//添加driver的属性
error = driver_create_file(drv, &driver_attr_uevent);
if (error) {
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: uevent attr (%s) failed\n",
__func__, drv->name);
}
error = driver_add_groups(drv, bus->drv_groups);
if (error) {
/* How the hell do we get out of this pickle? Give up */
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: driver_create_groups(%s) failed\n",
__func__, drv->name);
}
if (!drv->suppress_bind_attrs) {
error = add_bind_files(drv);
if (error) {
/* Ditto */
printk(KERN_ERR "%s: add_bind_files(%s) failed\n",
__func__, drv->name);
}
}
return 0;
out_unregister:
kobject_put(&priv->kobj);
kfree(drv->p);
drv->p = NULL;
out_put_bus:
bus_put(bus);
return error;
}
int driver_attach(struct device_driver *drv)
{
return bus_for_each_dev(drv->bus, NULL, drv, __driver_attach);
}可以看到当向系统中注册一个platform驱动时,同样会调用__driver_attach函数进行设备的匹配,匹配完成后会执行probe函数。
还需要在驱动卸载函数中通过 platform_driver_unregister 函数卸载 platform 驱动,platform_driver_unregister 函数原型如下:
void platform_driver_unregister(struct platform_driver *drv)
{
driver_unregister(&drv->driver);
}4.实验
4.1 无设备树的platform设备注册
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
/*
* 寄存器地址定义
*/
#define CCM_CCGR1_BASE (0X020C406C)
#define SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE (0X020E0068)
#define SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE (0X020E02F4)
#define GPIO1_DR_BASE (0X0209C000)
#define GPIO1_GDIR_BASE (0X0209C004)
#define REGISTER_LENGTH 4
/* @description : 释放flatform设备模块的时候此函数会执行
* @param - dev : 要释放的设备
* @return : 无
*/
static void led_release(struct device *dev)
{
printk("led device released!\r\n");
}
/*
* 设备资源信息,也就是LED0所使用的所有寄存器
*/
static struct resource led_resources[] = {
[0] = {
.start = CCM_CCGR1_BASE,
.end = (CCM_CCGR1_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[1] = {
.start = SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE,
.end = (SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[2] = {
.start = SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE,
.end = (SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[3] = {
.start = GPIO1_DR_BASE,
.end = (GPIO1_DR_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
[4] = {
.start = GPIO1_GDIR_BASE,
.end = (GPIO1_GDIR_BASE + REGISTER_LENGTH - 1),
.flags = IORESOURCE_MEM,
},
};
/*
* platform设备结构体
*/
static struct platform_device leddevice = {
.name = "imx6ul-led",
.id = -1,
.dev = {
.release = &led_release,
},
.num_resources = ARRAY_SIZE(led_resources),
.resource = led_resources,
};
/*
* @description : 设备模块加载
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static int __init leddevice_init(void)
{
return platform_device_register(&leddevice);
}
/*
* @description : 设备模块注销
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static void __exit leddevice_exit(void)
{
platform_device_unregister(&leddevice);
}
module_init(leddevice_init);
module_exit(leddevice_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");4.2 无设备树的platform驱动
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#define LEDDEV_CNT 1 /* 设备号长度 */
#define LEDDEV_NAME "platled" /* 设备名字 */
#define LEDOFF 0
#define LEDON 1
/* 寄存器名 */
static void __iomem *IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1;
static void __iomem *SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03;
static void __iomem *SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03;
static void __iomem *GPIO1_DR;
static void __iomem *GPIO1_GDIR;
/* leddev设备结构体 */
struct leddev_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
};
struct leddev_dev leddev; /* led设备 */
/*
* @description : LED打开/关闭
* @param - sta : LEDON(0) 打开LED,LEDOFF(1) 关闭LED
* @return : 无
*/
void led0_switch(u8 sta)
{
u32 val = 0;
if(sta == LEDON){
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val &= ~(1 << 3);
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
}else if(sta == LEDOFF){
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val|= (1 << 3);
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
}
}
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode
* @param - filp : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量
* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &leddev; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - filp : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
int retvalue;
unsigned char databuf[1];
unsigned char ledstat;
retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);
if(retvalue < 0) {
return -EFAULT;
}
ledstat = databuf[0]; /* 获取状态值 */
if(ledstat == LEDON) {
led0_switch(LEDON); /* 打开LED灯 */
}else if(ledstat == LEDOFF) {
led0_switch(LEDOFF); /* 关闭LED灯 */
}
return 0;
}
/* 设备操作函数 */
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.write = led_write,
};
/*
* @description : flatform驱动的probe函数,当驱动与
* 设备匹配以后此函数就会执行
* @param - dev : platform设备
* @return : 0,成功;其他负值,失败
*/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
int i = 0;
int ressize[5];
u32 val = 0;
struct resource *ledsource[5];
printk("led driver and device has matched!\r\n");
/* 1、获取资源 */
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
ledsource[i] = platform_get_resource(dev, IORESOURCE_MEM, i); /* 依次MEM类型资源 */
if (!ledsource[i]) {
dev_err(&dev->dev, "No MEM resource for always on\n");
return -ENXIO;
}
ressize[i] = resource_size(ledsource[i]);
}
/* 2、初始化LED */
/* 寄存器地址映射 */
IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1 = ioremap(ledsource[0]->start, ressize[0]);
SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(ledsource[1]->start, ressize[1]);
SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03 = ioremap(ledsource[2]->start, ressize[2]);
GPIO1_DR = ioremap(ledsource[3]->start, ressize[3]);
GPIO1_GDIR = ioremap(ledsource[4]->start, ressize[4]);
val = readl(IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
val &= ~(3 << 26); /* 清除以前的设置 */
val |= (3 << 26); /* 设置新值 */
writel(val, IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
/* 设置GPIO1_IO03复用功能,将其复用为GPIO1_IO03 */
writel(5, SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
writel(0x10B0, SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
/* 设置GPIO1_IO03为输出功能 */
val = readl(GPIO1_GDIR);
val &= ~(1 << 3); /* 清除以前的设置 */
val |= (1 << 3); /* 设置为输出 */
writel(val, GPIO1_GDIR);
/* 默认关闭LED1 */
val = readl(GPIO1_DR);
val |= (1 << 3) ;
writel(val, GPIO1_DR);
/* 注册字符设备驱动 */
/*1、创建设备号 */
if (leddev.major) { /* 定义了设备号 */
leddev.devid = MKDEV(leddev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
} else { /* 没有定义设备号 */
alloc_chrdev_region(&leddev.devid, 0, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME); /* 申请设备号 */
leddev.major = MAJOR(leddev.devid); /* 获取分配号的主设备号 */
}
/* 2、初始化cdev */
leddev.cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
cdev_init(&leddev.cdev, &led_fops);
/* 3、添加一个cdev */
cdev_add(&leddev.cdev, leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT);
/* 4、创建类 */
leddev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LEDDEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(leddev.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(leddev.class);
}
/* 5、创建设备 */
leddev.device = device_create(leddev.class, NULL, leddev.devid, NULL, LEDDEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(leddev.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(leddev.device);
}
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : platform驱动的remove函数,移除platform驱动的时候此函数会执行
* @param - dev : platform设备
* @return : 0,成功;其他负值,失败
*/
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
iounmap(IMX6U_CCM_CCGR1);
iounmap(SW_MUX_GPIO1_IO03);
iounmap(SW_PAD_GPIO1_IO03);
iounmap(GPIO1_DR);
iounmap(GPIO1_GDIR);
cdev_del(&leddev.cdev);/* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(leddev.class, leddev.devid);
class_destroy(leddev.class);
return 0;
}
/* platform驱动结构体 */
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led", /* 驱动名字,用于和设备匹配 */
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
/*
* @description : 驱动模块加载函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static int __init leddriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&led_driver);
}
/*
* @description : 驱动模块卸载函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static void __exit leddriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);
}
module_init(leddriver_init);
module_exit(leddriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");4.3 有设备树的platform驱动
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/ide.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/gpio.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/of_gpio.h>
#include <linux/semaphore.h>
#include <linux/timer.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/fcntl.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <asm/mach/map.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#define LEDDEV_CNT 1 /* 设备号长度 */
#define LEDDEV_NAME "dtsplatled" /* 设备名字 */
#define LEDOFF 0
#define LEDON 1
/* leddev设备结构体 */
struct leddev_dev{
dev_t devid; /* 设备号 */
struct cdev cdev; /* cdev */
struct class *class; /* 类 */
struct device *device; /* 设备 */
int major; /* 主设备号 */
struct device_node *node; /* LED设备节点 */
int led0; /* LED灯GPIO标号 */
};
struct leddev_dev leddev; /* led设备 */
/*
* @description : LED打开/关闭
* @param - sta : LEDON(0) 打开LED,LEDOFF(1) 关闭LED
* @return : 无
*/
void led0_switch(u8 sta)
{
if (sta == LEDON )
gpio_set_value(leddev.led0, 0);
else if (sta == LEDOFF)
gpio_set_value(leddev.led0, 1);
}
/*
* @description : 打开设备
* @param - inode : 传递给驱动的inode
* @param - filp : 设备文件,file结构体有个叫做private_data的成员变量
* 一般在open的时候将private_data指向设备结构体。
* @return : 0 成功;其他 失败
*/
static int led_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
filp->private_data = &leddev; /* 设置私有数据 */
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : 向设备写数据
* @param - filp : 设备文件,表示打开的文件描述符
* @param - buf : 要写给设备写入的数据
* @param - cnt : 要写入的数据长度
* @param - offt : 相对于文件首地址的偏移
* @return : 写入的字节数,如果为负值,表示写入失败
*/
static ssize_t led_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t cnt, loff_t *offt)
{
int retvalue;
unsigned char databuf[2];
unsigned char ledstat;
retvalue = copy_from_user(databuf, buf, cnt);
if(retvalue < 0) {
printk("kernel write failed!\r\n");
return -EFAULT;
}
ledstat = databuf[0];
if (ledstat == LEDON) {
led0_switch(LEDON);
} else if (ledstat == LEDOFF) {
led0_switch(LEDOFF);
}
return 0;
}
/* 设备操作函数 */
static struct file_operations led_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = led_open,
.write = led_write,
};
/*
* @description : flatform驱动的probe函数,当驱动与
* 设备匹配以后此函数就会执行
* @param - dev : platform设备
* @return : 0,成功;其他负值,失败
*/
static int led_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
{
printk("led driver and device was matched!\r\n");
/* 1、设置设备号 */
if (leddev.major) {
leddev.devid = MKDEV(leddev.major, 0);
register_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
} else {
alloc_chrdev_region(&leddev.devid, 0, LEDDEV_CNT, LEDDEV_NAME);
leddev.major = MAJOR(leddev.devid);
}
/* 2、注册设备 */
cdev_init(&leddev.cdev, &led_fops);
cdev_add(&leddev.cdev, leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT);
/* 3、创建类 */
leddev.class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, LEDDEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(leddev.class)) {
return PTR_ERR(leddev.class);
}
/* 4、创建设备 */
leddev.device = device_create(leddev.class, NULL, leddev.devid, NULL, LEDDEV_NAME);
if (IS_ERR(leddev.device)) {
return PTR_ERR(leddev.device);
}
/* 5、初始化IO */
leddev.node = of_find_node_by_path("/gpioled");
if (leddev.node == NULL){
printk("gpioled node nost find!\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
leddev.led0 = of_get_named_gpio(leddev.node, "led-gpio", 0);
if (leddev.led0 < 0) {
printk("can't get led-gpio\r\n");
return -EINVAL;
}
gpio_request(leddev.led0, "led0");
gpio_direction_output(leddev.led0, 1); /* led0 IO设置为输出,默认高电平 */
return 0;
}
/*
* @description : platform驱动的remove函数,移除platform驱动的时候此函数会执行
* @param - dev : platform设备
* @return : 0,成功;其他负值,失败
*/
static int led_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
{
gpio_set_value(leddev.led0, 1); /* 卸载驱动的时候关闭LED */
gpio_free(leddev.led0); /* 释放IO */
cdev_del(&leddev.cdev); /* 删除cdev */
unregister_chrdev_region(leddev.devid, LEDDEV_CNT); /* 注销设备号 */
device_destroy(leddev.class, leddev.devid);
class_destroy(leddev.class);
return 0;
}
/* 匹配列表 */
static const struct of_device_id led_of_match[] = {
{ .compatible = "atkalpha-gpioled" },
{ /* Sentinel */ }
};
/* platform驱动结构体 */
static struct platform_driver led_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "imx6ul-led", /* 驱动名字,用于和设备匹配 */
.of_match_table = led_of_match, /* 设备树匹配表 */
},
.probe = led_probe,
.remove = led_remove,
};
/*
* @description : 驱动模块加载函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static int __init leddriver_init(void)
{
return platform_driver_register(&led_driver);
}
/*
* @description : 驱动模块卸载函数
* @param : 无
* @return : 无
*/
static void __exit leddriver_exit(void)
{
platform_driver_unregister(&led_driver);
}
module_init(leddriver_init);
module_exit(leddriver_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");