144.二叉树的前序遍历
方法一:递归
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
let arr = []
const preorder = root =>{
//递归的出口
if(root==null){
return
}
arr.push(root.val)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
}
preorder(root)
return arr
};
方法二:迭代 使用栈
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[]}
优秀是一种习惯 迭代实现
*/
var preorderTraversal = function(root) {
if(!root) return []
let arr = []
let stack = [root]
while(stack.length){
let node = stack.pop()
arr.push(node.val)
node.right&&stack.push(node.right)
node.left&&stack.push(node.left)
}
return arr
};
94.二叉树的中序遍历
方法一:递归
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
//递归
let arr = []
const inorder = root =>{
if(!root) return []
inorder(root.left)
arr.push(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(root)
return arr
};
方法二:迭代
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
//迭代
let arr = []
let stack = []
//也就是 root == null
if(!root) return []
//左节点一直入栈
while(root){
stack.push(root)
root = root.left
}
//开始出栈
while(stack.length){
let node = stack.pop()
arr.push(node.val)
let temp = node.right
//当前的结点出栈之后,检查其右侧结点的情况 依次入栈
while(temp){
stack.push(temp)
temp = temp.left
}
}
return arr
};
145.二叉树的后序遍历
方法一:递归
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
//递归
let arr = []
const postorder = root =>{
//递归出去的条件
if(!root) return
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
arr.push(root.val)
}
postorder(root)
return arr
};
方法二:迭代 使用栈
var postorderTraversal = function(root) {
//先将root的值放入到arr中,然后将root.right left 最终得到的结果与后序遍历的结果正好相反
let arr = []
let stack = [root]
if(!root) return []
while(stack.length){
let node = stack.pop()
arr.push(node.val)
node.left&&stack.push(node.left)
node.right&&stack.push(node.right)
}
return arr.reverse()
};
102.二叉树的层序遍历
方法一:递归
var levelOrder = function(root) {
//递归实现
let arr = []
const level = (root,i) =>{
if(!root) return
level(root.left,i+1)
// arr[i] = arr[i]?arr[i].push(root.val):[root.val]
arr[i]?arr[i].push(root.val):arr[i] = [root.val]
level(root.right,i+1)
}
level(root,0)
return arr
};
方法二:迭代 使用队列
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
层序遍历相当于广度优先遍历 需要借助一个队列
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
//使用队列
let arr = []
let queue = [root]
let i = 0
if(!root) return []
while(queue.length){
//记录当前队列的长度
let len = queue.length
//用来存储当前层结点
let tempArr = []
for(let i=0;i<len;i++){
//出队
let node = queue.shift()
tempArr.push(node.val)
node.left&&queue.push(node.left)
node.right&&queue.push(node.right)
}
arr.push(tempArr)
}
return arr
};
617.合并二叉树
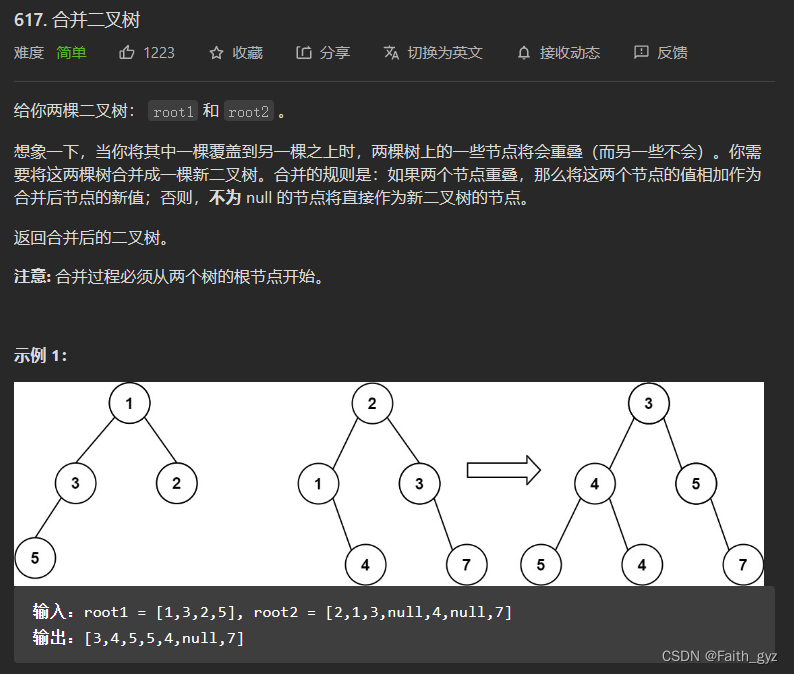
方法一:递归
当看不懂递归的时候,参考二叉树的递归执行过程
var mergeTrees = function(root1, root2) {
//使用递归
const merge = (root1,root2) =>{
//递归跳出的条件
if(root1==null){
return root2
}
if(root2==null){
return root1
}
//创建新的结点
//递归的过程是 ①创建newNode 调用27行的递归 一直到左侧递归的最深层次,返回一个root 返回上一个递归函数(这个递归函数会继续执行28行递归,直到其right结点全都为空) 真的很复杂
let newNode = new TreeNode(root1.val+root2.val)
newNode.left = merge(root1.left,root2.left)
newNode.right = merge(root1.right,root2.right)
return newNode
}
return merge(root1,root2)
};
//这里直接修改root1
var mergeTrees = function(root1, root2) {
//重新去写一遍
const merge = (root1,root2) =>{
//递归的出口
if(root1==null){
return root2
}
if(root2==null){
return root1
}
//这里用的是前序遍历
root1.val += root2.val
root1.left = merge(root1.left,root2.left)
root1.right = merge(root1.right,root2.right)
//返回上一层递归
return root1
}
return merge(root1,root2)
};
方法二:使用队列
var mergeTrees = function(root1, root2) {
//root1 root2进入同一个栈
if(root1==null) return root2
if(root2==null) return root1
let queue = []
queue.push(root1)
queue.push(root2)
while(queue.length){
let node1 = queue.shift()
let node2 = queue.shift()
node1.val += node2.val
if(node1.left!==null&&node2.left!==null){
queue.push(node1.left)
queue.push(node2.left)
}
if(node1.left==null&&node2.left!==null){
node1.left = node2.left
}
if(node1.right&&node2.right){
queue.push(node1.right)
queue.push(node2.right)
}
if(node1.right==null&&node2.right!==null){
node1.right = node2.right
}
}
return root1
};
226.翻转二叉树
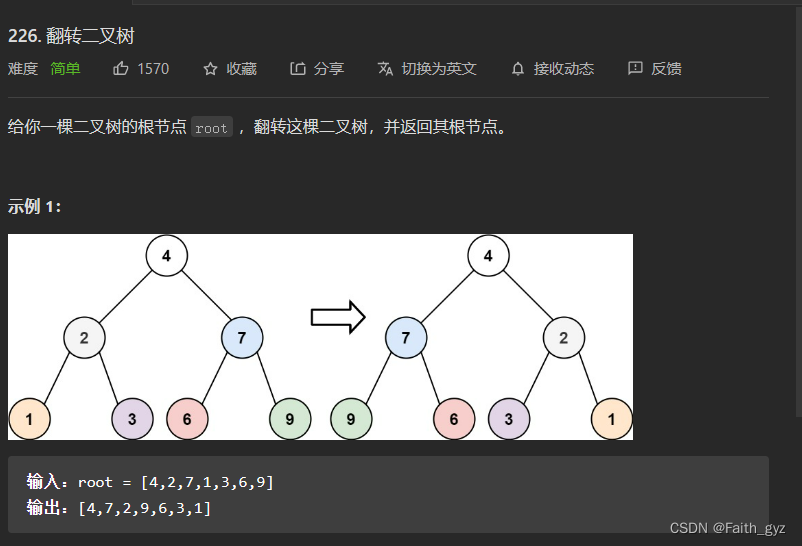
方法一:递归
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
整个树的交换过程中,会把真个node结点下面的所有的结点都会交换过来
*/
var invertTree = function(root) {
//递归实现
if(!root) return root
const invert = root =>{
//递归出去的条件
if(root==null) return null
//递归
let temp = invert(root.left)
root.left = invert(root.right)
root.right = temp
return root
}
return invert(root)
};
方法二:前序遍历过程中实现交换
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
整个树的交换过程中,会把真个node结点下面的所有的结点都会交换过来
*/
var invertTree = function(root) {
//前序遍历的过程中实现翻转
if(root==null) return root
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return root
let stack = [root]
while(stack.length){
//出栈
let node = stack.pop()
//进行交换 如果node.left不存在 那么node.left=null
let temp = node.left
node.left = node.right
node.right = temp
//入栈
node.left&&stack.push(node.left)
node.right&&stack.push(node.right)
}
return root
};
方法三:层序遍历过程中实现交换
var invertTree = function(root) {
//层序遍历过程中实现
if(root==null) return root
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null) return root
let queue = [root]
while(queue.length){
//出队
let node = queue.shift()
//进行交换
let temp = node.left
node.left = node.right
node.right = temp
//入队
node.left&&queue.push(node.left)
node.right&&queue.push(node.right)
}
return root
};
101.对称二叉树
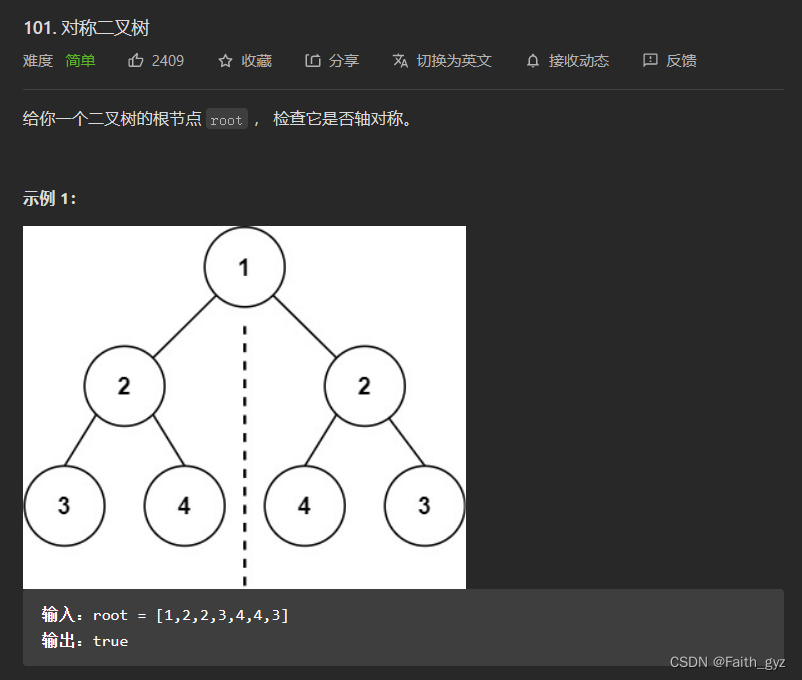
方法一:递归
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
//同时进去两个节点 left and right
const compare = (root1,root2) =>{
if(root1==null&&root2==null){
return true
}else if(root1==null&&root2!==null || root1!==null&&root2==null){
return false
}else if(root1.val!==root2.val){
return false
}
//递归持续下去的条件 左右都得满足
let outside = compare(root1.left,root2.right)
let inside = compare(root1.right,root2.left)
return outside&&inside
}
return compare(root.left,root.right)
};
方法二:使用队列
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
//队列实现
if(root==null){
return true
}else if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return true
}else if(root.left!==null&&root.right==null || root.left==null&&root.right!==null){
return false
}
let queue = []
queue.push(root.left)
queue.push(root.right)
while(queue.length){
let node1 = queue.shift()
let node2 = queue.shift()
if(node1.val!==node2.val){
return false
}
if(node1.left==null&&node2.right!==null || node1.left!==null&&node2.right==null){
return false
}
if(node1.right==null&&node2.left!==null || node1.right!==null&&node2.left==null){
return false
}
node1.left&&queue.push(node1.left)
node2.right&&queue.push(node2.right)
node1.right&&queue.push(node1.right)
node2.left&&queue.push(node2.left)
}
return true
};
//或者
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
//队列实现
if(root==null){
return true
}
//入队 先去入队 出队的时候再去判断是否为空
let queue = []
queue.push(root.left)
queue.push(root.right)
//如果root.left right都是空的话 就不会有下面的while循环 直接跳出去了
while(queue.length){
let leftNode = queue.shift()
let rightNode = queue.shift()
if(leftNode==null&&rightNode==null){
//进入下一层循环
continue
}
if(leftNode==null || rightNode==null || leftNode.val!==rightNode.val){
return false
}
queue.push(leftNode.left)
queue.push(rightNode.right)
queue.push(leftNode.right)
queue.push(rightNode.left)
}
return true
};
方法三:使用栈实现
var isSymmetric = function(root) {
//栈实现
let stack = []
if(root==null){
return true
}
stack.push(root.left)
stack.push(root.right)
while(stack.length){
let leftNode = stack.pop()
let rightNode = stack.pop()
if(leftNode==null&&rightNode==null){
//进入下一层循环
continue
}
if(leftNode==null || rightNode==null || leftNode.val!==rightNode.val){
return false
}
stack.push(leftNode.left)
stack.push(rightNode.right)
stack.push(leftNode.right)
stack.push(rightNode.left)
}
return true
};
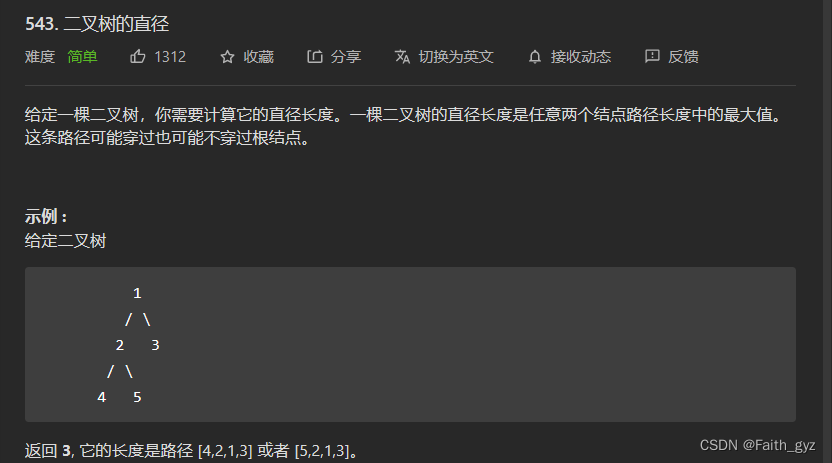
543.二叉树的直径
var diameterOfBinaryTree = function(root) {
//二叉树的直径==根节点左右两侧高度之和的最大值
let res = 0 //用来记录递归过程中遇到的和的最大值
if(!root) return 0
const diameter = root =>{
if(root==null) return 0
let leftHeight = diameter(root.left)
let rightHeight = diameter(root.right)
res = Math.max(res,(leftHeight+rightHeight))
return Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight)+1 //这是返回给上一层递归的结果值
}
diameter(root)
return res
};
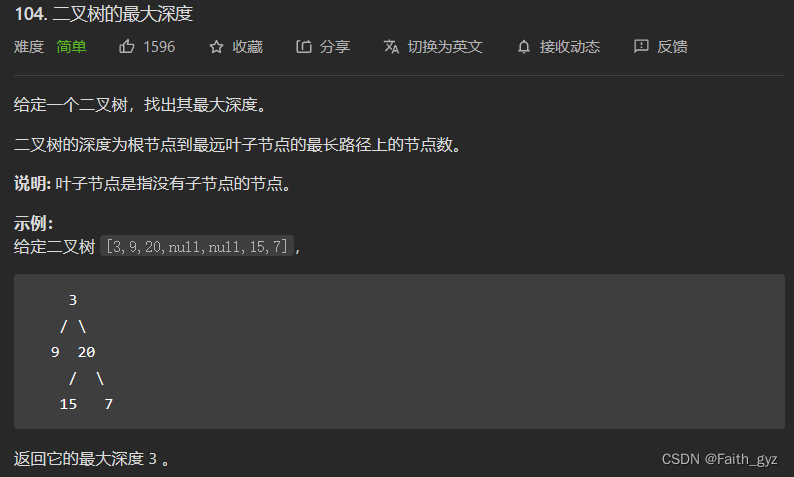
104.二叉树的最大深度
方法一:层序遍历之后,计算res的length
var maxDepth = function(root) {
//方法一:层序遍历之后,将其放入到数组中,然后判断数组的长度
let res = []
if(root==null) return 0
const level = (root,i) =>{
if(root==null){
return
}
//中序遍历的过程中进行压栈处理
level(root.left,i+1)
res[i]?res[i].push(root.val):res[i]=[root.val]
level(root.right,i+1)
}
level(root,0)
return res.length
};
//层序遍历过程中 不进行压栈处理
var maxDepth = function(root) {
//层序遍历的过程中动态记录最大的深度
let max = 0
if(root==null) return 0
const level = (root,i)=>{
if(root==null){
return
}
level(root.left,i+1)
max = Math.max(max,i)
level(root.right,i+1)
}
level(root,0)
return max+1
};
方法二:同二叉树最大直径的求解过程
var maxDepth = function(root) {
//利用二叉树最大直径的处理过程中 类似
const maxit = root =>{
if(root==null) return 0
let leftHeight = maxit(root.left)
let rightHeight = maxit(root.right)
return Math.max(leftHeight,rightHeight) +1
}
return maxit(root)
};
方法三:使用队列
var maxDepth = function(root) {
//使用队列
if(root==null) return 0
let queue = [root]
let arr = []
while(queue.length){
let len = queue.length
let temp = []
for(let i=0;i<len;i++){
let node = queue.shift()
temp.push(node.val)
node.left&&queue.push(node.left)
node.right&&queue.push(node.right)
}
arr.push(temp)
}
return arr.length
};
//优化
var maxDepth = function(root) {
//使用队列
if(root==null) return 0
let queue = [root]
let max = 0
while(queue.length){
let len = queue.length
for(let i=0;i<len;i++){
let node = queue.shift()
node.left&&queue.push(node.left)
node.right&&queue.push(node.right)
}
max++
}
return max
};