重学Java设计模式-行为型模式-中介者模式
内容摘自:https://bugstack.cn/md/develop/design-pattern/2020-06-27-重学 Java 设计模式《实战中介者模式》.html#重学-java-设计模式-实战中介者模式「按照mybatis原理手写orm框架-给jdbc方式操作数据库增加中介者场景」
中介者模式介绍

- 图片来自:https://refactoringguru.cn/design-patterns/mediator(opens new window)
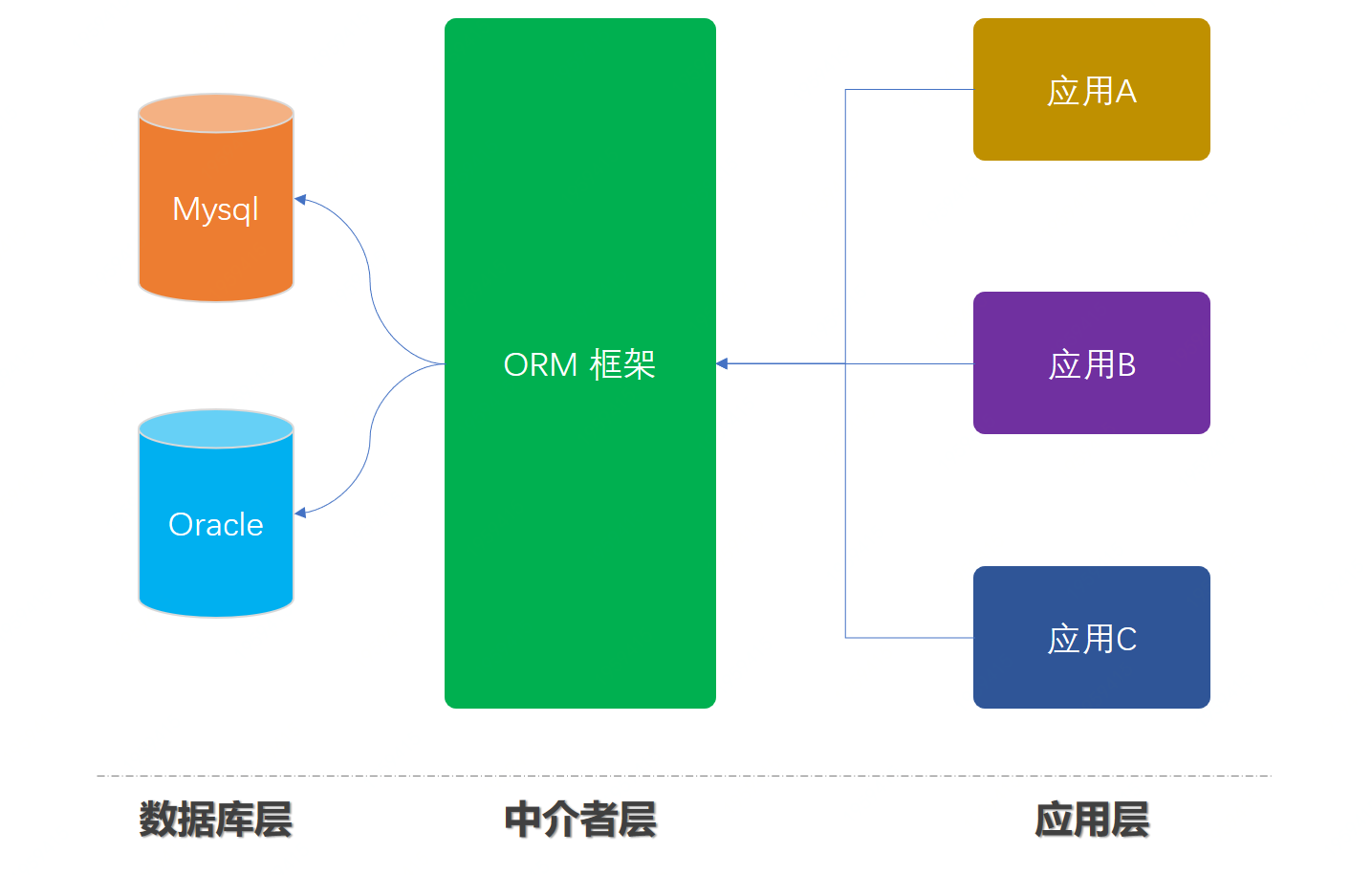
中介者模式要解决的就是复杂功能应用之间的重复调用,在这中间添加一层中介者包装服务,对外提供简单、通用、易扩展的服务能力。
这样的设计模式几乎在我们日常生活和实际业务开发中都会见到,例如;飞机🛬降落有小姐姐在塔台喊话、无论哪个方向来的候车都从站台上下、公司的系统中有一个中台专门为你包装所有接口和提供统一的服务等等,这些都运用了中介者模式。除此之外,你用到的一些中间件,他们包装了底层多种数据库的差异化,提供非常简单的方式进行使用。
案例场景模拟
在本案例中我们通过模仿Mybatis手写ORM框架,通过这样操作数据库学习中介者运用场景
除了这样的中间件层使用场景外,对于一些外部接口,例如N种奖品服务,可以由中台系统进行统一包装对外提供服务能力。也是中介者模式的一种思想体现。
在本案例中我们会把jdbc层进行包装,让用户在使用数据库服务的时候,可以和使用mybatis一样简单方便,通过这样的源码方式学习中介者模式,也方便对源码知识的拓展学习,增强知识栈。
用一坨坨代码实现
这是一种关于数据库操作最初的方式
基本上每一个学习开发的人都学习过直接使用jdbc方式连接数据库,进行CRUD操作。以下的例子可以当做回忆。
1. 工程结构
itstack-demo-design-16-01
└── src
└── main
└── java
└── org.itstack.demo.design
└── JDBCUtil.java
- 这里的类比较简单只包括了一个数据库操作类。
2. 代码实现
public class JDBCUtil {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JDBCUtil.class);
public static final String URL = "jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/itstack-demo-design";
public static final String USER = "root";
public static final String PASSWORD = "123456";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1. 加载驱动程序
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2. 获得数据库连接
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(URL, USER, PASSWORD);
//3. 操作数据库
Statement stmt = conn.createStatement();
ResultSet resultSet = stmt.executeQuery("SELECT id, name, age, createTime, updateTime FROM user");
//4. 如果有数据 resultSet.next() 返回true
while (resultSet.next()) {
logger.info("测试结果 姓名:{} 年龄:{}", resultSet.getString("name"),resultSet.getInt("age"));
}
}
}
- 以上是使用JDBC的方式进行直接操作数据库,几乎大家都使用过这样的方式。
3. 测试结果
15:38:10.919 [main] INFO org.itstack.demo.design.JDBCUtil - 测试结果 姓名:水水 年龄:18
15:38:10.922 [main] INFO org.itstack.demo.design.JDBCUtil - 测试结果 姓名:豆豆 年龄:18
15:38:10.922 [main] INFO org.itstack.demo.design.JDBCUtil - 测试结果 姓名:花花 年龄:19
Process finished with exit code 0
- 从测试结果可以看到这里已经查询到了数据库中的数据。只不过如果在全部的业务开发中都这样实现,会非常的麻烦。
中介模式开发ORM框架
`接下来就使用中介模式的思想完成模仿Mybatis的ORM框架开发~
1. 工程结构
itstack-demo-design-16-02
└── src
├── main
│ ├── java
│ │ └── org.itstack.demo.design
│ │ ├── dao
│ │ │ ├── ISchool.java
│ │ │ └── IUserDao.java
│ │ ├── mediator
│ │ │ ├── Configuration.java
│ │ │ ├── DefaultSqlSession.java
│ │ │ ├── DefaultSqlSessionFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── Resources.java
│ │ │ ├── SqlSession.java
│ │ │ ├── SqlSessionFactory.java
│ │ │ ├── SqlSessionFactoryBuilder.java
│ │ │ └── XNode.java
│ │ └── po
│ │ ├── School.java
│ │ └── User.java
│ └── resources
│ ├── mapper
│ │ ├── School_Mapper.xml
│ │ └── User_Mapper.xml
│ └── mybatis-config-datasource.xml
└── test
└── java
└── org.itstack.demo.design.test
└── ApiTest.java
中介者模式模型结构

- 以上是对ORM框架实现的核心类,包括了;加载配置文件、对xml解析、获取数据库session、操作数据库以及结果返回。
- 左上是对数据库的定义和处理,基本包括我们常用的方法;
<T> T selectOne、<T> List<T> selectList等。 - 右侧蓝色部分是对数据库配置的开启session的工厂处理类,这里的工厂会操作
DefaultSqlSession - 之后是红色地方的
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder,这个类是对数据库操作的核心类;处理工厂、解析文件、拿到session等。
接下来我们就分别介绍各个类的功能实现过程。
2. 代码实现
2.1 定义SqlSession接口
public interface SqlSession {
<T> T selectOne(String statement);
<T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter);
<T> List<T> selectList(String statement);
<T> List<T> selectList(String statement, Object parameter);
void close();
}
- 这里定义了对数据库操作的查询接口,分为查询一个结果和查询多个结果,同时包括有参数和没有参数的方法。
2.2 SqlSession具体实现类
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private Connection connection;
private Map<String, XNode> mapperElement;
public DefaultSqlSession(Connection connection, Map<String, XNode> mapperElement) {
this.connection = connection;
this.mapperElement = mapperElement;
}
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement) {
try {
XNode xNode = mapperElement.get(statement);
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(xNode.getSql());
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
List<T> objects = resultSet2Obj(resultSet, Class.forName(xNode.getResultType()));
return objects.get(0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> List<T> selectList(String statement) {
XNode xNode = mapperElement.get(statement);
try {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(xNode.getSql());
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
return resultSet2Obj(resultSet, Class.forName(xNode.getResultType()));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// ...
private <T> List<T> resultSet2Obj(ResultSet resultSet, Class<?> clazz) {
List<T> list = new ArrayList<>();
try {
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
// 每次遍历行值
while (resultSet.next()) {
T obj = (T) clazz.newInstance();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
Object value = resultSet.getObject(i);
String columnName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
String setMethod = "set" + columnName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + columnName.substring(1);
Method method;
if (value instanceof Timestamp) {
method = clazz.getMethod(setMethod, Date.class);
} else {
method = clazz.getMethod(setMethod, value.getClass());
}
method.invoke(obj, value);
}
list.add(obj);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return list;
}
@Override
public void close() {
if (null == connection) return;
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 这里包括了接口定义的方法实现,也就是包装了jdbc层。
- 通过这样的包装可以让对数据库的jdbc操作隐藏起来,外部调用的时候对入参、出参都有内部进行处理。
2.3 定义SqlSessionFactory接口
public interface SqlSessionFactory {
SqlSession openSession();
}
- 开启一个
SqlSession, 这几乎是大家在平时的使用中都需要进行操作的内容。虽然你看不见,但是当你有数据库操作的时候都会获取每一次执行的SqlSession。
2.4 SqlSessionFactory具体实现类
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
private final Configuration configuration;
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory(Configuration configuration) {
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration.connection, configuration.mapperElement);
}
}
DefaultSqlSessionFactory,是使用mybatis最常用的类,这里我们简单的实现了一个版本。- 虽然是简单的版本,但是包括了最基本的核心思路。当开启
SqlSession时会进行返回一个DefaultSqlSession - 这个构造函数中向下传递了
Configuration配置文件,在这个配置文件中包括;Connection connection、Map<String, String> dataSource、Map<String, XNode> mapperElement。如果有你阅读过Mybatis源码,对这个就不会陌生。
2.5 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder实现
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public DefaultSqlSessionFactory build(Reader reader) {
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
try {
saxReader.setEntityResolver(new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
Document document = saxReader.read(new InputSource(reader));
Configuration configuration = parseConfiguration(document.getRootElement());
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(configuration);
} catch (DocumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
private Configuration parseConfiguration(Element root) {
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.setDataSource(dataSource(root.selectNodes("//dataSource")));
configuration.setConnection(connection(configuration.dataSource));
configuration.setMapperElement(mapperElement(root.selectNodes("mappers")));
return configuration;
}
// 获取数据源配置信息
private Map<String, String> dataSource(List<Element> list) {
Map<String, String> dataSource = new HashMap<>(4);
Element element = list.get(0);
List content = element.content();
for (Object o : content) {
Element e = (Element) o;
String name = e.attributeValue("name");
String value = e.attributeValue("value");
dataSource.put(name, value);
}
return dataSource;
}
private Connection connection(Map<String, String> dataSource) {
try {
Class.forName(dataSource.get("driver"));
return DriverManager.getConnection(dataSource.get("url"), dataSource.get("username"), dataSource.get("password"));
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
// 获取SQL语句信息
private Map<String, XNode> mapperElement(List<Element> list) {
Map<String, XNode> map = new HashMap<>();
Element element = list.get(0);
List content = element.content();
for (Object o : content) {
Element e = (Element) o;
String resource = e.attributeValue("resource");
try {
Reader reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read(new InputSource(reader));
Element root = document.getRootElement();
//命名空间
String namespace = root.attributeValue("namespace");
// SELECT
List<Element> selectNodes = root.selectNodes("select");
for (Element node : selectNodes) {
String id = node.attributeValue("id");
String parameterType = node.attributeValue("parameterType");
String resultType = node.attributeValue("resultType");
String sql = node.getText();
// ? 匹配
Map<Integer, String> parameter = new HashMap<>();
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("(#\\{(.*?)})");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(sql);
for (int i = 1; matcher.find(); i++) {
String g1 = matcher.group(1);
String g2 = matcher.group(2);
parameter.put(i, g2);
sql = sql.replace(g1, "?");
}
XNode xNode = new XNode();
xNode.setNamespace(namespace);
xNode.setId(id);
xNode.setParameterType(parameterType);
xNode.setResultType(resultType);
xNode.setSql(sql);
xNode.setParameter(parameter);
map.put(namespace + "." + id, xNode);
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
return map;
}
}
- 在这个类中包括的核心方法有;
build(构建实例化元素)、parseConfiguration(解析配置)、dataSource(获取数据库配置)、connection(Map<String, String> dataSource) (链接数据库)、mapperElement (解析sql语句) - 接下来我们分别介绍这样的几个核心方法。
build(构建实例化元素)
这个类主要用于创建解析xml文件的类,以及初始化SqlSession工厂类DefaultSqlSessionFactory。另外需要注意这段代码saxReader.setEntityResolver(new XMLMapperEntityResolver());,是为了保证在不联网的时候一样可以解析xml,否则会需要从互联网获取dtd文件。
parseConfiguration(解析配置)
是对xml中的元素进行获取,这里主要获取了;dataSource、mappers,而这两个配置一个是我们数据库的链接信息,另外一个是对数据库操作语句的解析。
connection(Map<String, String> dataSource) (链接数据库)
链接数据库的地方和我们常见的方式是一样的;Class.forName(dataSource.get("driver"));,但是这样包装以后外部是不需要知道具体的操作。同时当我们需要链接多套数据库的时候,也是可以在这里扩展。
mapperElement (解析sql语句)
这部分代码块内容相对来说比较长,但是核心的点就是为了解析xml中的sql语句配置。在我们平常的使用中基本都会配置一些sql语句,也有一些入参的占位符。在这里我们使用正则表达式的方式进行解析操作。
解析完成的sql语句就有了一个名称和sql的映射关系,当我们进行数据库操作的时候,这个组件就可以通过映射关系获取到对应sql语句进行操作。
3. 测试验证
在测试之前需要导入sql语句到数据库中;
- 库名:
itstack-demo-design - 表名:
user、school
CREATE TABLE school ( id bigint NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(64), address varchar(256), createTime datetime, updateTime datetime, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into school (id, name, address, createTime, updateTime) values (1, '北京大学', '北京市海淀区颐和园路5号', '2019-10-18 13:35:57', '2019-10-18 13:35:57');
insert into school (id, name, address, createTime, updateTime) values (2, '南开大学', '中国天津市南开区卫津路94号', '2019-10-18 13:35:57', '2019-10-18 13:35:57');
insert into school (id, name, address, createTime, updateTime) values (3, '同济大学', '上海市彰武路1号同济大厦A楼7楼7区', '2019-10-18 13:35:57', '2019-10-18 13:35:57');
CREATE TABLE user ( id bigint(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(32), age int(4), address varchar(128), entryTime datetime, remark varchar(64), createTime datetime, updateTime datetime, status int(4) DEFAULT '0', dateTime varchar(64), PRIMARY KEY (id), INDEX idx_name (name) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into user (id, name, age, address, entryTime, remark, createTime, updateTime, status, dateTime) values (1, '水水', 18, '吉林省榆树市黑林镇尹家村5组', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', '无', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', 0, '20200309');
insert into user (id, name, age, address, entryTime, remark, createTime, updateTime, status, dateTime) values (2, '豆豆', 18, '辽宁省大连市清河湾司马道407路', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', '无', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', 1, null);
insert into user (id, name, age, address, entryTime, remark, createTime, updateTime, status, dateTime) values (3, '花花', 19, '辽宁省大连市清河湾司马道407路', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', '无', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', '2019-12-22 00:00:00', 0, '20200310');
3.1 创建数据库对象类
用户类
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
// ... get/set
}
学校类
public class School {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Date createTime;
private Date updateTime;
// ... get/set
}
- 这两个类都非常简单,就是基本的数据库信息。
3.2 创建DAO包
用户Dao
public interface IUserDao {
User queryUserInfoById(Long id);
}
学校Dao
public interface ISchoolDao {
School querySchoolInfoById(Long treeId);
}
3.3 ORM配置文件
链接配置
<configuration>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/itstack_demo_design?useUnicode=true"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mapper/User_Mapper.xml"/>
<mapper resource="mapper/School_Mapper.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
- 这个配置与我们平常使用的mybatis基本是一样的,包括了数据库的连接池信息以及需要引入的mapper映射文件。
操作配置(用户)
<mapper namespace="org.itstack.demo.design.dao.IUserDao">
<select id="queryUserInfoById" parameterType="java.lang.Long" resultType="org.itstack.demo.design.po.User">
SELECT id, name, age, createTime, updateTime
FROM user
where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="queryUserList" parameterType="org.itstack.demo.design.po.User" resultType="org.itstack.demo.design.po.User">
SELECT id, name, age, createTime, updateTime
FROM user
where age = #{age}
</select>
</mapper>
操作配置(学校)
<mapper namespace="org.itstack.demo.design.dao.ISchoolDao">
<select id="querySchoolInfoById" resultType="org.itstack.demo.design.po.School">
SELECT id, name, address, createTime, updateTime
FROM school
where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
3.4 单个结果查询测试
@Test
public void test_queryUserInfoById() {
String resource = "mybatis-config-datasource.xml";
Reader reader;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
try {
User user = session.selectOne("org.itstack.demo.design.dao.IUserDao.queryUserInfoById", 1L);
logger.info("测试结果:{}", JSON.toJSONString(user));
} finally {
session.close();
reader.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 这里的使用方式和
Mybatis是一样的,都包括了;资源加载和解析、SqlSession工厂构建、开启SqlSession以及最后执行查询操作selectOne
测试结果
16:56:51.831 [main] INFO org.itstack.demo.design.demo.ApiTest - 测试结果:{"age":18,"createTime":1576944000000,"id":1,"name":"水水","updateTime":1576944000000}
Process finished with exit code 0
- 从结果上看已经满足了我们的查询需求。
3.5 集合结果查询测试
@Test
public void test_queryUserList() {
String resource = "mybatis-config-datasource.xml";
Reader reader;
try {
reader = Resources.getResourceAsReader(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlMapper = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(reader);
SqlSession session = sqlMapper.openSession();
try {
User req = new User();
req.setAge(18);
List<User> userList = session.selectList("org.itstack.demo.design.dao.IUserDao.queryUserList", req);
logger.info("测试结果:{}", JSON.toJSONString(userList));
} finally {
session.close();
reader.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 这个测试内容与以上只是查询方法有所不同;
session.selectList,是查询一个集合结果。
测试结果
16:58:13.963 [main] INFO org.itstack.demo.design.demo.ApiTest - 测试结果:[{"age":18,"createTime":1576944000000,"id":1,"name":"水水","updateTime":1576944000000},{"age":18,"createTime":1576944000000,"id":2,"name":"豆豆","updateTime":1576944000000}]
Process finished with exit code 0
- 测试验证集合的结果也是正常的,目前位置测试全部通过。