个人简介:Java领域新星创作者;阿里云技术博主、星级博主、专家博主;正在Java学习的路上摸爬滚打,记录学习的过程~
个人主页:.29.的博客
学习社区:进去逛一逛~

资源操作:Spring Resources
- 一、Resource接口
- 🚀 Resource接口实现类:
- ⚪UrlResource
- ⚪ClassPathResource
- ⚪FileSystemResource
- ⚪ServletContextResource
- ⚪InputStreamResource
- ⚪ByteArrayResource
- 二、ResourceLoader 接口
- 三、ResourceLoaderAware接口
- 四、让Spring为Bean实例依赖注入资源(建议)
一、Resource接口
Spring 的 Resource 接口位于 org.springframework.core.io 中。 旨在成为一个更强大的接口,用于抽象对低级资源的访问。以下显示了Resource接口定义的方法
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
boolean isReadable();
boolean isOpen();
boolean isFile();
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
ReadableByteChannel readableChannel() throws IOException;
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
其中一些重要的方法:
getInputStream(): 找到并打开资源,返回一个InputStream以从资源中读取。预计每次调用都会返回一个新的InputStream(),调用者有责任关闭每个流exists(): 返回一个布尔值,表明某个资源是否以物理形式存在isOpen: 返回一个布尔值,指示此资源是否具有开放流的句柄。如果为true,InputStream就不能够多次读取,只能够读取一次并且及时关闭以避免内存泄漏。对于所有常规资源实现,返回false,但是InputStreamResource除外。getDescription(): 返回资源的描述,用来输出错误的日志。这通常是完全限定的文件名或资源的实际URL。
其他方法:
- isReadable(): 表明资源的目录读取是否通过getInputStream()进行读取。
- isFile(): 表明这个资源是否代表了一个文件系统的文件。
- getURL(): 返回一个URL句柄,如果资源不能够被解析为URL,将抛出IOException
- getURI(): 返回一个资源的URI句柄
- getFile(): 返回某个文件,如果资源不能够被解析称为绝对路径,将会抛出FileNotFoundException
- lastModified(): 资源最后一次修改的时间戳
- createRelative(): 创建此资源的相关资源
- getFilename(): 资源的文件名是什么 例如:最后一部分的文件名 myfile.txt
🚀 Resource接口实现类:
⚪UrlResource
Resource的一个实现类,用来访问网络资源,它支持URL的绝对路径。
http:------该前缀用于访问基于HTTP协议的网络资源。
ftp:------该前缀用于访问基于FTP协议的网络资源
file: ------该前缀用于从文件系统中读取资源
案例:
import org.springframework.core.io.UrlResource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-01 9:11
*/
public class urlResources {
public static void loadAndReadUrlResources(String path){
UrlResource url = null;
try {
url = new UrlResource(path);
//获取资源名
System.out.println(url.getURL());
System.out.println(url.getFilename());
//获取资源描述
System.out.println(url.getDescription());
//获取资源内容
System.out.println(url.getInputStream().read());
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//访问网络资源,测试UrlResource功能
// loadAndReadUrlResources("http://www.baidu.com");
//方法二:读取文件获取路径
loadAndReadUrlResources("file:baidu.txt");
}
}
注意:file:前缀,读取的是根路径下的类容!
http:前缀测试结果:
file:前缀测试结果:
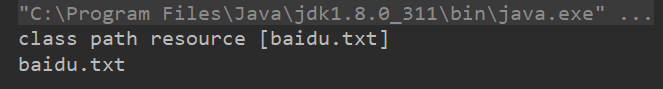
⚪ClassPathResource
ClassPathResource 用来访问类加载路径下的资源,相对于其他的 Resource 实现类,其主要优势是方便访问类加载路径里的资源,尤其对于 Web 应用,ClassPathResource 可自动搜索位于 classes 下的资源文件,无须使用绝对路径访问。
案例:
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 20:20
*/
//测试ClassPathResource();
public class ClassPathResourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
loadClassPathResource("baidu.txt");
}
public static void loadClassPathResource(String path){
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(path);
//获取文件信息
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
//获取文件内容
try {
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
if(inputStream.read(bytes) != -1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
⚪FileSystemResource
Spring 提供的 FileSystemResource 类用于访问文件系统资源,使用 FileSystemResource 来访问文件系统资源并没有太大的优势,因为 Java 提供的 File 类也可用于访问文件系统资源。
案例:
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 20:32
*/
public class FileSystemResourceDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
loadFileSystemResource("d:\\haojin.txt"); //path是绝对路径
}
public static void loadFileSystemResource(String path){
FileSystemResource fileSystemResource = new FileSystemResource(path);
//获取系统资源的信息
System.out.println(fileSystemResource.getFilename());
System.out.println(fileSystemResource.getDescription());
//获取资源内容
try {
InputStream inputStream = fileSystemResource.getInputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
if(inputStream.read(bytes) != 1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
⚪ServletContextResource
这是ServletContext资源的Resource实现,它解释相关Web应用程序根目录中的相对路径。它始终支持流(stream)访问和URL访问,但只有在扩展Web应用程序存档且资源实际位于文件系统上时才允许java.io.File访问。无论它是在文件系统上扩展还是直接从JAR或其他地方(如数据库)访问,实际上都依赖于Servlet容器。
⚪InputStreamResource
InputStreamResource 是给定的输入流(InputStream)的Resource实现。它的使用场景在没有特定的资源实现的时候使用(感觉和@Component 的适用场景很相似)。与其他Resource实现相比,这是已打开资源的描述符。 因此,它的isOpen()方法返回true。如果需要将资源描述符保留在某处或者需要多次读取流,请不要使用它。
⚪ByteArrayResource
字节数组的Resource实现类。通过给定的数组创建了一个ByteArrayInputStream。它对于从任何给定的字节数组加载内容非常有用,而无需求助于单次使用的InputStreamResource。
二、ResourceLoader 接口
Spring将采用和ApplicationContext相同的策略来访问资源。也就是说,如果ApplicationContext是FileSystemXmlApplicationContext,res就是FileSystemResource实例;如果ApplicationContext是ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,res就是ClassPathResource实例
当Spring应用需要进行资源访问时,实际上并不需要直接使用Resource实现类,而是调用ResourceLoader实例的getResource()方法来获得资源,ReosurceLoader将会负责选择Reosurce实现类,也就是确定具体的资源访问策略,从而将应用程序和具体的资源访问策略分离开来
案例:
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.FileSystemXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 20:53
*/
public class ResourceLoaderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
//示例一:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext();
Resource resource = context.getResource("baidu.txt");
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------");
//示例二:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext context2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext();
Resource resource2 = context.getResource("baidu.txt");
System.out.println(resource2.getFilename());
System.out.println(resource2.getDescription());
}
}
三、ResourceLoaderAware接口
ResourceLoaderAware接口实现类的实例将获得一个ResourceLoader的引用,ResourceLoaderAware接口也提供了一个setResourceLoader()方法,该方法将由Spring容器负责调用,Spring容器会将一个ResourceLoader对象作为该方法的参数传入。
如果把实现ResourceLoaderAware接口的Bean类部署在Spring容器中,Spring容器会将自身当成ResourceLoader作为setResourceLoader()方法的参数传入。由于ApplicationContext的实现类都实现了ResourceLoader接口,Spring容器自身完全可作为ResorceLoader使用。
案例:
1.创建接口实现类:
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 21:08
*/
public class testBean implements ResourceLoaderAware {
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
//实现ResourceLoaderAware接口必须实现的方法
//如果把该Bean部署在Spring容器中,该方法将会有Spring容器负责调用。
//SPring容器调用该方法时,Spring会将自身作为参数传给该方法。
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
//返回resourceLoader对象的方法
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader(){
return this.resourceLoader;
}
}
2.配置实现类的bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "testBean" class="com.haojin.spring.resources.ResourceLoaderAwareDemo.testBean"></bean>
</beans>
3.测试:
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 21:12
*/
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
testBean testBean = context.getBean("testBean", testBean.class);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = testBean.getResourceLoader();
System.out.println("Spring容器将自身注入到ResourceLoaderAware Bean 中:" + (context == resourceLoader));
}
}
四、让Spring为Bean实例依赖注入资源(建议)
当程序获取 Resource 实例时,总需要提供 Resource 所在的位置,不管通过 FileSystemResource 创建实例,还是通过 ClassPathResource 创建实例,或者通过 ApplicationContext 的 getResource() 方法获取实例,都需要提供资源位置。这意味着:资源所在的物理位置将被耦合到代码中,如果资源位置发生改变,则必须改写程序。因此,通常建议采用依赖注入,让 Spring 为 Bean 实例依赖注入资源。
案例:
1.创建依赖注入类,定义属性和方法:
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 21:36
*/
public class ResourceBean {
//Resource实现类对象
private Resource resource;
//对象的Getter() 和 Setter()
public Resource getResource() {
return resource;
}
public void setResource(Resource resource) {
this.resource = resource;
}
//输出资源信息的方法
public void parse(){
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
System.out.println(resource.getFilename());
}
}
2.创建spring配置文件,配置依赖注入:
利用依赖注入,以后只需要在配置文件中修改资源文件位置即可
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id = "resourceBean" class="com.haojin.spring.resources.DI.ResourceBean">
<property name="resource" value="baidu.txt"/>
</bean>
</beans>
3.测试:
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author .29.
* @create 2023-03-02 21:38
*/
public class testDI {
public static void main(String[] args){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
ResourceBean resourceBean = context.getBean("resourceBean", ResourceBean.class);
resourceBean.parse();
}
}