🐶博主主页:@ᰔᩚ. 一怀明月ꦿ
❤️🔥专栏系列:线性代数,C初学者入门训练,题解C,C的使用文章,「初学」C++
🔥座右铭:“不要等到什么都没有了,才下定决心去做”
🚀🚀🚀大家觉不错的话,就恳求大家点点关注,点点小爱心,指点指点🚀🚀🚀
目录
🐰顺序表
🏡顺序表的定义
🏡顺序表的初始化
🏡顺序表空间的检查
🏡顺序表中指定位置插入数据
🏡顺序表中指定位置删除数据
🏡顺序表中的头插数据
🏡顺序表中的尾插数据
🏡顺序表中的头删数据
🏡顺序表中的尾删数据
🏡顺序表中查找数据
🏡顺序表中改动数据
🏡顺序表中的打印数据
🏡顺序表中的销毁数据
🏡顺序表中的源码
🌸main文件
🌸头文件test.h
🌸test.c文件
🐰顺序表
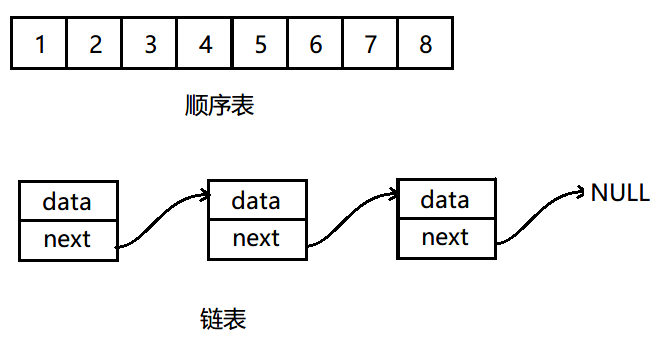
🏡顺序表的定义
有两种顺序表的定义,一种是静态的,一种是动态的
1.静态顺序表的定义
静态顺序表 1.空间是固定的,没有办法存储超过空间的数据 2.如果空间开辟大了,浪费空间 不推荐使用静态顺序表,没有实际用途 #define N 10 typedef int SLDatatype; struct SeqList { int a[N]; int size; };2.动态顺序表的定义
动态定义的顺序表,有效规避了静态的不足 typedef int SLDatatype; typedef struct SeqList { SLDatatype* a;//有效数据 SLDatatype size;//存储的有效数据个数 SLDatatype capacity;//存放数据的最大容量 }SL;🏡顺序表的初始化
初始时,顺序表动态开辟了4个空间,有效数据的个数为0,最大容量为4
void SLInit(SL* psl) { assert(psl); psl->a=(SLDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(SLDatatype)*4);//初始化时开辟4个SLDatatype类型的空间给a if(psl->a==NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return ; } psl->size=0; psl->capacity=4; }🏡顺序表空间的检查
我们在给顺序表插入数据之前,我们应该检查一下顺序表的空间是否充足,如果充足我们就插入数据,如果不充足,就开辟更大的空间,然后再进行插入数据
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl) { assert(psl); if(psl->size==psl->capacity) { SLDatatype* tmp=(SLDatatype*)realloc(psl->a,sizeof(SLDatatype)*psl->capacity*2);//在原来的的空间,扩为原来空间的二倍 if(tmp==NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); return ; } else { psl->a=tmp; psl->capacity=psl->capacity*2; } } }🏡顺序表中指定位置插入数据
我们可以在自己指定的位置插入数据,这里需要注意的是,我们指定的位置必须合法,也就说,只能从头到尾之间插入数据,且尾也可以插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* psl,int pos,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); assert(pos>=0&&pos<=psl->size);//判断插入位置是否符合合法 SLCheckCapacity(psl); int end=psl->size-1; while(end>=pos) { psl->a[end+1]=psl->a[end]; end--; } psl->a[pos]=x; psl->size++; }🏡顺序表中指定位置删除数据
我们可以在自己指定的位置删除数据,这里需要注意的是,我们指定的位置必须合法,也就说,只能从头到尾之间删除数据
void SLEarse(SL* psl,int pos) { assert(psl); assert(pos>=0&&pos<psl->size);//判断插入位置是否符合合法 int start=pos+1; while(start<psl->size) { psl->a[start-1]=psl->a[start]; start++; } psl->size--; }🏡顺序表中的头插数据
顺序表中的头插数据有两种方法
1.第一种方法
这种方法就是将最后的数据移动到后一个位置,然后倒数第二个数据往最后一个位置移动,依此类推,直到第一个数据移到第二个位置,然后在第一个位置插入数据
void SLPushFront(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); SLCheckCapacity(psl); //从后往前移动数据 int end=psl->size-1; while(end>=0) { psl->a[end+1]=psl->a[end]; end--; } psl->a[0]=x; psl->size++; }1.第二种方法
这种方法复用了顺序表中指定位置插入数据
void SLPushFront(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); SLInsert(psl,0,x); }🏡顺序表中的尾插数据
顺序表中的尾插数据有两种方法
1.第一种
直接在最后一个数据的位置后面插入数据
void SLPushBack(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); SLCheckCapacity(psl); psl->a[psl->size]=x; psl->size++; }2.第二种
这种方法复用了顺序表中指定位置插入数据
void SLPushBack(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); SLInsert(psl,psl->size,x); }🏡顺序表中的头删数据
顺序表中的头删数据有两种方法
1.第一种:
将第二个数据放到第一个数据的位置,把第三个的数据放到第二个数据最开始的位置,以此类推,直到最后一个数据放到倒数第二个数据最开始的位置
void SLPopFront(SL* psl) { assert(psl); assert(psl->size>0); //从前往后移动 int start=0; while(start<psl->size-1) { psl->a[start]=psl->a[start+1]; start++; } psl->size--; }2.第二种:
这种方法复用了顺序表中指定位置删除数据
void SLPopFront(SL* psl) { assert(psl); SLEarse(psl,0); }🏡顺序表中的尾删数据
顺序表中的头删数据有两种方法
1.第一种
void SLPophBack(SL* psl) { assert(psl); //(1)if是温柔处理顺序表为空 if(psl->size==0) { printf("顺序表数据为空,不能尾删\n"); return ; } else { psl->size--; } //(2)暴力解法 assert(psl->size>0); psl->size--; }2.第二种
这种方法复用了顺序表中指定位置删除数据
void SLPophBack(SL* psl) { assert(psl); SLEarse(psl,psl->a[psl->size-1]); }🏡顺序表中查找数据
如果找到数据我们就返回它的下标位置,如果找不到就返回-1,这里这种算法有一点缺陷,就是如果数据中有重复的数据,则只会返回这个数据第一次出现的位置
int SLFind(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); for(int i=0;i<psl->size;i++) { if(psl->a[i]==x) { return i; } } return -1; }🏡顺序表中改动数据
直接在想要改变数据的位置,直接赋新值,但是要注意想要改变数据的位置是合法的
void SLModify(SL* psl,int pos,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); assert(pos>=0&&pos<psl->size); psl->a[pos]=x; }🏡顺序表中的打印数据
依次打印出顺序表中存储的数据
void SLPrint(SL* psl) { assert(psl); for(int i=0;i<psl->size;i++) { printf("%d ",psl->a[i]); } printf("\n"); }🏡顺序表中的销毁数据
将动态分配的空间归还给系统,将数据个数置为0,最大容量置为0
void SLDestroy(SL* psl) { assert(psl); free(psl->a); psl->a=NULL; psl->size=0; psl->capacity=0; }🏡顺序表中的源码
为了更形象观察顺序表,这里使用了菜单,如果想要方便调试,建议大家不要使用菜单
🌸main文件
//顺序表 //顺序表的本质就是一个数组 //链表不支持二分查找,数组可以 //顺序表的增、删、查、改 #include"test.h" void menu(void) { printf("****************顺序表****************\n"); printf(" 1.头插数据 2.尾插数据 \n"); printf(" 3.头删数据 4.尾删数据 \n"); printf(" 5.自定义插数据 6.自定义删数据 \n"); printf(" 7.查找数据 8.修改数据 \n"); printf(" 9.打印数据 x.销毁数据 \n"); printf(" e.退出 \n"); printf("*************************************\n"); } void test(void) { SL s1; SLInit(&s1); char input=0; do { menu(); printf("请选择:>"); scanf("%c",&input); if(input=='1') { SLDatatype x=0; printf("请输入插入的数据\n"); scanf("%d",&x); SLPushFront(&s1,x); printf("数据完成插入^_^\n"); } else if(input=='2') { SLDatatype x=0; printf("请输入插入的数据\n"); scanf("%d",&x); SLPushFront(&s1,x); printf("数据完成插入^_^\n"); } else if(input=='3') { SLPophBack(&s1); printf("数据完成删除@_@\n"); } else if(input=='4') { SLPophBack(&s1); printf("数据完成删除@_@\n"); } else if(input=='5') { int pos=0; int x=0; printf("请输入你想要插入数据的位置\n"); scanf("%d",&pos); printf("请输入插入的数据\n"); scanf("%d",&x); SLInsert(&s1,pos,x); printf("数据完成插入^_^\n"); } else if(input=='6') { int pos=0; printf("请输入你想要删除数据的位置\n"); scanf("%d",&pos); SLEarse(&s1,pos); printf("数据完成删除@_@\n"); } else if(input=='7') { int x=0; printf("请输入查找的数据\n"); scanf("%d",&x); int num=SLFind(&s1,x); if(num!=-1) printf("数据的位置为%d\n",num); else printf("顺序表里没有此数据\n"); } else if(input=='8') { int pos=0; printf("请输入你想要修改数据的位置\n"); scanf("%d",&pos); int x=0; printf("请输入修改的数据\n"); scanf("%d",&x); SLModify(&s1,pos,x); printf("修改数据成功O_o\n"); } else if(input=='9') { SLPrint(&s1); printf("打印完成...\n"); } else if(input=='x') { SLDestroy(&s1); printf("销毁数据成功...\n"); } else if(input=='e') { printf("退出顺序表...\n"); } else { printf("无此选项,请重新选择\n"); } getchar(); }while(input!='e'); } int main() { test(); return 0; }🌸头文件test.h
#ifndef test_h #define test_h #include <stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #endif /* test_h */ #include<assert.h> //静态顺序表 //1.空间是固定的,没有办法存储超过空间的数据 //2.如果空间开辟大了,浪费空间 //不推荐使用静态顺序表,没有实际用途 //#define N 10 //typedef int SLDatatype; // //struct SeqList //{ // int a[N]; // int size; //}; typedef int SLDatatype; typedef struct SeqList { SLDatatype* a; SLDatatype size;//存储的有效数据个数 SLDatatype capacity;//容量 }SL; //STL的命名风格(C++) //顺序表的初始化 void SLInit(SL* psl); //打印顺序表 void SLPrint(SL* psl); //销毁顺序表 void SLDestroy(SL* psl); //尾插数据 void SLPushBack(SL* psl,SLDatatype x); //头插数据 void SLPushFront(SL* psl,SLDatatype x); //尾删数据 void SLPophBack(SL* psl); //头删数据 void SLPopFront(SL* psl); //在pos位置插入一个数据 void SLInsert(SL* psl,int pos,SLDatatype x); //在pos位置删除一个数据 void SLEarse(SL* psl,int pos); //查找数据 //找到了返回下标,没找到返回-1 int SLFind(SL* psl,SLDatatype x); //修改指定位置的数据 void SLModify(SL* psl,int pos,SLDatatype x);🌸test.c文件
#include"test.h" void SLInit(SL* psl) { assert(psl); psl->a=(SLDatatype*)malloc(sizeof(SLDatatype)*4);//初始化时开辟4个SLDatatype类型的空间给a if(psl->a==NULL) { perror("malloc fail"); return ; } psl->size=0; psl->capacity=4; } void SLDestroy(SL* psl) { assert(psl); free(psl->a); psl->a=NULL; psl->size=0; psl->capacity=0; } void SLPrint(SL* psl) { assert(psl); for(int i=0;i<psl->size;i++) { printf("%d ",psl->a[i]); } printf("\n"); } //插入的时候要去判断容量是否充足 //可以写一个检查容量是否充足的函数 //如果空间不足,就需要扩容 void SLCheckCapacity(SL* psl) { assert(psl); if(psl->size==psl->capacity) { SLDatatype* tmp=(SLDatatype*)realloc(psl->a,sizeof(SLDatatype)*psl->capacity*2);//在原来的的空间,扩为原来空间的二倍 if(tmp==NULL) { perror("realloc fail"); return ; } else { psl->a=tmp; psl->capacity=psl->capacity*2; } } } //尾插数据 //尾插数据的原理:在最后一个数据后面再添加一个数据 void SLPushBack(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); // SLCheckCapacity(psl); // psl->a[psl->size]=x; // psl->size++; SLInsert(psl,psl->size,x); } //头插数据 void SLPushFront(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); SLCheckCapacity(psl); //从后往前移动数据 int end=psl->size-1; while(end>=0) { psl->a[end+1]=psl->a[end]; end--; } psl->a[0]=x; psl->size++; // SLInsert(psl,0,x); } //尾删数据 void SLPophBack(SL* psl) { assert(psl); // if是温柔处理顺序表为空 // if(psl->size==0) // { // printf("顺序表数据为空,不能尾删\n"); // return ; // } // else // { // psl->size--; // } // 暴力解法 // assert(psl->size>0); // psl->size--; SLEarse(psl,psl->a[psl->size-1]); } //头删数据 void SLPopFront(SL* psl) { assert(psl); //方法一: // assert(psl->size>0); // //从前往后移动 // int start=0; // while(start<psl->size-1) // { // psl->a[start]=psl->a[start+1]; // start++; // } // psl->size--; //方法二: SLEarse(psl,0); } void SLInsert(SL* psl,int pos,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); assert(pos>=0&&pos<=psl->size);//判断插入位置是否符合合法 SLCheckCapacity(psl); int end=psl->size-1; while(end>=pos) { psl->a[end+1]=psl->a[end]; end--; } psl->a[pos]=x; psl->size++; } void SLEarse(SL* psl,int pos) { assert(psl); assert(pos>=0&&pos<psl->size);//判断插入位置是否符合合法 int start=pos+1; while(start<psl->size) { psl->a[start-1]=psl->a[start]; start++; } psl->size--; } int SLFind(SL* psl,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); for(int i=0;i<psl->size;i++) { if(psl->a[i]==x) { return i; } } return -1; } void SLModify(SL* psl,int pos,SLDatatype x) { assert(psl); assert(pos>=0&&pos<psl->size); psl->a[pos]=x; }
🌸🌸🌸如果大家还有不懂或者建议都可以发在评论区,我们共同探讨,共同学习,共同进步。谢谢大家! 🌸🌸🌸





![[考研数据结构] 第3章之队列的基本知识与操作](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/41b1225bc0ff4e84a9a696d852ffc869.png)