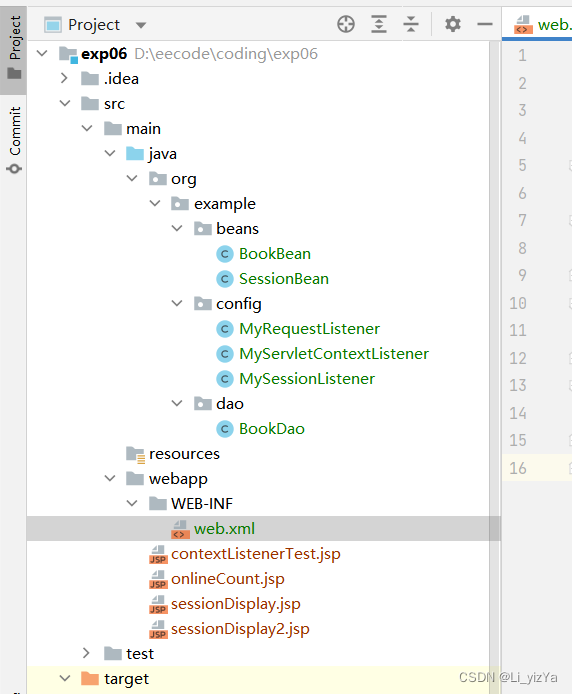
1. 创建一个名为exp06的Web项目,编写、部署、测试一个ServletContext事件监听器。

BookBean代码
package org.example.beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Li_yizYa
* Date: 2023—04—29
* Time: 18:39
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class BookBean implements Serializable {
private String bookId;
private String title;
private String author;
private String publisher;
private double price;
public String getBookId() {
return bookId;
}
public void setBookId(String bookId) {
this.bookId = bookId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getPublisher() {
return publisher;
}
public void setPublisher(String publisher) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
BookDao代码
package org.example.dao;
import org.example.beans.BookBean;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Li_yizYa
* Date: 2023—04—29
* Time: 18:41
*/
public class BookDao {
private static Connection c;
public BookDao() {
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/web_test";
c = DriverManager.getConnection(url, "root", "142516");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public List<BookBean> getBooks() {
try {
String sql = "select * from books";
PreparedStatement ps = c.prepareStatement(sql);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
List<BookBean> books = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {
BookBean b = new BookBean();
b.setBookId(rs.getString("book_id"));
b.setAuthor(rs.getString("author"));
b.setTitle(rs.getString("title"));
b.setPublisher(rs.getString("publisher"));
b.setPrice(rs.getDouble("price"));
books.add(b);
}
return books;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("查询数据库出错", e);
}
}
}
【步骤1】编写监听器类MyServletContextListener.java,Web应用程序启动时创建一个数据源对象,并将其保存在ServletContext作用域中,Web应用销毁时将其清除;在ServletContext对象上添加属性、删除属性和替换属性时,在Tomcat日志中记录有关信息,包括提示信息、属性名和属性值等。
MyServletContextListener.java
package org.example.config;
import javax.servlet.*;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Li_yizYa
* Date: 2023—04—26
* Time: 22:40
*/
public class MyServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener, ServletContextAttributeListener {
private ServletContext context = null;
@Override
public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent servletContextAttributeEvent) {
context = servletContextAttributeEvent.getServletContext();
context.log("添加属性: " + servletContextAttributeEvent.getName()
+ ": " + servletContextAttributeEvent.getValue());
}
@Override
public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent servletContextAttributeEvent) {
context = servletContextAttributeEvent.getServletContext();
context.log("删除属性: " + servletContextAttributeEvent.getName()
+ ": " + servletContextAttributeEvent.getValue());
}
@Override
public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent servletContextAttributeEvent) {
context = servletContextAttributeEvent.getServletContext();
context.log("替换属性: " + servletContextAttributeEvent.getName()
+ ": " + servletContextAttributeEvent.getValue());
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
context = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
context.log("应用程序已启动: " + new Date());
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
context = servletContextEvent.getServletContext();
context.log("应用程序已销毁: " + new Date());
}
}
【步骤2】在web.xml文件中注册监听器类。
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.example.config.MyServletContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>【步骤3】编写监听器测试页面:contextListenerTest.jsp:使用监听器创建的数据源对象连接是一次实验创建的MySQL数据库test,以表格的形式显示其中books数据表的所有内容。
contextListenerTest.jsp
<%@ page import="java.util.*" %>
<%@ page import="org.example.beans.*" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<jsp:useBean id="book" class="org.example.dao.BookDao" scope="session" />
<html>
<head>
<title>contextListenerTest</title>
</head>
<body>
<table width="500" height="256" border="1">
<tr>
<th scope="col">bookid</th>
<th scope="col">title</th>
<th scope="col">author</th>
<th scope="col">publisher</th>
<th scope="col">price</th>
</tr>
<%
List<BookBean> bookList = book.getBooks();
for (BookBean books : bookList) {
String book_id = books.getBookId();
String title = books.getTitle();
String author = books.getAuthor();
String publisher = books.getPublisher();
double price = books.getPrice();
%>
<tr>
<td><%=book_id%> </td>
<td><%=title%></td>
<td><%=author%></td>
<td><%=publisher%></td>
<td><%=price%></td>
</tr>
<% } %>
</table>
</body>
</html>

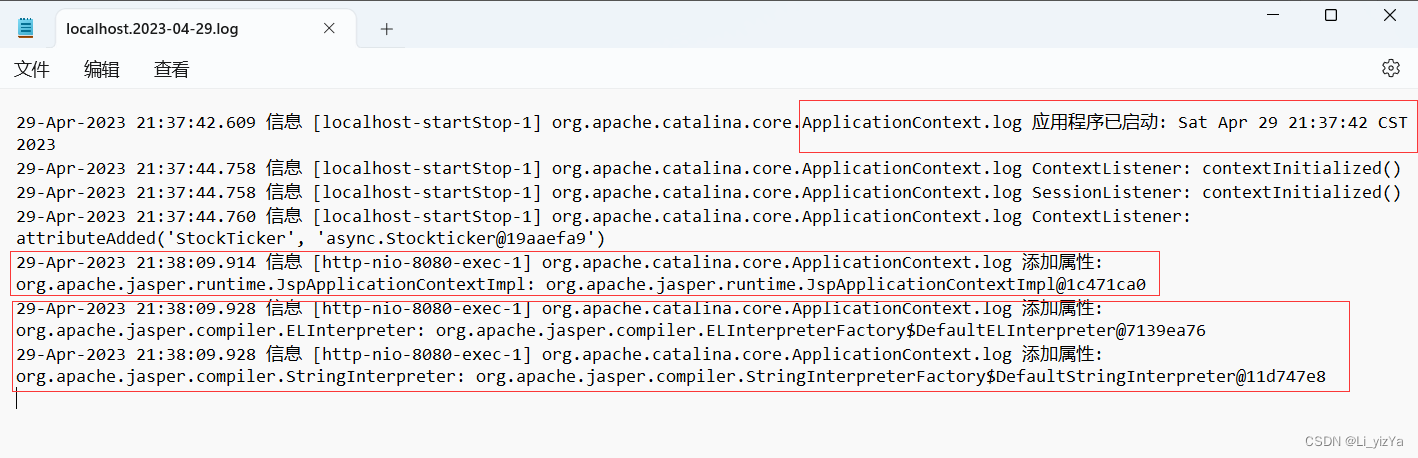
【步骤5】检查日志文件
打开<CATALINA_HOME>\logs目录中的localhost.yyyy-mm-dd.log日志文件,查看执行事件监听器后写到日志文件中的信息。
2. 编写一个HttpSession事件监听器用来记录当前在线人数。
首先创建一个SessionBean类,用来记录sessionID和注册时间
package org.example.beans;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Li_yizYa
* Date: 2023—04—29
* Time: 22:17
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class SessionBean implements Serializable {
private String id;
private String creationTime;
public SessionBean(String id, String creationTime) {
this.id = id;
this.creationTime = creationTime;
}
public SessionBean() {}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCreationTime() {
return creationTime;
}
public void setCreationTime(String creationTime) {
this.creationTime = creationTime;
}
}
【步骤1】编写MySessionListener监听器处理类,监视Web应用会话创建事件:每创建一个新的会话对象,就将其保存到会话对象的列表数组中,并将用户会话对象列表保存在ServletContext作用域中的sessionList属性中,同时向日志中写入“创建一个新会话”以及该会话的ID。当一个会话对象被删除时,从用户会话对象列表中删除该会话对象并保存,同时向日志中写入“删除一个会话”以及该会话的ID。
package org.example.config;
import org.example.beans.SessionBean;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Li_yizYa
* Date: 2023—04—29
* Time: 21:59
*/
public class MySessionListener implements HttpSessionListener {
@Override
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) {
ServletContext application = httpSessionEvent.getSession().getServletContext();
List<SessionBean> sessionList = (List<SessionBean>)application.getAttribute("sessionList");
if (sessionList == null) {
sessionList = new ArrayList<>();
application.setAttribute("sessionList", sessionList);
}
long time = httpSessionEvent.getSession().getCreationTime();
Date date = new Date(time);
SimpleDateFormat sd = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String creationTime = sd.format(date);
SessionBean sessionBean = new SessionBean(httpSessionEvent.getSession().getId(),
creationTime);
sessionList.add(sessionBean);
application.log("创建一个新会话,其id为: " + httpSessionEvent.getSession().getId());
}
@Override
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) {
ServletContext application = httpSessionEvent.getSession().getServletContext();
List<SessionBean> sessionList = (List<SessionBean>)application.getAttribute("sessionList");
String sessionId = httpSessionEvent.getSession().getId();
for(SessionBean session : sessionList) {
if (session.getId().equals(sessionId)) {
sessionList.remove(session);
}
}
application.log("删除一个新会话,其id为: " + sessionId);
application.setAttribute("sessionList", sessionList);
}
}
【步骤2】在web.xml文件中注册该事件监听器。
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.example.config.MyServletContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.example.config.MySessionListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>【步骤3】编写一个测试该监听器的页面sessionDisplay.jsp,显示当前应用所有在线的会话对象的id及创建时间。多打开几个浏览器窗口,模拟多用户访问,查看多用户会话统计出的结果。
<%@ page import="java.util.*" %>
<%@ page import="org.example.beans.*" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>sessionDisplay</title>
<style>
td{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<table width="500" height="256" border="1">
<tr>
<th scope="col">会话id</th>
<th scope="col">创建时间</th>
</tr>
<%
ServletContext context = getServletConfig().getServletContext();
List<SessionBean> sessionList = (List<SessionBean>) context.getAttribute("sessionList");
for (SessionBean s : sessionList) {
String id = s.getId();
String creationTime = s.getCreationTime();
%>
<tr>
<td><%=id%> </td>
<td><%=creationTime%></td>
</tr>
<% } %>
</table>
</body>
</html> 
3. 编写一个ServletRequestListener监听器,记录某个页面自应用程序启动以来被访问的次数。
【步骤1】编写监听器接口MyRequestListener,在对指定页面onlineCount.jsp发送请求时进行该页面访问次数计数器累加,并将计数器变量保存到应用作用域的属性中。
package org.example.config;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequestEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequestListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* Description:
* User: Li_yizYa
* Date: 2023—04—30
* Time: 0:04
*/
public class MyRequestListener implements ServletRequestListener {
private int count = 0;
@Override
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent servletRequestEvent) {
}
@Override
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent servletRequestEvent) {
HttpServletRequest request1 = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequestEvent.getServletRequest();
if(request1.getRequestURI().equals("/exp06/onlineCount.jsp")){
count++;
servletRequestEvent.getServletContext().setAttribute("count",new Integer(count));
}
}
}
【步骤2】在web.xml文件中注册该监听器。
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC
"-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" >
<web-app>
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.example.config.MyServletContextListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.example.config.MySessionListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.example.config.MyRequestListener</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>【步骤3】编写一个JSP页面onlineCount.jsp。
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=utf-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head><title>Listener test</title>
</head>
<body>
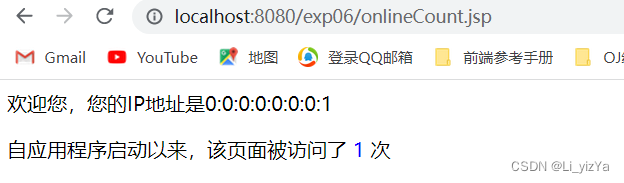
欢迎您,您的IP地址是<%= request.getRemoteAddr() %>
<p>自应用程序启动以来,该页面被访问了
<font color="blue" ><%=application.getAttribute("count")%>
</font>次<br>
</body>
</html>【步骤4】启动多个浏览器窗口访问该jsp页面,展示并分析程序的运行结果。


![Linux学习[8]查找文件指令:which whereis locate find](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7e39389d51dc4c6fae0e4fbc03b8c3e2.png)