C++11 并发指南四( 详解三 std::future & std::shared_future)
文章目录
- C++11 并发指南四( 详解三 std::future & std::shared_future)
- std::future 介绍
- std::future 成员函数
- std::shared_future 介绍
- std::future_error 介绍
- 其他与 std::future 相关的函数介绍
- 其他与 std::future 相关的枚举类介绍
上一讲《C++11 并发指南四( 详解二 std::packaged_task 介绍)》主要介绍了 头文件中的 std::packaged_task 类,本文主要介绍 std::future,std::shared_future 以及 std::future_error,另外还会介绍 头文件中的 std::async,std::future_category 函数以及相关枚举类型。
std::future 介绍
前面已经多次提到过 std::future,那么 std::future 究竟是什么呢?简单地说,std::future 可以用来获取异步任务的结果,因此可以把它当成一种简单的线程间同步的手段。std::future 通常由某个 Provider 创建,你可以把 Provider 想象成一个异步任务的提供者,Provider 在某个线程中设置共享状态的值,与该共享状态相关联的 std::future 对象调用 get(通常在另外一个线程中) 获取该值,如果共享状态的标志不为 ready,则调用 std::future::get 会阻塞当前的调用者,直到 Provider 设置了共享状态的值(此时共享状态的标志变为 ready),std::future::get 返回异步任务的值或异常(如果发生了异常)。
一个有效(valid)的 std::future 对象通常由以下三种 Provider 创建,并和某个共享状态相关联。Provider 可以是函数或者类,其实我们前面都已经提到了,他们分别是:
- std::async 函数,本文后面会介绍 std::async() 函数。
- std::promise::get_future,get_future 为 promise 类的成员函数,详见 C++11 并发指南四( 详解一 std::promise 介绍)。
- std::packaged_task::get_future,此时 get_future为 packaged_task 的成员函数,详见C++11 并发指南四( 详解二 std::packaged_task 介绍)。
一个 std::future 对象只有在有效(valid)的情况下才有用(useful),由 std::future 默认构造函数创建的 future 对象不是有效的(除非当前非有效的 future 对象被 move 赋值另一个有效的 future 对象)。
在一个有效的 future 对象上调用 get 会阻塞当前的调用者,直到 Provider 设置了共享状态的值或异常(此时共享状态的标志变为 ready),std::future::get 将返回异步任务的值或异常(如果发生了异常)。
下面以一个简单的例子说明上面一段文字吧(参考):
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
// future example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <future> // std::async, std::future
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::milliseconds
// a non-optimized way of checking for prime numbers:
bool
is_prime(int x)
{
for (int i = 2; i < x; ++i)
if (x % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
int
main()
{
// call function asynchronously:
std::future < bool > fut = std::async(is_prime, 444444443);
// do something while waiting for function to set future:
std::cout << "checking, please wait";
std::chrono::milliseconds span(100);
while (fut.wait_for(span) == std::future_status::timeout)
std::cout << '.';
bool x = fut.get(); // retrieve return value
std::cout << "\n444444443 " << (x ? "is" : "is not") << " prime.\n";
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
std::future 成员函数
std::future 构造函数
std::future 一般由 std::async, std::promise::get_future, std::packaged_task::get_future 创建,不过也提供了构造函数,如下表所示:
| default (1) | future() noexcept; |
|---|---|
| copy [deleted] (2) | future (const future&) = delete; |
| move (3) | future (future&& x) noexcept; |
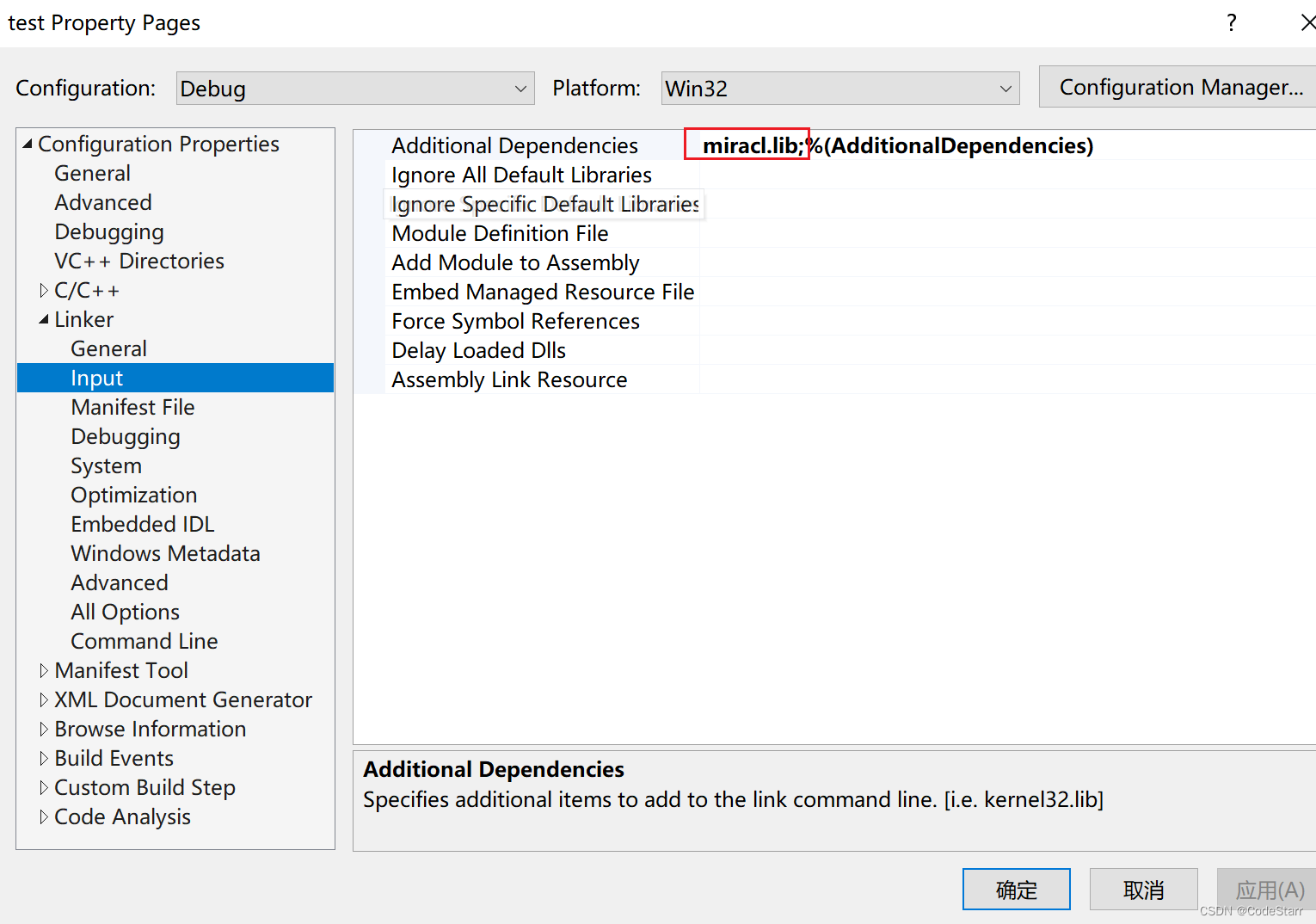
不过 std::future 的拷贝构造函数是被禁用的,只提供了默认的构造函数和 move 构造函数(注:C++ 新特新)。另外,std::future 的普通赋值操作也被禁用,只提供了 move 赋值操作。如下代码所示:
std::future<int> fut; // 默认构造函数
fut = std::async(do_some_task); // move-赋值操作。
std::future::share()
返回一个 std::shared_future 对象(本文后续内容将介绍 std::shared_future ),调用该函数之后,该 std::future 对象本身已经不和任何共享状态相关联,因此该 std::future 的状态不再是 valid 的了。
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <future> // std::async, std::future, std::shared_future
int do_get_value() { return 10; }
int main ()
{
std::future<int> fut = std::async(do_get_value);
std::shared_future<int> shared_fut = fut.share();
// 共享的 future 对象可以被多次访问.
std::cout << "value: " << shared_fut.get() << '\n';
std::cout << "its double: " << shared_fut.get()*2 << '\n';
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
std::future::get()
std::future::get 一共有三种形式,如下表所示(参考):
| generic template (1) | T get(); |
|---|---|
| reference specialization (2) | R& future<R&>::get(); // when T is a reference type (R&) |
| void specialization (3) | void future<void>::get(); // when T is void |
当与该 std::future 对象相关联的共享状态标志变为 ready 后,调用该函数将返回保存在共享状态中的值,如果共享状态的标志不为 ready,则调用该函数会阻塞当前的调用者,而此后一旦共享状态的标志变为 ready,get 返回 Provider 所设置的共享状态的值或者异常(如果抛出了异常)。
请看下面的程序:
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <iostream> // std::cin, std::cout, std::ios
#include <functional> // std::ref
#include <thread> // std::thread
#include <future> // std::promise, std::future
#include <exception> // std::exception, std::current_exception
void get_int(std::promise<int>& prom) {
int x;
std::cout << "Please, enter an integer value: ";
std::cin.exceptions (std::ios::failbit); // throw on failbit
try {
std::cin >> x; // sets failbit if input is not int
prom.set_value(x);
} catch (std::exception&) {
prom.set_exception(std::current_exception());
}
}
void print_int(std::future<int>& fut) {
try {
int x = fut.get();
std::cout << "value: " << x << '\n';
} catch (std::exception& e) {
std::cout << "[exception caught: " << e.what() << "]\n";
}
}
int main ()
{
std::promise<int> prom;
std::future<int> fut = prom.get_future();
std::thread th1(get_int, std::ref(prom));
std::thread th2(print_int, std::ref(fut));
th1.join();
th2.join();
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
std::future::valid()
检查当前的 std::future 对象是否有效,即释放与某个共享状态相关联。一个有效的 std::future 对象只能通过 std::async(), std::future::get_future 或者 std::packaged_task::get_future 来初始化。另外由 std::future 默认构造函数创建的 std::future 对象是无效(invalid)的,当然通过 std::future 的 move 赋值后该 std::future 对象也可以变为 valid。
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <future> // std::async, std::future
#include <utility> // std::move
int do_get_value() { return 11; }
int main ()
{
// 由默认构造函数创建的 std::future 对象,
// 初始化时该 std::future 对象处于为 invalid 状态.
std::future<int> foo, bar;
foo = std::async(do_get_value); // move 赋值, foo 变为 valid.
bar = std::move(foo); // move 赋值, bar 变为 valid, 而 move 赋值以后 foo 变为 invalid.
if (foo.valid())
std::cout << "foo's value: " << foo.get() << '\n';
else
std::cout << "foo is not valid\n";
if (bar.valid())
std::cout << "bar's value: " << bar.get() << '\n';
else
std::cout << "bar is not valid\n";
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
std::future::wait()
等待与当前std::future 对象相关联的共享状态的标志变为 ready.
如果共享状态的标志不是 ready(此时 Provider 没有在共享状态上设置值(或者异常)),调用该函数会被阻塞当前线程,直到共享状态的标志变为 ready。
一旦共享状态的标志变为 ready,wait() 函数返回,当前线程被解除阻塞,但是 wait() 并不读取共享状态的值或者异常。下面的代码说明了 std::future::wait() 的用法(参考)
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <future> // std::async, std::future
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::milliseconds
// a non-optimized way of checking for prime numbers:
bool do_check_prime(int x) // 为了体现效果, 该函数故意没有优化.
{
for (int i = 2; i < x; ++i)
if (x % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
// call function asynchronously:
std::future < bool > fut = std::async(do_check_prime, 194232491);
std::cout << "Checking...\n";
fut.wait();
std::cout << "\n194232491 ";
if (fut.get()) // guaranteed to be ready (and not block) after wait returns
std::cout << "is prime.\n";
else
std::cout << "is not prime.\n";
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
执行结果如下:
concurrency ) ./Future-wait
Checking...
194232491 is prime.
concurrency )
std::future::wait_for()
与 std::future::wait() 的功能类似,即等待与该 std::future 对象相关联的共享状态的标志变为 ready,该函数原型如下:
template <class Rep, class Period>
future_status wait_for (const chrono::duration<Rep,Period>& rel_time) const;
而与 std::future::wait() 不同的是,wait_for() 可以设置一个时间段 rel_time,如果共享状态的标志在该时间段结束之前没有被 Provider 设置为 ready,则调用 wait_for 的线程被阻塞,在等待了 rel_time 的时间长度后 wait_until() 返回,返回值如下:
| 返回值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| future_status::ready | 共享状态的标志已经变为 ready,即 Provider 在共享状态上设置了值或者异常。 |
| future_status::timeout | 超时,即在规定的时间内共享状态的标志没有变为 ready。 |
| future_status::deferred | 共享状态包含一个 deferred 函数。 |
请看下面的例子:
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <future> // std::async, std::future
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::milliseconds
// a non-optimized way of checking for prime numbers:
bool do_check_prime(int x) // 为了体现效果, 该函数故意没有优化.
{
for (int i = 2; i < x; ++i)
if (x % i == 0)
return false;
return true;
}
int main()
{
// call function asynchronously:
std::future < bool > fut = std::async(do_check_prime, 194232491);
std::cout << "Checking...\n";
std::chrono::milliseconds span(1000); // 设置超时间隔.
// 如果超时,则输出".",继续等待
while (fut.wait_for(span) == std::future_status::timeout)
std::cout << '.';
std::cout << "\n194232491 ";
if (fut.get()) // guaranteed to be ready (and not block) after wait returns
std::cout << "is prime.\n";
else
std::cout << "is not prime.\n";
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
std::future::wait_until()
与 std::future::wait() 的功能类似,即等待与该 std::future 对象相关联的共享状态的标志变为 ready,该函数原型如下:
template <class Rep, class Period>
future_status wait_until (const chrono::time_point<Clock,Duration>& abs_time) const;
而 与 std::future::wait() 不同的是,wait_until() 可以设置一个系统绝对时间点 abs_time,如果共享状态的标志在该时间点到来之前没有被 Provider 设置为 ready,则调用 wait_until 的线程被阻塞,在 abs_time 这一时刻到来之后 wait_for() 返回,返回值如下:
| 返回值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| future_status::ready | 共享状态的标志已经变为 ready,即 Provider 在共享状态上设置了值或者异常。 |
| future_status::timeout | 超时,即在规定的时间内共享状态的标志没有变为 ready。 |
| future_status::deferred | 共享状态包含一个 deferred 函数。 |
std::shared_future 介绍
std::shared_future 与 std::future 类似,但是 std::shared_future 可以拷贝、多个 std::shared_future 可以共享某个共享状态的最终结果(即共享状态的某个值或者异常)。shared_future 可以通过某个 std::future 对象隐式转换(参见 std::shared_future 的构造函数),或者通过 std::future::share() 显示转换,无论哪种转换,被转换的那个 std::future 对象都会变为 not-valid.
std::shared_future 构造函数
std::shared_future 共有四种构造函数,如下表所示:
| default (1) | shared_future() noexcept; |
|---|---|
| copy (2) | shared_future (const shared_future& x); |
| move (3) | shared_future (shared_future&& x) noexcept; |
| move from future (4) | shared_future (future<T>&& x) noexcept; |
最后 move from future(4) 即从一个有效的 std::future 对象构造一个 std::shared_future,构造之后 std::future 对象 x 变为无效(not-valid)。
std::shared_future 其他成员函数
std::shared_future 的成员函数和 std::future 大部分相同,如下(每个成员函数都给出了连接):
-
operator=
赋值操作符,与 std::future 的赋值操作不同,std::shared_future 除了支持 move 赋值操作外,还支持普通的赋值操作。
-
get
获取与该 std::shared_future 对象相关联的共享状态的值(或者异常)。
-
valid
有效性检查。
-
wait
等待与该 std::shared_future 对象相关联的共享状态的标志变为 ready。
-
wait_for
等待与该 std::shared_future 对象相关联的共享状态的标志变为 ready。(等待一段时间,超过该时间段wait_for 返回。)
-
wait_until
等待与该 std::shared_future 对象相关联的共享状态的标志变为 ready。(在某一时刻前等待,超过该时刻 wait_until 返回。)
std::future_error 介绍
class future_error : public logic_error;
std::future_error 继承子 C++ 标准异常体系中的 logic_error,有关 C++ 异常的继承体系,请参考相关的C++教程 😉。
其他与 std::future 相关的函数介绍
与 std::future 相关的函数主要是 std::async(),原型如下:
| unspecified policy (1) | template <class Fn, class... Args> future<typename result_of<Fn(Args...)>::type> async(Fn&& fn, Args&&... args); |
|---|---|
| specific policy (2) | template <class Fn, class... Args> future<typename result_of<Fn(Args...)>::type> async(launch policy, Fn&& fn, Args&&... args); |
上面两组 std::async() 的不同之处是第一类 std::async 没有指定异步任务(即执行某一函数)的启动策略(launch policy),而第二类函数指定了启动策略,详见 std::launch 枚举类型,指定启动策略的函数的 policy 参数可以是launch::async,launch::deferred,以及两者的按位或( | )。
std::async() 的 fn 和 args 参数用来指定异步任务及其参数。另外,std::async() 返回一个 std::future 对象,通过该对象可以获取异步任务的值或异常(如果异步任务抛出了异常)。
下面介绍一下 std::async 的用法。
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <chrono>
#include <future>
#include <iostream>
double ThreadTask(int n) {
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< " start computing..." << std::endl;
double ret = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
ret += std::sin(i);
}
std::cout << std::this_thread::get_id()
<< " finished computing..." << std::endl;
return ret;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
std::future<double> f(std::async(std::launch::async, ThreadTask, 100000000));
#if 0
while(f.wait_until(std::chrono::system_clock::now() + std::chrono::seconds(1))
!= std::future_status::ready) {
std::cout << "task is running...\n";
}
#else
while(f.wait_for(std::chrono::seconds(1))
!= std::future_status::ready) {
std::cout << "task is running...\n";
}
#endif
std::cout << f.get() << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
其他与 std::future 相关的枚举类介绍
下面介绍与 std::future 相关的枚举类型。与 std::future 相关的枚举类型包括:
enum class future_errc;
enum class future_status;
enum class launch;
下面分别介绍以上三种枚举类型:
std::future_errc 类型
std::future_errc 类型描述如下(参考):
| 类型 | 取值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| broken_promise | 0 | 与该 std::future 共享状态相关联的 std::promise 对象在设置值或者异常之前一被销毁。 |
| future_already_retrieved | 1 | 与该 std::future 对象相关联的共享状态的值已经被当前 Provider 获取了,即调用了 std::future::get 函数。 |
| promise_already_satisfied | 2 | std::promise 对象已经对共享状态设置了某一值或者异常。 |
| no_state | 3 | 无共享状态。 |
std::future_status 类型(参考)
std::future_status 类型主要用在 std::future(或std::shared_future)中的 wait_for 和 wait_until 两个函数中的。
| 类型 | 取值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| future_status::ready | 0 | wait_for(或wait_until) 因为共享状态的标志变为 ready 而返回。 |
| future_status::timeout | 1 | 超时,即 wait_for(或wait_until) 因为在指定的时间段(或时刻)内共享状态的标志依然没有变为 ready 而返回。 |
| future_status::deferred | 2 | 共享状态包含了 deferred 函数。 |
std::launch 类型
该枚举类型主要是在调用 std::async 设置异步任务的启动策略的。**
**
| 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| launch::async | Asynchronous: 异步任务会在另外一个线程中调用,并通过共享状态返回异步任务的结果(一般是调用 std::future::get() 获取异步任务的结果)。 |
| launch::deferred | Deferred: 异步任务将会在共享状态被访问时调用,相当与按需调用(即延迟(deferred)调用)。 |
请看下例(参考):
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <future> // std::async, std::future, std::launch
#include <chrono> // std::chrono::milliseconds
#include <thread> // std::this_thread::sleep_for
void
do_print_ten(char c, int ms)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(ms));
std::cout << c;
}
}
int
main()
{
std::cout << "with launch::async:\n";
std::future < void >foo =
std::async(std::launch::async, do_print_ten, '*', 100);
std::future < void >bar =
std::async(std::launch::async, do_print_ten, '@', 200);
// async "get" (wait for foo and bar to be ready):
foo.get();
bar.get();
std::cout << "\n\n";
std::cout << "with launch::deferred:\n";
foo = std::async(std::launch::deferred, do_print_ten, '*', 100);
bar = std::async(std::launch::deferred, do_print_ten, '@', 200);
// deferred "get" (perform the actual calls):
foo.get();
bar.get();
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
[ ](javascript:void(0)😉
](javascript:void(0)😉
在我的机器上执行结果:
with launch::async:
*@**@**@**@**@*@@@@@
with launch::deferred:
**********@@@@@@@@@@
bar.get();
std::cout << “\n\n”;
std::cout << "with launch::deferred:\n";
foo = std::async(std::launch::deferred, do_print_ten, '*', 100);
bar = std::async(std::launch::deferred, do_print_ten, '@', 200);
// deferred "get" (perform the actual calls):
foo.get();
bar.get();
std::cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
[[外链图片转存中...(img-eE6GGkx5-1674832496916)]](javascript:void(0);)
在我的机器上执行结果:
with launch::async:
@@@@@@@@@@
with launch::deferred:
**********@@@@@@@@@@