文章目录
- 说明
- Day51 KNN 分类器
- 1.KNN
- 2.代码
- 1.aff内容解读
- 2.代码理解
说明
闵老师的文章链接: 日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
自己也把手敲的代码放在了github上维护:https://github.com/fulisha-ok/sampledata
Day51 KNN 分类器
今天开始学习机器学习,这是自己之前未接触过的,若在理解过程中有问题,欢迎批评指正~
1.KNN
正如物以类聚,人以群居。越是相似的东西就越有可能是一类东西。从这张图片来看,判断Xu属于那种类别,可以取Xu最近的K个邻居(距离),在这个K个点中,那一类东西的概率最高,就把他定位为那个类别。其中计算距离的方式有两种:
欧式距离(多维空间):
d
=
∑
i
=
1
n
(
x
i
−
x
j
)
2
d = \sqrt{{\sum_{i=1}^{n}}(x _{i}-x _{j} ) ^2}
d=i=1∑n(xi−xj)2
曼哈顿距离:
d
=
∣
x
1
−
x
2
∣
+
∣
y
1
−
y
2
∣
d = \mid x1 -x2 \mid + \mid y1 -y2 \mid
d=∣x1−x2∣+∣y1−y2∣
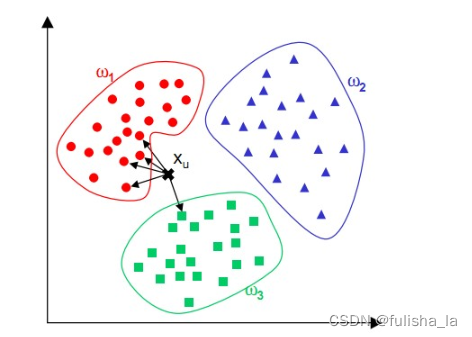
KNN算法最简单粗暴的就是将预测点与所有点距离进行计算,然后保存并排序,选出前面K个值看看哪些类别比较多。(在电商中,可以根据消费者选择的东西去推荐他们可能感兴趣的的商品,还可以在一些网站可以看到相似用户这些。)
2.代码
在写代码前要导入一个jar包。下载jar包的网址:https://mvnrepository.com/
1.aff内容解读
在aff文件中有3种类型的花(山鸢尾(Iris-setosa),变色鸢尾(Iris-versicolor),维吉尼亚鸢尾(Iris-virginica)),每一个花类有50个数据,每条记录有 4 项特征(花萼长度、花萼宽度、花瓣长度、花瓣宽度)
2.代码理解
- 解析文本内容,获取数据集
- 根据获取的数据集划分训练集和测试集,对获取的数据集先打乱数据索引位置再进行分割,以保证在取数时更有说服性trainingSet(代码中是分了120个数据集)和testingSet(30个训练集)
- 对测试集数据进行遍历预测:对每一个测试数据,计算他到所有训练集的距离,取他的k个邻居,这k个邻居是距离这个测试数据最近得k个点(代码中计算距离用的欧式距离)
- 取出测试集的预测结果与数据集中的结果进行比较,判断预测正确率
package machinelearing.knn;
import weka.core.Instance;
import weka.core.Instances;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @author: fulisha
* @date: 2023/5/15 9:43
* @description:
*/
public class KnnClassification {
/**
* Manhattan distance.
*/
public static final int MANHATTAN = 0;
/**
* Euclidean distance(欧几里得距离)
*/
public static final int EUCLIDEAN = 1;
/**
* The distance measure
*/
public int distanceMeasure = EUCLIDEAN;
/**
* a random instance
*/
public static final Random random = new Random();
/**
* The number of neighbors
*/
int numNeighbors = 7;
/**
* The whole dataset
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* The training set. Represented by the indices of the data
*/
int[] trainingSet;
/**
* The testing set. Represented by the indices of the data.
*/
int[] testingSet;
/**
* the predictions
*/
int[] predictions;
/**
* the first constructor
* @param paraFilename The arff filename.
*/
public KnnClassification(String paraFilename) {
try {
FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(fileReader);
// the last attribute is the decision class
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
fileReader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Error occurred while trying to read \'" + paraFilename + "\' in KnnClassification constructor.\r\n" + e);
System.exit(0);
}
}
/**
* get a random indices for data randomization
* @param paraLength the length of the sequence
* @return An array of indices. eg.{4, 3, 1, 5, 0, 2} with length 6
*/
public static int[] getRandomIndices(int paraLength) {
int[] resultIndices = new int[paraLength];
//step1. Initialize
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
resultIndices[i] = i;
}
//step2 Randomly swap
int tempFirst, tempSecond, tempValue;
for (int i = 0; i < paraLength; i++) {
//Generate two random indices
tempFirst = random.nextInt(paraLength);
tempSecond = random.nextInt(paraLength);
//swap
tempValue = resultIndices[tempFirst];
resultIndices[tempFirst] = resultIndices[tempSecond];
resultIndices[tempSecond] = tempValue;
}
return resultIndices;
}
public void splitTrainingTesting(double paraTrainingFraction) {
int tempSize = dataset.numInstances();
int[] tempIndices = getRandomIndices(tempSize);
int tempTrainingSize = (int) (tempSize * paraTrainingFraction);
trainingSet = new int[tempTrainingSize];
testingSet = new int[tempSize - tempTrainingSize];
for (int i = 0; i < tempTrainingSize; i++) {
trainingSet[i] = tempIndices[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < tempSize - tempTrainingSize; i++) {
testingSet[i] = tempIndices[tempTrainingSize + i];
}
}
/**
* Predict for the whole testing set. The results are stored in predictions
*/
public void predict() {
predictions = new int[testingSet.length];
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
predictions[i] = predict(testingSet[i]);
}
}
/**
* Predict for given instance
* @param paraIndex
* @return
*/
public int predict(int paraIndex) {
int[] tempNeighbors = computeNearests(paraIndex);
int resultPrediction = simpleVoting(tempNeighbors);
return resultPrediction;
}
/**
* The distance between two instance
* @param paraI The index of the first instance
* @param paraJ The index of the second instance
* @return The distance
*/
public double distance(int paraI, int paraJ) {
double resultDistance = 0;
double tempDifference;
switch (distanceMeasure) {
case MANHATTAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
if (tempDifference < 0) {
resultDistance -= tempDifference;
}else {
resultDistance += tempDifference;
}
}
break;
case EUCLIDEAN:
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numAttributes() - 1; i++) {
tempDifference = dataset.instance(paraI).value(i) - dataset.instance(paraJ).value(i);
resultDistance += tempDifference*tempDifference;
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Unsupported distance measure: " + distanceMeasure);
}
return resultDistance;
}
/**
* Get the accuracy of the classifier
* @return
*/
public double getAccuracy() {
// A double divides an int gets another double
double tempCorrect = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < predictions.length; i++) {
if (predictions[i] == dataset.instance(testingSet[i]).classValue()) {
tempCorrect++;
}
}
return tempCorrect / testingSet.length;
}
/**
* compute the nearnest k neighbors.select one neighbor in each scan.
* @param paraCurrent
* @return
*/
public int[] computeNearests(int paraCurrent) {
int[] resultNearests = new int[numNeighbors];
boolean[] tempSelected = new boolean[trainingSet.length];
double tempMinimalDistance;
int tempMinimalIndex = 0;
//compute all distance to avoid redundant computation
double[] tempDistances = new double[trainingSet.length];
for (int i = 0; i < trainingSet.length; i ++) {
tempDistances[i] = distance(paraCurrent, trainingSet[i]);
}
// Select the nearest paraK indices.
for (int i = 0; i < numNeighbors; i++) {
tempMinimalDistance = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < trainingSet.length; j++) {
if (tempSelected[j]) {
continue;
}
if (tempDistances[j] < tempMinimalDistance) {
tempMinimalDistance = tempDistances[j];
tempMinimalIndex = j;
}
}
resultNearests[i] = trainingSet[tempMinimalIndex];
tempSelected[tempMinimalIndex] = true;
}
System.out.println("The nearest of " + paraCurrent + " are: " + Arrays.toString(resultNearests));
return resultNearests;
}
/**
* Voting using the instances
* @param paraNeighbors The indices of the neighbors.
* @return The predicted label.
*/
public int simpleVoting(int[] paraNeighbors) {
int[] tempVotes = new int[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < paraNeighbors.length; i++) {
tempVotes[(int) dataset.instance(paraNeighbors[i]).classValue()]++;
}
int tempMaximalVotingIndex = 0;
int tempMaximalVoting = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numClasses(); i++) {
if (tempVotes[i] > tempMaximalVoting) {
tempMaximalVoting = tempVotes[i];
tempMaximalVotingIndex = i;
}
}
return tempMaximalVotingIndex;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
KnnClassification tempClassifier = new KnnClassification("D:/fulisha/iris.arff");
tempClassifier.splitTrainingTesting(0.8);
tempClassifier.predict();
System.out.println("The accuracy of the classifier is: " + tempClassifier.getAccuracy());
}
}
运行结果:
The nearest of 56 are: [51, 91, 127, 86, 70, 138, 63]
The nearest of 11 are: [29, 7, 26, 30, 24, 6, 49]
The nearest of 21 are: [19, 17, 4, 48, 0, 40, 43]
The nearest of 119 are: [72, 68, 146, 113, 123, 101, 142]
The nearest of 12 are: [1, 9, 37, 34, 45, 30, 25]
The nearest of 85 are: [70, 51, 91, 61, 138, 63, 127]
The nearest of 83 are: [101, 142, 149, 123, 127, 72, 138]
The nearest of 103 are: [116, 137, 111, 147, 134, 108, 149]
The nearest of 93 are: [60, 98, 81, 80, 79, 59, 69]
The nearest of 66 are: [84, 55, 96, 61, 95, 88, 94]
The nearest of 104 are: [140, 124, 143, 120, 144, 116, 100]
The nearest of 32 are: [33, 19, 48, 10, 16, 5, 4]
The nearest of 132 are: [111, 140, 116, 147, 115, 137, 145]
The nearest of 90 are: [94, 55, 96, 89, 99, 95, 92]
The nearest of 54 are: [58, 75, 76, 86, 74, 65, 51]
The nearest of 47 are: [42, 6, 29, 45, 30, 9, 37]
The nearest of 136 are: [148, 115, 100, 144, 140, 124, 143]
The nearest of 38 are: [8, 42, 13, 45, 6, 29, 30]
The nearest of 3 are: [29, 30, 45, 42, 8, 9, 37]
The nearest of 129 are: [125, 130, 102, 107, 139, 108, 124]
The nearest of 128 are: [111, 116, 137, 147, 140, 115, 108]
The nearest of 2 are: [6, 45, 42, 29, 1, 35, 9]
The nearest of 133 are: [72, 123, 127, 63, 111, 77, 146]
The nearest of 46 are: [19, 48, 4, 10, 44, 0, 17]
The nearest of 57 are: [98, 60, 81, 80, 59, 79, 69]
The nearest of 126 are: [123, 127, 138, 146, 63, 72, 149]
The nearest of 67 are: [92, 82, 99, 69, 94, 95, 96]
The nearest of 112 are: [139, 140, 120, 145, 124, 116, 147]
The nearest of 78 are: [91, 63, 61, 97, 55, 73, 138]
The nearest of 27 are: [28, 39, 0, 17, 48, 7, 4]
The accuracy of the classifier is: 0.9666666666666667