在BeanFactory中,主要的流程就是创建Bean的过程,
// 核心方法: 创建Bean实列对象,并且生命周期的动作大部分都在这里。
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
Bean的生命周期包括:
- 实例化
- 设置属性值
- 初始化值
- 销毁
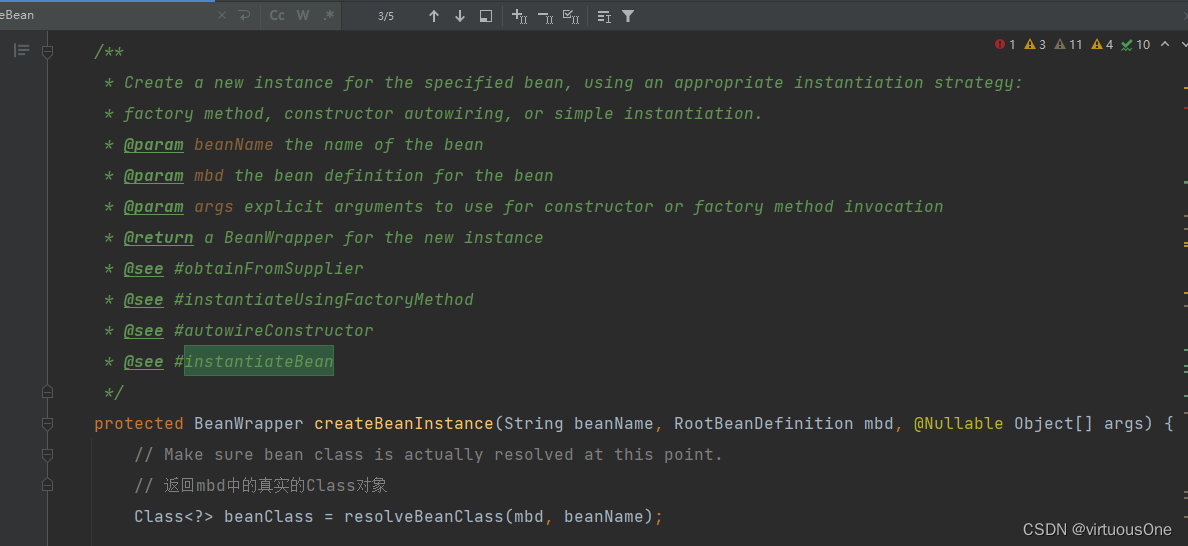
实例化Bean在源码中
// 该方法创建出来真实的 bean实列,并且将其包装到BeanWrapper实列中。
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
if (beanClass != null && !Modifier.isPublic(beanClass.getModifiers()) && !mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Bean class isn't public, and non-public access not allowed: " + beanClass.getName());
}
三个条件表达的意思是: mbd 中如果nonPublicAccessAllowed字段的值为true; 就可以创建实例
以下有两种方式创建Bean。默认使用无参构造
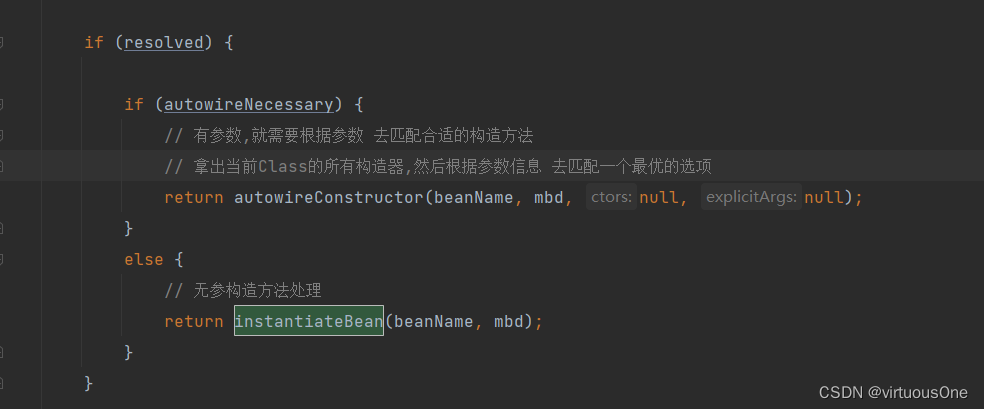
有参创建 :推断处理的 构造器方法不为null或者开启自动装配或者 使用指定入参的构造方法
// 根据当前的class 构造器集合 筛选出一个优先级最高的 构造器方法
public BeanWrapper autowireConstructor(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd,
@Nullable Constructor<?>[] chosenCtors, @Nullable Object[] explicitArgs) {
BeanWrapperImpl bw = new BeanWrapperImpl();
// 1.向wrapper中注册 conversion
// 2.向wrapper中注册 属性编辑器
this.beanFactory.initBeanWrapper(bw);
// 实例化反射调用的构造器
Constructor<?> constructorToUse = null;
// 实例化
ArgumentsHolder argsHolderToUse = null;
// 实例化时使用的参数。
Object[] argsToUse = null;
if (explicitArgs != null) {
argsToUse = explicitArgs;
}
else {
// 表示 构造器参数需要做转化的参数引用
Object[] argsToResolve = null;
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
// 条件成立: 说明当前getBean() 生成实例,不是第一次,缓存中有解析好的构造器方法可以直接拿来反射调用
// mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved 说明构造器参数已经解析过了。
if (constructorToUse != null && mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved) {
// Found a cached constructor...
argsToUse = mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments;
if (argsToUse == null) {
argsToResolve = mbd.preparedConstructorArguments;
}
}
}
// 条件成立: 参数是null,那么 preparedConstructorArguments 一定有值
if (argsToResolve != null) {
// 可以认为 preparedConstructorArguments 不是完全解析,需要继续解析
argsToUse = resolvePreparedArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, constructorToUse, argsToResolve, true);
}
}
// 条件成立,说明缓存机制失败,需要进行构造器匹配逻辑
if (constructorToUse == null || argsToUse == null) {
// Take specified constructors, if any.
// chosenCtors? 什么时候有数据,构造方法上有@Autowired注解时,有值。
Constructor<?>[] candidates = chosenCtors;
// 说明外部程序调用当前autowiredConstructors方法时,并没有提供好可选用的构造器
if (candidates == null) {
//
Class<?> beanClass = mbd.getBeanClass();
try {
// isNonPublicAccessAllowed 返回true,表示当前bd中的class 非public的方法也可以访问
//
candidates = (mbd.isNonPublicAccessAllowed() ?
beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors() : beanClass.getConstructors());
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +
"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);
}
}
// 执行到这里,可选用的构造方法,已经准备好了,具体使用哪一个还不清楚
if (candidates.length == 1 && explicitArgs == null && !mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues()) {
Constructor<?> uniqueCandidate = candidates[0];
// 条件成立: 说明当前这个唯一可选项, 构造器 就是 无参构造器
if (uniqueCandidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {
synchronized (mbd.constructorArgumentLock) {
mbd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = uniqueCandidate;
mbd.constructorArgumentsResolved = true;
mbd.resolvedConstructorArguments = EMPTY_ARGS;
}
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, uniqueCandidate, EMPTY_ARGS));
return bw;
}
}
// Need to resolve the constructor.
boolean autowiring = (chosenCtors != null ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR);
ConstructorArgumentValues resolvedValues = null;
// 表示构造器参数个数
int minNrOfArgs;
if (explicitArgs != null) {
minNrOfArgs = explicitArgs.length;
}
else {
ConstructorArgumentValues cargs = mbd.getConstructorArgumentValues();
resolvedValues = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
minNrOfArgs = resolveConstructorArguments(beanName, mbd, bw, cargs, resolvedValues);
}
// 给可选用的构造器数组排序
AutowireUtils.sortConstructors(candidates);
// 这个值越低,说明构造器参数列表类型和构造参数匹配度越高。
int minTypeDiffWeight = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Set<Constructor<?>> ambiguousConstructors = null;
LinkedList<UnsatisfiedDependencyException> causes = null;
for (Constructor<?> candidate : candidates) {
// 获取当前处理的构造器参数个数.....
int parameterCount = candidate.getParameterCount();
if (constructorToUse != null && argsToUse != null && argsToUse.length > parameterCount) {
// Already found greedy constructor that can be satisfied ->
// do not look any further, there are only less greedy constructors left.
break;
}
// parameterCount 表示当前构造器参数个数
if (parameterCount < minNrOfArgs) {
continue;
}
ArgumentsHolder argsHolder;
// 当前构造器的参数类型数组
Class<?>[] paramTypes = candidate.getParameterTypes();
if (resolvedValues != null) {
try {
//
String[] paramNames = ConstructorPropertiesChecker.evaluate(candidate, parameterCount);
if (paramNames == null) {
ParameterNameDiscoverer pnd = this.beanFactory.getParameterNameDiscoverer();
if (pnd != null) {
paramNames = pnd.getParameterNames(candidate);
}
}
//
argsHolder = createArgumentArray(beanName, mbd, resolvedValues, bw, paramTypes, paramNames,
getUserDeclaredConstructor(candidate), autowiring, candidates.length == 1);
}
catch (UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Ignoring constructor [" + candidate + "] of bean '" + beanName + "': " + ex);
}
// Swallow and try next constructor.
if (causes == null) {
causes = new LinkedList<>();
}
causes.add(ex);
continue;
}
}
else {
// Explicit arguments given -> arguments length must match exactly.
if (parameterCount != explicitArgs.length) {
continue;
}
argsHolder = new ArgumentsHolder(explicitArgs);
}
// 反向匹配度,值越低,匹配度越高
int typeDiffWeight = (mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution() ?
argsHolder.getTypeDifferenceWeight(paramTypes) : argsHolder.getAssignabilityWeight(paramTypes));
// Choose this constructor if it represents the closest match.
if (typeDiffWeight < minTypeDiffWeight) {
constructorToUse = candidate;
argsHolderToUse = argsHolder;
argsToUse = argsHolder.arguments;
minTypeDiffWeight = typeDiffWeight;
ambiguousConstructors = null;
}
// 条件成立: 说明当前处理的构造器, 计算出来的diffWeight值,与上一选的值一致。
else if (constructorToUse != null && typeDiffWeight == minTypeDiffWeight) {
if (ambiguousConstructors == null) {
ambiguousConstructors = new LinkedHashSet<>();
ambiguousConstructors.add(constructorToUse);
}
ambiguousConstructors.add(candidate);
}
}
// 条件成立: 说明未找到可以使用的构造器,跑错
if (constructorToUse == null) {
if (causes != null) {
UnsatisfiedDependencyException ex = causes.removeLast();
for (Exception cause : causes) {
this.beanFactory.onSuppressedException(cause);
}
throw ex;
}
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Could not resolve matching constructor " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities)");
}
else if (ambiguousConstructors != null && !mbd.isLenientConstructorResolution()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Ambiguous constructor matches found in bean '" + beanName + "' " +
"(hint: specify index/type/name arguments for simple parameters to avoid type ambiguities): " +
ambiguousConstructors);
}
// 条件成立: 说明匹配成功,进入缓存,便于后面使用。
if (explicitArgs == null && argsHolderToUse != null) {
argsHolderToUse.storeCache(mbd, constructorToUse);
}
}
Assert.state(argsToUse != null, "Unresolved constructor arguments");
// 进行实例化
bw.setBeanInstance(instantiate(beanName, mbd, constructorToUse, argsToUse));
return bw;
}
Spring Bean 实例化前阶段、Spring Bean 实例化阶段、Spring Bean 实例化后阶段等阶段。这里有几个概念
1.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
- Spring Bean 实例化前阶段: 第一次调用后置处理器 postProcessBeforeInstantiation 方法 默认实现是判断是否需要代理放入map中
- Spring Bean 实例化后置阶段: 第五次调用后置处理器 postProcessAfterInstantiation方法 属性赋值(Populate)判断是否需要属性填充
- populateBean属性赋值 : 第六次调用后置处理器:postProcessPropertyValues 为bean填充属性包括依赖注入的属性
2.martInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 后置处理器:
第二次调用后置处理器determineCandidateConstructors获取最优构造方法实例化对象
3.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器
第四次调用后置处理器getEarlyBeanReference解决循环依赖的问题
4.InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor初始化后置处理器
Spring Bean 初始化前阶段 postProcessBeforeInitialization
Spring Bean 初始化后阶段:postProcessAfterInitialization
![[附源码]java毕业设计网上报销管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/18008705ec2c4f8e88cf78a1457956c2.png)


![[附源码]java毕业设计网上点餐系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/a998850121c149148f2ea6742b4bca52.png)



![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA基于JSP技术的新电商助农平台](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/e1e0e8cd1e9c4d2c904077787f324ed9.png)
![[附源码]计算机毕业设计JAVA基于JSP学生信息管理系统](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/b36ea57a8658499baeac5937628e87b1.png)