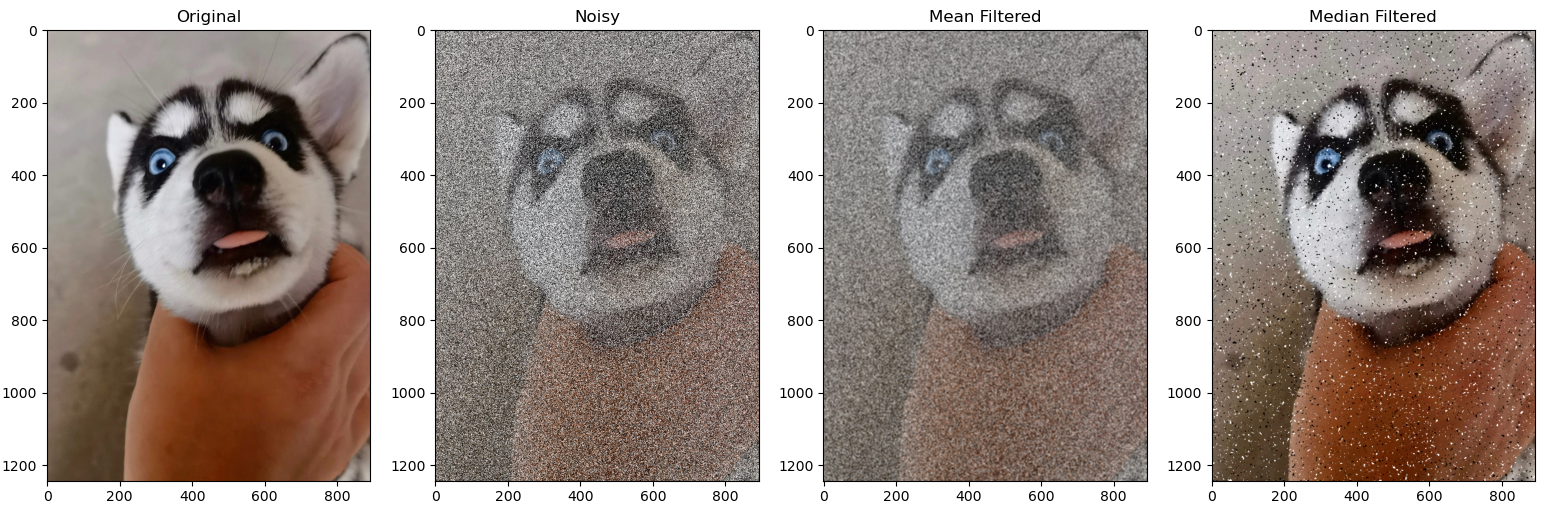
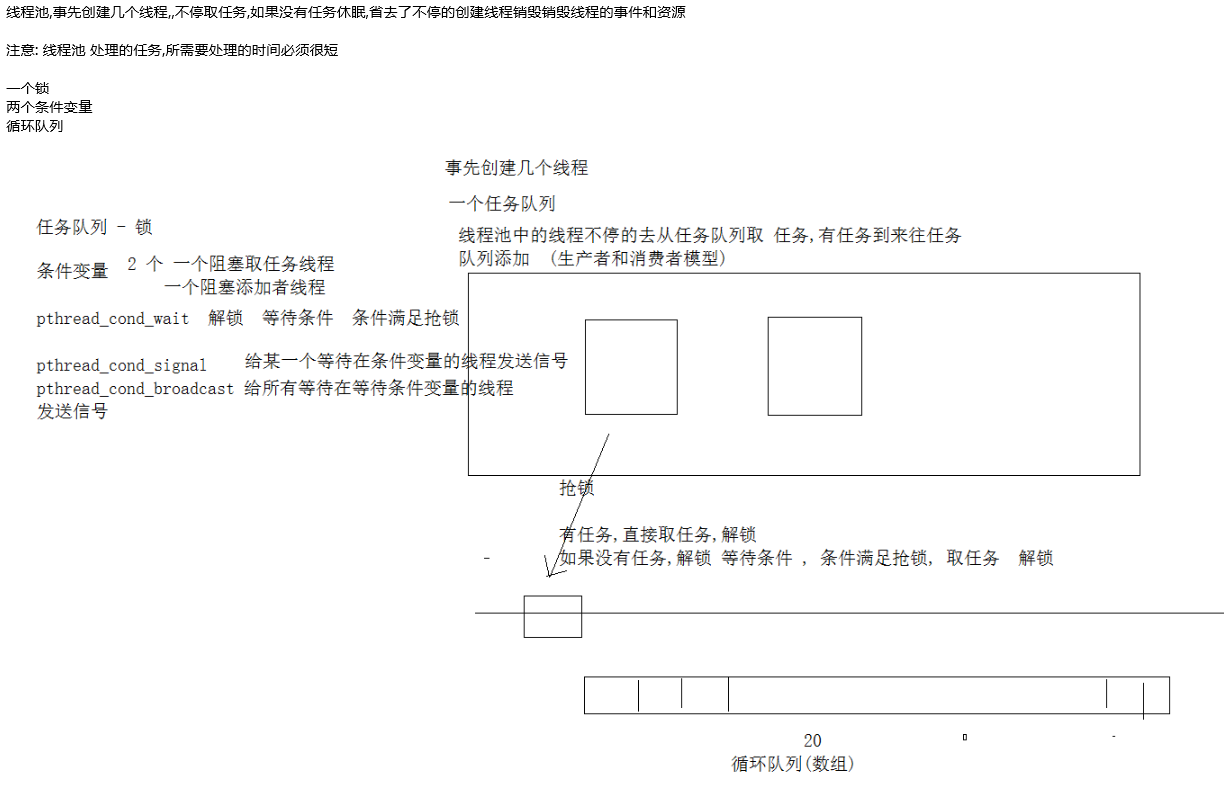
线程池技术是一种典型的生产者-消费者模型。
线程池技术是指能够保证所创建的任一线程都处于繁忙状态,而不需要频繁地为了某一任务而创建和销毁线程,因为系统在创建和销毁线程时所耗费的cpu资源很大。如果任务很多,频率很高,为了单个任务起线程而后销线程,那么这种情况效率相当低下的。线程池技术就是用于解决这样一种应用场景而应运而生的。
线程池允许一个线程可以多次复用,且每次复用的线程内部的消息处理可以不相同,将创建与销毁的开销省去而不必来一个请求开一个线程。
如果一个应用需要频繁的创建和销毁线程,而任务执行的时间又非常短,这样线程创建和销毁的带来的开销就不容忽视,这时也是线程池该出场的机会了。
线程池的工作原理
在起先就创建一定数量的线程以队列形式存在,并为其分配一个工作队列,当工作队列为空时,表示没有任务,此时所有线程挂起等待新的工作到来。当新的工作到来时,线程队列头开始执行这个任务,然后依次是第二、第三个线程执行新到来的任务,当其中某个线程处理完任务后,那么该线程立马开始接受任务分派,从而让所有线程都处于忙碌的状态,提高并行处理效率。
创建线程池的原因
- 降低资源消耗。通过重复利用已创建的线程降低线程的创建和销毁造成的消耗。
- 提高响应速度。当任务到达时,任务可以不需要等到线程创建就能立即执行。
- 提高线程的可管理性。线程为稀缺资源,如果无限制地创建,不仅会消耗系统资源,还会降低系统的稳定性,使用线程池可以进行统一分配、调优和监控。但是,要做到合理利用线程池,必须对其实现原理了如指掌。
线程池的实现流程
- 创建一个线程池,初始化其中属性,可创建一定数量线程,放入队列,或者不初始化
- 线程都处于阻塞等待状态,不占用cpu,当超时等待,可以自己结束线程
- 当需要执行函数,则把函数包装成任务,并把任务传入空闲线程进行运行
- 当没有空闲进程且小于最大线程数要求,则创建线程执行任务
- 执行完任务的线程不需要退出,阻塞等待即可(或者设置等待时间)
- 若有线程池销毁通知,确保任务执行完退出销毁
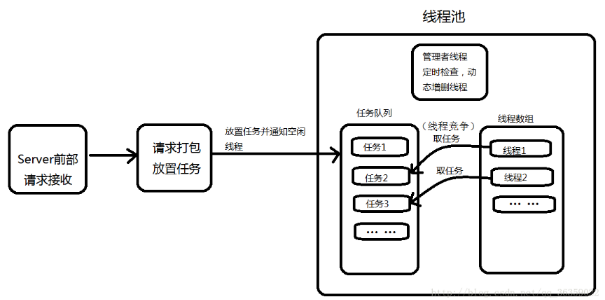
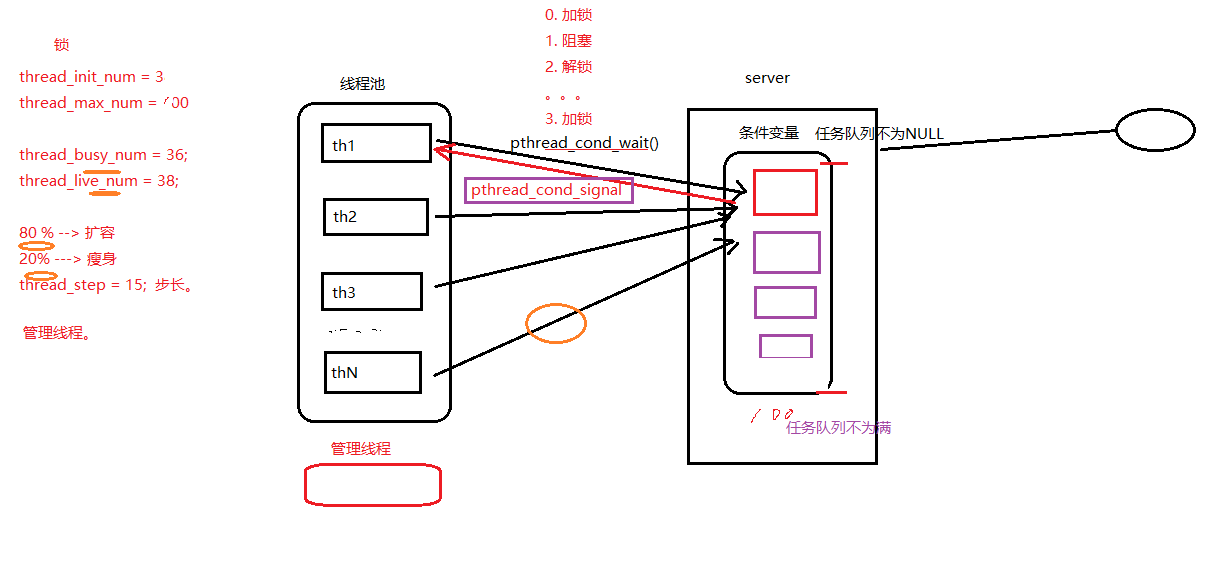
线程池总体结构 (重)
线程池主要组成就三个部分
- task_t类型的结构体
- threadpool_t类型结构体
- 多个实现函数
/* 创建线程池 */ threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size) /* 线程池中各个工作线程 */ void *threadpool_thread(void *threadpool) /* 管理线程 */ void *adjust_thread(void *threadpool) /* 向线程池中 添加一个任务 */ int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void*(*function)(void *arg), void *arg) /* 销毁线程池 */ int threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool)
一:任务结构体
任务结构体中包含了一个可以放置多种不同任务函数的函数指针,一个传入该任务函数的void*类型的参数;
/* 任务 */
typedef struct {
void *(*function)(void *); /* 函数指针,回调函数 */
void *arg; /* 上面函数的参数 */
} threadpool_task_t; /* 各子线程任务结构体 */二:线程池结构体
定义那么多关于线程的变量其实都是为了方便我们去管理线程。
结构体 threadpool_t 中包含线程池状态信息,任务队列信息以及多线程操作中的互斥锁;
- 线程池状态信息:描述当前线程池的基本信息,如是否开启、最小线程数、最大线程数、存活线程数、忙线程数、待销毁线程数等… …
- 任务队列信息:描述当前任务队列基本信息,如最大任务数、队列不为满条件变量、队列不为空条件变量等… …
- 多线程互斥锁:保证在同一时间点上只有一个线程在任务队列中取任务并修改任务队列信息、修改线程池信息;
/* 描述线程池相关信息 */
struct threadpool_t {
pthread_mutex_t lock; /* 用于锁住本结构体 */
pthread_mutex_t thread_counter; /* 记录忙状态线程个数de琐 -- busy_thr_num */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_full; /* 当任务队列满时,添加任务的线程阻塞,等待此条件变量 */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_empty; /* 任务队列里不为空时,通知等待任务的线程 */
pthread_t *threads; /* 存放线程池中每个线程的tid。数组 */
pthread_t adjust_tid; /* 存管理线程tid */
threadpool_task_t *task_queue; /* 任务队列(数组首地址) */
int min_thr_num; /* 线程池最小线程数 */
int max_thr_num; /* 线程池最大线程数 */
int live_thr_num; /* 当前存活线程个数 */
int busy_thr_num; /* 忙状态线程个数 */
int wait_exit_thr_num; /* 要销毁的线程个数 */
int queue_front; /* task_queue队头下标 */
int queue_rear; /* task_queue队尾下标 */
int queue_size; /* task_queue队中实际任务数 */
int queue_max_size; /* task_queue队列可容纳任务数上限 */
int shutdown; /* 标志位,线程池使用状态,true或false */
};/* 创建线程池 */
threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size)
{
int i;
threadpool_t *pool = NULL; /* 线程池 结构体 */
do {
if((pool = (threadpool_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_t))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc threadpool fail");
break; /*跳出do while*/
}
pool->min_thr_num = min_thr_num;
pool->max_thr_num = max_thr_num;
pool->busy_thr_num = 0;
pool->live_thr_num = min_thr_num; /* 活着的线程数 初值=最小线程数 */
pool->wait_exit_thr_num = 0;
pool->queue_size = 0; /* 有0个产品 */
pool->queue_max_size = queue_max_size; /* 最大任务队列数 */
pool->queue_front = 0;
pool->queue_rear = 0;
pool->shutdown = false; /* 不关闭线程池 */
/* 根据最大线程上限数, 给工作线程数组开辟空间, 并清零 */
pool->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);
if (pool->threads == NULL) {
printf("malloc threads fail");
break;
}
memset(pool->threads, 0, sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);
/* 给 任务队列 开辟空间 */
pool->task_queue = (threadpool_task_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_task_t)*queue_max_size);
if (pool->task_queue == NULL) {
printf("malloc task_queue fail");
break;
}
/* 初始化互斥琐、条件变量 */
if (pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->lock), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->thread_counter), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_empty), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_full), NULL) != 0)
{
printf("init the lock or cond fail");
break;
}
/* 启动 min_thr_num 个 work thread */
for (i = 0; i < min_thr_num; i++) {
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool); /*pool指向当前线程池*/
printf("start thread 0x%x...\n", (unsigned int)pool->threads[i]);
}
pthread_create(&(pool->adjust_tid), NULL, adjust_thread, (void *)pool); /* 创建管理者线程 */
return pool;
} while (0);
threadpool_free(pool); /* 前面代码调用失败时,释放poll存储空间 */
return NULL;
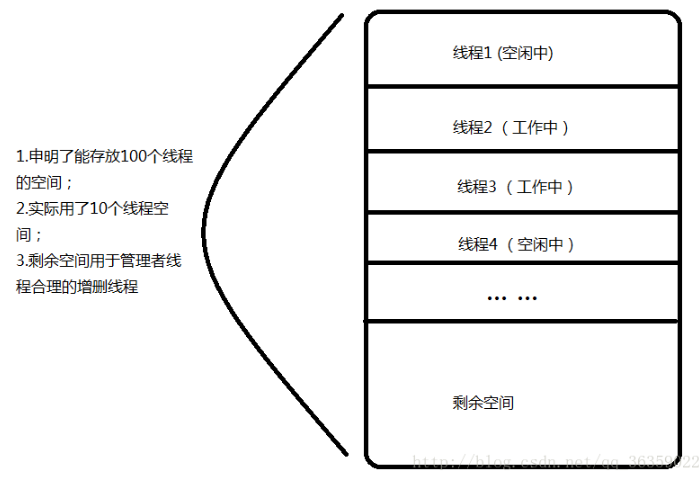
}三:线程数组
线程数组实际上是在线程池初始化时开辟的一段存放一堆线程 tid 的空间,在逻辑上形成一个池,里面放置着提前创建的线程;这段空间中包含了正在工作的线程,等待工作的线程(空闲线程),等待被销毁的线程,申明但没有初始化的线程空间。
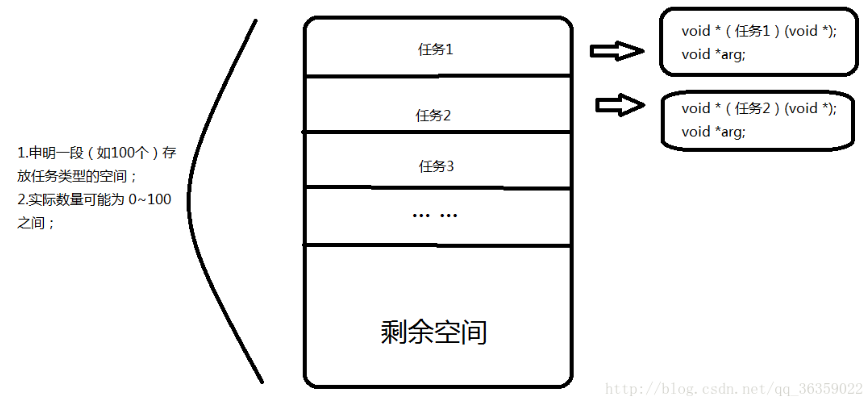
四:任务队列
任务队列的存在形式与线程数组相似;在线程池初始化时根据传入的最大任务数开辟空间;当服务器前方后请求到来后,分类并打包消息成为任务,将任务放入任务队列并通知空闲线程来取;不同之处在于任务队列有明显的先后顺序,先进先出;而线程数组中的线程则是一个竞争关系去拿到互斥锁争取任务;
/*向线程池的任务队列中添加一个任务*/
int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void*(*function)(void *arg), void *arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
/* ==为真,队列已经满, 调wait阻塞 */
while ((pool->queue_size == pool->queue_max_size) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_full), &(pool->lock));
}
/* 如果线程池处于关闭状态 */
if (pool->shutdown) {
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return 0;
}
/* 清空 工作线程 调用的回调函数 的参数arg */
if (pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg != NULL) {
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg = NULL;
}
/*添加任务到任务队列里*/
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].function = function;
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg = arg;
pool->queue_rear = (pool->queue_rear + 1) % pool->queue_max_size; /* 队尾指针移动, 模拟环形 */
pool->queue_size++; /* 向任务队列添加一个任务 */
/*添加完任务后,队列不为空,唤醒线程池中 等待处理任务的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return 0;
}五:管理者线程
作为线程池的管理者,该线程的主要功能包括:检查线程池内线程的存活状态,工作状态;负责根据服务器当前的请求状态去动态的增加或删除线程,保证线程池中的线程数量维持在一个合理高效的平衡上;
它就是一个单独的线程,定时的去检查,根据我们的一个维持平衡算法去增删线程;
/* 管理线程 */
void *adjust_thread(void *threadpool)
{
int i;
threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t *)threadpool;
while (!pool->shutdown) {
sleep(DEFAULT_TIME); /*定时 对线程池管理*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
int queue_size = pool->queue_size; /* 关注 任务数 */
int live_thr_num = pool->live_thr_num; /* 存活 线程数 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
int busy_thr_num = pool->busy_thr_num; /* 忙着的线程数 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
/* 创建新线程 算法: 任务数大于最小线程池个数, 且存活的线程数少于最大线程个数时 如:30>=10 && 40<100*/
if (queue_size >= MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM && live_thr_num < pool->max_thr_num) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
int add = 0;
/*一次增加 DEFAULT_THREAD 个线程*/
for (i = 0; i < pool->max_thr_num && add < DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY
&& pool->live_thr_num < pool->max_thr_num; i++) {
if (pool->threads[i] == 0 || !is_thread_alive(pool->threads[i])) {
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool);
add++;
pool->live_thr_num++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
}
/* 销毁多余的空闲线程 算法:忙线程X2 小于 存活的线程数 且 存活的线程数 大于 最小线程数时*/
if ((busy_thr_num * 2) < live_thr_num && live_thr_num > pool->min_thr_num) {
/* 一次销毁DEFAULT_THREAD个线程, 隨機10個即可 */
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
pool->wait_exit_thr_num = DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY; /* 要销毁的线程数 设置为10 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
for (i = 0; i < DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY; i++) {
/* 通知处在空闲状态的线程, 他们会自行终止*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
}
}
}
return NULL;
}/* 线程是否存活 */
int is_thread_alive(pthread_t tid)
{
int kill_rc = pthread_kill(tid, 0); //发0号信号,测试线程是否存活
if (kill_rc == ESRCH) {
return false;
}
return true;
}六:释放 销毁
/* 释放线程池 */
int threadpool_free(threadpool_t *pool)
{
if (pool == NULL) {
return -1;
}
if (pool->task_queue) {
free(pool->task_queue);
}
if (pool->threads) {
free(pool->threads);
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->thread_counter));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_full));
}
free(pool);
pool = NULL;
return 0;
}/* 销毁线程池 */
int threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int i;
if (pool == NULL) {
return -1;
}
pool->shutdown = true;
/*先销毁管理线程*/
pthread_join(pool->adjust_tid, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < pool->live_thr_num; i++) {
/*通知所有的空闲线程*/
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
}
for (i = 0; i < pool->live_thr_num; i++) {
pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL);
}
threadpool_free(pool);
return 0;
}案例代码详解
一:各模块流程分析



二:具体代码实现
/* threadpool.c */
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include "threadpool.h"
#define DEFAULT_TIME 10 /*10s检测一次*/
#define MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM 10 /*如果queue_size > MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM 添加新的线程到线程池*/
#define DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY 10 /*每次创建和销毁线程的个数*/
#define true 1
#define false 0
typedef struct {
void *(*function)(void *); /* 函数指针,回调函数 */
void *arg; /* 上面函数的参数 */
} threadpool_task_t; /* 各子线程任务结构体 */
/* 描述线程池相关信息 */
struct threadpool_t {
pthread_mutex_t lock; /* 用于锁住本结构体 */
pthread_mutex_t thread_counter; /* 记录忙状态线程个数de琐 -- busy_thr_num */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_full; /* 当任务队列满时,添加任务的线程阻塞,等待此条件变量 */
pthread_cond_t queue_not_empty; /* 任务队列里不为空时,通知等待任务的线程 */
pthread_t *threads; /* 存放线程池中每个线程的tid。数组 */
pthread_t adjust_tid; /* 存管理线程tid */
threadpool_task_t *task_queue; /* 任务队列(数组首地址) */
int min_thr_num; /* 线程池最小线程数 */
int max_thr_num; /* 线程池最大线程数 */
int live_thr_num; /* 当前存活线程个数 */
int busy_thr_num; /* 忙状态线程个数 */
int wait_exit_thr_num; /* 要销毁的线程个数 */
int queue_front; /* task_queue队头下标 */
int queue_rear; /* task_queue队尾下标 */
int queue_size; /* task_queue队中实际任务数 */
int queue_max_size; /* task_queue队列可容纳任务数上限 */
int shutdown; /* 标志位,线程池使用状态,true或false */
};
void *threadpool_thread(void *threadpool);
void *adjust_thread(void *threadpool);
int is_thread_alive(pthread_t tid);
int threadpool_free(threadpool_t *pool);
//threadpool_create(3,100,100);
threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size)
{
int i;
threadpool_t *pool = NULL; /* 线程池 结构体 */
do {
if((pool = (threadpool_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_t))) == NULL) {
printf("malloc threadpool fail");
break; /*跳出do while*/
}
pool->min_thr_num = min_thr_num;
pool->max_thr_num = max_thr_num;
pool->busy_thr_num = 0;
pool->live_thr_num = min_thr_num; /* 活着的线程数 初值=最小线程数 */
pool->wait_exit_thr_num = 0;
pool->queue_size = 0; /* 有0个产品 */
pool->queue_max_size = queue_max_size; /* 最大任务队列数 */
pool->queue_front = 0;
pool->queue_rear = 0;
pool->shutdown = false; /* 不关闭线程池 */
/* 根据最大线程上限数, 给工作线程数组开辟空间, 并清零 */
pool->threads = (pthread_t *)malloc(sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);
if (pool->threads == NULL) {
printf("malloc threads fail");
break;
}
memset(pool->threads, 0, sizeof(pthread_t)*max_thr_num);
/* 给 任务队列 开辟空间 */
pool->task_queue = (threadpool_task_t *)malloc(sizeof(threadpool_task_t)*queue_max_size);
if (pool->task_queue == NULL) {
printf("malloc task_queue fail");
break;
}
/* 初始化互斥琐、条件变量 */
if (pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->lock), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_mutex_init(&(pool->thread_counter), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_empty), NULL) != 0
|| pthread_cond_init(&(pool->queue_not_full), NULL) != 0)
{
printf("init the lock or cond fail");
break;
}
/* 启动 min_thr_num 个 work thread */
for (i = 0; i < min_thr_num; i++) {
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool); /*pool指向当前线程池*/
printf("start thread 0x%x...\n", (unsigned int)pool->threads[i]);
}
pthread_create(&(pool->adjust_tid), NULL, adjust_thread, (void *)pool); /* 创建管理者线程 */
return pool;
} while (0);
threadpool_free(pool); /* 前面代码调用失败时,释放poll存储空间 */
return NULL;
}
/* 向线程池中 添加一个任务 */
//threadpool_add(thp, process, (void*)&num[i]); /* 向线程池中添加任务 process: 小写---->大写*/
int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void*(*function)(void *arg), void *arg)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
/* ==为真,队列已经满, 调wait阻塞 */
while ((pool->queue_size == pool->queue_max_size) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_full), &(pool->lock));
}
/* 如果线程池处于关闭状态 */
if (pool->shutdown) {
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return 0;
}
/* 清空 工作线程 调用的回调函数 的参数arg */
if (pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg != NULL) {
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg = NULL;
}
/*添加任务到任务队列里*/
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].function = function;
pool->task_queue[pool->queue_rear].arg = arg;
pool->queue_rear = (pool->queue_rear + 1) % pool->queue_max_size; /* 队尾指针移动, 模拟环形 */
pool->queue_size++; /* 向任务队列添加一个任务 */
/*添加完任务后,队列不为空,唤醒线程池中 等待处理任务的线程*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return 0;
}
/* 线程池中各个工作线程 */
void *threadpool_thread(void *threadpool)
{
threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t *)threadpool;
threadpool_task_t task;
while (true) {
/* Lock must be taken to wait on conditional variable */
/*刚创建出线程,等待任务队列里有任务,否则阻塞等待任务队列里有任务后再唤醒接收任务*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
/*queue_size == 0 说明没有任务,调 wait 阻塞在条件变量上, 若有任务,跳过该while*/
while ((pool->queue_size == 0) && (!pool->shutdown)) {
printf("thread 0x%x is waiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_cond_wait(&(pool->queue_not_empty), &(pool->lock));
/*清除指定数目的空闲线程,如果要结束的线程个数大于0,结束线程*/
if (pool->wait_exit_thr_num > 0) {
pool->wait_exit_thr_num--;
/*如果线程池里线程个数大于最小值时可以结束当前线程*/
if (pool->live_thr_num > pool->min_thr_num) {
printf("thread 0x%x is exiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pool->live_thr_num--;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
}
/*如果指定了true,要关闭线程池里的每个线程,自行退出处理---销毁线程池*/
if (pool->shutdown) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
printf("thread 0x%x is exiting\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_detach(pthread_self());
pthread_exit(NULL); /* 线程自行结束 */
}
/*从任务队列里获取任务, 是一个出队操作*/
task.function = pool->task_queue[pool->queue_front].function;
task.arg = pool->task_queue[pool->queue_front].arg;
pool->queue_front = (pool->queue_front + 1) % pool->queue_max_size; /* 出队,模拟环形队列 */
pool->queue_size--;
/*通知可以有新的任务添加进来*/
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_full));
/*任务取出后,立即将 线程池琐 释放*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
/*执行任务*/
printf("thread 0x%x start working\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter)); /*忙状态线程数变量琐*/
pool->busy_thr_num++; /*忙状态线程数+1*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
(*(task.function))(task.arg); /*执行回调函数任务*/
//task.function(task.arg); /*执行回调函数任务*/
/*任务结束处理*/
printf("thread 0x%x end working\n", (unsigned int)pthread_self());
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
pool->busy_thr_num--; /*处理掉一个任务,忙状态数线程数-1*/
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
/* 管理线程 */
void *adjust_thread(void *threadpool)
{
int i;
threadpool_t *pool = (threadpool_t *)threadpool;
while (!pool->shutdown) {
sleep(DEFAULT_TIME); /*定时 对线程池管理*/
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
int queue_size = pool->queue_size; /* 关注 任务数 */
int live_thr_num = pool->live_thr_num; /* 存活 线程数 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
int busy_thr_num = pool->busy_thr_num; /* 忙着的线程数 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
/* 创建新线程 算法: 任务数大于最小线程池个数, 且存活的线程数少于最大线程个数时 如:30>=10 && 40<100*/
if (queue_size >= MIN_WAIT_TASK_NUM && live_thr_num < pool->max_thr_num) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
int add = 0;
/*一次增加 DEFAULT_THREAD 个线程*/
for (i = 0; i < pool->max_thr_num && add < DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY
&& pool->live_thr_num < pool->max_thr_num; i++) {
if (pool->threads[i] == 0 || !is_thread_alive(pool->threads[i])) {
pthread_create(&(pool->threads[i]), NULL, threadpool_thread, (void *)pool);
add++;
pool->live_thr_num++;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
}
/* 销毁多余的空闲线程 算法:忙线程X2 小于 存活的线程数 且 存活的线程数 大于 最小线程数时*/
if ((busy_thr_num * 2) < live_thr_num && live_thr_num > pool->min_thr_num) {
/* 一次销毁DEFAULT_THREAD个线程, 隨機10個即可 */
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
pool->wait_exit_thr_num = DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY; /* 要销毁的线程数 设置为10 */
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
for (i = 0; i < DEFAULT_THREAD_VARY; i++) {
/* 通知处在空闲状态的线程, 他们会自行终止*/
pthread_cond_signal(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
int threadpool_destroy(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int i;
if (pool == NULL) {
return -1;
}
pool->shutdown = true;
/*先销毁管理线程*/
pthread_join(pool->adjust_tid, NULL);
for (i = 0; i < pool->live_thr_num; i++) {
/*通知所有的空闲线程*/
pthread_cond_broadcast(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
}
for (i = 0; i < pool->live_thr_num; i++) {
pthread_join(pool->threads[i], NULL);
}
threadpool_free(pool);
return 0;
}
int threadpool_free(threadpool_t *pool)
{
if (pool == NULL) {
return -1;
}
if (pool->task_queue) {
free(pool->task_queue);
}
if (pool->threads) {
free(pool->threads);
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->lock));
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
pthread_mutex_destroy(&(pool->thread_counter));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_empty));
pthread_cond_destroy(&(pool->queue_not_full));
}
free(pool);
pool = NULL;
return 0;
}
int threadpool_all_threadnum(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int all_threadnum = -1; // 总线程数
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->lock));
all_threadnum = pool->live_thr_num; // 存活线程数
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->lock));
return all_threadnum;
}
int threadpool_busy_threadnum(threadpool_t *pool)
{
int busy_threadnum = -1; // 忙线程数
pthread_mutex_lock(&(pool->thread_counter));
busy_threadnum = pool->busy_thr_num;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&(pool->thread_counter));
return busy_threadnum;
}
int is_thread_alive(pthread_t tid)
{
int kill_rc = pthread_kill(tid, 0); //发0号信号,测试线程是否存活
if (kill_rc == ESRCH) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
/*测试*/
#if 1
/* 线程池中的线程,模拟处理业务 */
void *process(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 0x%x working on task %d\n ",(unsigned int)pthread_self(),(int)arg);
sleep(1); //模拟 小---大写
printf("task %d is end\n",(int)arg);
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
/*threadpool_t *threadpool_create(int min_thr_num, int max_thr_num, int queue_max_size);*/
threadpool_t *thp = threadpool_create(3,100,100); /*创建线程池,池里最小3个线程,最大100,队列最大100*/
printf("pool inited");
//int *num = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*20);
int num[20], i;
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
num[i] = i;
printf("add task %d\n",i);
/*int threadpool_add(threadpool_t *pool, void*(*function)(void *arg), void *arg) */
threadpool_add(thp, process, (void*)&num[i]); /* 向线程池中添加任务 */
}
sleep(10); /* 等子线程完成任务 */
threadpool_destroy(thp);
return 0;
}
#endif