目录
1:静态资源
1.1:静态资源访问
1.2:静态资源源码解析-到WebMvcAutoConfiguration
2:Rest请求绑定(设置put和delete)
2.1:代码实例
2.2:源码分析到-WebMvcAutoConfiguration
3:请求参数处理
3.1:代码实例
3.2:转发重定向
3.2:源码分析到-DispatcherServlet
4:响应返回值处理
4.1:代码实例
4.2:源码分析到-DispatcherServlet
1:静态资源
1.1:静态资源访问
在springBoot项目中,我们首先来查看静态资源的访问位置,当我们配置项目,我们直接访问项目可以查看这些路径中的资源。
一个问题:
1:我们怎么知道静态资源放到哪里可以直接访问?
首先查看项目路径和配置文件如下
#默认静态资源访问路径 默认路径路径是/static(或/public或/resources或/META-INF/resources) #3.png路径错误访问不了
spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/**
##修改静态资源访问路径 http://localhost:8080/res/4.png 静态资源前边必须加 res 和文件路径无关
#配置自定义路径 欢迎页面进不来 需要http://localhost:8080/res/index.html
#spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/res/**
上边的下边的二选一配置即可
#自定义静态资源位置 add-mappings=false 禁用掉静态资源访问
spring.web.resources.add-mappings=true
#静态资源缓存 默认是秒
spring.web.resources.cache.period=1001
#自定义 静态资源缓存 会覆盖掉系统默认的静态资源路径
spring.web.resources.static-locations=classpath:/自定义静态资源路径/
#开启rest请求 WebMvcAutoConfiguration中查看源码
spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter.enabled=true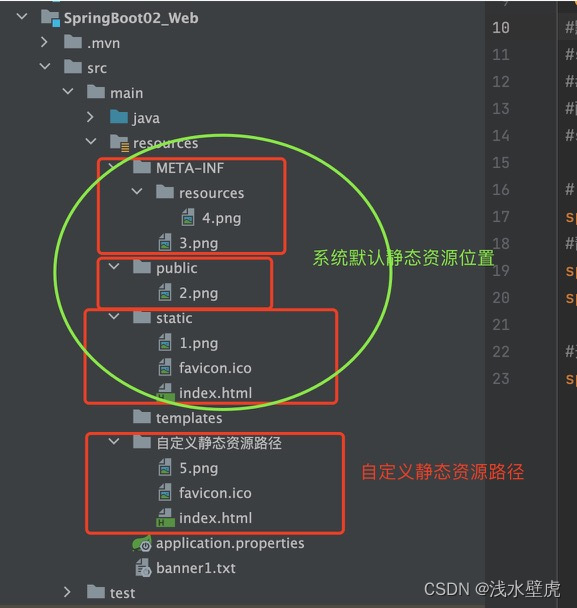
然后访问浏览器
http://localhost:8080/ 进入static下边的index.html
http://localhost:8080/1.png 或者2.png 4.png都可以访问,但是3.png不行
1.2:静态资源源码解析-到WebMvcAutoConfiguration
回到上边的问题,我们怎么知道静态资源应该放到哪里?可以顺利访问呢?
查看源码如下,主要看第一的解释,所以3.png的路径不对 访问不了
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
//第一:WebMvcProperties.class spring.mvc 配置
//默认静态资源访问路径 默认路径路径是/static(或/public或/resources或/META-INF/resources) 3.png路径错误访问不了
//spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/*
//修改静态资源访问路径 http://localhost:8080/res/4.png 静态资源前边必须加res,和文件路径无关,配置自定义路径,欢迎页面进不来
//#spring.mvc.static-path-pattern=/res/**
//第二:WebProperties.class spring.web 配置
// 自定义静态资源位置 add-mappings=false 禁用掉静态资源访问
// spring.web.resources.add-mappings=true
// 静态资源缓存 默认是秒
// spring.web.resources.cache.period=1001
// spring.web.resources.static-locations=classpath:/自定义静态资源路径/
// 开启rest请求 WebMvcAutoConfiguration中查看源码
// spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter.enabled=true
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, WebProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer, ServletContextAware {
//此处代码省略
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(WebProperties webProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties,
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider,
ObjectProvider<WebMvcAutoConfiguration.ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath,
ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) {
//在getResources() 可以看到默认的访问路径是
// private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
// "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
this.resourceProperties = webProperties.getResources();
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations;
this.mvcProperties.checkConfiguration();
}
//静态资源文件路径 处理方法
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> {
//resourceProperties.getStaticLocations() 自己不配置 默认是系统的静态资源路径
//resourceProperties.getStaticLocations() 自己配置的话自定义的文件路径
//spring.web.resources.static-locations=classpath:/自定义静态资源路径/
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION);
registration.addResourceLocations(resource);
}
});
}源码分析我们知道在WebMvcAutoConfiguration类中,默认了静态资源的位置,所以才可以直接访问的。如果自己配置了自定义的静态资源,那么系统默认的失效,以自己为准。
2:Rest请求绑定(设置put和delete)
2.1:代码实例
Java代码如下:
@RestController
public class RestControllerTest {
@GetMapping(value = "user")
public String get() {
System.out.println("get请求!");
return "get请求!";
}
@PostMapping(value = "user")
public String post() {
System.out.println("post请求!");
return "post请求!";
}
@PutMapping(value = "user")
public String put() {
System.out.println("put请求!");
return "put请求!";
}
@DeleteMapping(value = "user")
public String delete() {
System.out.println("delete请求!");
return "delete请求!";
}
}
html表单如下:
<form method="get" action="user">
<input type="submit" value="get提交">
</form>
<form method="post" action="user">
<input type="submit" value="post提交">
</form>
<form method="post" action="user">
<!-- 隐藏表单,设置除了get、post以外的表单属性,表单必须是post,name必须是_method-->
<input name="method" value="PUT" hidden="hidden">
<input type="submit" value="put提交">
</form>
<form method="post" action="user">
<!-- 隐藏表单,设置除了get、post以外的表单属性,表单必须是post,name必须是_method-->
<input name="method" value="DELETE" hidden="hidden">
<input type="submit" value="delete提交">
</form>
开启rest请求
#开启rest请求 WebMvcAutoConfiguration中查看源码
spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter.enabled=true结果如下:点击put,到后台的put的Controller
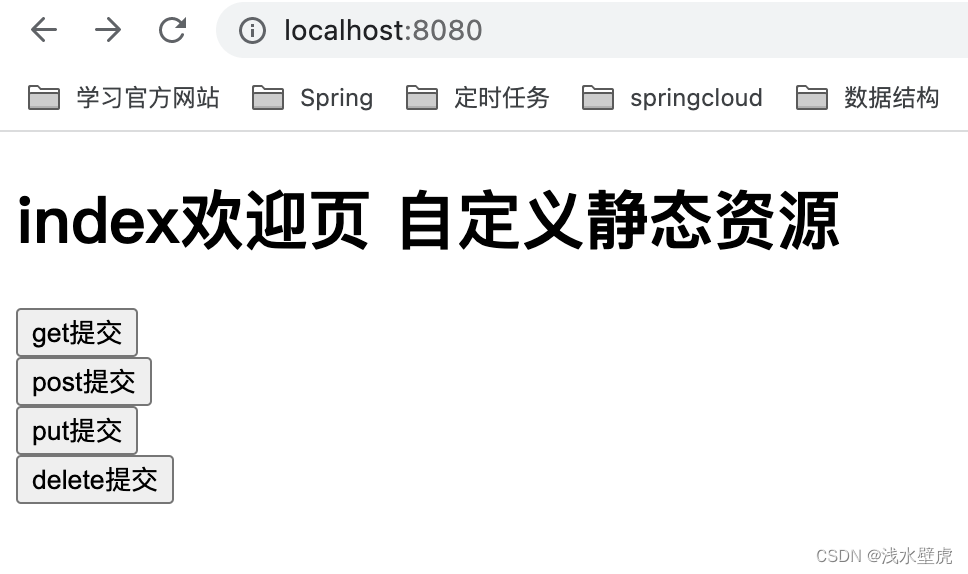
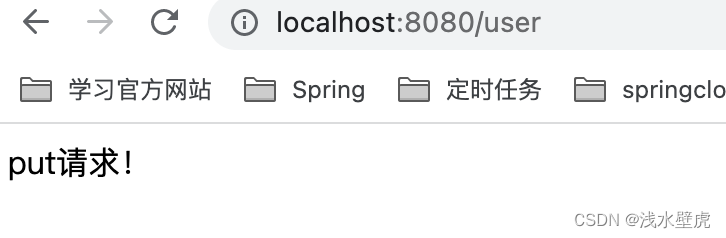
总结:表单要有隐藏域,name默认是_method,提交方式是post
2.2:源码分析到WebMvcAutoConfiguration
//如果没有HiddenHttpMethodFilter的bean
//如果没有开启配置 默认是spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter=false
//不会创建HiddenHttpMethodFilter 只有配置了true 才会执行下边的代码
//默认spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter=false 没有开启处理Rest的filter
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = "enabled")
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
//HiddenHttpMethodFilter 代码分析
/** 默认的name参数必须是_method */
public static final String DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM = "_method";
private String methodParam = DEFAULT_METHOD_PARAM;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest requestToUse = request;
//代码分析 form表单只有post才能设置 put delete请求
if ("POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && request.getAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_EXCEPTION_ATTRIBUTE) == null) {
//获取input标签中的 name= "_method" 的属性 这里是put delete
String paramValue = request.getParameter(this.methodParam);
if (StringUtils.hasLength(paramValue)) {
String method = paramValue.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
//大小写转换 装饰器模式 创建新的HttpMethodRequestWrapper 这里是装饰器模式request
//ALLOWED_METHODS=(delete,put,patch)
if (ALLOWED_METHODS.contains(method)) {
requestToUse = new HttpMethodRequestWrapper(request, method);
}
}
}
//执行过滤链 这里调用链模式
filterChain.doFilter(requestToUse, response);
}
//分割线 我的表单时name是method不是_method这个时候就需要我们配置自己的HiddenHttpMethodFilter
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){
HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
//设置自定义的name为method 这个时候会覆盖系统的_method
hiddenHttpMethodFilter.setMethodParam("method");
return hiddenHttpMethodFilter;
}
3:请求参数处理
3.1:代码实例
@RestController
public class 请求参数Controller {
/**
* 路径参数 @PathVariable
* 请求头 @RequestHeader
* 方法参数 @RequestParam
* cookie参数 @CookieValue
* 他们都能封装成map 但是map有缺陷 key想同会丢失参数
*
* @RequestParam Map<String, String> paramMap 会丢失key一致的参数 多个likes 只能保存一个
*
*/
//http://localhost:8080/t1/1/blog/test?name=张三&age=28&likes=语文&likes=数学
@GetMapping(value = "/t1/{id}/blog/{type}")
public Map t1(
@PathVariable("id") Integer id,//绑定指定的路径id到参数
@PathVariable("type") String type,//绑定指定的路径type到参数
@PathVariable Map<String,String> pathMap,//绑定所有的路径参数到Map
@RequestHeader("Accept") String accept, //绑定指定的head到参数
@RequestHeader Map<String,String> headMap, //绑定所有的head到Map
@RequestParam(value = "name",required = false) String name,//绑定指定参数
@RequestParam(value = "age",required = false) Integer age,//绑定指定参数
@RequestParam(value = "likes",required = false) List<String> likes,//绑定指定参数到likes
@RequestParam Map<String, String> paramMap, //绑定所有的参数到Map 因为是map类型 会丢失key一致的参数 比如like
@CookieValue(value = "__utma",required = false) String cookieId,
@CookieValue(value = "__utmv",required = false) Cookie cookie
) {
System.out.println("=======请求路径参数==========");
System.out.println("rest路径参数id:"+id);
System.out.println("rest路径参数type:"+type);
pathMap.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.println(key+"=="+value));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=======请求头参数==========");
System.out.println("rest路径head参数Accept:"+accept);
headMap.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key+"=="+value);
});
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=======请求参数==========");
System.out.println("rest路径请求参数name:"+name);
System.out.println("rest路径请求参数age:"+age);
for (String like : likes) {
System.out.println("rest路径请求参数like:"+like);
}
paramMap.forEach((key,value)->{
System.out.println(key+"=="+value);
});
System.out.println();
System.out.println("=======请求cookie==========");
System.out.println("rest路径请求参数cookie:"+cookieId);
System.out.println(cookie.getName()+":"+cookie.getValue());
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("请求","参数");
return map;
}
/**
* @RequestBody 获取post的请求体参数
*/
//http://localhost:8080/t2/2 body的参数postMan 自己创造
@PostMapping(value = "/t2/{id}")
public Map t2(
@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@RequestParam("name") String name,
@RequestBody String body //获取post的请求体参数
) {
System.out.println("=======post获取请求体==========");
System.out.println("rest路径参数id:"+id);
System.out.println("rest请求参数name:"+name);
System.out.println("rest请求body的参数:"+body);
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("请求","参数");
return map;
}
/**
* 矩阵变量 @PathVariable
* http://localhost:8080/t3/2;low=34;like=eng;like=yuwen
* http://localhost:8080/t3/1;low=34;likes=eng;likes=yuwen/2;demo=dd
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/t3/{path}/{path1}")
public Map t3(
@PathVariable("path") String path,
@PathVariable("path1") String path1,
@MatrixVariable(value = "low",pathVar = "path") String low,
@MatrixVariable(value = "likes",pathVar = "path") List<String> likes,
@MatrixVariable(value = "demo",pathVar = "path1") String demo
) {
System.out.println("=======get获取矩阵变量==========");
System.out.println("rest路径矩阵变量path:"+path);
System.out.println("rest路径矩阵变量path1:"+path1);
System.out.println("rest路径矩阵变量demo:"+demo);
System.out.println("rest路径矩阵变量low:"+low);
for (String like : likes) {
System.out.println("rest路径矩阵变量like:"+like);
}
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap();
map.put("请求","参数");
return map;
}
/**
* 请求参数转换实体
* http://localhost:8080/person?id=1&name=张三&date=2023-03-04 14:30:38&cat.id=2&cat.name=波斯猫
*/
@GetMapping("/person")
public Person get(Person person){
System.out.println(person);
return person;
}
}
3.2:转发重定向
@Controller
public class 转发重定向Controller {
/**
*
* http://localhost:8080/request1
* 转发测试 forward 不能使用@RestController
* @RequestAttribute(value = "name") 绑定转发的请求属性
*
* http://localhost:8080/request1
*/
@GetMapping("/request1")
public String request1(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("进入转发请求1");
request.setAttribute("name","中文");
return "forward:/request2";
}
@GetMapping("/request2")
@ResponseBody
public String request2(@RequestAttribute(value = "name") String name){
System.out.println("进入转发请求2");
System.out.println("获取转发的请求参数name:"+name);
return "转发";
}
/**
*
* http://localhost:8080/request11
*
* 参数的map、model 的数据会放到request域中,相当于setAttribute
*/
@GetMapping("/request11")
public String request11(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Map map, Model model){
System.out.println("进入转发请求11");
map.put("map","hello map");
model.addAttribute("model","hello model");
request.setAttribute("name","中文");
Cookie cookie=new Cookie("cookie","cookie_value");
response.addCookie(cookie);
return "forward:/request22";
}
@GetMapping("/request22")
@ResponseBody
public String request22(@RequestAttribute(value = "name") String name,HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("进入转发请求22");
System.out.println("获取转发的请求参数name:"+name);
System.out.println("request获取属性name:"+request.getAttribute("name"));
System.out.println("request获取属性map:"+request.getAttribute("map"));
System.out.println("request获取属性model:"+request.getAttribute("model"));
Cookie[] cookies = request.getCookies();
for (Cookie cookie : cookies) {
System.out.println(cookie.getName()+":"+cookie.getValue());
}
return "转发";
}
/**
* http://localhost:8080/request3
* 重定向测试 redirect
* @RequestAttribute(value = "name") 绑定指定的值
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/request3")
public String request3(HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println("进入重定向请求1");
request.setAttribute("name","中文");
return "redirect:request4";
}
@GetMapping("/request4")
@ResponseBody
public String request4(String name,String aa){
System.out.println("进入重定向请求2");
System.out.println("获取重定向的请求参数name:"+name);
return "重定向";
}
}
3.2:源码分析到-DispatcherServlet
我们以一下代码做分析,将请求参数封装到Person
/**
* 请求参数转换实体
* http://localhost:8080/person?id=1&name=张三&date=2023-03-04 14:30:38&cat.id=2&cat.name=波斯猫
*/
@GetMapping("/person")
public Person get(Person person){
//这一行输出代码打断点 debug运行
System.out.println(person);
return person;
}在源码分析之前,我想知道请求流程是怎么处理的,请求的参数是怎么绑定到我们指定的参数、或者pojo、或者map中的
我们先上一张SpringWeb的执行流程图,然后格局源码分析。
我们查看源码
1:调用DispatcherServlet的doService()方法,DispatcherServlet也是个Servlet,从继承关系层层调用到doService方法
2:doService()方法调用了doDispatch(request, response);这个方法是核心,我们查看代码分析
从源码结合上边的流程图可以详细的看到具体流程
//核心代码
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
//检查是不是Multipart 文件上传的请求
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 确认当前的请求 从5个handlerMapping中匹配到合适
//这里就是RequestHandlerMapping 因为使用了@RequestMapping注解
//这5个handlerMapping 分别是Request、welcome、BeanNamesUrl、RouterFunction等handlerMapping
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 根据前边的mappedHandler 找到HandlerAdapter
//从4个中Adapter找到了RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 还是因为使用了@RequestMapping注解
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
//执行拦截器的Pre方法 在Controller前执行
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
//执行真正的controller方法 反射调用
//因为反射知道了Controller方法的参数和类型 所以我们就可以把request的参数
//通过反射绑定到Controller的方法参数中 这就是核心原理
//执行流程 核心方法 重点五颗星 具体的跳转流程已经标志 不做代码截取
//handle->(没哈意思,只是跳转)
handleInternal->(没哈意思,只是跳转)
invokeHandlerMethod->(加载参数解析器27个、返回值参数解析器15个)
invokeAndHandle->(调用执行invokeForRequest方法,获取返回值)
invokeForRequest->(调用执行Controller方法,获取返回值)执行绑定参数方法
getMethodArgumentValues->(对方法的参数遍历 调用参数绑定方法) 返回绑定好的pojo
resolveArgument(逐个参数进行绑定,调用指定的参数解析器) 绑定到Pojo 返回
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
//调用拦截器的后置方法PostHandle controller后执行执行
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
//调用拦截器的after方法 最终执行
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
handlerMapping(5个)和handlerAdapters(4个)
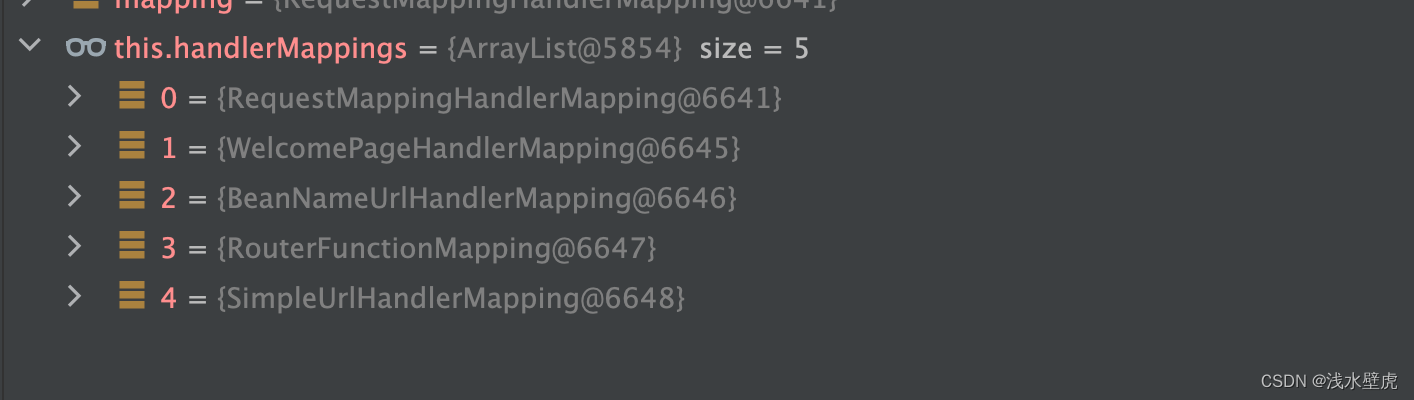
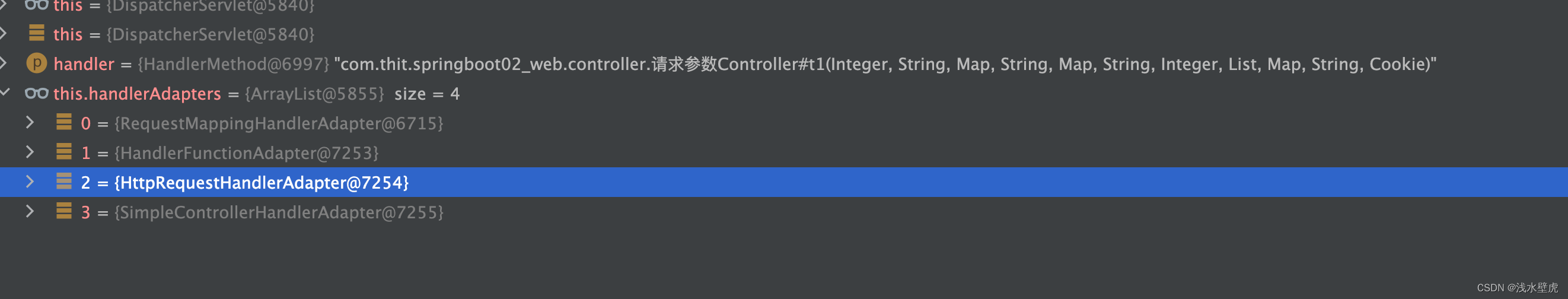
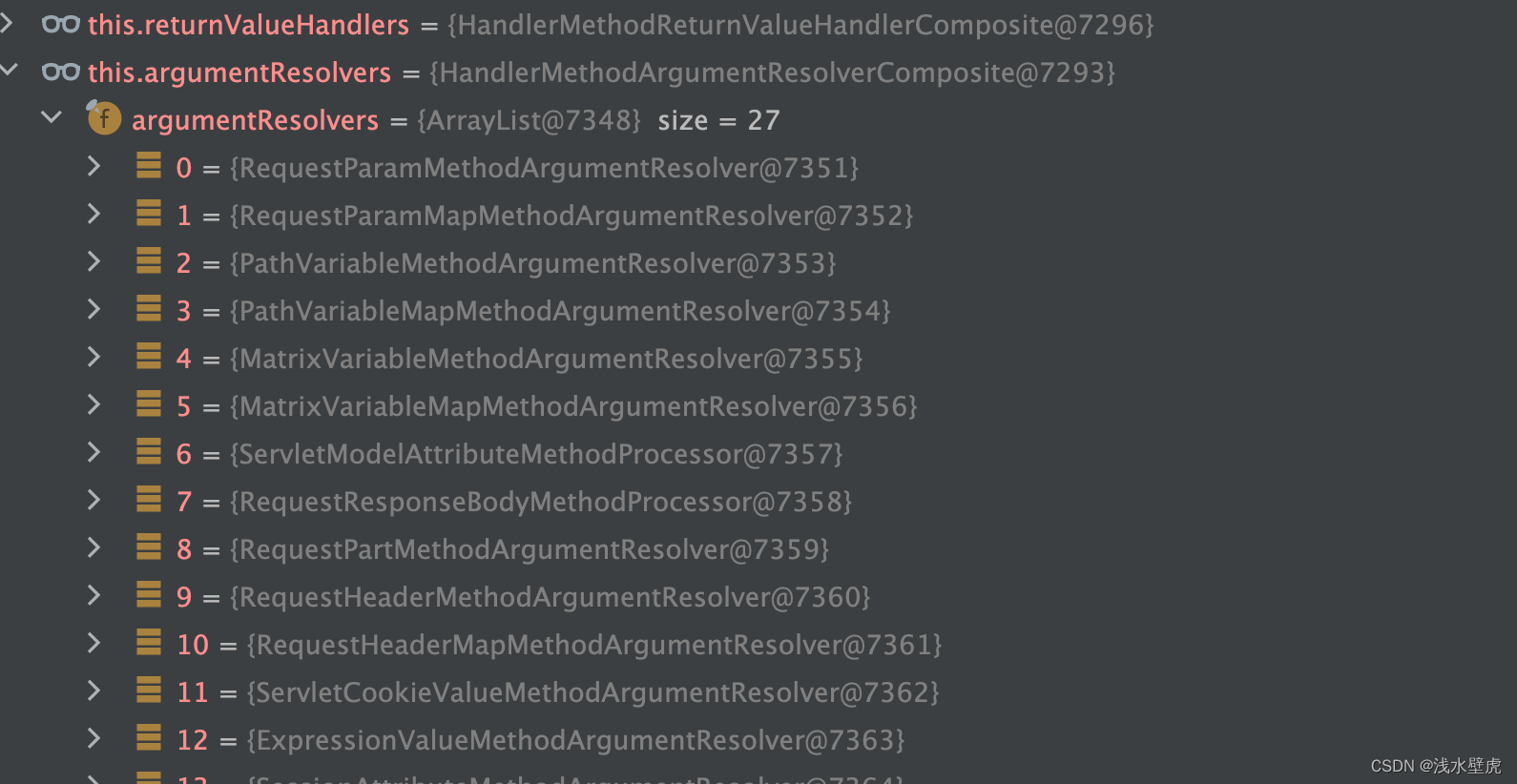
参数解析器(27个,对应各种注解比如@PathVariable、 @RequestHeader、@RequestParam、@CookieValue等注解的解析器)
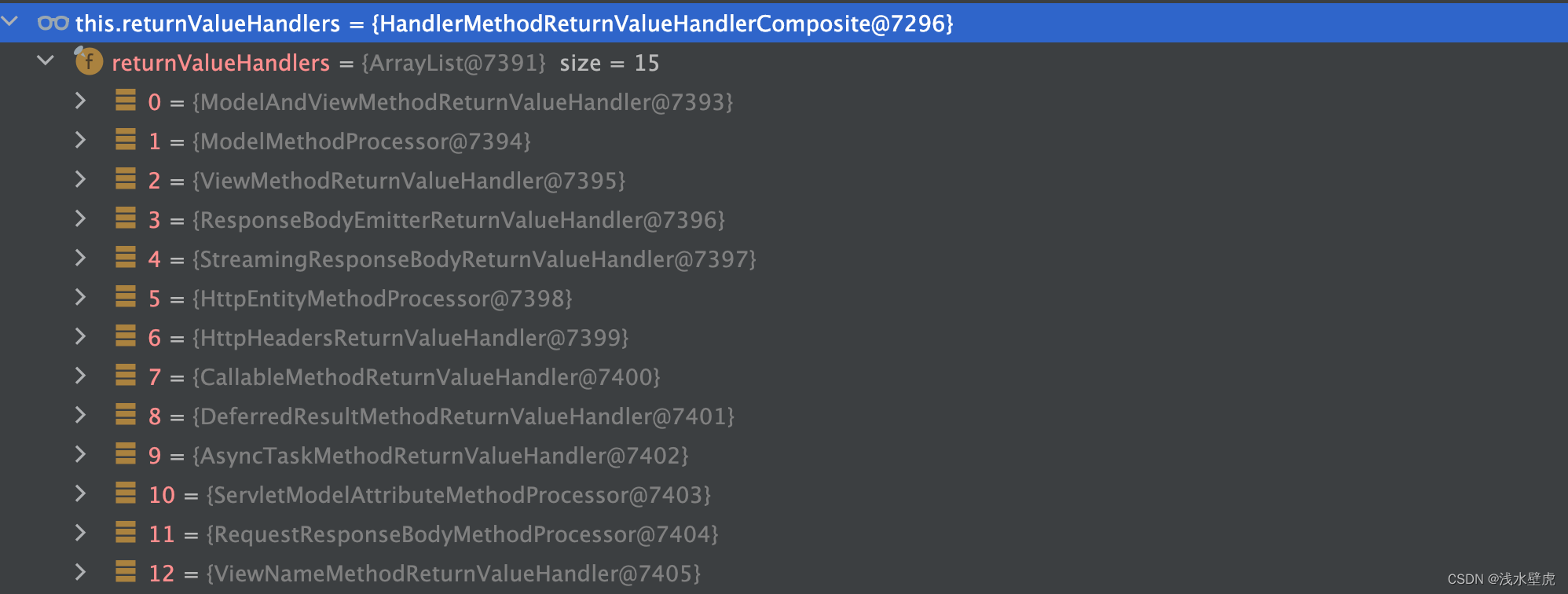
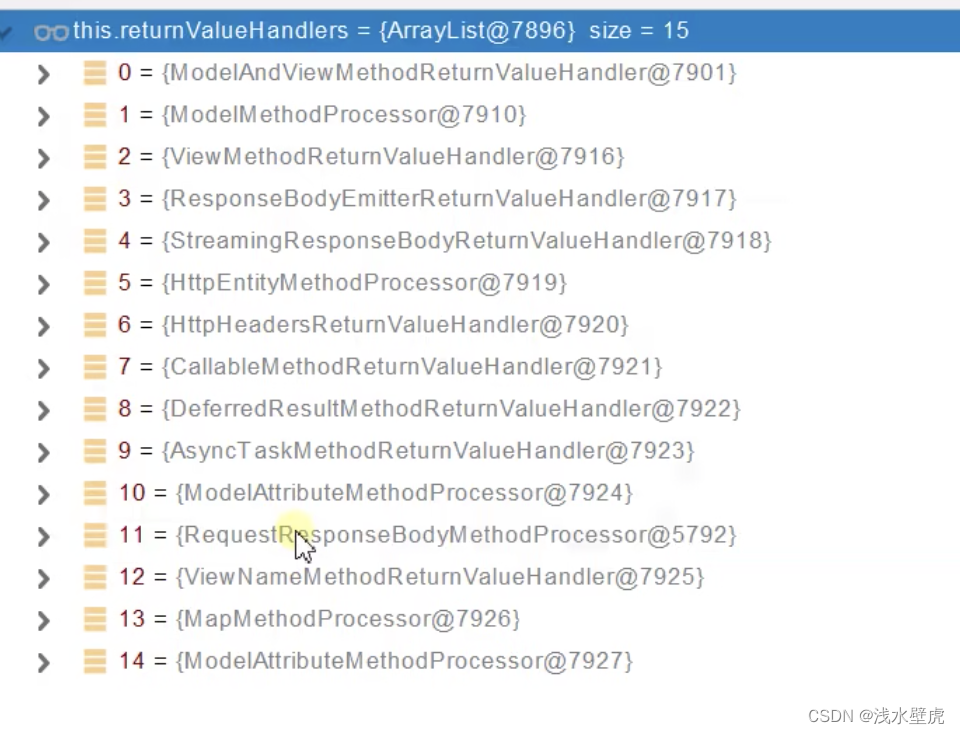
返回值解析器(15个,对应ModelAndView、model、@responseBody的注解的解析器)
4:响应返回值处理
主要分析响应的返回值怎么在DispatcherServlet的doDispatch()方法中的执行流程
4.1:代码实例
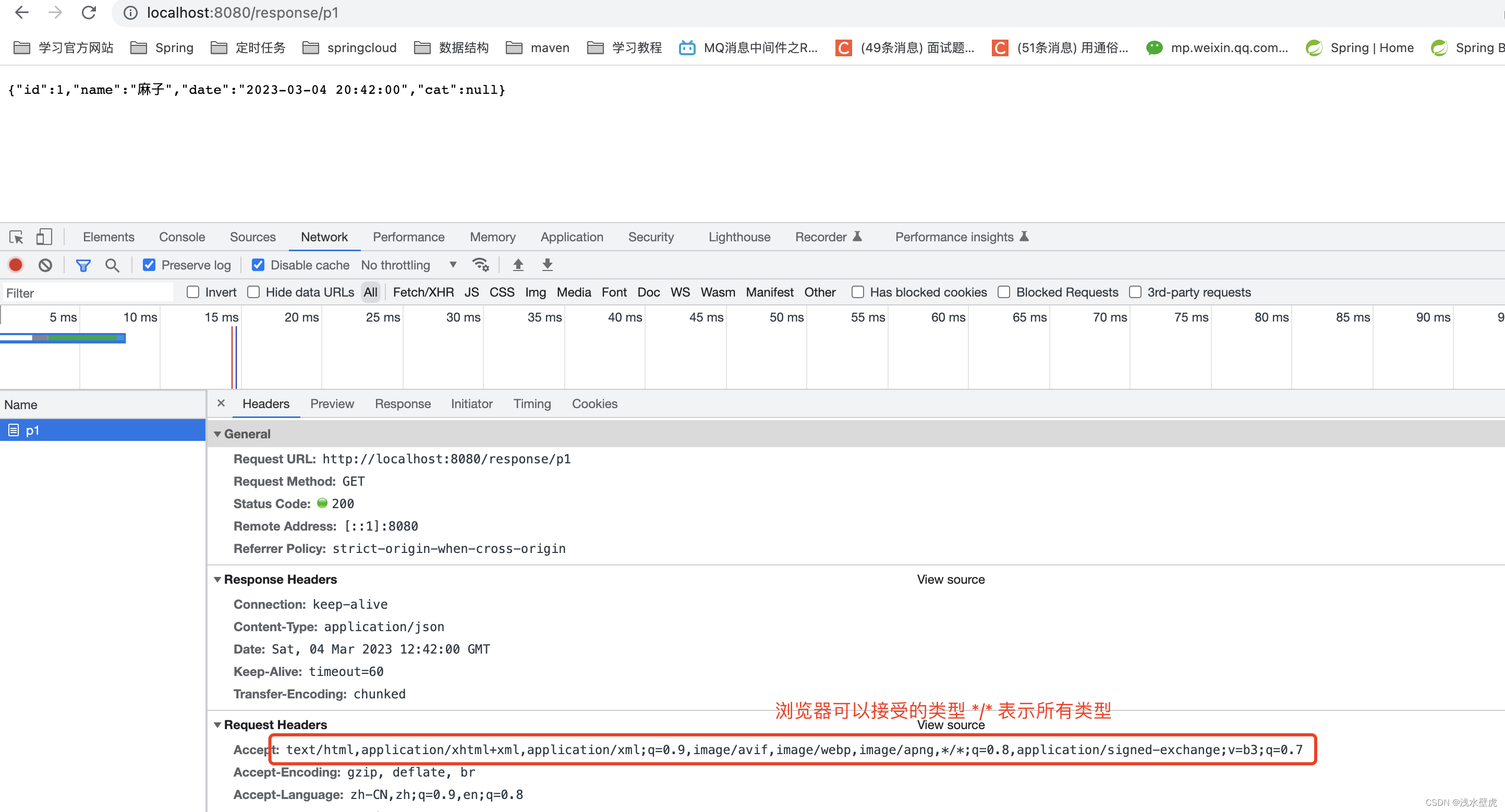
/**
* http://localhost:8080/response/p1
*
* @ResponseBody 注解返回json
*/
@GetMapping("/response/p1")
@ResponseBody
public Person p1(){
Person person=new Person();
person.setId(1);
person.setName("麻子");
person.setDate(new Date());
return person;
}
4.2:源码分析到-DispatcherServlet
源码分析第一步:执行controller方法,得到返回值。
源码分析第二步:根据返回值找到15个返回值处理器,遍历根据注解@ResponseBody,找到合适的返回值处理器
源码分析第三步:根据返回值处理器,去他的方法里边处理返回值
源码分析第四步:选择消息转换器(转换器很多,这里是jackson的消息转换器,把pojo转换成json)
//第一步 :执行controller方法,得到返回值
public void invokeAndHandle (ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object...providedArgs) throws Exception {
//这里就是执行controller方法得到的返回值
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
setResponseStatus(webRequest);
if (returnValue == null) {
if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
disableContentCachingIfNecessary(webRequest);
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
} else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
return;
}
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);
Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");
try {
//将返回值封装成为自己指定的类型 比如json 或者xml等
this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(
returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);
} catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
//第二步:根据返回值找到15个返回值处理器,遍历 根据注解@ResponseBody,找到合适的返回值处理器
@Override
public void handleReturnValue (@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {
//在很多的返回值(15个如下图)处理器中选择合适的 返回json使用的是
//RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor 处理返回json的处理器
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler handler = selectHandler(returnValue, returnType);
if (handler == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unknown return value type: " + returnType.getParameterType().getName());
}
//指定的json返回值处理方法
handler.handleReturnValue(returnValue, returnType, mavContainer, webRequest);
}
//第三步:注解 @ResponseBody的方法 使用RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor处理器
@Override
public void handleReturnValue (@Nullable Object returnValue, MethodParameter returnType,
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, NativeWebRequest webRequest)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage = createInputMessage(webRequest);
ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage = createOutputMessage(webRequest);
// Try even with null return value. ResponseBodyAdvice could get involved.
//消息转化器 处理成json的方法
writeWithMessageConverters(returnValue, returnType, inputMessage, outputMessage);
}
//第四步:选择消息转换器(转换器很多,这里是jackson的消息转换器,把pojo转换成json)
protected <T > void writeWithMessageConverters (@Nullable T value, MethodParameter returnType,
ServletServerHttpRequest inputMessage, ServletServerHttpResponse outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException, HttpMessageNotWritableException {
Object body;
Class<?> valueType;
Type targetType;
if (value instanceof CharSequence) {
body = value.toString();
valueType = String.class;
targetType = String.class;
} else {
body = value;//value就是返回值 比如pojo的User的值
valueType = getReturnValueType(body, returnType);//返回值类型User
targetType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveType(getGenericType(returnType), returnType.getContainingClass());
}
if (isResourceType(value, returnType)) {
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.ACCEPT_RANGES, "bytes");
if (value != null && inputMessage.getHeaders().getFirst(HttpHeaders.RANGE) != null &&
outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() == 200) {
Resource resource = (Resource) value;
try {
List<HttpRange> httpRanges = inputMessage.getHeaders().getRange();
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.PARTIAL_CONTENT.value());
body = HttpRange.toResourceRegions(httpRanges, resource);
valueType = body.getClass();
targetType = RESOURCE_REGION_LIST_TYPE;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
outputMessage.getHeaders().set(HttpHeaders.CONTENT_RANGE, "bytes */" + resource.contentLength());
outputMessage.getServletResponse().setStatus(HttpStatus.REQUESTED_RANGE_NOT_SATISFIABLE.value());
}
}
}
MediaType selectedMediaType = null;
MediaType contentType = outputMessage.getHeaders().getContentType();
boolean isContentTypePreset = contentType != null && contentType.isConcrete();
if (isContentTypePreset) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Found 'Content-Type:" + contentType + "' in response");
}
selectedMediaType = contentType;
} else {
HttpServletRequest request = inputMessage.getServletRequest();
List<MediaType> acceptableTypes;
try {
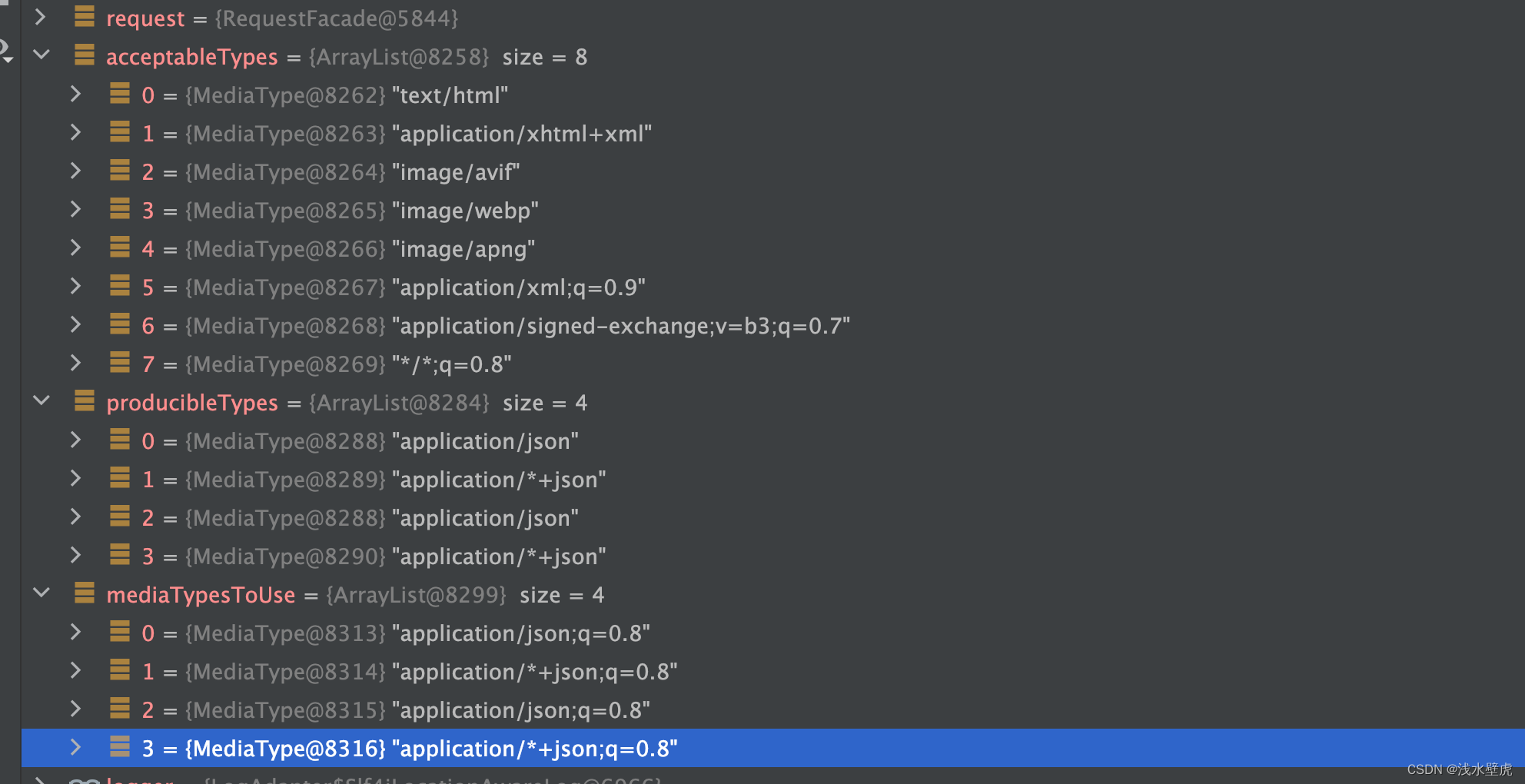
//这里是request的accept的类型 表示浏览器接受的类型 9个 逗号分割
// Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,
// image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,
// application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7
acceptableTypes = getAcceptableMediaTypes(request);
} catch (HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException ex) {
int series = outputMessage.getServletResponse().getStatus() / 100;
if (body == null || series == 4 || series == 5) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Ignoring error response content (if any). " + ex);
}
return;
}
throw ex;
}
//这里就是服务器生产数据的类型
//application.json等4个
List<MediaType> producibleTypes = getProducibleMediaTypes(request, valueType, targetType);
if (body != null && producibleTypes.isEmpty()) {
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter found for return value of type: " + valueType);
}
List<MediaType> mediaTypesToUse = new ArrayList<>();
//服务器产出类型和浏览器接受类型的匹配
for (MediaType requestedType : acceptableTypes) {
for (MediaType producibleType : producibleTypes) {
if (requestedType.isCompatibleWith(producibleType)) {
mediaTypesToUse.add(getMostSpecificMediaType(requestedType, producibleType));
}
}
}
if (mediaTypesToUse.isEmpty()) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No match for " + acceptableTypes + ", supported: " + producibleTypes);
}
if (body != null) {
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(producibleTypes);
}
return;
}
MediaType.sortBySpecificityAndQuality(mediaTypesToUse);
for (MediaType mediaType : mediaTypesToUse) {
if (mediaType.isConcrete()) {
selectedMediaType = mediaType;
break;
} else if (mediaType.isPresentIn(ALL_APPLICATION_MEDIA_TYPES)) {
selectedMediaType = MediaType.APPLICATION_OCTET_STREAM;
break;
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using '" + selectedMediaType + "', given " +
acceptableTypes + " and supported " + producibleTypes);
}
}
if (selectedMediaType != null) {
selectedMediaType = selectedMediaType.removeQualityValue();
//这里就是消息转换器的类型messageConverters 遍历 有转json、xml、Model、modelView、view等好多个
//找到转jackson的消息转换器
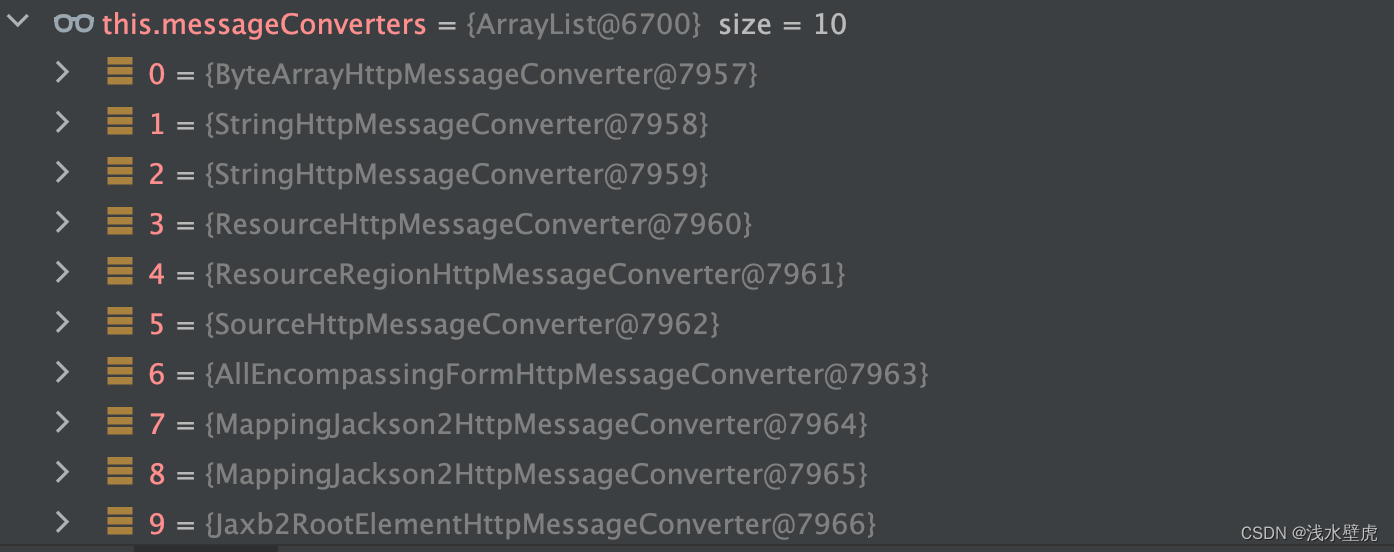
for (HttpMessageConverter<?> converter : this.messageConverters) {
GenericHttpMessageConverter genericConverter = (converter instanceof GenericHttpMessageConverter ?
(GenericHttpMessageConverter<?>) converter : null);
if (genericConverter != null ?
((GenericHttpMessageConverter) converter).canWrite(targetType, valueType, selectedMediaType) :
converter.canWrite(valueType, selectedMediaType)) {
body = getAdvice().beforeBodyWrite(body, returnType, selectedMediaType,
(Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>>) converter.getClass(),
inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (body != null) {
Object theBody = body;
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn ->
"Writing [" + LogFormatUtils.formatValue(theBody, !traceOn) + "]");
addContentDispositionHeader(inputMessage, outputMessage);
if (genericConverter != null) {
genericConverter.write(body, targetType, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
} else {
//这里就是真正的调用jacksonConverter消息转换器 将实体转换成json 放到Response中
//依赖ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
//String json = mapper.writeValueAsString(User);
((HttpMessageConverter) converter).write(body, selectedMediaType, outputMessage);
}
} else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Nothing to write: null body");
}
}
return;
}
}
}
if (body != null) {
Set<MediaType> producibleMediaTypes =
(Set<MediaType>) inputMessage.getServletRequest()
.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PRODUCIBLE_MEDIA_TYPES_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isContentTypePreset || !CollectionUtils.isEmpty(producibleMediaTypes)) {
throw new HttpMessageNotWritableException(
"No converter for [" + valueType + "] with preset Content-Type '" + contentType + "'");
}
throw new HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException(getSupportedMediaTypes(body.getClass()));
}
}
}
响应的参数解析的返回值处理器如下15个
浏览器接受格式、服务器返回格式、交集
消息转换器10个(可以处理String、byte、json、Resource等)