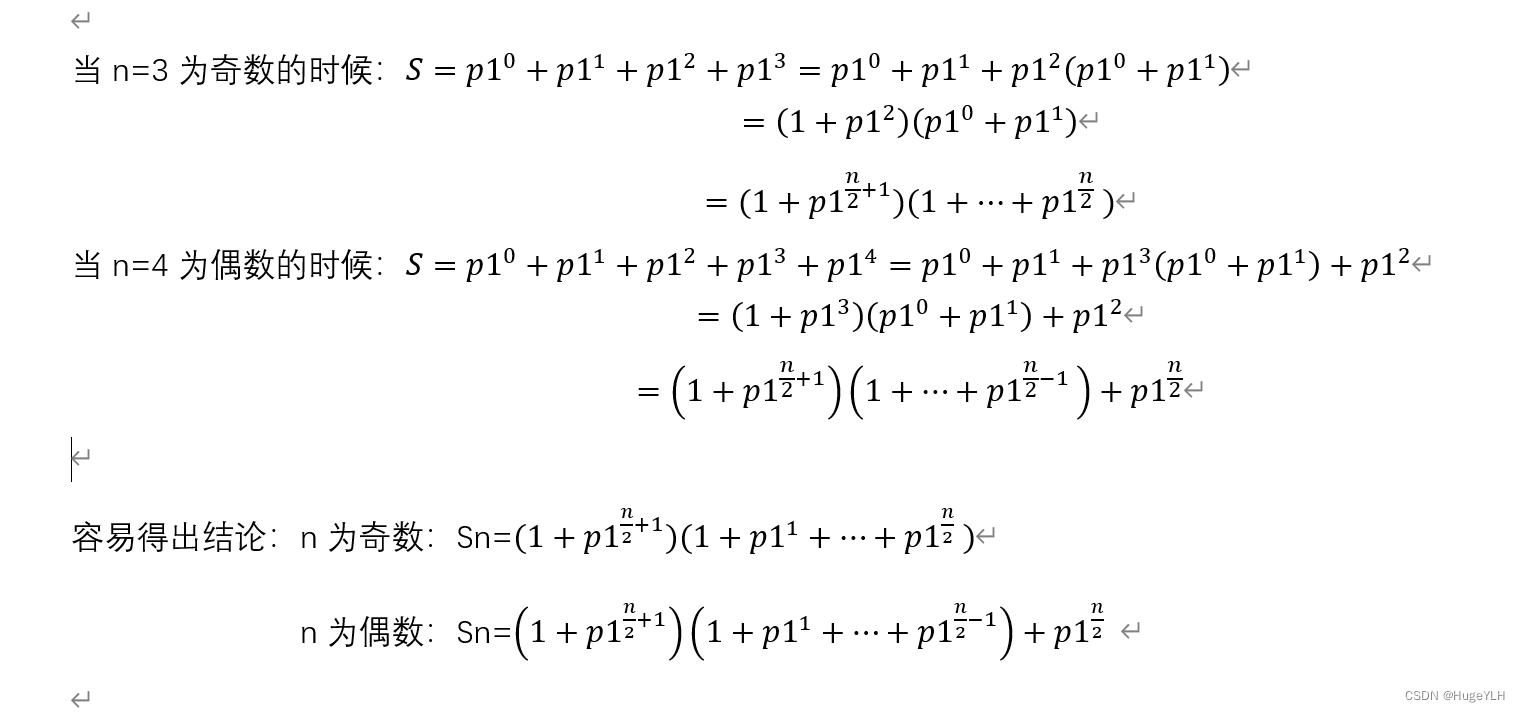安卓S开机动画流程
开机动画是在SurfaceFlinger实例通过调用startBootAnim()启动的,BootAnim是如何启动和结束的,总体框架图如下:
1.SurfaceFlinger进程启动
# /frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/surfaceflinger.rc
service surfaceflinger /system/bin/surfaceflinger
class core animation
user system
group graphics drmrpc readproc
capabilities SYS_NICE
onrestart restart zygote
task_profiles HighPerformance
socket pdx/system/vr/display/client stream 0666 system graphics u:object_r:pdx_display_client_endpoint_socket:s0
socket pdx/system/vr/display/manager stream 0666 system graphics u:object_r:pdx_display_manager_endpoint_socket:s0
socket pdx/system/vr/display/vsync stream 0666 system graphics u:object_r:pdx_display_vsync_endpoint_socket:s0
init进程会根据surfaceflinger.rc配置启动surfaceflinger进程,surfaceflinger进程(/system/bin/surfaceflinger)启动,会走到main函数里面。
# /frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/Android.bp
filegroup {
name: "surfaceflinger_binary_sources",
srcs: [
":libsurfaceflinger_sources",
"main_surfaceflinger.cpp",
],
}
cc_binary {
name: "surfaceflinger",
defaults: ["libsurfaceflinger_binary"],
init_rc: ["surfaceflinger.rc"],
srcs: [
":surfaceflinger_binary_sources",
// Note: SurfaceFlingerFactory is not in the filegroup so that it
// can be easily replaced.
"SurfaceFlingerFactory.cpp",
],
shared_libs: [
"libSurfaceFlingerProp",
],
logtags: ["EventLog/EventLogTags.logtags"],
}
可以看到编译surfaceflinger二进制进程的源文件为surfaceflinger_binary_sources和SurfaceFlingerFactory.cpp,其中surfaceflinger_binary_sources来源于main_surfaceflinger.cpp
2.注册启动surfaceflinger服务
// /frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/main_surfaceflinger.cpp
int main(int, char**) {
// ...
sp<SurfaceFlinger> flinger = surfaceflinger::createSurfaceFlinger(); //创建surfaceflinger服务实例
// ...
flinger->init(); // 初始化flinger实例
// 向ServiceManager注册surfaceflinger服务
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
sm->addService(String16(SurfaceFlinger::getServiceName()), flinger, false,
IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PRIORITY_CRITICAL | IServiceManager::DUMP_FLAG_PROTO);
// ...
flinger->run(); // 启动surfaceflinger服务
return 0;
}
调用SurfaceFlinger对象的init方法
// /frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
void SurfaceFlinger::init() {
// ...
mStartPropertySetThread = getFactory().createStartPropertySetThread(presentFenceReliable);
if (mStartPropertySetThread->Start() != NO_ERROR) {
ALOGE("Run StartPropertySetThread failed!");
}
ALOGV("Done initializing");
}
SurfaceFlinger调用init方法时会获取mStartPropertySetThread,调用该对象的Start方法,其实是准备启动一个线程去启动BootAnimation
// /frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/StartPropertySetThread.cpp
status_t StartPropertySetThread::Start() {
return run("SurfaceFlinger::StartPropertySetThread", PRIORITY_NORMAL);
}
bool StartPropertySetThread::threadLoop() {
// Set property service.sf.present_timestamp, consumer need check its readiness
property_set(kTimestampProperty, mTimestampPropertyValue ? "1" : "0");
// 清除BootAnimation退出标志位service.bootanim.exit
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "0");
// 设置bootanim的进度为0
property_set("service.bootanim.progress", "0");
// 通过service.bootanim.exit
property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");
// 立即退出
return false;
}
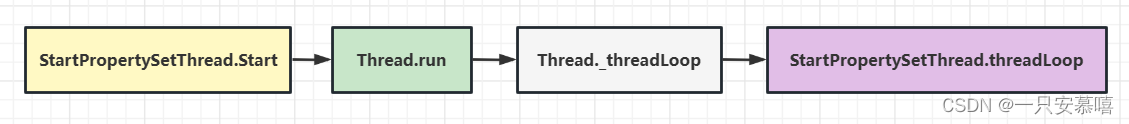
- 这里一开始看起来比较疑惑,首先是StartPropertySetThread::Start函数,在
StartPropertySetThread.h表明StartPropertySetThread继承自父类Thread,而父类Thread是由<utils/Thread.h> 引入的,所以这里是子类引用父类方法,这里的run函数就是就是thread的run方法。这里会启动一个线程去运行,线程名为"StartPropertySetThread",线程优先级为PRIORITY_NORMAL。线程启动以后,最终会调用_threadLoop函数,它会去调用threadLoop函数。这里整个函数调用栈就清楚了:
- 当系统属性发生改变时,init进程就会接收到一个系统属性变化通知,这个通知最终是由在init进程中的函数handle_property_set_fd来处理
3.bootanim进程启动
// /frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/bootanimation_main.cpp
int main()
{
setpriority(PRIO_PROCESS, 0, ANDROID_PRIORITY_DISPLAY);
bool noBootAnimation = bootAnimationDisabled();
ALOGI_IF(noBootAnimation, "boot animation disabled");
if (!noBootAnimation) {
// 启动Binder线程池
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
sp<BootAnimation> boot = new BootAnimation(audioplay::createAnimationCallbacks());
waitForSurfaceFlinger();
boot->run("BootAnimation", PRIORITY_DISPLAY);
// ...
}
return 0;
}
bool bootAnimationDisabled() {
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
// 如果debug.sf.nobootanimation=1,则不会显示动画
property_get("debug.sf.nobootanimation", value, "0");
if (atoi(value) > 0) {
return true;
}
// 如果ro.boot.quiescent=1,则不显示开机动画
property_get("ro.boot.quiescent", value, "0");
if (atoi(value) > 0) {
// Only show the bootanimation for quiescent boots if this system property is set to enabled
if (!property_get_bool("ro.bootanim.quiescent.enabled", false)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
判断完BootAnimation是不是disabled之后,如果noBootAnimation为false,则创建一个BootAnimation对象。创建完了BootAnimation对象后,调用其run方法,由于BootAnimation也继承了Thread,所以最终也会走到对应的threadLoop方法
bool BootAnimation::threadLoop()
{
bool r;
if (mZipFileName == NULL) {
...
} else {
r = movie(); // 调用movie方法
}
// 销毁 opengl 和 egl
eglMakeCurrent(mDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
eglDestroyContext(mDisplay, mContext);
eglDestroySurface(mDisplay, mSurface);
mFlingerSurface.clear();
mFlingerSurfaceControl.clear();
eglTerminate(mDisplay);
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
return r;
}
bool BootAnimation::movie()
{
String8 desString;
// 读取 desc.txt 配置文件
if (!readFile("desc.txt", desString)) {
return false;
}
char const* s = desString.string();
// 解析描述文件
for (;;) {
...
}
for (size_t i=0 ; i<pcount ; i++) {
for (int r=0 ; !part.count || r<part.count ; r++) {
// opengl 绘制操作
glClearColor(
part.backgroundColor[0],
part.backgroundColor[1],
part.backgroundColor[2],
1.0f);
for (size_t j=0 ; j<fcount && (!exitPending() || part.playUntilComplete) ; j++) {
const Animation::Frame& frame(part.frames[j]);
nsecs_t lastFrame = systemTime();
...
if (r > 0) {
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid);
} else {
...
initTexture(frame);
}
// specify the y center as ceiling((mHeight - animation.height) / 2)
// which is equivalent to mHeight - (yc + animation.height)
glDrawTexiOES(xc, mHeight - (yc + animation.height),
0, animation.width, animation.height);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
// 不断绘制时检测是否需要退出
checkExit();
}
// 如果退出了就跳出结束绘制
if(exitPending() && !part.count)
break;
}
// free the textures for this part
if (part.count != 1) {
for (size_t j=0 ; j<fcount ; j++) {
const Animation::Frame& frame(part.frames[j]);
glDeleteTextures(1, &frame.tid);
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 读取 service.bootanim.exit 值是否是 1
#define EXIT_PROP_NAME "service.bootanim.exit"
void BootAnimation::checkExit() {
// Allow surface flinger to gracefully request shutdown
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get(EXIT_PROP_NAME, value, "0");
int exitnow = atoi(value);
if (exitnow) {
requestExit();
if (mAudioPlayer != NULL) {
mAudioPlayer->requestExit();
}
}
}
启动动画底层采用的是 opengles 的方式来渲染绘制的,绘制的内容是本地的一个启动动画资源包,在绘制的过程中会不断的判断是否需要退出,读取的字段是 service.bootanim.exit ,为 1 代表需要 break 退出循环绘制。因此我们只需要找到 service.bootanim.exit 在哪里设置为 1 的,便可找到退出启动动画的入口。关闭动画的入口还是在 SurfaceFlinger 中只是这个调用流程比较复杂而已:
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume) {
ActivityClientRecord r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide);
if (r != null) {
if (!r.onlyLocalRequest) {
r.nextIdle = mNewActivities;
mNewActivities = r;
// 添加了一个 IdleHandler 消息
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler());
}
} else {
...
}
}
private class Idler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler {
@Override
public final boolean queueIdle() {
ActivityClientRecord a = mNewActivities;
if (a != null) {
mNewActivities = null;
IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
ActivityClientRecord prev;
do {
if (a.activity != null && !a.activity.mFinished) {
try {
// 调用 AMS 的 activityIdle
am.activityIdle(a.token, a.createdConfig, stopProfiling);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
}
} while (a != null);
}
return false;
}
}
@Override
public final void activityIdle(IBinder token, Configuration config, boolean stopProfiling) {
synchronized (this) {
ActivityStack stack = ActivityRecord.getStackLocked(token);
if (stack != null) {
ActivityRecord r = mStackSupervisor.activityIdleInternalLocked(token, false, config);
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
// Checked.
final ActivityRecord activityIdleInternalLocked(final IBinder token, boolean fromTimeout,
Configuration config) {
ActivityRecord r = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(token);
if (r != null) {
...
if (isFrontStack(r.task.stack) || fromTimeout) {
booting = checkFinishBootingLocked();
}
}
...
return r;
}
private boolean checkFinishBootingLocked() {
final boolean booting = mService.mBooting;
boolean enableScreen = false;
mService.mBooting = false;
if (!mService.mBooted) {
mService.mBooted = true;
enableScreen = true;
}
if (booting || enableScreen) {
mService.postFinishBooting(booting, enableScreen);
}
return booting;
}
void enableScreenAfterBoot() {
mWindowManager.enableScreenAfterBoot();
synchronized (this) {
updateEventDispatchingLocked();
}
}
public void performEnableScreen() {
synchronized(mWindowMap) {
if (!mBootAnimationStopped) {
// 向SurfaceFlinger 进程发起关闭开机界面的消息
try {
IBinder surfaceFlinger = ServiceManager.getService("SurfaceFlinger");
if (surfaceFlinger != null) {
Parcel data = Parcel.obtain();
data.writeInterfaceToken("android.ui.ISurfaceComposer");
// 向SurfaceComposer发送
surfaceFlinger.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // BOOT_FINISHED
data, null, 0);
data.recycle();
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
...
}
mBootAnimationStopped = true;
}
...
}
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
enum ISurfaceComposerTag {
BOOT_FINISHED = IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION,
// ...
}
// /frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp
status_t BnSurfaceComposer::onTransact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags){
switch(code) {
// ...
case BOOT_FINISHED: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(ISurfaceComposer, data, reply);
bootFinished();
return NO_ERROR;
}
// ...
}
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
void SurfaceFlinger::bootFinished() {
// ...
// 把 service.bootanim.exit 属性设置为 1 ,bootanim 进程读到 1 时就会退出开机启动动画
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "1");
}
关闭开机启动动画的流程还是比较复杂的,我们来缕一缕整个逻辑,我们的 Launcher 进程启动后会启动我们 Launcher Activity 界面,而 Activity 的生命周期调用都是由 ActivityThread 来执行的,其中就会执行到 handleResumeActivity 方法,在该方法中会添加一个 IdleHandler 消息,会调用到 AMS 的 activityIdle 方法,AMS 会调用 WMS 的 enableScreenAfterBoot 方法,WMS 会跨进程通知 SurfaceFlinger 去关闭我们的开机启动动画。
4.开机动画包里有什么
这里建议先看一下官方文档:/frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/FORMAT.md
开机动画指的是以bootanimation.zip方式存在,启动的时候会依次选择一个bootanimation.zip加载
- /system/media/bootanimation-encrypted.zip (if getprop(“vold.decrypt”) = ‘1’)
- /system/media/bootanimation.zip
- /oem/media/bootanimation.zip
bootanimation.zip 文件中包含:
desc.txt - a text file
part0 \
part1 \ directories full of PNG frames
... /
partN /
“desc.txt”:用来描述用户自定义的开机动画是如何显示的。
以下面的例子为例:
1280 720 1
p 1 1 part0
p 0 1 part1
第一行的三个数字分别表示开机动画在屏幕中的显示宽度、高度以及帧速(fps)。剩余的每一行都用来描述一个动画片断,这些行必须要以字符“p”来开头,后面紧跟着两个数字以及一个文件目录路径名称。
第一个数字表示一个片断的循环显示次数,如果它的值等于0,那么就表示无限循环地显示该动画片断。
第二个数字表示每一个片断在两次循环显示之间的时间间隔。这个时间间隔是以一个帧的时间为单位的。
文件目录下面保存的是一系列png文件,这些png文件会被依次显示在屏幕中。
参考资料:
- https://blog.51cto.com/u_11176305/3796348
- https://www.cnblogs.com/lufeibin/p/13529981.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_36044720/article/details/117277602?spm=1001.2014.3001.5506