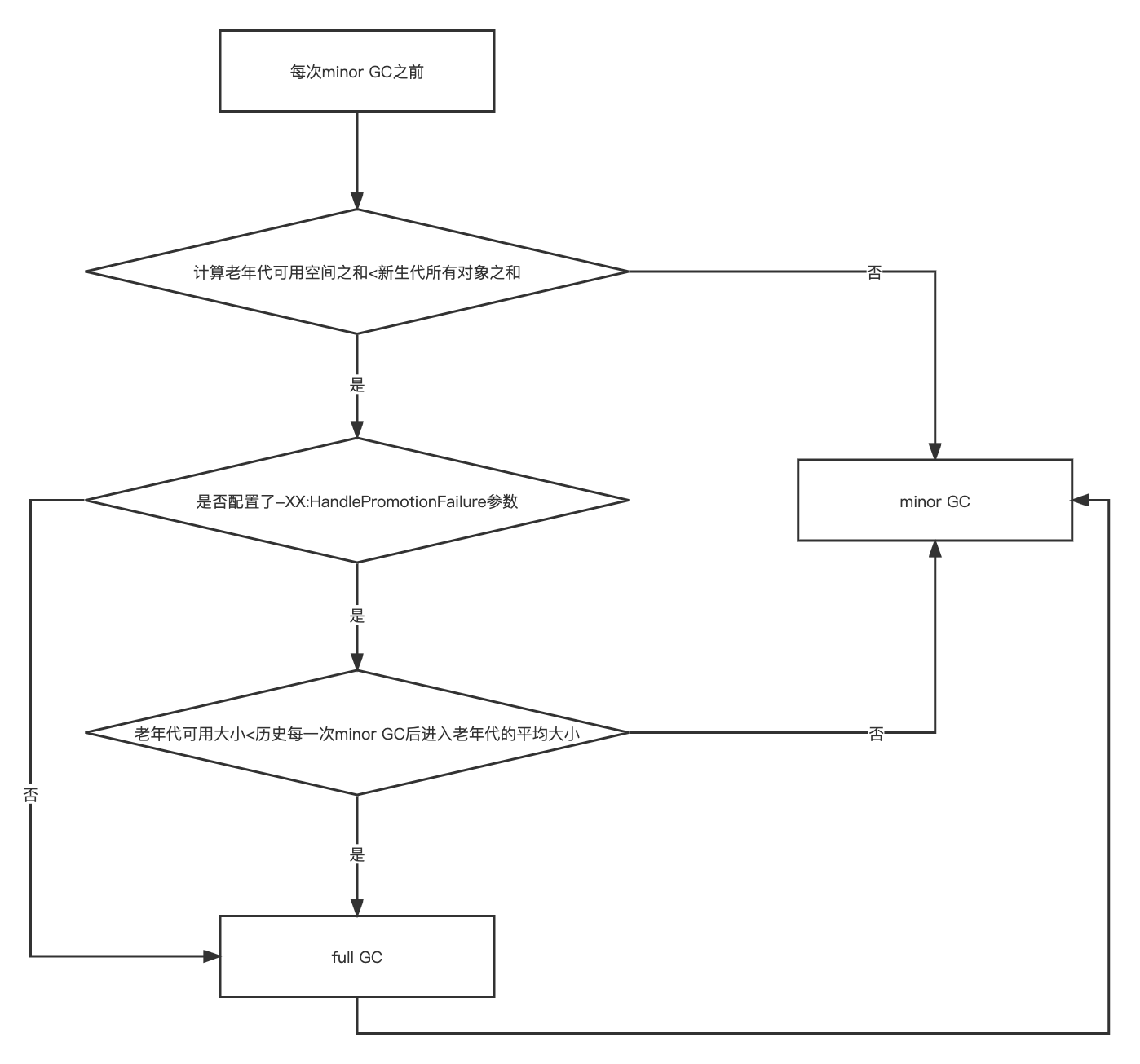
前言
看到这个标题的时候,也许你会认为我写错了,Activity不是只有四种启动模式吗?分别为startard,singleTop,singleTask,singleInstance这四种。
一般来说是四种,但是android12的时候新加入了singleInstancePerTask类型,所以就有5种了。
介绍这五种类型之前,我们先略微介绍一下这五种类型在源码中的定义。
首先,我们先看一下官方注释的位置下,这五种类型的注释在attrs_manifest.xml文件中:
<attr name="launchMode">
<!-- The default mode, which will usually create a new instance of
the activity when it is started, though this behavior may change
with the introduction of other options such as
{@link android.content.Intent#FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK}. -->
<enum name="standard" value="0" />
<!-- If, when starting the activity, there is already an
instance of the same activity class in the foreground that is
interacting with the user, then
re-use that instance. This existing instance will receive a call to
{@link android.app.Activity#onNewIntent Activity.onNewIntent()} with
the new Intent that is being started. -->
<enum name="singleTop" value="1" />
<!-- If, when starting the activity, there is already a task running
that starts with this activity, then instead of starting a new
instance the current task is brought to the front. The existing
instance will receive a call to {@link android.app.Activity#onNewIntent
Activity.onNewIntent()}
with the new Intent that is being started, and with the
{@link android.content.Intent#FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT} flag set. This is a superset
of the singleTop mode, where if there is already an instance
of the activity being started at the top of the stack, it will
receive the Intent as described there (without the
FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT flag set). See the
<a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/fundamentals/tasks-and-back-stack.html">Tasks and Back
Stack</a> document for more details about tasks.-->
<enum name="singleTask" value="2" />
<!-- Only allow one instance of this activity to ever be
running. This activity gets a unique task with only itself running
in it; if it is ever launched again with the same Intent, then that
task will be brought forward and its
{@link android.app.Activity#onNewIntent Activity.onNewIntent()}
method called. If this
activity tries to start a new activity, that new activity will be
launched in a separate task. See the
<a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/fundamentals/tasks-and-back-stack.html">Tasks and Back
Stack</a> document for more details about tasks.-->
<enum name="singleInstance" value="3" />
<!-- The activity can only be running as the root activity of the task, the first activity
that created the task, and therefore there will only be one instance of this activity
in a task. In constrast to the {@code singleTask} launch mode, this activity can be
started in multiple instances in different tasks if the
{@code FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK} or {@code FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT} is set.-->
<enum name="singleInstancePerTask" value="4" />
</attr>其次,在看一下这五种模式在Java文件中的定义,在ActivityInfo类中,如下:
/**
* Constant corresponding to <code>standard</code> in
* the {@link android.R.attr#launchMode} attribute.
/
public static final int LAUNCH_MULTIPLE = 0;
/*
* Constant corresponding to <code>singleTop</code> in
* the {@link android.R.attr#launchMode} attribute.
/
public static final int LAUNCH_SINGLE_TOP = 1;
/*
* Constant corresponding to <code>singleTask</code> in
* the {@link android.R.attr#launchMode} attribute.
/
public static final int LAUNCH_SINGLE_TASK = 2;
/*
* Constant corresponding to <code>singleInstance</code> in
* the {@link android.R.attr#launchMode} attribute.
/
public static final int LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE = 3;
/*
* Constant corresponding to <code>singleInstancePerTask</code> in
* the {@link android.R.attr#launchMode} attribute.
*/
public static final int LAUNCH_SINGLE_INSTANCE_PER_TASK = 4;接下来,我们就依次讲解这五种类型的定义和作用。
一.standard类型
首先讲解standard类型,这也是一个最基本最常用的一种类型。
官方解释
先看官方注释中的描述:
<!-- The default mode, which will usually create a new instance of
the activity when it is started, though this behavior may change
with the introduction of other options such as
{@link android.content.Intent#FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK}. -->翻译后:
默认的类型,每次使用时通常创建一个新的活动对象,虽然这样的行为会因为引入其它参数配置而发生改变,比如Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK。
实验验证
我们再来通过实验进行验证,创建三个Activity,分别为Test1Activity,Test2Activity,Test3Activity,如下:
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity" />然后我们在代码中设置如下跳转顺序:Test1->Test2->Test3->Test1
接下来就是实验,按照上面流程跳转后,使用adb命令捕获当前Activity的栈状态如下:
adb命令:adb shell dumpsys activity activities
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{54bb09b #190 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=4}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{75f3f53 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t190}
* ActivityRecord{f91f056 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t191}
* ActivityRecord{777cf91 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t190}
* ActivityRecord{83d9d17 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t190}整个流程如下图所示,Test3跳转Test1的时候,会直接在Test3上面入栈一个新的Test1。所以Task中有4条ActivityRecrod,从下往上的顺序为:Test1,Test2,Test3,Test1。
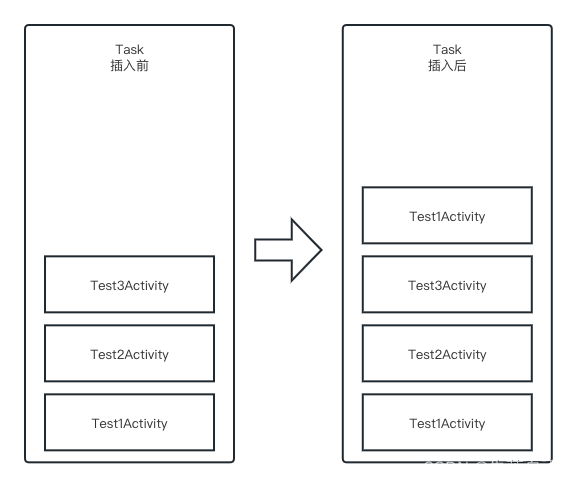
总结:
首先这里我们就不验证添加参数的类型了。
standard类型的启动方式,是不断的往一个Task栈上面添加新的Activity,哪怕有同样的Activity,也会重新创建一个添加到栈里面。
二.singleInstance类型
为什么把singleInstance拿到前面来说呢?因为后面singleTop类型中的验证会涉及到singleInstance类型的知识点,所以就拿到前面提前来讲了。
官方解释
<!-- Only allow one instance of this activity to ever be
running. This activity gets a unique task with only itself running
in it; if it is ever launched again with the same Intent, then that
task will be brought forward and its
{@link android.app.Activity#onNewIntent Activity.onNewIntent()}
method called. If this
activity tries to start a new activity, that new activity will be
launched in a separate task. See the
<a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/fundamentals/tasks-and-back-stack.html">Tasks and Back
Stack</a> document for more details about tasks.-->翻译后:
只允许一个Activity的实例运行。这个Activity会有唯一的task栈只允许它自身在其中运行,每次被加载的时候都被会把这个栈带到前台,同时会调用Activity的onNewIntent方法进行通知。如果这个Activity尝试去启动一个新的Activity,那么新创建的Activity和当前Activity必须是不同的Task栈。
实验验证
我们仍然是三个Activity,其中Test2Activity设置为singleInstance的模式,
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity" />
<activity
android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity"
android:launchMode="singleInstance" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity" />设置跳转顺序: Test1->Test2->Test3->Test1->Test2->Test3
执行操作,结果如下,我们可以发现Test2单独占用一个Task
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{40cbc68 #196 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=5}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{cd9b41f u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t196}
* ActivityRecord{9e73f05 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t196}
* ActivityRecord{8fcaaee u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t196}
* ActivityRecord{5e3a630 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t196}
* ActivityRecord{9768990 u0 com.xt.client/.MainActivity} t196}
* Task{17dfc90 #197 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=1}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{e147b53 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t197}我们发现区别于第一种类型,这种类型下会有两个Task栈,这两个Task的taskAffinity是一样的。
Test2启动Test3的时候,流程图如下所示。首先前台任务栈从Task2切换到了Task1,Task1中也增加了一条Test3的Activity记录,此时显示在前台的就是Test3了。

总结:
singleInstance类型的启动方式中,
如果不存在包含目标Activity的栈,则创建一个新的Task,这个Task中是目标Activity所独有的,并且只会创建一次,后续如果在启动其它的Activity,这些新的Acitivty属于其parent的task栈。
如果存在包含目标Activity的栈,则直接把包含目标Activity的Task栈挪到前台进行显示。
三.singleTop类型
singleTop相对于startard多了一个复用的概念,就是说某些场景下,会复用已有的Activity而不是每次都新建。
官方解释
<!-- If, when starting the activity, there is already an
instance of the same activity class in the foreground that is
interacting with the user, then
re-use that instance. This existing instance will receive a call to
{@link android.app.Activity#onNewIntent Activity.onNewIntent()} with
the new Intent that is being started. -->翻译后:
在启动Activity的时候,如果前台中存在一个相同Activity类的实例与用户交互,则直接使用这个实例。这个存在的实例在启动的时候会通过onNewIntent方法收到通知。
实验验证
这里为了体现singleTop的作用,我们做一个对比实验。
首先,我们设置Test3为singleInstance模式,其他的都是默认的standard模式。
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity" />
<activity
android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity"
android:launchMode="singleInstance" />然后设置跳转顺序:Test1->Test2->Test3->Test2
结果如下:
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{54bb09b #190 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=4}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{75f3f53 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t190}
* ActivityRecord{777cf91 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t190}
* ActivityRecord{83d9d17 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t190}
* ActivityRecord{6979f3f u0 com.xt.client/.MainActivity} t190}
* Task{e1b8d7 #191 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=1}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{f91f056 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t191}我们可以看到有两个Task栈,Task1中有3个Activity记录,分别是Test1,Test2,Test2。而Task2中则只有一个Test3的记录。
此时,我们做一个改动,把Test2设置为singleTop类型,如下:
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity"
android:launchMode="singleTop" />
<activity
android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity"
android:launchMode="singleInstance" />同样的跳转顺序:Test1->Test2->Test3->Test2
结果如下:
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{54bb09b #190 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=4}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{777cf91 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t190}
* ActivityRecord{83d9d17 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t190}
* Task{e1b8d7 #191 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=1}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{f91f056 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t191}我们发现,只有Task2仍然只有一条Test3的记录,但是Task1中,只有两条记录了,分别为Test1和Test2。相对于上一次实验,这次少了一个Test2的记录。
Test3跳转Test2的流程图如下,前台任务栈从Task1切换到了Task2,并且Test2没有新建,而是直接复用栈顶的实例对象。

总结:
总结一下,singleTop类型的启动方式,当从别的Task任务栈切换回当前任务栈时,如果栈顶实例就是同样的Activity,则直接进行复用,并且通过onNewIntent方法进行通知。
四.singleTask类型
singleTask类型其实就是singleTop类型的增强版,我们来看下他们的区别。
官方解释
<!-- If, when starting the activity, there is already a task running
that starts with this activity, then instead of starting a new
instance the current task is brought to the front. The existing
instance will receive a call to {@link android.app.Activity#onNewIntent
Activity.onNewIntent()}
with the new Intent that is being started, and with the
{@link android.content.Intent#FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT
Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT} flag set. This is a superset
of the singleTop mode, where if there is already an instance
of the activity being started at the top of the stack, it will
receive the Intent as described there (without the
FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT flag set). See the
<a href="{@docRoot}guide/topics/fundamentals/tasks-and-back-stack.html">Tasks and Back
Stack</a> document for more details about tasks.-->翻译后:
在启动Activity的时候,如果栈中存在一个这样的Activity,会通过在当前栈中把Activity对象带到前台的方式来替代新创建一个对象。启动的时候那个已存在的实例对象中onNewIntent方法会收到通知,并且会有Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT的标记。这是singleTop类型的扩展,如果目标Activity就处于栈顶部,则不会有FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT标记。
实验验证
我们采取和singeTop类似的方式,仍然进行对比实验。
仍然是三个Activity,其中Test1Activity设置为singleTask的模式,如下:
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity"
android:launchMode="singleInstance" />区别于singeTop中的方式,我们这里设置Test3跳转回Test1。
设置如下跳转顺序:Test1->Test2->Test3->Test1
进行操作,使用adb命令捕获栈结构如下:
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{d44dd11 #198 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=4}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{5902bb5 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t198}
* ActivityRecord{46c4832 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t198}
* ActivityRecord{6e48322 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t198}
* Task{9bdbdf4 #199 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=1}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{f0693c7 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t199}Task1中有Test1,Test2,Test1三条记录,Task2中只有Test3一条记录。
我们再把Test1改为singleTask类型,如下:
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity"
android:launchMode="singleTask" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity"
android:launchMode="singleInstance" />同样的跳转顺序:Test1->Test2->Test3->Test1,再次进行实验,结果如下:
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{9de4b6a #200 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=2}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{4bdcfd7 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t200}
* Task{af6f1f0 #201 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=1}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{66c6a33 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t201}这时候我们发现区别于上一个实验,这时Task1中只有一条Test1的记录了。
整个流程如下图所示,Test3中启动Test1的时候,前台任务栈从Task2切换到Task1,并且直接把Task1中Test2记录进行出栈操作,此时显示在前台的就是Test1了。
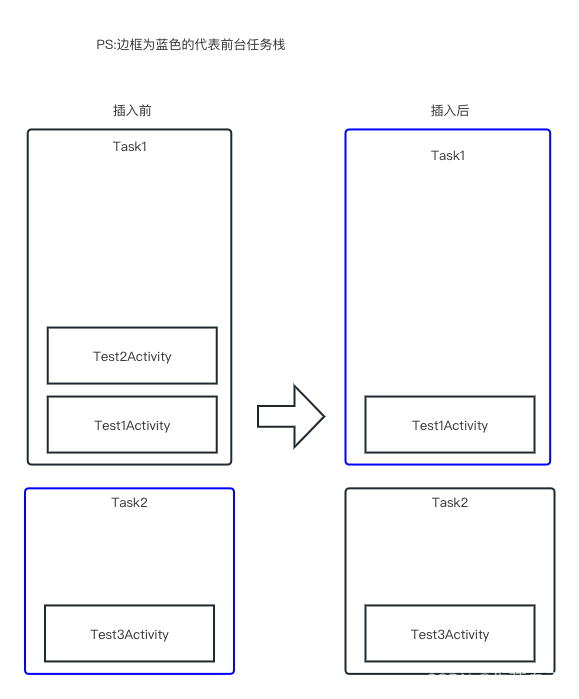
总结:
使用singleTask类型后,如果发现目标任务栈Task中存在相同的Activity实例时,则会出栈该实例上面的所有其它类型的实例,从而让该实例展示到前台。
六.singleInstancePerTask
singleInstancePerTask由其名可知,是singleInstance类型的增强版,其实在我看来,更像是singleInstance和singleTask的结合体,接下来我们来看下区别。
官方解释
<!-- The activity can only be running as the root activity of the task, the first activity
that created the task, and therefore there will only be one instance of this activity
in a task. In constrast to the {@code singleTask} launch mode, this activity can be
started in multiple instances in different tasks if the
{@code FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK} or {@code FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_DOCUMENT} is set.-->翻译后:
Activity只能作为Task栈的根结点(第一个被创建)运行,因此栈中只可能有一个该Activity的实例。对比singleTask类型,如果设置了FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK标记该Activity可以在不同的栈生成多个不同的实例。
实验验证
设置三个Activity,其中Test3Activity设置为singleInstancePerTask的模式,如下:
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test1Activity" />
<activity android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test2Activity" />
<activity
android:name="com.xt.client.activitys.test.Test3Activity"
android:launchMode="singleInstancePerTask" />设置如下跳转顺序:Test1->Test2->Test3->Test1->Test2->Test3->Test1
进行操作,使用adb命令捕获栈结构如下:
Application tokens in top down Z order:
* Task{e77ae1e #206 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=true visibleRequested=true mode=fullscreen translucent=false sz=2}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{a818f11 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t206}
* ActivityRecord{632e259 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test3Activity} t206}
* Task{6ef6ec0 #205 type=standard A=10234:com.xt.client U=0 visible=false visibleRequested=false mode=fullscreen translucent=true sz=3}
bounds=[0,0][1080,2340]
* ActivityRecord{9918e35 u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test2Activity} t205}
* ActivityRecord{25df40c u0 com.xt.client/.activitys.test.Test1Activity} t205}可以看到,虽然启动了两次Test3,但是仍然只有两个Task栈,可以证明singleInstancePerTask类型是栈单例的,一个被声明的Activity只会拥有唯一的一个栈(不设置标记的前提下)。
如下图所示,区别于singleInstance类型的是,在这个归属Test3的栈中,是可以放入其它的Activity的,比如这里的Test1。
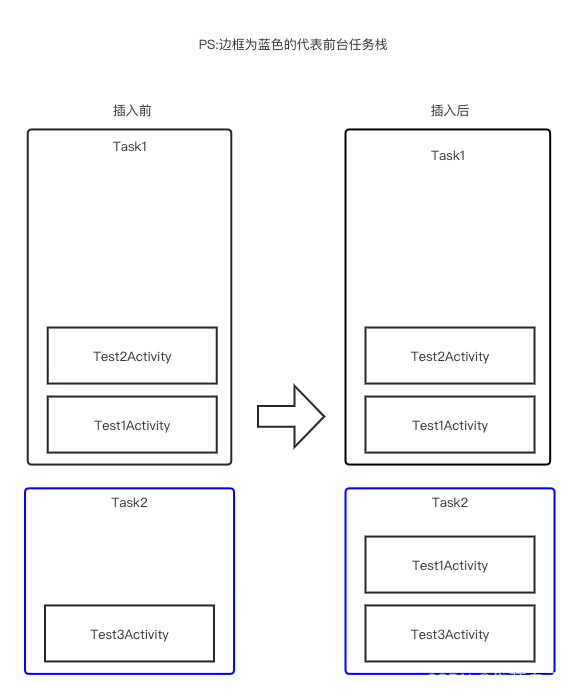
总结
singleInstancePerTask类型的启动方式中,
如果不存在包含目标Activity的栈,则创建一个新的Task,这个Task中是目标Activity所独有的,并且只会创建一次,后续如果在启动其它的Activity,这些新的Acitivty仍然当前的task栈。
如果存在包含目标Activity的栈,则把包含目标Activity的Task栈挪到前台,并且把该栈中目标Activity上面的所有Activity进行出栈操作,从而实现目标Activity显示在前台的效果。
当然,如官方文档所描述,如果启动singleInstancePerTask类型的Activity时,同时设置FLAG_ACTIVITY_MULTIPLE_TASK标记,应该是可以启动多个包含目标Activity的Task栈的,这里就不做实验了。
扩展性问题:
问题1:如果一个Task中的Activity全部出栈,会退到哪里?
答:假设Task1启动了Task2,那么Task2中的Activity如果全部出栈,就会把Task1推到前台,Task1中栈顶的Activity就会被显示。
我们以singleInstance类型中的流程为例,假设启动流程如下:
MainActivity(Task1)->Test1(Task2)->Test2(Task2)->Test3(Task3)->Test1(Task2)->Test2(Task3)->Test3(Task2)。
最终Test3属于Task2的栈,所以Task2中的4个Activity记录全部出栈后,会返回Task1的MainActivity,而不是Test2。
问题2:如何区分是首次创建还是从栈中返回的?
答:这个注释中就告诉我们了,栈中复用的回调用onNewIntent方法。
问题3:如何区分是从栈顶复用还是栈中复用的?
答:首先解释下栈顶复用还是栈中复用。如下图所示,如果启动的是Test3,就是栈顶复用,如果启动的是Test2或者Test1,那么就是栈中复用。

这个其实官方文档的注释中也告诉我们结果了,如果是栈中复用,则onNewIntent方法中,其flags参数中会包含Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_BROUGHT_TO_FRONT标记,可以通过这个来区别。