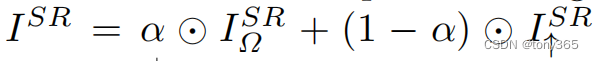文章目录
- 3. Super-Resolution by Predicting Offsets
- 3.1. 这篇论文用于处理栅格化图像的超分,不知道这样翻译对不对,
- 3.2. 作者认为栅格图像的边缘比较规则,可以训练一个offset map移动栅格图像的 边缘点(背景和前景像素 移动 和交换)
- 3.3 fusion
3. Super-Resolution by Predicting Offsets
3.1. 这篇论文用于处理栅格化图像的超分,不知道这样翻译对不对,
栅格化图像是锯齿形状的图像,如下
上面时栅格图像,很多锯齿。 放大尺寸的时候,最近邻插值的效果就是这种,观感不好。因此作者想办法优化
下面时混淆图像,边缘重叠不清晰

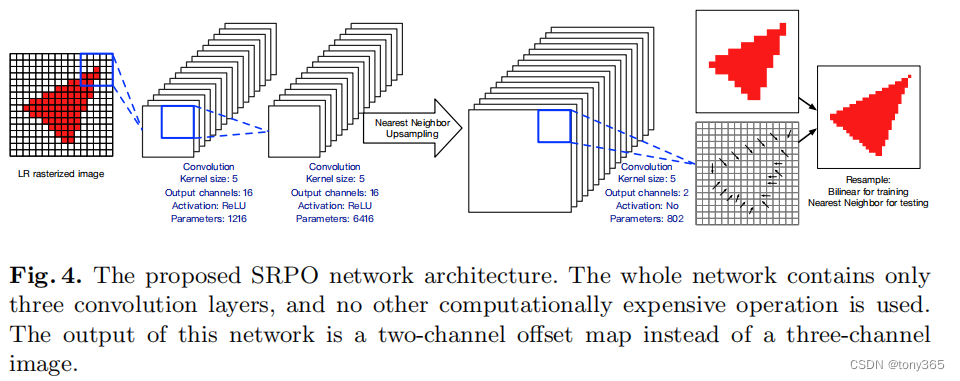
3.2. 作者认为栅格图像的边缘比较规则,可以训练一个offset map移动栅格图像的 边缘点(背景和前景像素 移动 和交换)
整体框架比较简单,三个卷积层:
def initialize_weights(net_l, scale=1):
if not isinstance(net_l, list):
net_l = [net_l]
for net in net_l:
for m in net.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, a=0, mode='fan_in')
m.weight.data *= scale # for residual block
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, a=0, mode='fan_in')
m.weight.data *= scale
if m.bias is not None:
m.bias.data.zero_()
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias.data, 0.0)
''' Checked '''
def NNresampling(lr, hr_shifts, mode='bilinear'):
'''
lr.shape = b, c, h, w
hr_shifts.shape = b, 2, h*2, w*2
mode: bilinear when training, nearest for testing
'''
b, c, h, w = lr.shape
_coor_x = torch.arange(0, w * 2).repeat(b, 1, h * 2, 1).type_as(hr_shifts)
_coor_y = torch.arange(0, h * 2).repeat(b, 1, w * 2, 1).transpose(2, 3).type_as(hr_shifts)
sr_coor_x = _coor_x + hr_shifts[:, :1, :, :]
sr_coor_x = 2.0 * sr_coor_x[:, :, :, :] / max(w * 2 - 1, 1) - 1.0
sr_coor_y = _coor_y + hr_shifts[:, 1:, :, :]
sr_coor_y = 2.0 * sr_coor_y[:, :, :, :] / max(h * 2 - 1, 1) - 1.0
_coor_norm = torch.cat([sr_coor_x, sr_coor_y], dim=1)
sr = F.grid_sample(lr.type_as(hr_shifts), _coor_norm.permute(0, 2, 3, 1), mode=mode)
return sr
def NNresamplingx3(lr, hr_shifts, mode='bilinear'):
'''
lr.shape = b, c, h, w
hr_shifts.shape = b, 2, h*2, w*2
mode: bilinear when training, nearest for testing
'''
b, c, h, w = lr.shape
_coor_x = torch.arange(0, w * 3).repeat(b, 1, h * 3, 1).type_as(hr_shifts)
_coor_y = torch.arange(0, h * 3).repeat(b, 1, w * 3, 1).transpose(2, 3).type_as(hr_shifts)
sr_coor_x = _coor_x + hr_shifts[:, :1, :, :]
sr_coor_x = 2.0 * sr_coor_x[:, :, :, :] / max(w * 3 - 1, 1) - 1.0
sr_coor_y = _coor_y + hr_shifts[:, 1:, :, :]
sr_coor_y = 2.0 * sr_coor_y[:, :, :, :] / max(h * 3 - 1, 1) - 1.0
_coor_norm = torch.cat([sr_coor_x, sr_coor_y], dim=1)
sr = F.grid_sample(lr.type_as(hr_shifts), _coor_norm.permute(0, 2, 3, 1), mode=mode)
return sr
class V3_10(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_channel=3, l1_c=16, l1_k=5, l2_c=16, l2_k=5, l3_c=2, l3_k=5, offset_up_type='bilinear'):
super(V3_10, self).__init__()
'''First Conv'''
self.conv_first = []
self.conv_first.append(nn.Conv2d(input_channel, l1_c, l1_k, padding=l1_k // 2))
self.conv_first.append(nn.ReLU())
arch_util.initialize_weights(self.conv_first, 0.1)
'''Second Conv'''
self.conv_second = []
self.conv_second.append(nn.Conv2d(l1_c, l2_c, l2_k, padding=l2_k // 2))
self.conv_second.append(nn.ReLU())
arch_util.initialize_weights(self.conv_second, 0.1)
if offset_up_type == 'bilinear':
self.offset_up = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=3, mode='bilinear')
elif offset_up_type == 'nearest':
self.offset_up = nn.UpsamplingNearest2d(scale_factor=3)
'''Last Conv'''
self.conv_last = []
self.conv_last.append(nn.Conv2d(l2_c, l3_c, l3_k, padding=l3_k // 2))
arch_util.initialize_weights(self.conv_last, 0.1)
self.conv_first = nn.Sequential(*self.conv_first)
self.conv_second = nn.Sequential(*self.conv_second)
self.conv_last = nn.Sequential(*self.conv_last)
def forward(self, x, warp_type='nearest'):
''' When you test, warp_type = nearest '''
# Offset SR
fea_1 = self.conv_first(x)
fea_2 = self.conv_second(fea_1)
fea_up = self.offset_up(fea_2)
offset = self.conv_last(fea_up) # 这里类似一个光流了,表示的像素的位移
'''For x2'''
offset_sr = NNresampling(x, offset, mode=warp_type) # warp操作
'''For x3'''
# offset_sr = NNresamplingx3(x, offset, mode=warp_type)
output = torch.cat([offset_sr, offset], dim=1)
return None, output
3.3 fusion
offset net只对边缘进行了处理,大部分是0。对于平坦区域,可以采用Lanczos等插值方法,
对于边缘图像, 求出最近邻插值的图 和 net得到的offset,类似得到一个光流 ,然后NNresampling函数进行重映射操作(用到F.grid_sample函数)
然后两者进行blending处理,得到最终的 sr图像