一、双向链表 (不带头)
无头双向链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表
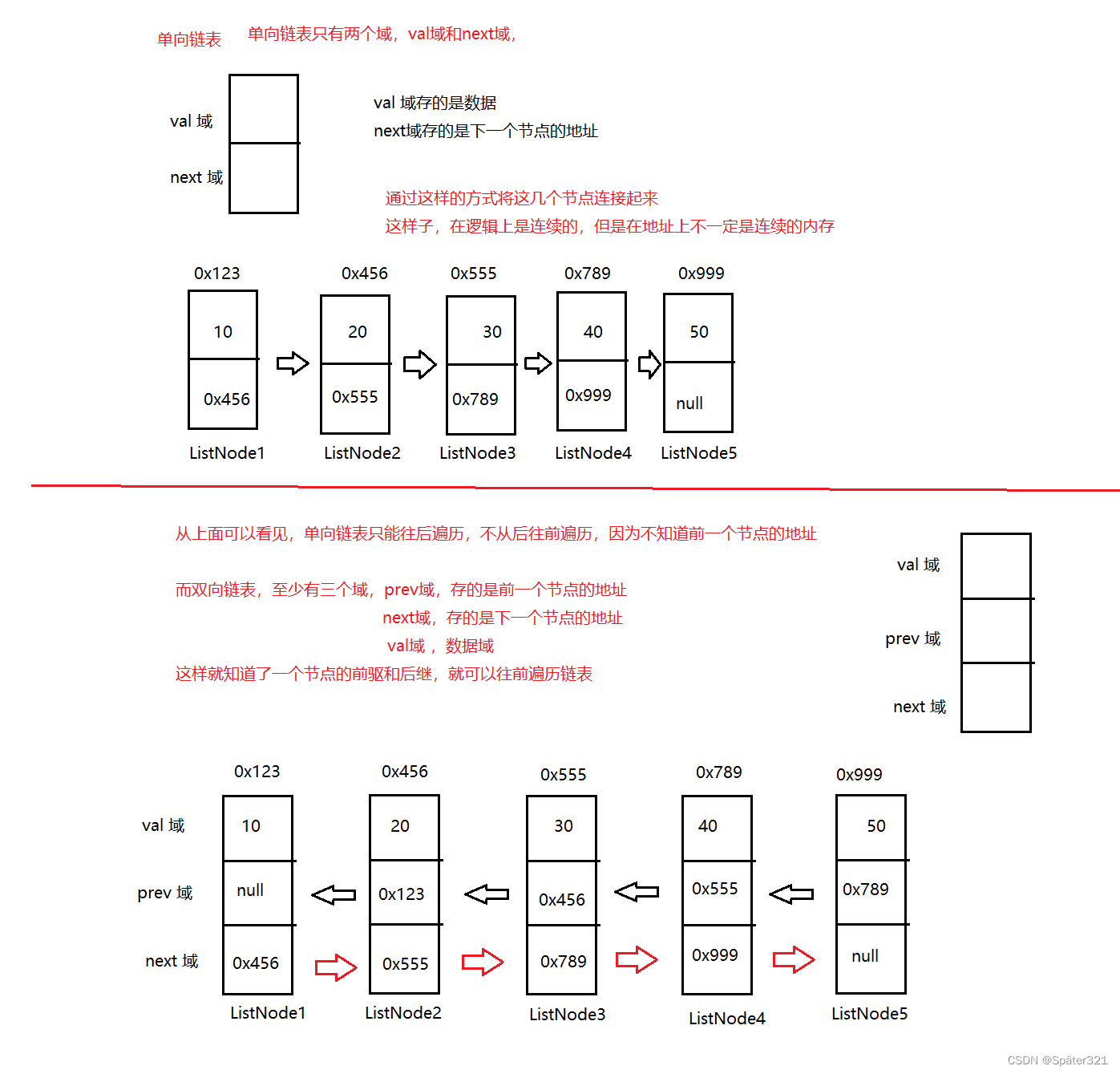
- 双向链表 和 单向链表的区别,就在于 双向 比 单向 多个 一个前驱地址。而且 你会发现 正因为有了前驱地址,所以所以这个链表,它有两种走向,这也是这个链表为什么叫做双向链表的原因之一
首先看看单链表是如何删除节点的
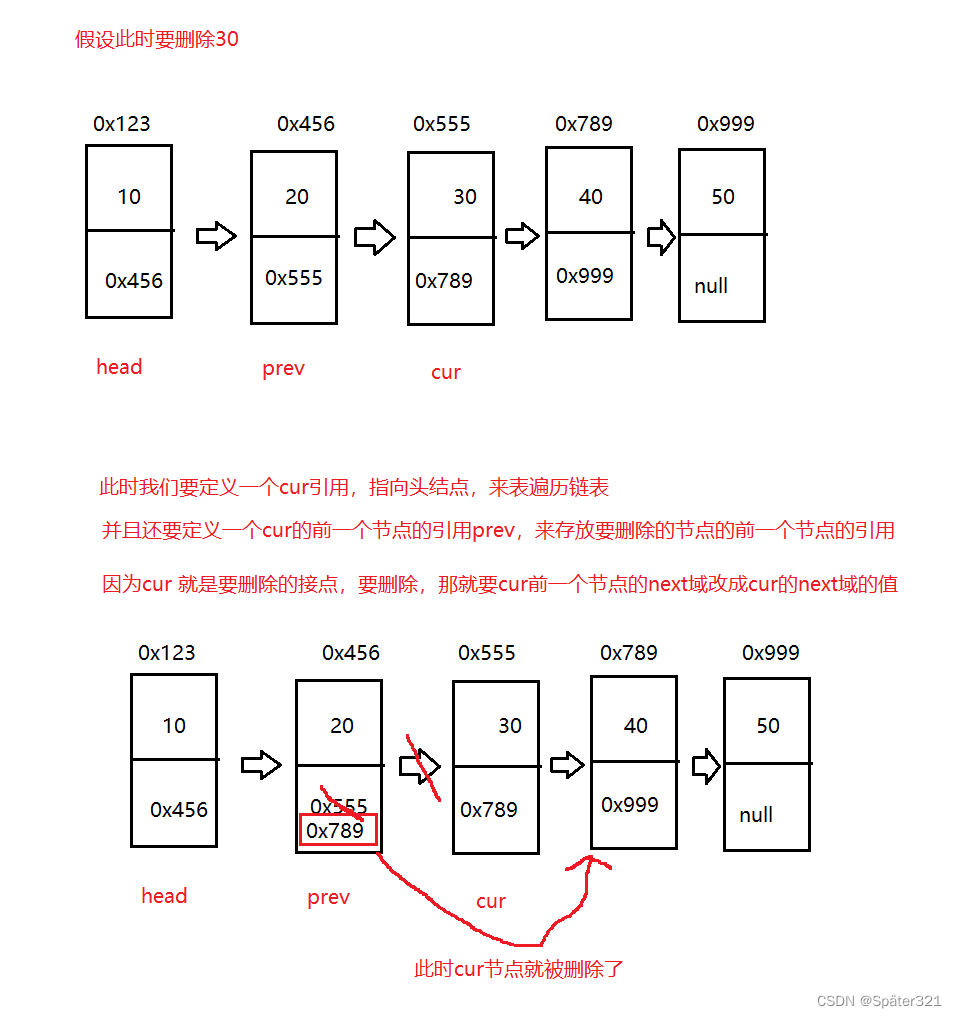
总结:
单向链表在删除一个节点的时候,需要借助前驱节点,才能删除。
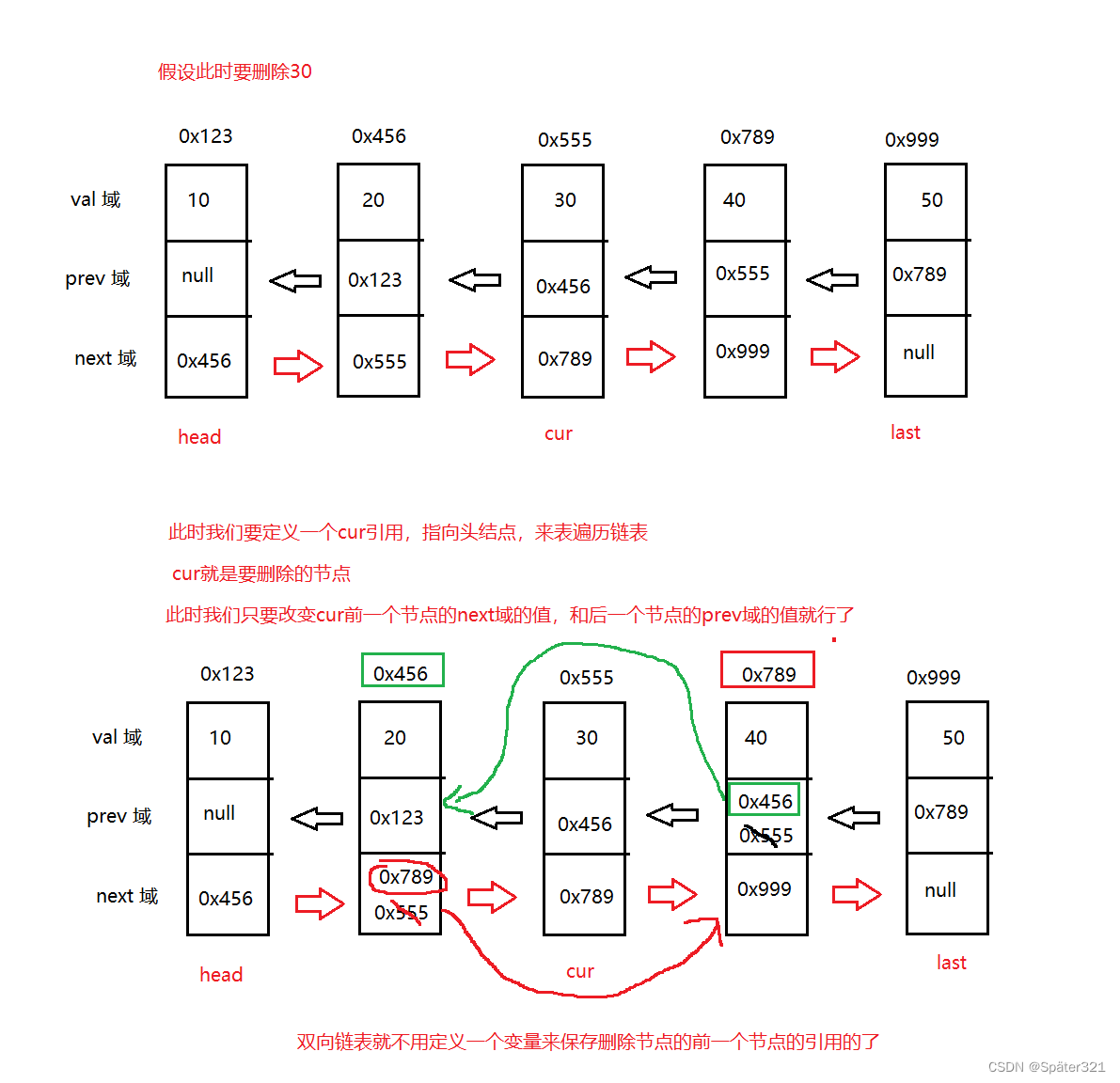
双向链表是如何删除节点的
双向链表删除节点,不需要借助前驱节点
因为双向链表,它存储前驱和后驱的节点的地址,它都知道。
另外双向链表会多一个引用last,这个引用永远指向此时链表的尾巴节点
head就是永远指向双向链表的头节点。
二、模拟实现双向链表
2.1、实现一个类,来表示双向链表的节点
class ListNode{
//存储int类型的数据
public int val;
//存储上一个节点的地址
public ListNode prev;
//存储下一个节点的地址
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
//构造方法
this.val = val;
}
}
2.2、实现一个类,来表示双向链表
public class MyLinkedList {
//指向双向链表的头结点
public ListNode head;
//指向双向链表的尾巴节点
public ListNode last;
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
};
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
};
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public boolean addIndex(int index,int data){
return true;
};
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
return true;
};
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
};
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
};
//得到单链表的长度
public int size(){
return 0;
};
public void display(){
};
public void clear(){
};
}
实现LinkedList中的所有方法
通过这些方法就可以操作链表
打印链表
//打印链表
public void display(){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
};
得到链表的长度
//得到链表的长度
public int size(){
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while(cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
};
查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
//找到返回true,找不到返回false
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
};
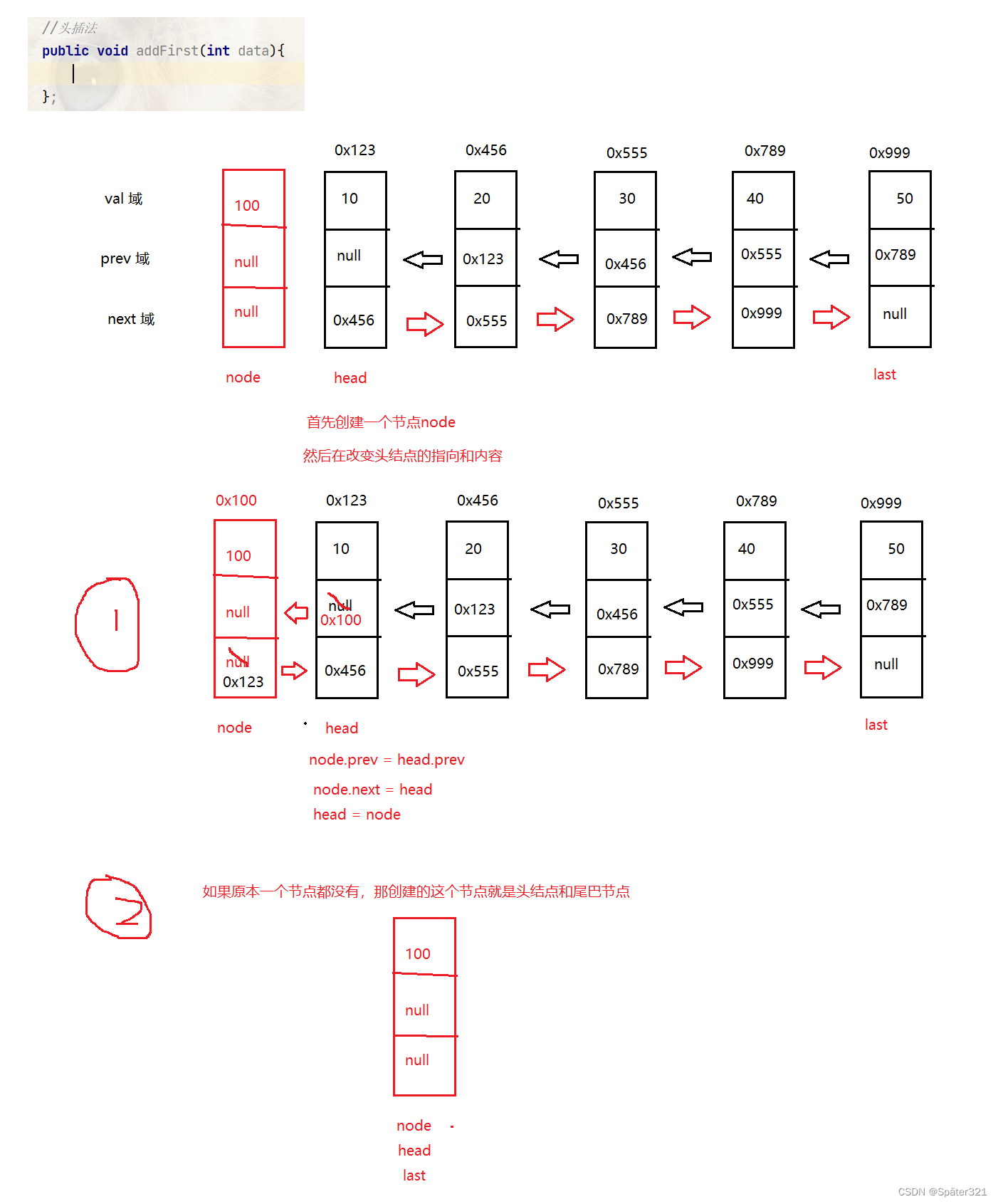
头插法
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
node.prev = this.head.prev;
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
};
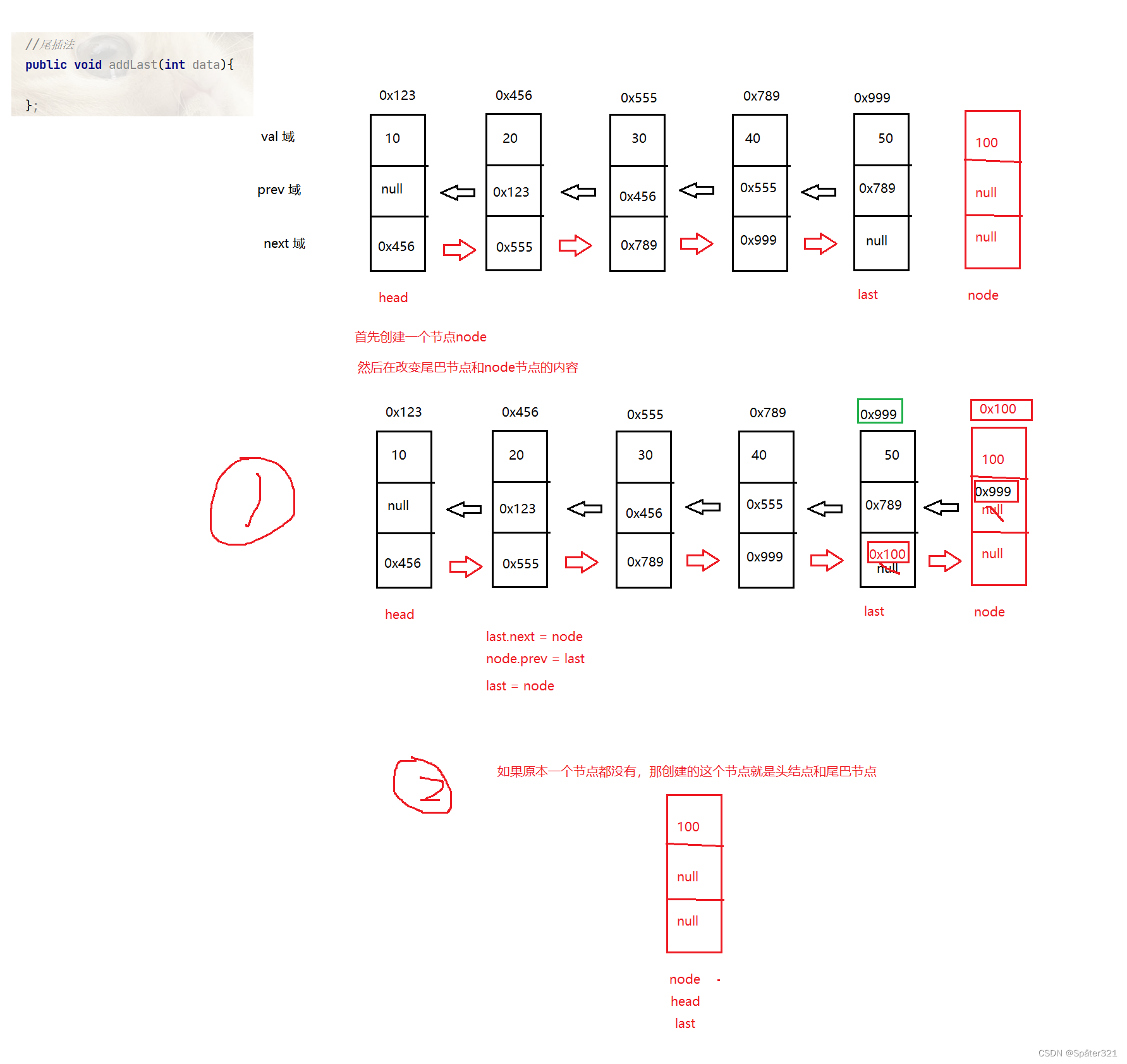
尾插法
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
this.last.next = node;
node.prev = this.last;
last = node;
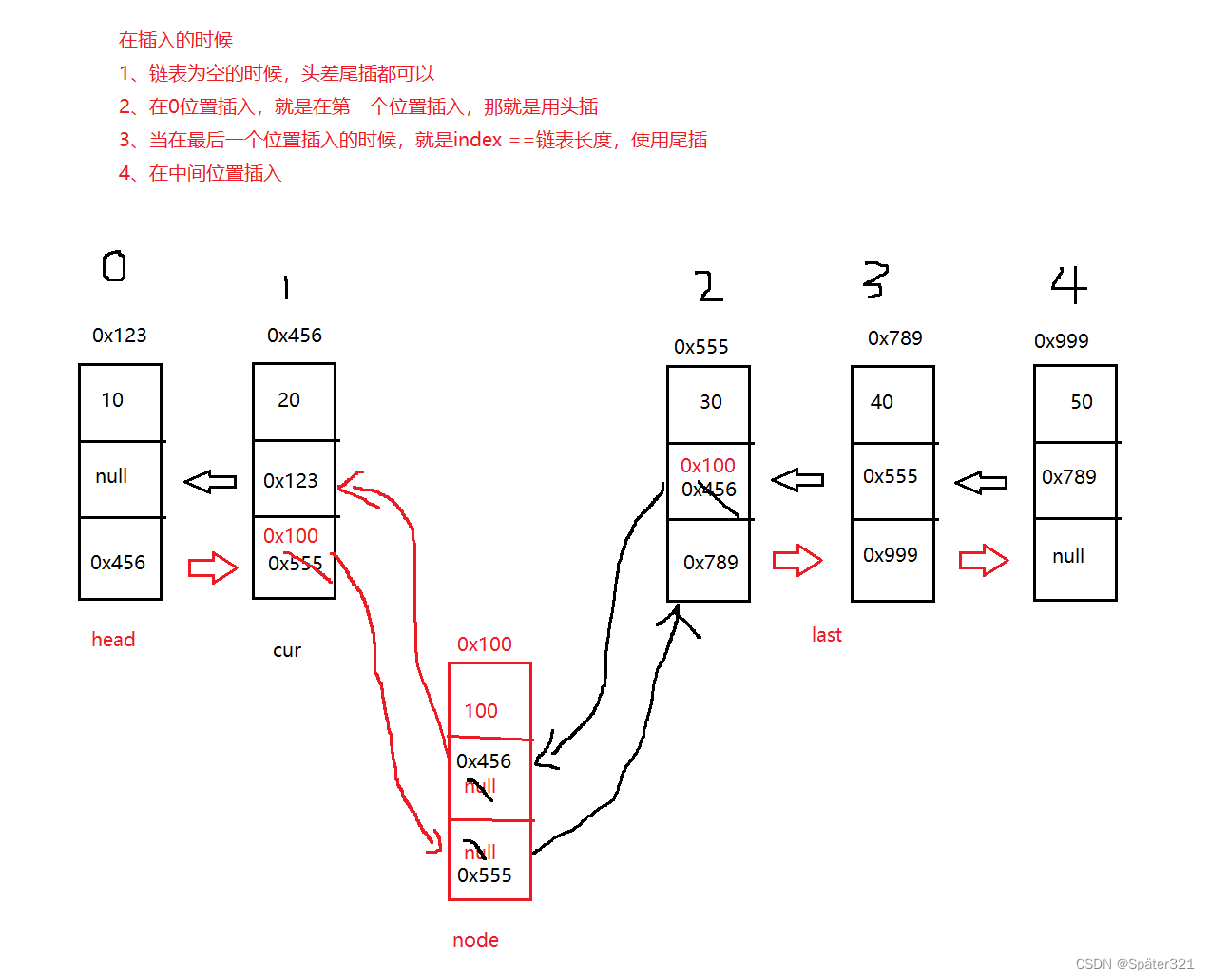
任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//当链表为空的时候
if(this.head == null){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
//当链表不为空的时候,
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(index-1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.prev = cur;
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
node.prev = cur.next.prev;
};
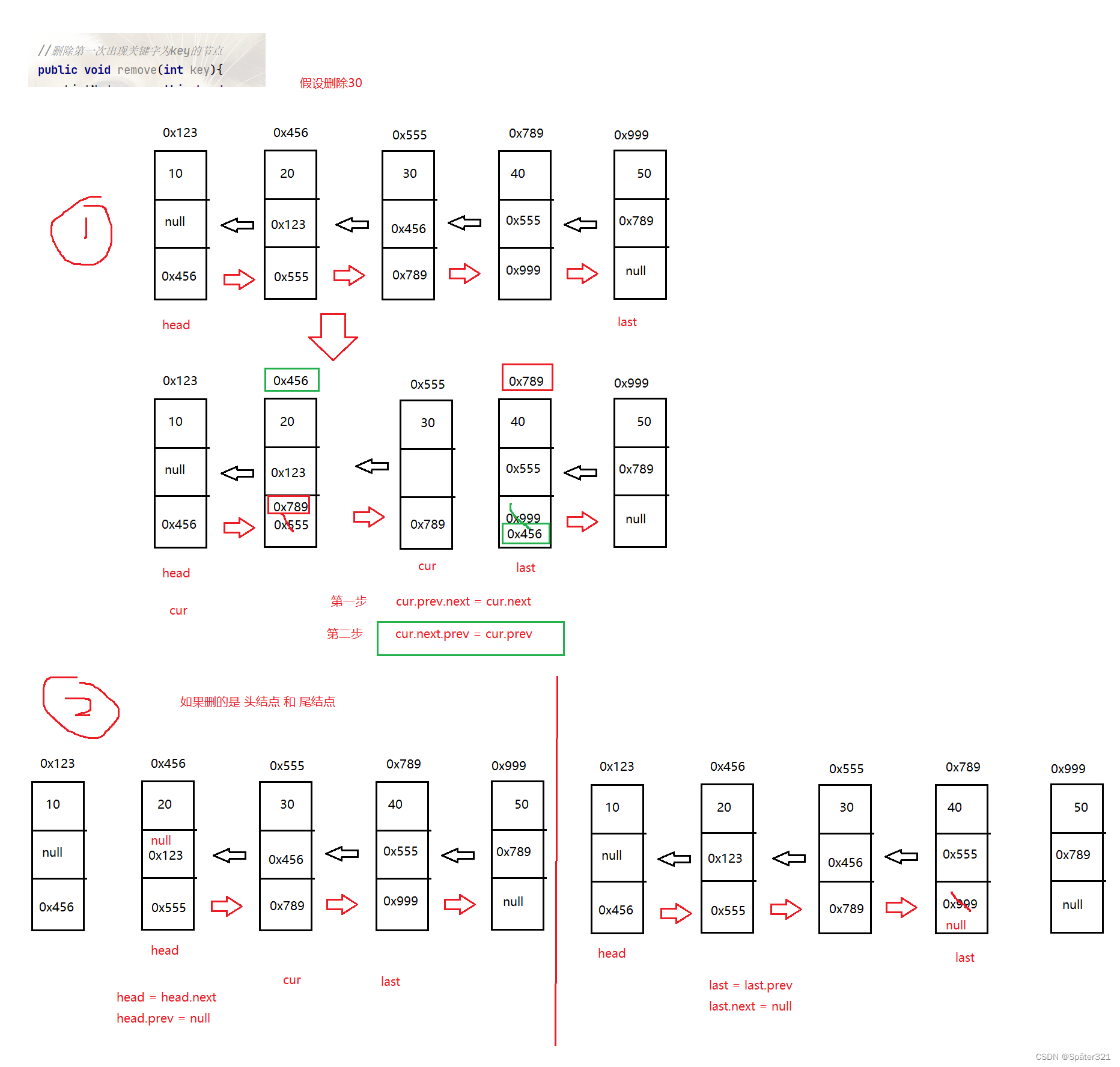
删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//如果删除的是头结点
if(this.head.val == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
this.head.prev = null;
return;
}
//如果删除的是尾巴结点
if(this.last.val == key){
this.last = this.last.prev;
this.last.next = null;
return;
}
//删除的是中间的节点
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
return ;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
};
删除所有值为key的节点
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
if(cur == this.head){
//如果key值是头结点
this.head = this.head.next;
if(head != null){
//不止一个节点
this.head.prev = null;
}else {
//如果只有一个节点,并且也是要删除的节点
this.last = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
//不是头结点
if(cur.next != null){
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
this.last = this.last.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
};
清空链表里面的元素
public void clear(){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
while (this.head != null){
ListNode headNext = this.head.next;
this.head.prev =null;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = headNext;// head 在此过程中,置为null,因为 最后一个元素的next 等null,
}
this.last = null;
};
总结 - 模拟实现双向链表
class ListNode{
//存储int类型的数据
public int val;
//存储上一个节点的地址
public ListNode prev;
//存储下一个节点的地址
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
//构造方法
this.val = val;
}
}
public class MyLinkedList {
//指向双向链表的头结点
public ListNode head;
//指向双向链表的尾巴节点
public ListNode last;
//得到链表的长度
public int size(){
ListNode cur = this.head;
int count = 0;
while(cur != null){
count++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return count;
};
//打印链表
public void display(){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
cur = cur.next;
}
System.out.println();
};
//头插法
public void addFirst(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
}else {
node.prev = this.head.prev;
node.next = head;
this.head = node;
}
};
//尾插法
public void addLast(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
this.last = node;
} else {
this.last.next = node;
node.prev = this.last;
last = node;
}
};
//任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标
public void addIndex(int index,int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
//当链表为空的时候
if(this.head == null){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
//当链表不为空的时候,
if(index == 0){
addFirst(data);
return;
}
if (index == size()){
addLast(data);
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(index-1 != 0){
cur = cur.next;
index--;
}
node.prev = cur;
node.next = cur.next;
cur.next = node;
node.prev = cur.next.prev;
};
//查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中
public boolean contains(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
return true;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return false;
};
//删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点
public void remove(int key){
ListNode cur = this.head;
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
//如果删除的是头结点
if(this.head.val == key){
this.head = this.head.next;
//this.head.prev = null;
return;
}
//如果删除的是尾巴结点
if(this.last.val == key){
this.last = this.last.prev;
this.last.next = null;
return;
}
//删除的是中间的节点
while (cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
return;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
};
//删除所有值为key的节点
public void removeAllKey(int key){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.val == key){
if(cur == this.head){
//如果key值是头结点
this.head = this.head.next;
if(head != null){
//不止一个节点
this.head.prev = null;
}else {
//如果只有一个节点,并且也是要删除的节点
this.last = null;
}
}else {
cur.prev.next = cur.next;
//不是头结点
if(cur.next != null){
cur.next.prev = cur.prev;
}else {
this.last = this.last.prev;
}
}
}
cur = cur.next;
}
};
public void clear(){
if(this.head == null){
System.out.println("链表为空!");
return;
}
while (this.head != null){
ListNode headNext = this.head.next;
this.head.prev =null;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = headNext;// head 在此过程中,置为null,因为 最后一个元素的next 等null,
}
this.last = null;
};
}
三、顺序表和链表的区别和联系
组织数据上:
- 1、顺序表底层是一个数组,他是一个逻辑上和物理上都是连续的
- 2、链表是一个由若干节点组成的一个数据结构,逻辑上是连续的但是在物理上【内存上】是不连续的。
操作数据上:
- 1、顺序表适合,查找相关的操作,因为,可以使用下标,直接获取到某个位置的元素。
- 2、链表适合于,频繁的插入和删除操作。此时不需要像顺序表一样,移动元素。链表的插入只需要修改指向即可。
- 3、顺序表还有不好的地方,就是你需要看满不满,满了要扩容,扩容了之后,不一定都能放完。所以,他的空间上的利用率不高。

![[附源码]计算机毕业设计疫情网课管理系统Springboot程序](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/9cb6ba6bb352464cabb23d4fa07935c1.png)



![[附源码]JAVA毕业设计计算机在线学习管理系统-(系统+LW)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/223f5c8f83854fe4a82a17c636ea7c0a.png)


![[附源码]计算机毕业设计springboot疫苗及注射管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/39fc41efab144f41b166637e732c359e.png)
![[附源码]Python计算机毕业设计Django基于Java的日用品在线电商平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/81b832ed4c684050a51d653368005779.png)