Set集合
Set接口也是Collection单列结合的一个子接口,set集合中没有提供其他额外的方法,但是相比较Collection集合新增了其他的特性。所有实现了Set接口的类都可以叫做Set集合。
Coliection接口中的方法:Collection集合的方法
Set集合不允许包含相同的元素,也就是元素唯一,其中元素的存储顺序大多数无序,部分有序。
Set集合的遍历方式和Collection集合一样:foreach和Iterator。
Set接口的常用实现类:HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet。

HashSet集合
HashSet类是Set接口的典型实现类,在使用Set集合的时候大多数使用的就是这个实现类。
java.util.HashSet底层使用的java.util.HashMap中的key进行存储数据,底层的实现是一个Hash表。

在JDK1.7以及之前,hash表存链表的方式是使用的头插法的方式,但是这样容易导致死循环(多线程)。
在JDK1.8及之后,链表节点由头插法改成了尾插法。
HashSet是按照Hash表进行存储数据,采用了Hash算法,因此具有很好的查询和查找性能。
如何使用HashSet集合判断两个元素是否相同?
HashSet集合判断两个元素相等的标准: 1、两个对象通过hashCode()方法比较hashCode是否相同, 2、比较两个元素对象的equals()方法返回值是否为true。 因此,存储到HashSet集合中的元素要重写hashCode和equals方法。
1、创建生日类:
public class Birthday {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public Birthday() {
}
public Birthday(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = result * prime + year;
result = result * prime + month;
result = result *prime + day;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj){return true;}
if (obj == null){return false;}
if (this.getClass() != obj.getClass()){return false;}
Birthday birthday = (Birthday) obj;
if (this.year!= birthday.year){return false;}
if (this.month != birthday.month){return false;}
if (this.day != birthday.day){return false;}
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Birthday{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
'}';
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
}
2、创建员工类:
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Birthday birthday;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(Integer id, String name, Birthday birthday) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = result * prime + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
result = result * prime + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = result * prime + ((birthday == null) ? 0 : birthday.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this==obj){return true;}
if (obj==null){return false;}
if (this.getClass()!=obj.getClass()){return false;}
Employee employeeOther = (Employee) obj;
if (this.id==null){
if (employeeOther.id!=null){return false;}
}else if (!this.id.equals(employeeOther.id)){return false;}
if (this.name==null){
if (employeeOther.name!=null){return false;}
}else if (!this.name.equals(employeeOther.name)){return false;}
if (this.birthday==null){
if (employeeOther.birthday!=null){return false;}
}else if (!this.birthday.equals(employeeOther.birthday)){return false;}
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Birthday getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Birthday birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
}
3、测试Set集合:
public class HashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Employee> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(new Employee(1001,"员工亿",new Birthday(1998,10,10)));
set.add(new Employee(1001,"员工亿",new Birthday(1998,10,10)));
set.add(new Employee(1002,"员工万",new Birthday(1999,11,6)));
set.add(new Employee(1003,"员工富",new Birthday(1998,10,7)));
for (Employee employee : set) {
System.out.println("employee = " + employee);
}
}
}
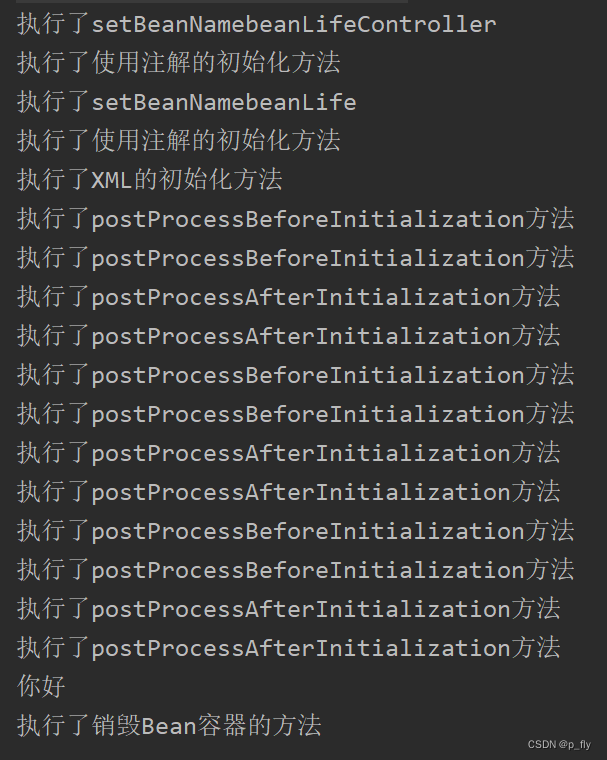
结果:

注意:可以看出来输出的结果和存入的顺序不一致,重复的元素只输出一个
LinkedHashSet集合
LinkedHashSet集合是HashSet集合的子类,也是位于java.util.LinkedHashSet包下的一个实现类。LinkedHashSet是在HashSet的基础上为每一个元素添加了before和after属性,保证了添加元素的前后顺序。LinkedHashSet的数据存储结构是:Hash表+链表。对于插入性能略低于HashSet,但是实现了有序,在迭代访问元素时有很好的性能。
LinkedHashSet的存储结构图:

代码测试:
public class LinkedHashSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<Employee> linkedHashSet = new LinkedHashSet<>();
linkedHashSet.add(new Employee(1001,"员工甲",new Birthday(2000,1,1)));
linkedHashSet.add(new Employee(1002 ,"员工乙",new Birthday(2000,2,2)));
linkedHashSet.add(new Employee(1003,"员工丙",new Birthday(2000,3,3)));
Iterator<Employee> iterator = linkedHashSet.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()){
Employee employee = iterator.next();
System.out.println("employee = " + employee);
}
}
}
结果:

这里可以看到结果是和存储数据的时候一致。
TreeSet集合
在上面的LinkedHashSet中实现了Set集合的有序性,而在TreeSet集合中实现了Set集合中元素的排序。
TreeSet集合是位于java.util包下的一个集合类,底层结构维护的一个TreeMap,是基于红黑树实现的一个集合。
红黑树:一种相对平衡的二叉树,查询效率高于链表,增删效率高于数组。
二叉搜索树:每个节点的左边所有子节点都小于或等于节点本身,每个节点的右边结点都大于或等于节点本身。
平衡二叉树:每个节点的左右子树高度差不能超过1
二叉树的遍历方式有:
- 前序遍历:中-左-右
- 中序遍历:左-中-右
- 后序遍历:左-右-中
在TreeSet集合中采用的遍历方式是中序遍历

- 前序遍历:33,15,11,6,12,18,40,34,62
- 中序遍历:6,11,12,15,18,33,34,40,62
- 后序遍历:6,12,11,18,15,34,62,40,33
TreeSet集合的特点:
- 元素唯一且无序
- 实现了排序
在TreeSet集合中如何实现排序的呢?
- 按照字符串的Unicode编码值进行排序
- 按照自定义排序:存入的元素实现Comparable接口中的重写compareTo(Object obj)方法进行排序
- 按照定制排序:在集合创建的过程中,构造器传入一个新建的Comparator接口,也就是匿名内部类的形式重写compare(Object o1,Object o2)方法
- 按照Unicode编码进行排序:
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<String> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
treeSet.add("set");
treeSet.add("hashSet");
treeSet.add("linkedHashSet");
treeSet.add("treeSet");
/*treeSet.add(1);
treeSet.add(7);
treeSet.add(5);
treeSet.add(3);
System.out.println("treeSet = " + treeSet); //treeSet = [1, 3, 5, 7]*/
System.out.println("treeSet = " + treeSet); //treeSet = [hashSet, linkedHashSet, set, treeSet]
}
}
String类也实现了Comparable接口
- 使用自定义的默认排序
public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee>{
private Integer id;
private String name;
@Override
public int compareTo(Employee o) {
int i = o.id.compareTo(this.id)==0? 0:o.id.compareTo(this.id);
i = o.name.compareTo(this.name)==0? i:o.name.compareTo(this.name);
return i;
}
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(Integer id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = result * prime + ((id == null) ? 0 : id.hashCode());
result = result * prime + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this==obj){return true;}
if (obj==null){return false;}
if (this.getClass()!=obj.getClass()){return false;}
Employee employeeOther = (Employee) obj;
if (this.id==null){
if (employeeOther.id!=null){return false;}
}else if (!this.id.equals(employeeOther.id)){return false;}
if (this.name==null){
if (employeeOther.name!=null){return false;}
}else if (!this.name.equals(employeeOther.name)){return false;}
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
测试:
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Employee> treeSet = new TreeSet<>();
treeSet.add(new Employee(1001,"员工甲"));
treeSet.add(new Employee(1002 ,"员工乙"));
treeSet.add(new Employee(1003,"员工丙"));
System.out.println("treeSet = " + treeSet);
}
}
注意:这里使用的是Employee重写的compareTo方法的排序规则
结果演示:

- 使用定制排序规则
不需要实现Comparable接口
public class Birthday {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public Birthday() {
}
public Birthday(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = result * prime + year;
result = result * prime + month;
result = result *prime + day;
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj){return true;}
if (obj == null){return false;}
if (this.getClass() != obj.getClass()){return false;}
Birthday birthday = (Birthday) obj;
if (this.year!= birthday.year){return false;}
if (this.month != birthday.month){return false;}
if (this.day != birthday.day){return false;}
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Birthday{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
'}';
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
}
实现匿名内部类
public class TreeSetTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Birthday> treeSet = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Birthday>() {
@Override
public int compare(Birthday o1, Birthday o2) {
int i =o1.getDay()-o2.getDay();
i = (o1.getMonth()-o2.getMonth())==0? i:(o1.getMonth()-o2.getMonth());
i = (o1.getYear()-o2.getYear()) == 0? i:(o1.getYear()-o2.getYear());
return i;
}
});
treeSet.add(new Birthday(1998,10,10));
treeSet.add(new Birthday(1999,11,6));
treeSet.add(new Birthday(1998,10,7));
System.out.println("treeSet = " + treeSet);
}
}
结果演示:

注意:在使用TreeSet集合进行出元素时,存入的元素会显赫已有的元素进行判断,如果判断结果为负数,则放到左边,判断结果为正数放到右边,如果为0则覆盖原来的值。