文章目录
- 链表类型算法题
- 一、链表介绍
- 本文使用的Java中链表类:
- 二、链表基础题
- 1、数组转链表
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 2、单链表翻转
- 题目:
- 代码:
- 解析:
- 测试:
- 补充:
- 3、合并两个有序链表
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 4、两两交换链表中结点
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 5、回文链表
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 三、中等难度题
- 1、合并K个升序链表
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 2、k个一组翻转链表
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 3、旋转链表
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 测试:
- 4、环形链表
- 题目:
- 解析:
- 代码:
- 四、难题
- 1、判断两链表是否相交,返回相交节点。
- 图解:
- 时间不够,我只解析了解题思路。
链表类型算法题
一、链表介绍
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
本文使用的Java中链表类:
class ListNode{
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(){};
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val,ListNode next){
this.val=val;
this.next=next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "ListNode{" +
"val=" + val +
", next=" + next +
'}';
}
}
本文主要以相关算法为主,基础概念不过多赘述
二、链表基础题
1、数组转链表
是以下众多测试数据转链表的基础
代码:
// 数组给链表赋值
public static ListNode array2LinkedList(int[] arr){
ListNode res=new ListNode(arr[0]);
ListNode cur=res;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
ListNode node=new ListNode(arr[i]);
cur.next=node;
cur=cur.next;
}
return res;
}
测试:
System.out.println(array2LinkedList(new int[]{1,2,3,4}));
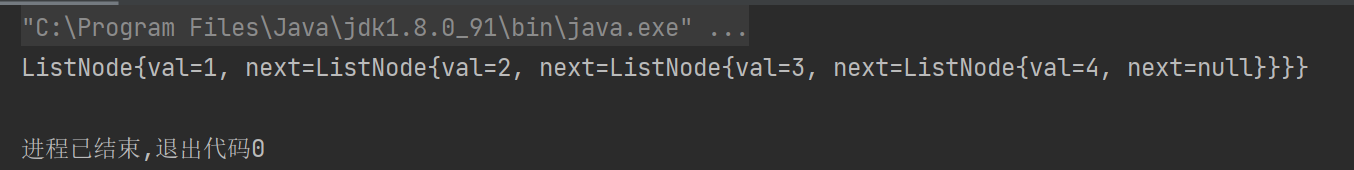
2、单链表翻转
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-linked-list/
题目:
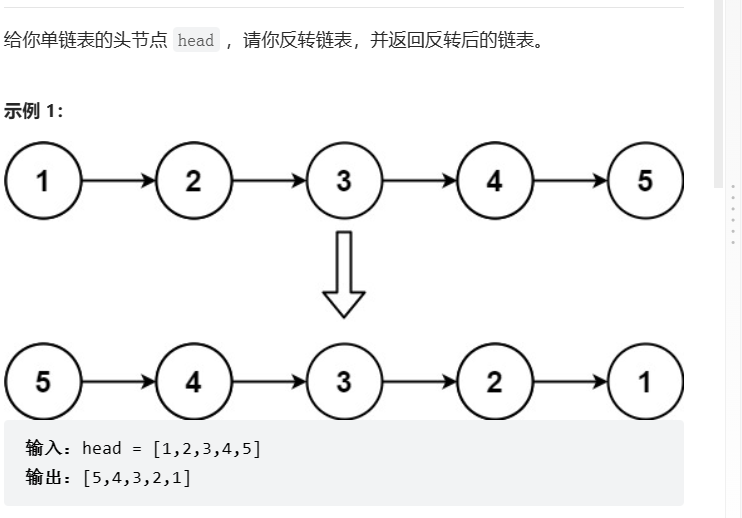
代码:
// 单链表翻转
public static ListNode reverseListNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur = reverseListNode(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return cur;
}
解析:
递归到底:
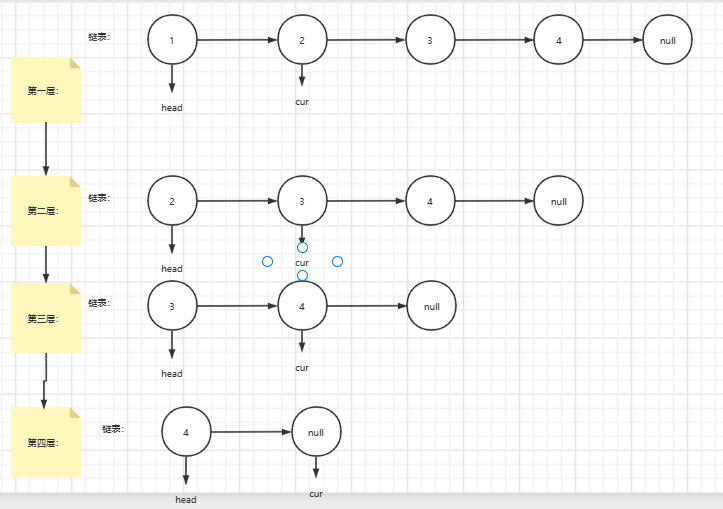
逐步返回:
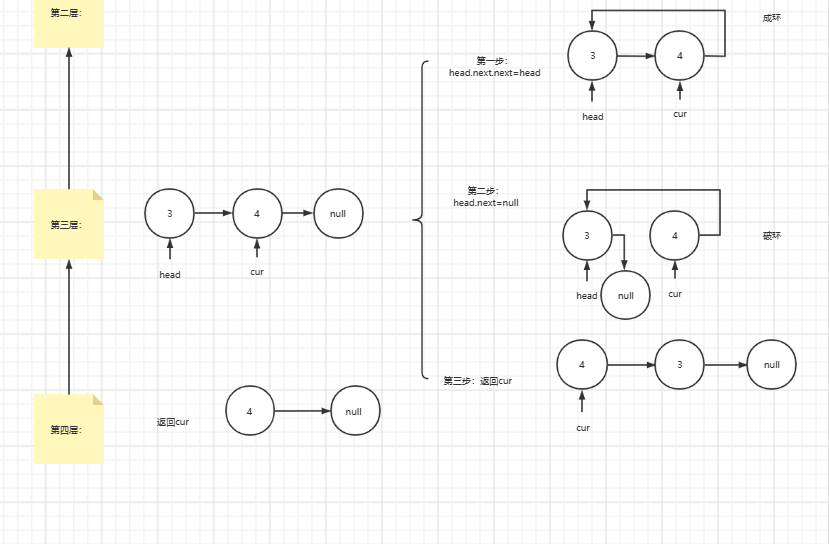
测试:
System.out.println(reverseListNode(array2LinkedList(new int[]{1,2,3,4})));
补充:
可以使用栈,进栈出栈可以完成逆序。
3、合并两个有序链表
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/
题目:
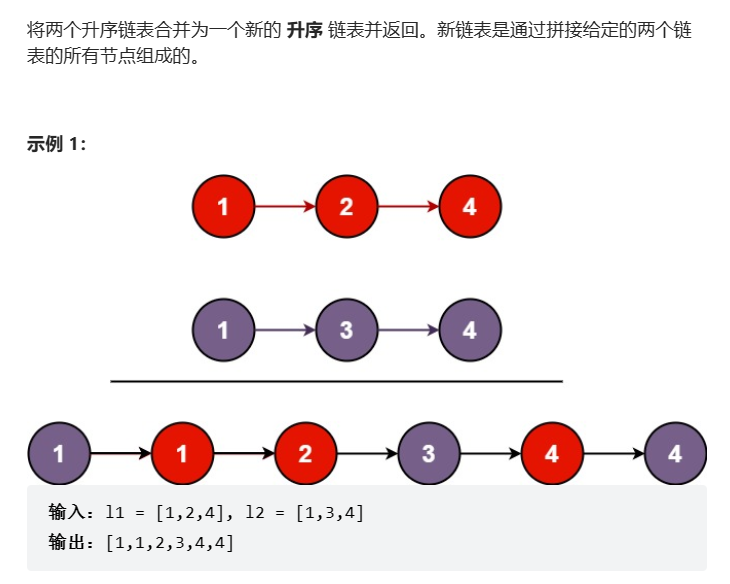
解析:

代码:
// 合并两个有序链表
public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
ListNode res = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur=res;
ListNode cur1=list1;
ListNode cur2=list2;
while (cur1!=null||cur2!=null){
if (cur1!=null&&cur2==null){
cur.next=cur1;
cur1=cur1.next;
cur=cur.next;
continue;
}
if (cur1==null){
cur.next=cur2;
cur2=cur2.next;
cur=cur.next;
continue;
}
if (cur1.val<=cur2.val){
cur.next=cur1;
cur1=cur1.next;
}else {
cur.next=cur2;
cur2=cur2.next;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return res.next;
}
测试:
System.out.println(mergeTwoLists(array2LinkedList(new int[]{1,2,4}),array2LinkedList(new int[]{2,3,4})));
4、两两交换链表中结点
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
题目:
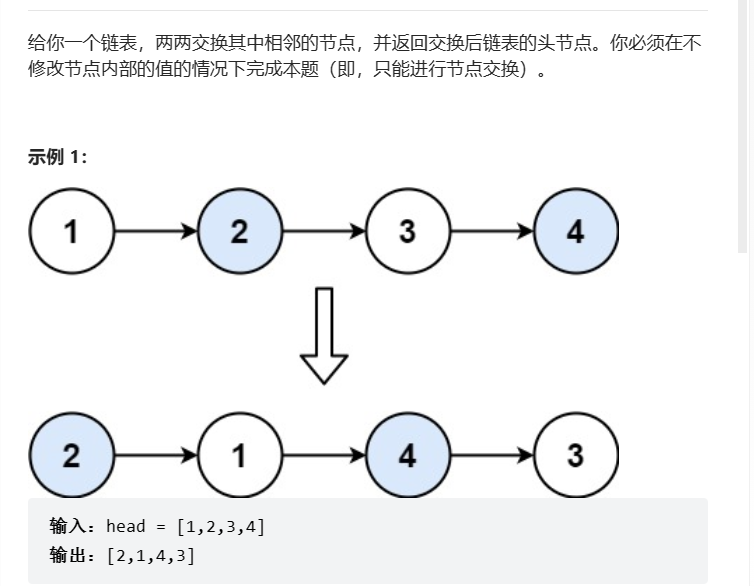
解析:
1、
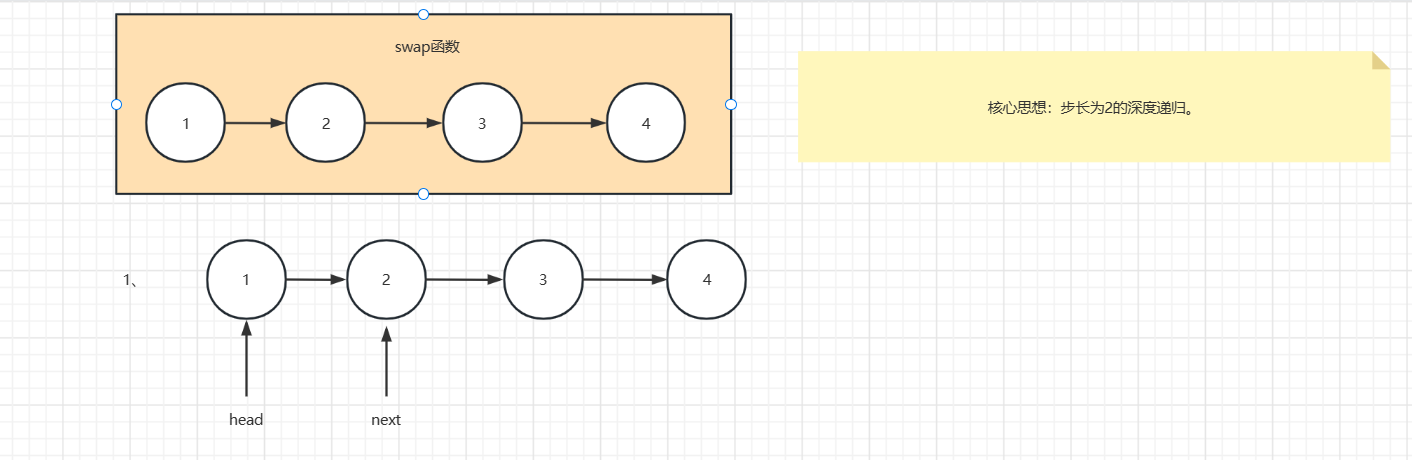
2、
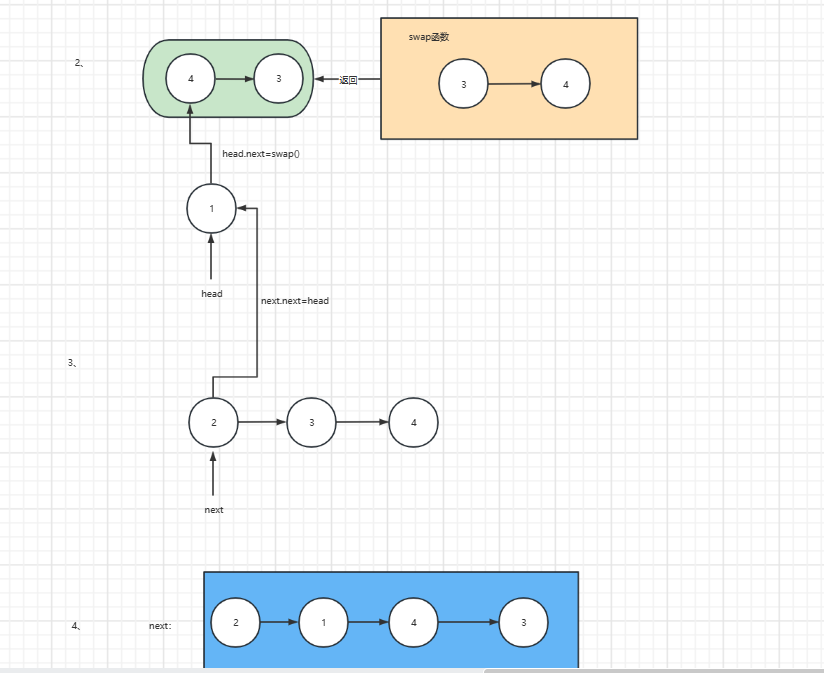
代码:
// 两两交换链表中结点
public static ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
if(head == null || head.next == null){
return head;
}
ListNode next = head.next;
head.next = swapPairs(next.next);
next.next = head;
return next;
}
测试:
int[] arr1={1,2,3,4};
ListNode listNode1 = array2LinkedList(arr1);
ListNode listNode = swapPairs(listNode1);
System.out.println(listNode.toString());

5、回文链表
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/palindrome-linked-list/
题目:
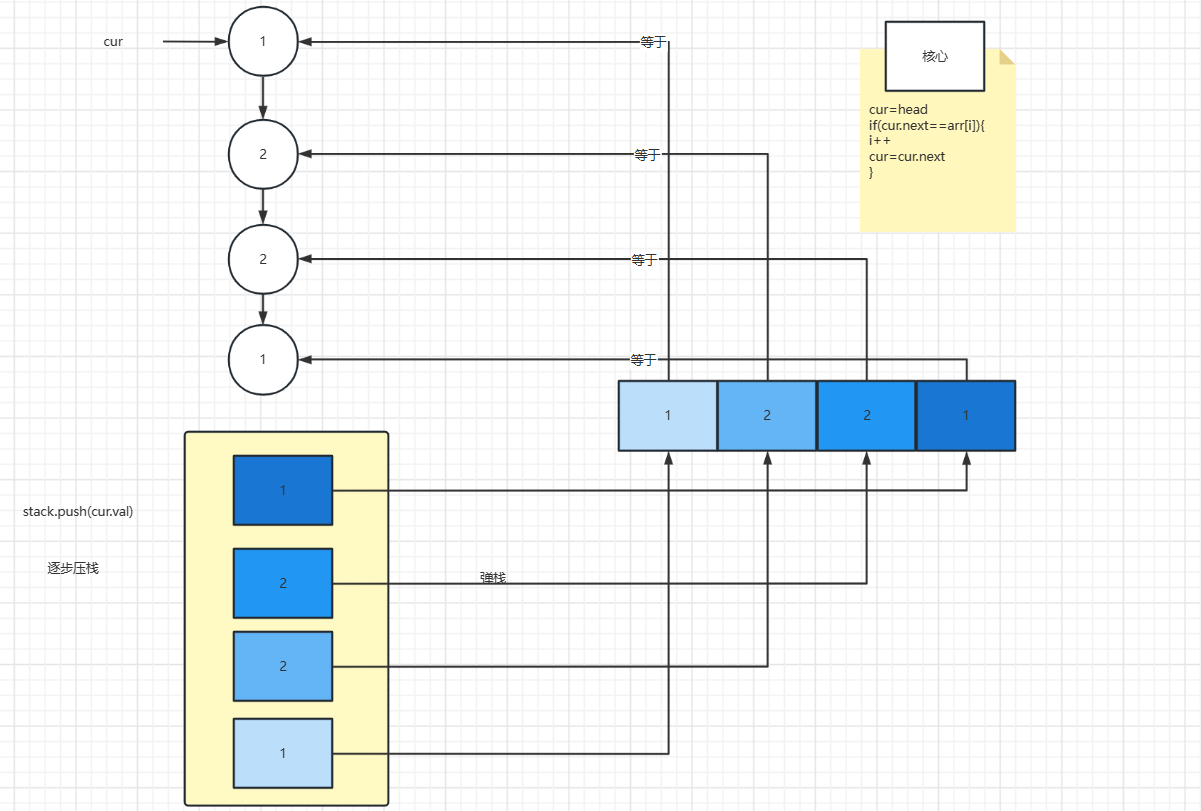
解析:
方式一:使用栈
方式二:利用翻转链表
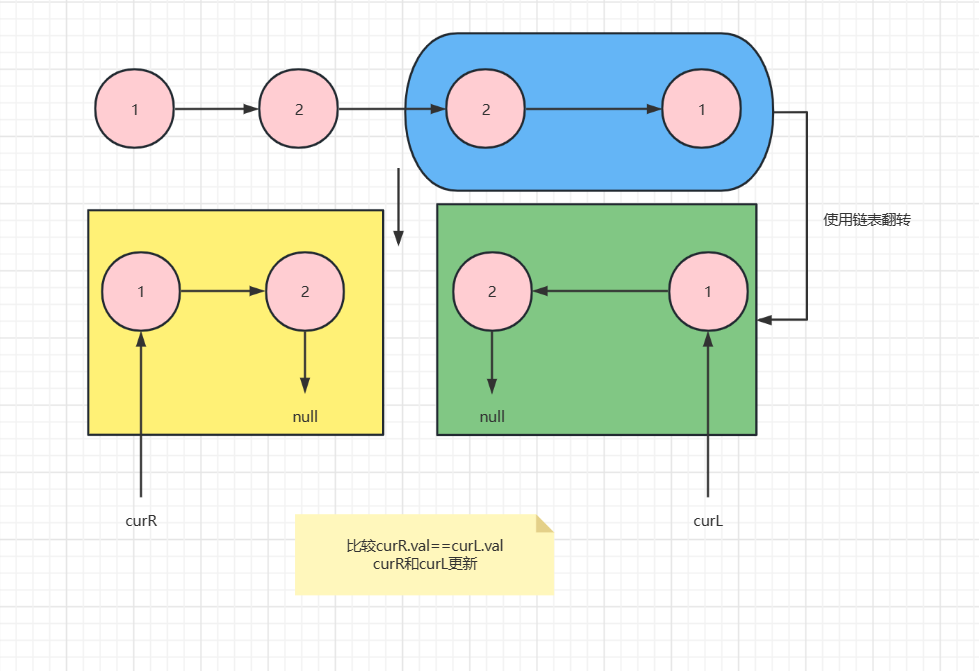
代码:
方式一:使用栈
// 回文结构判断(使用栈)
public static boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> S=new Stack<>();
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
S.add(new ListNode(cur.val));
cur=cur.next;
}
cur=head;
while (!S.isEmpty()){
if (S.pop().val!=cur.val) {
return false;
}
cur=cur.next;
}
return true;
}
方式二:利用链表翻转
// 回文结构判断不使用栈
public static boolean isPalindrome1(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return true;
}
ListNode curF=head;
ListNode curL=head;
while (curL.next!=null&&curL.next.next!=null){
curF=curF.next;
curL=curL.next.next;
}
ListNode next=curF.next;
curF.next=null;
ListNode node = reverseListNode(next);
ListNode cur=node;
curF=head;
while (cur!=null){
if (cur.val!= curF.val) {
return false;
}
cur=cur.next;
curF=curF.next;
}
return true;
}
测试:
int[] arr1={1,2,2,1};
ListNode listNode1 = array2LinkedList(arr1);
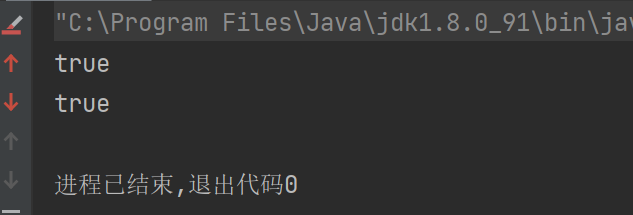
System.out.println(isPalindrome(listNode1));
System.out.println(isPalindrome1(listNode1));
三、中等难度题
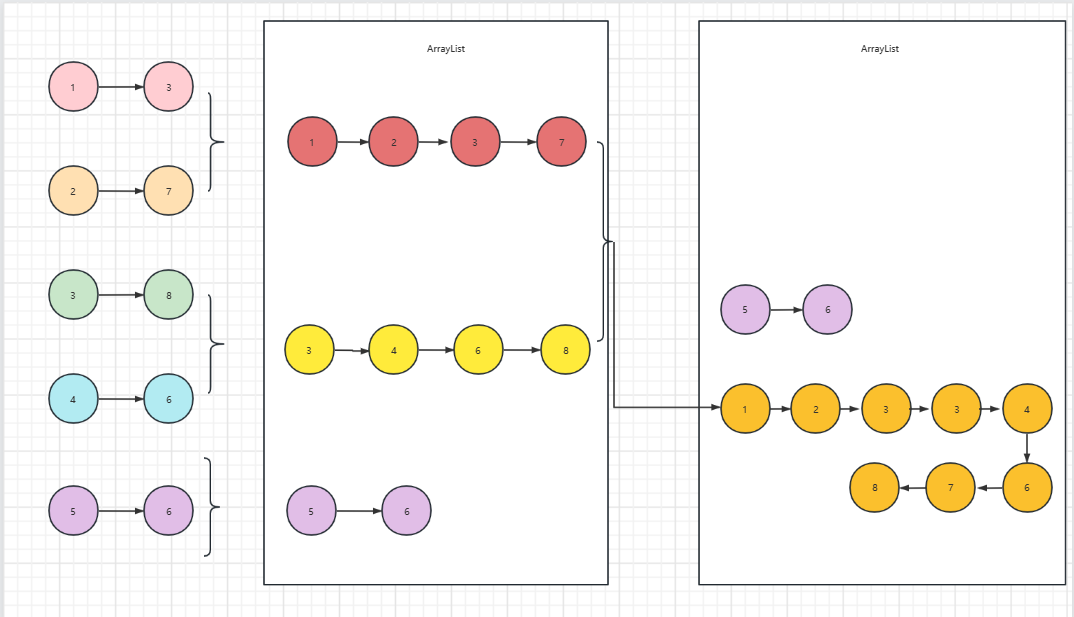
1、合并K个升序链表
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/
题目:

解析:
其中使用合并两个有序链表的函数mergeTwoLists。
代码:
// 合并有序链表数组
public static ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
if (lists.length<1) {
return null;
}
ArrayList<ListNode> LinkedList=new ArrayList<>();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < lists.length-1; i+=2) {
ListNode listNode = mergeTwoLists(lists[i], lists[i + 1]);
LinkedList.add(listNode);
}
if (i==lists.length-1){
LinkedList.add(lists[i]);
}
while (LinkedList.size()>1){
ListNode listNode = mergeTwoLists(LinkedList.get(0), LinkedList.get(1));
LinkedList.remove(0);
LinkedList.remove(0);
LinkedList.add(listNode);
}
return LinkedList.get(0);
}
测试:
int[] arr={4,5};
int[] arr1={1,2,3,4};
int[] arr2={2,6};
ListNode listNode0 = array2LinkedList(arr);
ListNode listNode1 = array2LinkedList(arr1);
ListNode listNode2 = array2LinkedList(arr2);
ListNode[] list={listNode0,listNode1,listNode2};
ListNode listNode = mergeKLists(list);
System.out.println(listNode.toString());
2、k个一组翻转链表
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/
题目:
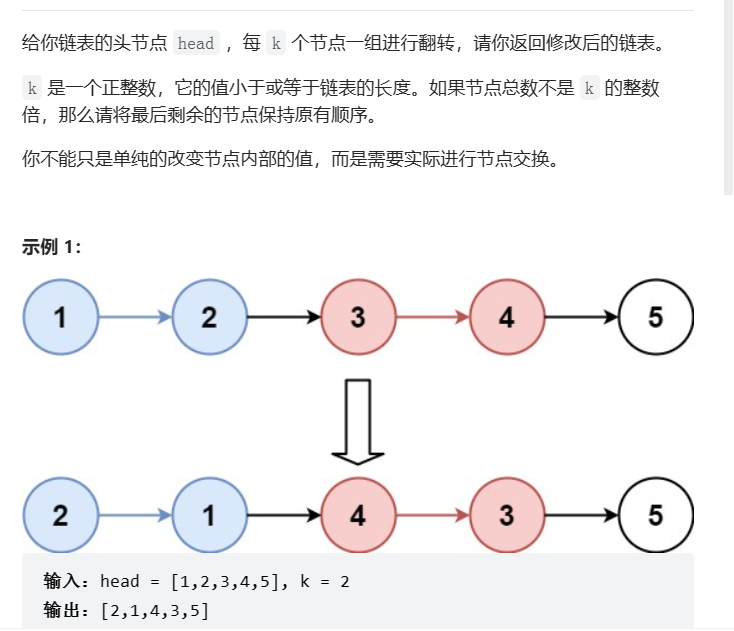
解析:
使用了单链表翻转函数reverseListNode
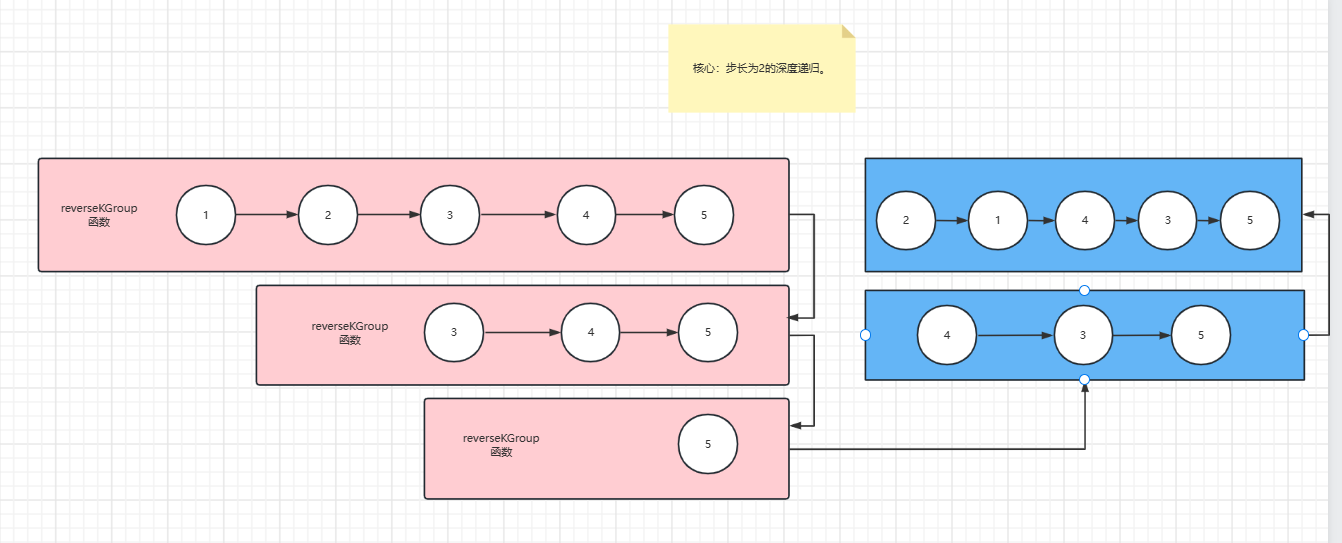
代码:
// k个一组翻转链表
public static ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
if (k<=1) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur=head;
int a=k;
while (a>1){
if (cur==null||cur.next==null) {
return head;
}
cur=cur.next;
a--;
}
ListNode node = reverseKGroup(cur.next, k);
cur.next=null;
ListNode node1 = reverseListNode(head);
while (cur.next!=null){
cur=cur.next;
}
cur.next=node;
return node1;
}
测试:
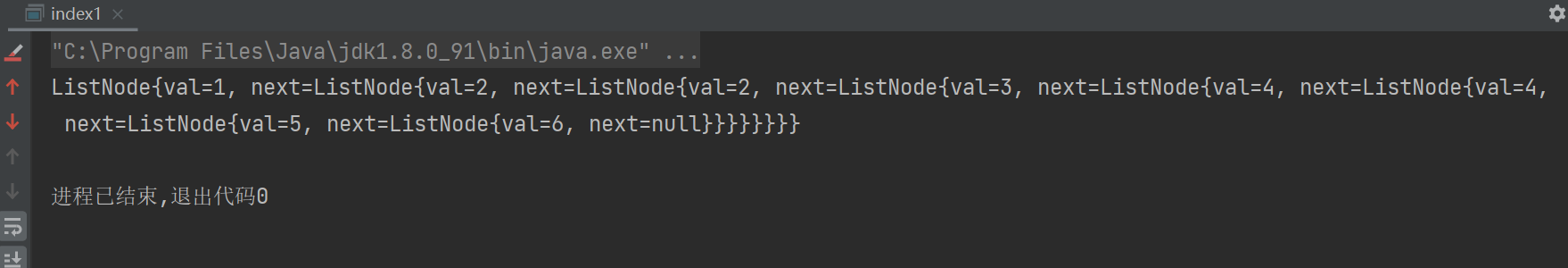
int[] arr1={1,2,3,4,5};
ListNode listNode1 = array2LinkedList(arr1);
System.out.println(reverseKGroup(listNode1, 2).toString());
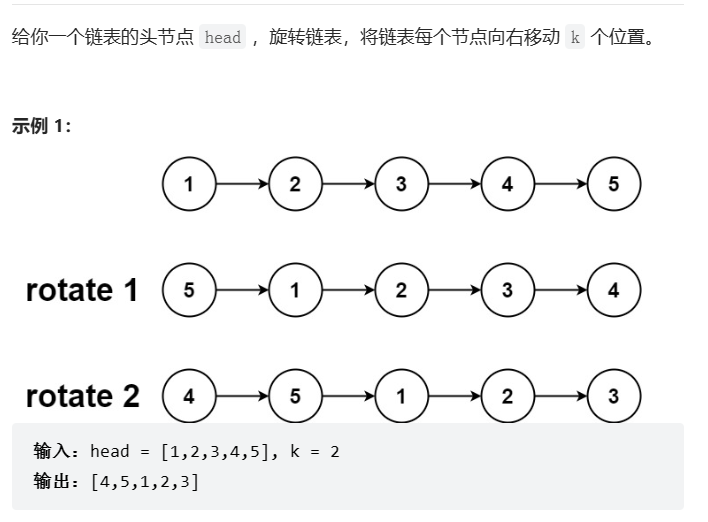
3、旋转链表
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/rotate-list/
题目:
解析:
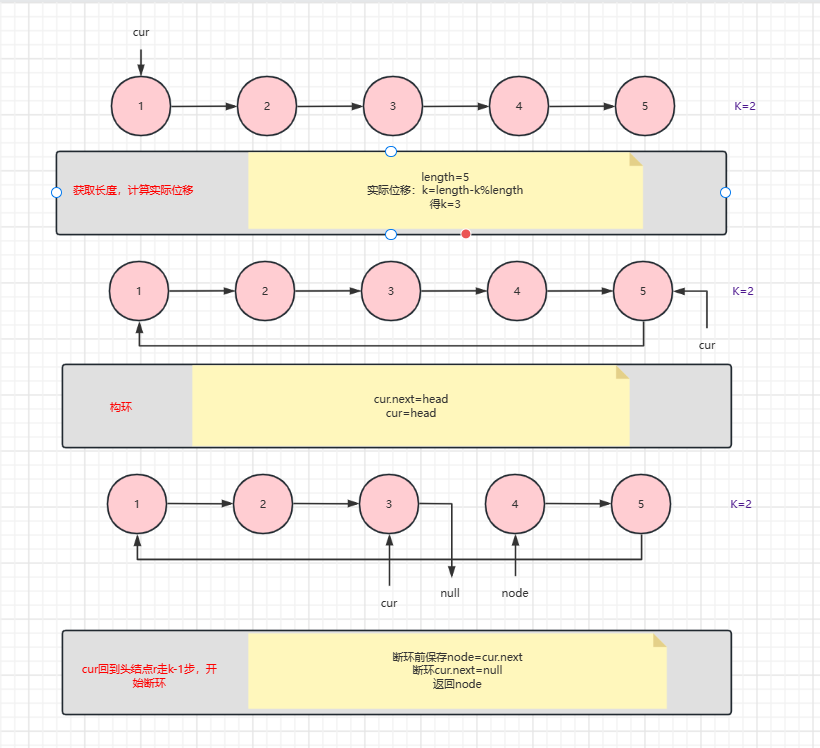
代码:
// 旋转链表正式
public static ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head==null||k==0) {
return head;
}
ListNode cur=head;
//长度
int length=0;
while (cur.next!=null){
cur=cur.next;
length++;
}
length++;
//计算实际位移
k=length-k%length;
if (k==0) {
//整数倍无需位移
return head;
}
cur.next=head;
cur=head;
//指针先走k步
while (k-1>0){
cur=cur.next;
k--;
}
ListNode node=cur.next;
cur.next=null;
return node;
}
测试:
int[] arr1={1,2,3,4,5};
ListNode listNode1 = array2LinkedList(arr1);
System.out.println(rotateRight(listNode1,2));
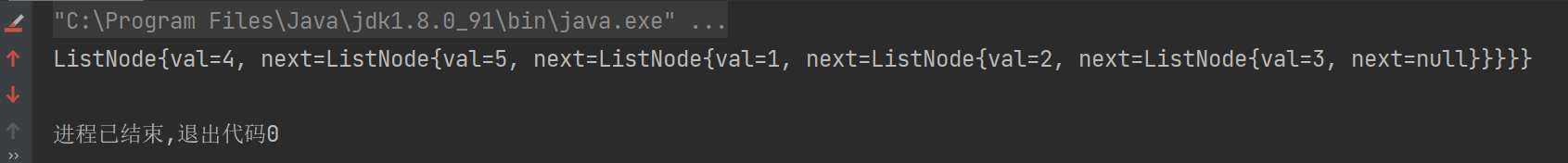
4、环形链表
LeetCode地址:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle/
题目:
(此题返回值稍作修改,有环返回如环节点,无环返回null)
解析:
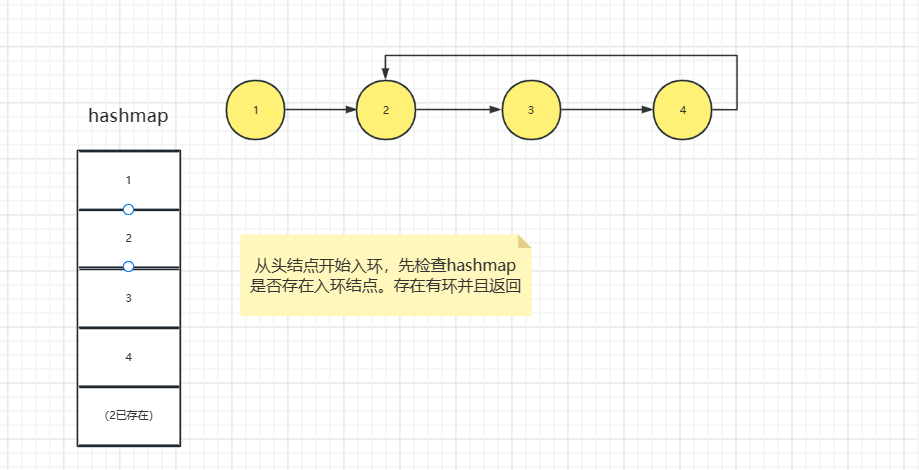
方式一:利用HashMap
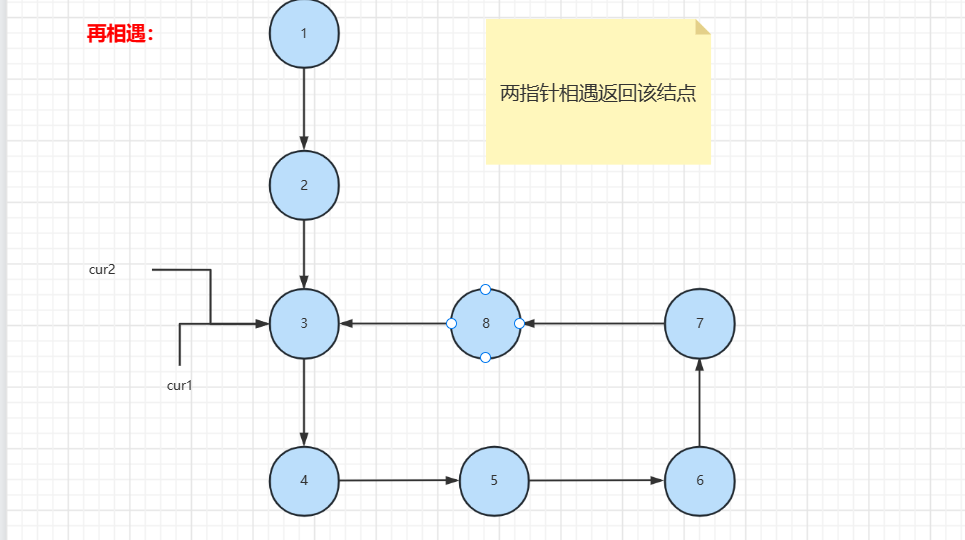
方式二:利用快慢指针

代码:
方式一:hashmap
// 判断链表是否有环(利用HashMap)
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
HashSet<ListNode> list=new LinkedHashSet<>();
ListNode cur=head;
while (cur!=null){
if (list.contains(cur)) {
return true;
}
list.add(cur);
cur=cur.next;
}
return false;
}
方式二:快慢指针
// 判断链表是否有环(快慢指针)有环返回入环结点
public ListNode hasCycle2(ListNode head) {
if (head==null||head.next==null) {
return null;
}
ListNode curF=head;
ListNode curL=head;
while (curF.next!=null&&curF.next.next!=null){
curF =curF.next.next;
curL=curL.next;
if (curF==curL){//确定有环寻找入环结点
curF=head;//返回头结点
while (curF!=curL){
curF=curF.next.next;
curL=curL.next;
}
return curF;
}
}
return null;
}
四、难题
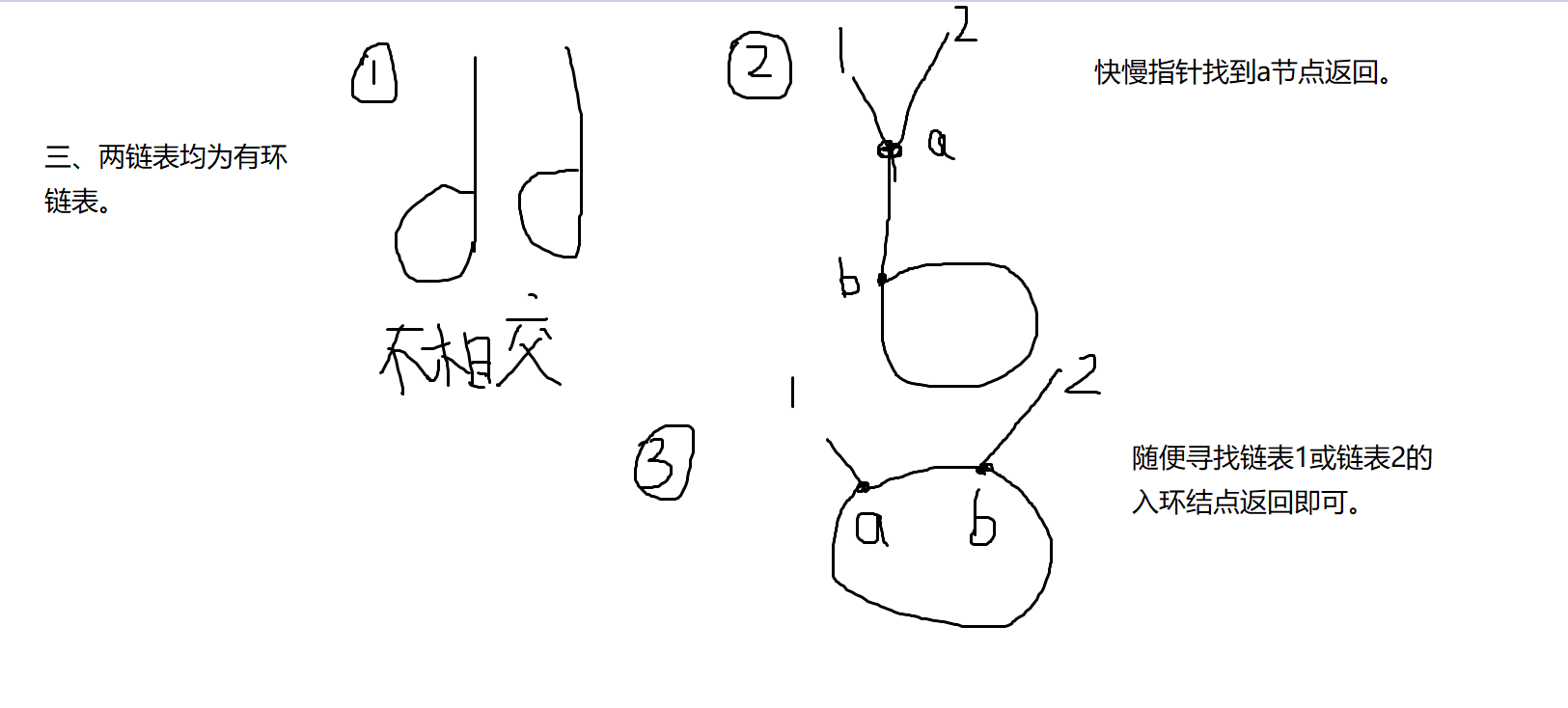
1、判断两链表是否相交,返回相交节点。
图解:
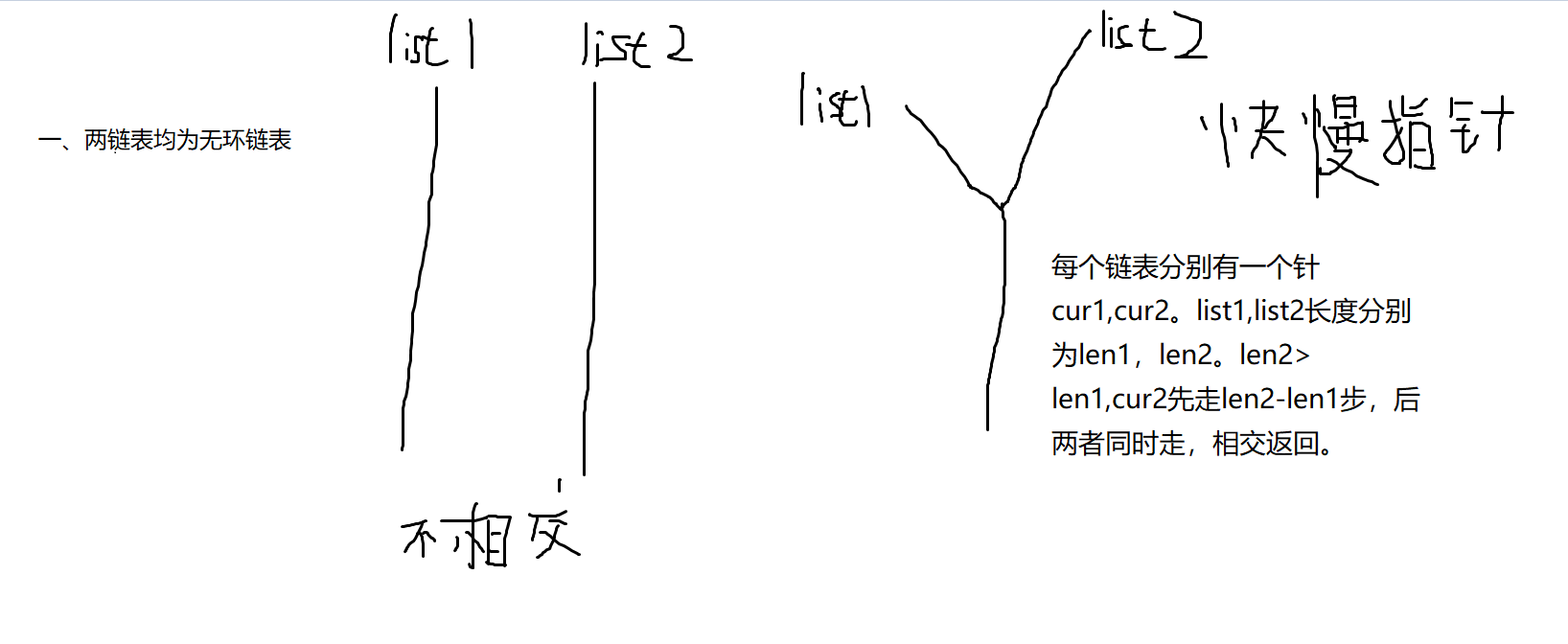
二、两链表中有一者为有环链表。
不存在相交