题目链接
1766C - Hamiltonian Wall Rating:1300
题目描述
Sir Monocarp Hamilton is planning to paint his wall. The wall can be represented as a grid, consisting of 2 rows and m columns. Initially, the wall is completely white.
Monocarp wants to paint a black picture on the wall. In particular, he wants cell (i,j) (the j-th cell in the i-th row) to be colored black, if ci,j= ‘B’, and to be left white, if ci,j= ‘W’. Additionally, he wants each column to have at least one black cell, so, for each j, the following constraint is satisfied: c1,j, c2,j or both of them will be equal to ‘B’.
In order for the picture to turn out smooth, Monocarp wants to place down a paint brush in some c e l l ( x 1 , y 1 ) cell (x1,y1) cell(x1,y1) and move it along the path ( x 1 , y 1 ) , ( x 2 , y 2 ) , … , ( x k , y k ) (x1,y1),(x2,y2),…,(xk,yk) (x1,y1),(x2,y2),…,(xk,yk) so that:
- for each i, (xi,yi) and (xi+1,yi+1) share a common side;
- all black cells appear in the path exactly once;
- white cells don’t appear in the path.
Determine if Monocarp can paint the wall.
Input
The first line contains a single integer t t t ( 1 ≤ t ≤ 1 0 4 1≤t≤10^4 1≤t≤104) — the number of testcases.
The first line of each testcase contains a single integer m ( 1 ≤ m ≤ 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 ) m (1≤m≤2⋅10^5) m(1≤m≤2⋅105) — the number of columns in the wall.
The i-th of the next two lines contains a string ci, consisting of m characters, where each character is either ‘B’ or ‘W’. ci,j is ‘B’, if the c e l l ( i , j ) cell (i,j) cell(i,j) should be colored black, and ‘W’, if the c e l l ( i , j ) cell (i,j) cell(i,j) should be left white.
Additionally, for each j, the following constraint is satisfied: c1,j, c2,j or both of them are equal to ‘B’.
The sum of m over all testcases doesn’t exceed 2 ⋅ 1 0 5 2⋅10^5 2⋅105.
Output
For each testcase, print "YES"if Monocarp can paint a wall. Otherwise, print "NO".
inputCopy
6
3
WBB
BBW
1
B
B
5
BWBWB
BBBBB
2
BW
WB
5
BBBBW
BWBBB
6
BWBBWB
BBBBBB
outputCopy
YES
YES
NO
NO
NO
YES
大致题意:
每次给你一个 2行 m列 的字符数组s。
s
[
i
]
[
j
]
=
=
′
B
′
s[i][j] == 'B'
s[i][j]==′B′ 代表这一块是黑色,
s
[
i
]
[
j
]
=
=
′
W
′
s[i][j] == 'W'
s[i][j]==′W′ 代表这一块是白色。
问是否存在一条路径包括了所有的黑色块,每个黑色块只在这条路径上出现一次。存在就打印 YES,否则打印NO。
这个例子存在这样的一条路径,所以打印 YES:
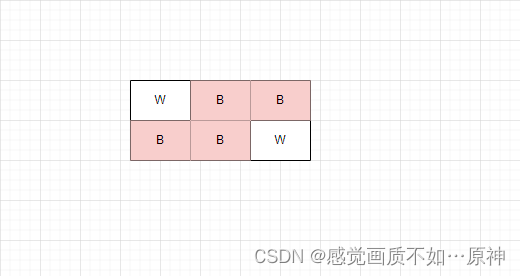
以下这个例子就不存在,所以打印NO:
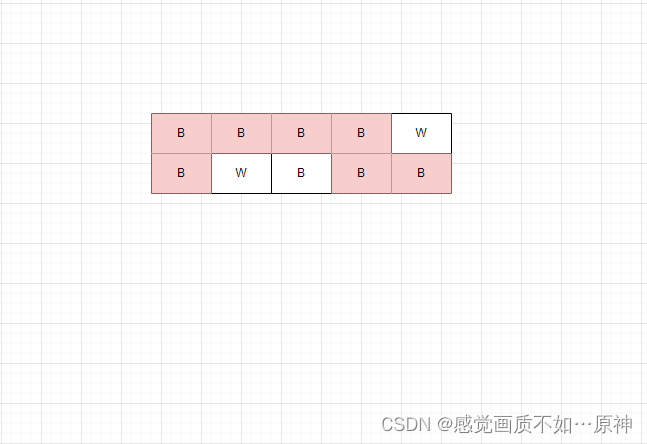
我们定义 f ( i , j ) ( 1 < = i < = 2 , 1 < = j < = n ) f(i,j) (1<=i<=2,1<=j<=n) f(i,j)(1<=i<=2,1<=j<=n) 为到达点 ( i , j ) (i,j) (i,j)的路径中包含的黑色块的数量。
最后我们只需要判断 m a x ( f ( 1 , n ) , f ( 2 , n ) ) = = 总的黑色块数量 max(f(1,n),f(2,n)) == 总的黑色块数量 max(f(1,n),f(2,n))==总的黑色块数量,如果等于说明确实存在这样一条路径;否则不存在。
分情况讨论:
当 s [ 1 ] [ j ] = = ′ B ′ s[1][j] == 'B' s[1][j]==′B′ 时,有以下三种情况:

- 当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ a n d f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' and f[2][j-1] == 'B' f[1][j−1]==′B′andf[2][j−1]==′B′时, f [ 1 ] [ j ] = f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 f[1][j] = f[1][j-1]+1 f[1][j]=f[1][j−1]+1
- 当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' f[1][j−1]==′B′时, f [ 1 ] [ j ] = f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 f[1][j] = f[1][j-1]+1 f[1][j]=f[1][j−1]+1
- 当 f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[2][j-1]=='B' f[2][j−1]==′B′时,这种情况不符合要求,忽略。
当 s [ 2 ] [ j ] = = ′ B ′ s[2][j] == 'B' s[2][j]==′B′ 时,有以下三种情况:

- 当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ a n d f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' and f[2][j-1] == 'B' f[1][j−1]==′B′andf[2][j−1]==′B′时, f [ 2 ] [ j ] = f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 f[2][j] = f[2][j-1]+1 f[2][j]=f[2][j−1]+1
- 当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' f[1][j−1]==′B′时,这种情况不符合要求,忽略。
- 当 f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[2][j-1]=='B' f[2][j−1]==′B′时, f [ 2 ] [ j ] = f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 f[2][j] = f[2][j-1]+1 f[2][j]=f[2][j−1]+1
当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ a n d f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' and f[2][j-1] == 'B' f[1][j−1]==′B′andf[2][j−1]==′B′时,有以下四种情况:

- 当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ a n d f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' and f[2][j-1] == 'B' f[1][j−1]==′B′andf[2][j−1]==′B′时,
-
- f [ 1 ] [ j ] = m a x ( f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 , f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] + 2 ) f[1][j] = max(f[1][j-1] + 1,f[2][j-1] + 2) f[1][j]=max(f[1][j−1]+1,f[2][j−1]+2)
-
- f [ 2 ] [ j ] = m a x ( f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 2 , f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 ) f[2][j] = max(f[1][j-1] + 2,f[2][j-1] + 1) f[2][j]=max(f[1][j−1]+2,f[2][j−1]+1)
- 当 f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[1][j-1]=='B' f[1][j−1]==′B′时,
-
- f [ 1 ] [ j ] = f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 f[1][j] = f[1][j-1] + 1 f[1][j]=f[1][j−1]+1
-
- f [ 2 ] [ j ] = f [ 1 ] [ j − 1 ] + 2 f[2][j] = f[1][j-1] + 2 f[2][j]=f[1][j−1]+2
- 当 f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] = = ′ B ′ f[2][j-1]=='B' f[2][j−1]==′B′时,
-
- f [ 1 ] [ j ] = f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] + 2 f[1][j] = f[2][j-1] + 2 f[1][j]=f[2][j−1]+2
-
- f [ 2 ] [ j ] = f [ 2 ] [ j − 1 ] + 1 f[2][j] = f[2][j-1] + 1 f[2][j]=f[2][j−1]+1
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5+10;
char s[3][N];
int f[3][N];
void solve(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1;i <= 2;i++){
scanf("%s",s[i] + 1);
}
memset(f,0,sizeof f);
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= 2;i++){
for(int j = 1;j <= n;j++){
if(s[i][j] == 'B') cnt++;
}
}
if(s[1][1] == 'B'&& s[2][1] == 'B'){
f[1][1] = 1;
f[2][1] = 1;
}
for(int j = 2;j <= n;j++){
if(s[1][j] == 'B' && s[2][j] == 'B'){
if(s[1][j-1] == 'B' && s[2][j-1] == 'B'){
f[1][j] = max(f[1][j-1] + 1,f[2][j-1] + 2);
f[2][j] = max(f[1][j-1] + 2,f[2][j-1] + 1);
}
else if(s[1][j-1] == 'B'){
f[1][j] = f[1][j-1] + 1;
f[2][j] = f[1][j-1] + 2;
}
else if(s[2][j-1] == 'B'){
f[1][j] = f[2][j-1] + 2;
f[2][j] = f[2][j-1] + 1;
}
}
else if(s[1][j] == 'B'){
if(s[1][j-1] == 'B' && s[2][j-1] == 'B') f[1][j] = f[1][j-1]+1;
else if(s[1][j-1] == 'B') f[1][j] = f[1][j-1] + 1;
}
else if(s[2][j] == 'B'){
if(s[1][j-1] == 'B' && s[2][j-1] == 'B') f[2][j] = f[2][j-1]+1;
else if(s[2][j-1] == 'B') f[2][j] = f[2][j-1] + 1;
}
}
int ans = max(f[1][n],f[2][n]);
//ans 相当于是连接 这个cnt个黑色块的边数 所以要+1 才是黑色块的数量
if(cnt == ans+1) puts("YES");
else puts("NO");
}
int main() {
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
solve();
}
return 0;
}
![[LeetCode周赛复盘] 第 330 场周赛20230129](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ea2a50c625fc4dcc9234d38f37ac074c.png)