第一章 SpringMVC的简介
Spring框架版本 4.3.29.RELEASE
- SpringMVC是什么
1 2 3 4 5 6
1. Spring家族的一个部分 2. 是JavaWeb三层架构中控制器层的解决方案 3. 是基于MVC思想的框架 -- Model -- View -- Controller

- SpringMVC知识点大纲

- SpringMVC功能简述
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
1. 作为spring框架的一部分天生与spring框架集成 2. 支持restful风格 3. 灵活的请求URL/控制器/页面的映射 4. 数据绑定在模型中,容易传递,前端可以很好的支持其他视图 5. 简单的数据绑定,数据验证,可以绑定多种数据结构 6. 强大的异常处理功能 7. 静态资源的支持 8. 文件上传/下载 9. 国际化 ...
- SpringMVC常用组件
1 2 3 4 5 6
-- 前端控制器: DispatcherServlet -- 视图解析器: ViewResolver -- 控制器/动作处理器: controller -- 国际化: LocalResolver -- 文件上传: MultipartResolver -- 异常处理器: HandlerExceptionResolver
第二章 SpringMVC快速入门
第1节 编写步骤
- 创建index.jsp/result.jsp页面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
index.jsp <a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/hello">Hello SpringMVC</a> result.jsp result.jsp页面要放到springmvc配置文件指定的解析目录下 - 创建SpringMVC的配置文件 spring-mvc.xml
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
<!-- 配置需要扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="cn.ukoko"/> <!-- 配置通用视图解析器 --> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!-- 配置前缀 --> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/"></property> <!-- 配置后缀 --> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property> </bean>
- 在web.xml配置文件中配置springmvc的核心servlet [DispatcherServlet]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
<servlet> <servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>springDispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <!--SpringMVC官网强调请求地址拦截使用/,拦截除JSP之外的一切请求--> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping>
- 编写处理核心业务逻辑代码的控制器[controller]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
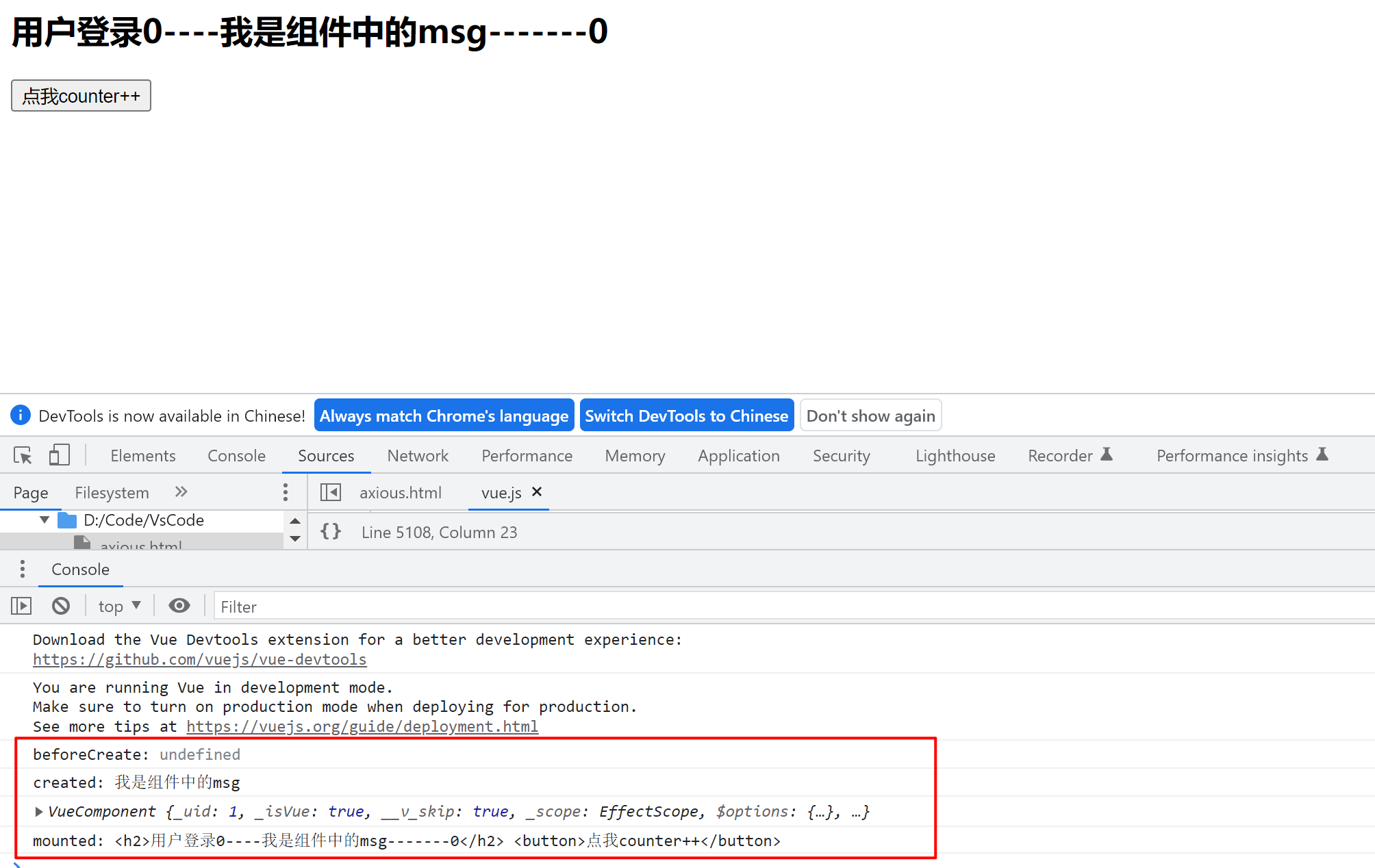
/*加入到IOC容器中*/ @Controller public class HelloController { /*映射请求地址*/ @RequestMapping("/hello") public String helloWorld() { System.out.println("HelloWorld"); //返回到指定结果页面result.jsp return "result"; } }
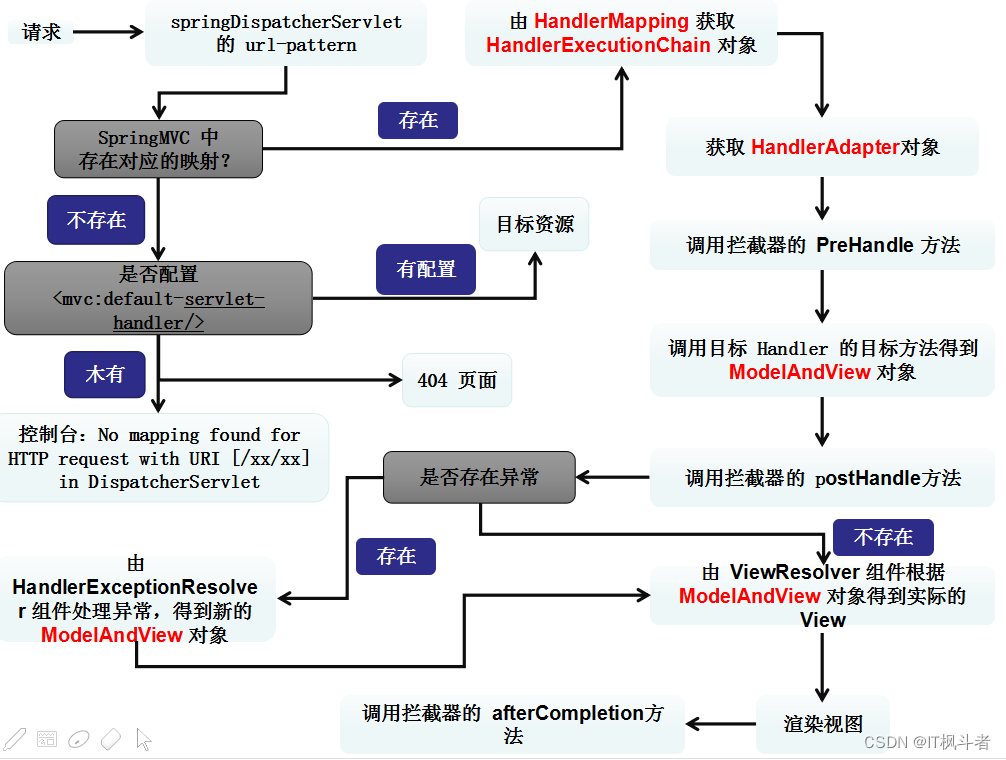
第2节 运行流程

1 2 3 4 5 6 | 简述运行流程 1.客户端发起请求到DispatcherServlet 2.由DispatcherServlet查找一个或多个HandlerMapping找到请求的handler(controller) 3.DispatcherServlet将请求提交到handler(controller) 4.Controller调用业务逻辑层处理后返回ModelAndView指定的视图 5.视图将结果返回给客户端 |
第3节 SpringMVC框架的另一种配置文件方式
1 | 将配置文件放到WEB-INF目录下取名为 springDispatcherServlet-servlet.xml 不需要在web.xml中单独配置 |
第4节 跨控制器页面跳转
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | <!--
跳过控制器,直接跳转视图
path: 设置请求地址
view-name: 跳转视图名称
-->
<mvc:view-controller path="/hello1" view-name="hello1"></mvc:view-controller>
<!--注意: 当使用view-controller 会让所有的注解失效,报404,所以需要添加注解驱动标签-->
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
|
第三章 SpringMVC数据绑定
第1节 常用注解介绍
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | @Controller : 将所标识的类加入到IOC容器中进行管理
@RequestMapping : 配置前端请求的映射地址以及请求参数的设置
- method=RequestMethod.GET
- method=RequestMethod.POST
- params:限定请求参数
- params是一个数组
- params={"name","no!=100","age=10"} : 表示请求参数包含name和no属性,并且no不能等于100,age一定等于10
- params={"!name"} : 表示请求参数不能有name参数
@PathVariable : 数据绑定
@RequestParam : 类似于servlet的request.getParameter("key");
- value : 要从请求域中获取参数的key值
- required : 参数是否必须
- defaultValue : 如果没有参数,那么走默认值
|
第2节 GET请求数据绑定风格介绍
2.1 风格一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | 使用?拼接的方式 hello?name=lilei&age=18
/**
* 通过名称匹配
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/hello")
public String hello02(String name,int age){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "result";
}
|
2.2 风格二
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | hello/lilei/18
/**
* 使用占位符加PathVariable注解的方式
*/
@GetMapping(value = "/hello/{name}/{age}")
public String hello03(@PathVariable("name") String name,@PathVariable("age") int age){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
return "result";
}
|
第3节 其他数据类型对象绑定
3.1 原生的JavaWeb的数据绑定
- 前端页面
1
<a href="testJavaWeb">原生的JavaWeb数据绑定测试</a>
- 后台控制器
1 2 3 4 5 6
@RequestMapping(value = "/testJavaWeb",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String testJavaWeb(HttpServletRequest request){ String name = request.getParameter("name"); System.out.println(name); return "result"; }
3.2 基本数据类型/字符类型
- 前端页面
1
<a href="testBase?name=Tom&age=18">基本数据类型/字符类型数据绑定测试</a>
- 后台控制器
1 2 3 4 5 6
@RequestMapping(value = "/testBase",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String testBase(String name,int age){ System.out.println(name); System.out.println(age); return "result"; }
3.3 数组
- 前端页面
1
<a href="testArray?roleId=1001&roleId=1002">数组类型数据绑定测试</a>
- 后台控制器
1 2 3 4 5
@RequestMapping(value = "/testArray",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String testArray(int[] roleId){ System.out.println(roleId); return "result"; }
3.4 自定义类型/嵌套类型
- 前端页面
1 2 3 4 5 6
<form action="testPOJO" method="post"> <input type="text" name="bookName"/> <%--嵌套提交--%> <input type="text" name="author.authorName"/> <input type="submit" value="提交"/> </form> - 模型对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public class Book { private String bookName; /*嵌套对象*/ private Author author; } public class Author { private String authorName; } - @DateTimeFormat(请求时间格式处理)
1 2
如果前端input空间的type类型为date类型,控制器接收参数的类型为Date类型时需要使用注解 @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd")进行转换
- 后台控制器
1 2 3 4 5
@RequestMapping(value = "/testPOJO",method = RequestMethod.POST) public String testPOJO(Book book){ System.out.println(book); return "result"; }
3.5 SpringMVC中文乱码解决(web.xml)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | <filter>
<filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>characterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
|
第4节 SpringMVC的数据类型转换器
1 | 通过传统的JavaWeb数据获取方式获取到的请求数据类型都是String类型,也就是说从前端传过来的数据默认都会变成String类型那么我们的SpringMVC是怎么将String类型转自动转换成其他数据类型的呢? |
4.1 SpringMVC内部提供的常见类型转换器
| 名称 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| StringToBooleanConverter | String 到 boolean 类型转换 |
| StringToCharacterConverter | String 到 Character 类型转换 |
| StringToEnumConverterFactory | String 到 Enum 类型转换 |
| StringToNumberConverterFactory | String 到 Number 类型转换 |
| StringToNumberConverterFactory | Locale 到 String 类型转换 |
| … | … |
详细见Spring官网地址:
1 2 3 | https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/4.3.29.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/htmlsingle/#core-convert 第9.5节 Spring Type Conversion(Spring的类型转换) |
Spring类型转换器介绍
1 2 3 4 | 1、类型转换是Spring3版本引入,默认是一种SPI(Service Provider Interface[服务发现机制])的机制帮助Spring进行类型转换. 2、提供了常见的API在运行时执行类型转换(例如上面表格中的自带的类型转换以及自定义类型转换). 3、在Spring容器中这个系统(类型转换)可以作为PropertyEditor的替换 4、将String类型转换成其他类型 |
4.2 自定义类型转换器
常见的自定义类型转换器 API 介绍
- Converter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
package org.springframework.core.convert.converter; public interface Converter<S, T> { T convert(S source); } 简答类型转换接口,将S类型转换成T类型,进行简单类型的转换比如将String转成Integer - ConverterFactory
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
package org.springframework.core.convert.converter; public interface ConverterFactory<S, R> { <T extends R> Converter<S, T> getConverter(Class<T> targetType); } 层级类型转换接口, S类型是要被转换的参数类型,R类型是目标转换类型的基类型,T类型是R类型的子类,比如String转枚举类型. - GenericConverter
1
复杂类型转换接口,当出现复杂类型的转换时,GenericConverter接口更灵活,支持多个源类型到目标类型的转换,并且在转换过程中提供了可以进行注解和泛型的驱动,比如数组Array到集合Collection的转换.
官方提示: 因为GenericConverter是一个复杂的SPI,当必须使用的时候在使用,否则最好是使用Converter or ConverterFactory 进行转换
- ConversionService
1
ConversionService是一个在运行时执行转换逻辑的统一API接口
使用Converter接口实现自定义类型转换器(时间类型转换
6 9 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
public class StringToDateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
@Override
public Date convert(String source) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Date date =null;
try {
date = sdf.parse(source);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}
}
|
将自定义Converter转换器加入到IOC容器中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | <!--设置类型转换器的服务-->
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"></mvc:annotation-driven>
<!--设置类型转换器-->
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<set>
<bean class="cn.ukoko.controller.StringToDateConverter"></bean>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
|
测试类型转换器
- 前端页面
1 2 3 4 5
<form action="testConverter" method="post"> <label for="createTime">时间:</label> <input id="createTime" type="text" name="createTime"/> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </form> - 控制器
1 2 3 4 5
@RequestMapping(value = "/testConverter",method = RequestMethod.POST) public String testConverter(Date createTime){ System.out.println("createTime="+createTime); return "result"; }
第四章 SpringMVC的RESTFUL风格
第1节 restful风格概念
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | Representational State Transfer :(资源)表现层状态转换 是目前最流行的一种互联网软件设计架构思想 资源(Resources):网络上的一个实体,或者说是网络上的一个具体信息。它可以是一段文本、一张图片、一首歌曲、一种服务,总之就是一个具体的存在。可以用一个URI(统一资源定位符)指向它,每种资源对应一个特定的 URI。要获取这个资源,访问它的URI就可以,因此 URI 即为每一个资源的独一无二的标识符。 表现层(Representation) 把资源具体呈现出来的形式,叫做它的表现层(Representation)。比如,文本可以用 txt格式表现,也可以用HTML格式、XML格式、JSON格式表现,甚至可以采用二进制格式。 状态转化(State Transfer): 每发出一个请求,就代表了客户端和服务器的一次交互过程。HTTP协议,是一个无状态协议,即所有的状态都保存在服务器端。因此,如果客户端想要操作服务器,必须通过某种手段,让服务器端发生“状态转化”(State Transfer)。而这种转化是建立在表现层之上的,所以就是“表现层状态转化”。具体说,就是HTTP 协议里面,四个表示操作方式的动词:GET、POST、PUT、DELETE。它们分别对应四种基本操作:GET 用来获取资源,POST 用来新建资源,PUT 用来更新资源,DELETE 用来删除资源 |
第2节 restful风格格式
1 2 3 4 | /book/1 HTTP GET :得到 id = 1 的 book /book/1 HTTP DELETE:删除 id = 1的 book /book/1 HTTP PUT :更新id = 1的 book /book HTTP POST :新增 book |
第3节 restful配置方式
1 | HiddenHttpMethodFilter:浏览器 form 表单只支持 GET 与 POST请求,而DELETE、PUT 等 method并不支持,Spring3.0添加了一个过滤器,可以将这些请求转换为标准的http方法,使得支持 GET、POST、PUT 与 DELETE 请求. |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | web.xml中配置 <filter> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> |
第4节 restfult风格使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | <form action="delete" method="post">
<!-- 用于状态转换 -->
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="DELETE"/>
<input type="submit" value="删除"/>
</form>
<form action="update" method="post">
<!-- 用于状态转换 -->
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT"/>
<input type="submit" value="更新"/>
</form>
|
- bug处理 405错误 JSPs only permit GET POST or HEAD
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
在进行资源状态转换时 POST --> DELETE POST --> PUT 由于tomcat8的问题造成的405错误 修复方式: 方式一: 换tomcat为7或者9 方式二: 在jsp页面中在设置 <% isErrorPage="true"%>
第五章 SpringMVC的模型数据
第1节 JavaWeb原生方式模型数据传递
1 2 3 4 5 6 | RequestMapping(value = "/testJavaWebModel")
public String testJavaWebModel(HttpServletRequest request){
//将数据使用原生方式放在request域中
request.setAttribute("userName","李雷");
return "result";
}
|
第2节 SpringMVC的模型数据传递
- 使用ModelAndView对象传递
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
@RequestMapping(value = "/testModelAndView") public ModelAndView testModelAndView(){ ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); //指定视图名称 mv.setViewName("result"); /*将数据保存到域对象中*/ mv.addObject("userName","李雷"); return mv; } - 使用Model对象传递
1 2 3 4 5 6
@RequestMapping(value = "/testModel") public String testModel(Model model){ /*向域对象中存数据*/ model.addAttribute("userName","李雷"); return "result"; } - 使用ModelMap对象传递
1 2 3 4 5 6
@RequestMapping(value = "/testModelMap") public String testModelMap(ModelMap modelMap){ /*向域对象中存数据*/ modelMap.addAttribute("userName","李雷"); return "result"; } - 使用Map对象传递
1 2 3 4 5 6
@RequestMapping(value = "/testMap") public String testMap(Map map){ /*向域对象中存数据*/ map.put("userName","李雷"); return "result"; } - Model/ModelMap/Map关系
第六章 SpringMVC的转发和重定向
- 一句话解释转发和重定向的本质
1
转发是服务器行为,重定向是客户端行为
- SpringMVC 返回值处理
1 2 3 4 5
一般情况下,控制器方法返回字符串类型的值会被当成逻辑视图名处理 如果返回的字符串中带forward:或redirect:前缀时,SpringMVC会对他们进行特殊处理:将 forward: 和 redirect: 当成指示符,其后的字符串作为 URL 来处理 redirect:ok:会完成一个到 ok的 @RequestMapping("/ok") 重定向的操作 redirect:/ok forward :ok:会完成一个到 ok的 @RequestMapping("/ok") 转发操作 forward:/ok
第七章 SpringMVC文件上传/下载
1 2 3 4 5 | 1. SpringMVC对文件上传提供了直接的支持 2. 通过即插即用的MultipartResolver实现 3. Spring用Jakarta Commons FileUpload技术实现一个MultipartResolver实现类 CommonsMultipartResovler 4. SpringMVC默认不会开启上传功能,使用需要在上下文中配置MultipartResolver 5. 编写表单设置enctype="multipart/form-data"开启上传文件功能 |
第1节 文件上传
- 依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
<dependency> <groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId> <artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId> <version>1.3.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>commons-io</groupId> <artifactId>commons-io</artifactId> <version>2.6</version> </dependency> - 在SpringMVC配置文件中进行配置
1 2 3 4 5
<!-- id名字不能随便起 --> <bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"> <property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> <property name="maxUploadSize" value="1048576"/><!--可以使用SpEL设置上传文件大小--> </bean>
- 前端页面
1 2 3 4
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/uploadFile" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="file" name="file"><br> <input type="submit" value="提交"> </form> - 控制器实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
@RequestMapping(value="/testUpload") public String testUpload(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile[] multipartFiles) throws IllegalStateException, IOException { for (MultipartFile multipartFile : multipartFiles) { if(!multipartFile.isEmpty()) { multipartFile.transferTo(new File("文件保存的路径"+multipartFile.getOriginalFilename())); } } return "result"; }
第2节 文件下载
- 前端页面
1
<a href="${pageContext.request.contextPath }/downloadFile">downloadFile</a> - 后端控制器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
@RequestMapping(value="/downloadFile",method=RequestMethod.GET) public ResponseEntity<byte[]> downloadFile() throws IOException{ BufferedInputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\abc.txt"))); byte[] body = new byte[in.available()]; in.read(body); //将输入流读到缓冲区 //文件名 String fileName="中国.txt"; //当文件名为中文时需要进行编码,否则会出现中文乱码 fileName=URLEncoder.encode(fileName, "UTF-8"); HttpHeaders header = new HttpHeaders(); //inline: 直接显示 //header.add("Content-Disposition", "inline;filename="+fileName); //附件下载 header.add("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=f.txt"); ResponseEntity<byte[]> result = new ResponseEntity<byte[]>(body,header,HttpStatus.OK); in.close(); return result; }
第八章 SpringMVC异常处理
1 2 | 1. SpringMVC通过HandlerExceptionResolver进行异常处理 2. DispaterServlet默认装配HandlerExceptionResolver异常处理器 |
第1节 单个异常处理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | //设置指定捕获当前类中的哪些异常,当前设置为Exception异常以及其子类都会被捕获到
@ExceptionHandler(value= {Exception.class})
public ModelAndView testException(Exception e){
System.out.println("error--->"+e.getMessage());
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("myException", e);
mv.setViewName("error");
return mv;
}
|
第2节 统一异常处理
1 2 3 4 5 | 1. 创建一个统一异常处理类 2. 在类上添加@ControllerAdvice注解 3. 定义异常方法,并添加@ExceptionHandler注解 4. 方法的返回值为ModelAndView,将异常消息返回给异常页面展示 5. 最后别忘记在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中配置注解驱动的标签<mvc:annotation-driven/> |
- 统一异常处理类
1 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
@ControllerAdvice public class CommonException { @ExceptionHandler(value = {Exception.class}) public ModelAndView testException(Exception e){ ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(); mv.addObject("msg",e.getMessage()); mv.setViewName("error"); return mv; } } - 异常的优先级
1
先查找当前类里面的异常处理,如果不存在在去统一异常处理类中匹配
第九章 SpringMVC静态资源处理
第1节 静态资源处理
-
哪些资源属于静态资源
1 2 3 4
1. 项目中用到的jquery函数库 2. 项目中自定义的js文件 3. 项目中用到的自定义css文件 ...
-
怎么解决静态资源导入问题(静态资源处于webapp下而不是WEB-INF下)
1 2 3
在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中添加如下标签 <mvc:default-servlet-handler></mvc:default-servlet-handler>
第2节 SpringMVC的拦截器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | SpringMVC提供了拦截器对请求进行拦截处理,我们可以通过自定义拦截器来实现特定功能
实现一个自定义拦截器步骤:
1. 实现HandlerInterceptor接口,重写里面的方法
1.1 perHandle
- 业务处理请求之前被调用
- 程序调用此拦截器之后还需要继续执行,那么返回true否则返回false
1.2 postHandle
- 业务处理器处理完请求之后,但是在DispatcherServlet向客户端返回响应前被调用,对用户请求进行处理
1.3 afterCompletion
- DispatcherServlet向客户端返回响应后被调用,可以进行一些资源清理的工作
2. 在SpringMVC核心配置文件中注册自定义拦截器
2.1 全局拦截器注册
<mvc:interceptors>
<bean id="empInterctptor" class="cn.ukoko.EmpInterctptor"></bean>
</mvc:interceptors>
2.2 拦截指定的某一个请求
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!-- 拦截emps地址的请求 -->
<mvc:mapping path="/emps"/>
<bean class="cn.ukoko.EmpInterctptor"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
|
第十章 SpringMVC的JSON数据交互
第1节 添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-core</artifactId> <version>2.9.8</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.8</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-annotations</artifactId> <version>2.9.8</version> </dependency> |
第2节 @ResponseBody/@RequestBody
- @ResponseBody
-
- @ResponseBody注解返回时间格式为long类型
1
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
- @ResponseBody注解返回时间格式为long类型
-
- @ResponseBody注解返回时间默认时区修改
1
@JsonFormat(timezone = "GMT+8")
- @ResponseBody注解返回时间默认时区修改
- @RequestBody
1 2 3
什么时候控制器中的方法入参使用@RequestBody注解? @requestBody注解常用来处理content-type不是默认的application/x-www-form-urlcoded,比如说:application/json或者是application/xml等。一般情况下来说常用其来处理application/json类型
-
- 前端页面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
//获取按钮对象 $("#btn1").click(function(){ var book={"bookId":1001,"bookName":"时间简史","authorName":"霍金","price":12.12}; $.ajax({ url:"savebook", type:"post", data:JSON.stringify(book), contentType:"application/json;charset=utf-8", success:function(msg){ alert(msg); }, dataType:"json" }); });
- 前端页面
-
- 控制器
1 2 3 4 5 6
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value="/savebook",method=RequestMethod.POST) public String savebook(@RequestBody Book book) { System.out.println("book:==: "+book); return "200"; }
- 控制器
第十一章 SpringMVC解决跨域调用
第1节 什么是跨域
1 | 当一个请求url的协议、域名、端口三者之间任意一个与当前页面url不同即为跨域 |
| 当前页面url | 被请求页面url | 是否跨域 | 原因 |
|---|---|---|---|
| http://www.test.com/ | http://www.test.com/index.html | 否 | 同源(协议、域名、端口号相同) |
| http://www.test.com/ | https://www.test.com/index.html | 跨域 | 协议不同(http/https) |
| http://www.test.com/ | 百度一下,你就知道 | 跨域 | 主域名不同(test/baidu) |
| http://www.test.com/ | http://blog.test.com/ | 跨域 | 子域名不同(www/blog) |
| http://www.test.com:8080/ | http://www.test.com:7001/ | 跨域 | 端口号不同(8080/7001) |
第2节 Spring解决跨域的方式
1 | SpringMVC的4.2版本提供了@CrossOrigin注解可以解决跨域问题 |
第十二章 SpringMVC Mock测试
第1节 Mock介绍
- 什么是Mock测试
1
Mock测试就是在测试过程中,对于某些不容易构造或者不容易获取的对象,用一个虚拟的对象来创建以便测试的测试方法
- 为什么要使用Mock测试
1 2
使用Mock进行测试,主要是用来模拟那些在应用中不容易构造(如HttpServletRequest必须在Servlet容器中才能构造出来)或者比较复杂的对象,从而使测试顺利进行的工具
- Mock测试用到的常用注解
WebAppConfiguratio
1 | 使用这个annotation会在跑单元测试的时候真实的启一个web服务,然后开始调用Controller的RestAPI,待单元测试跑完之后再将web服务停掉 |
ContextConfiguration
1 | 指定Bean的配置文件信息,可以有多种方式,这个例子使用的是文件路径形式,如果有多个配置文件,可以将括号中的信息配置为一个字符串数组来表示 |
RunWith
1 | 指定运行的测试容器 |
第2节 Mock测试环境的安装
1 | Spring MVC测试框架提供了两种方式,独立安装和集成Web环境测试(此种方式并不会集成真正的web环境,而是通过相应的Mock API进行模拟测试,无须启动服务器) |
- 添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
<dependency> <groupId>javax</groupId> <artifactId>javaee-api</artifactId> <version>7.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.0.1</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> 注意: 当前版本的spring框架需要3.0以上版本的servlet-api支持单元测试 - 创建MockMvc对象
安装测试环境 方式一(独立安装方式)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | /**
* 独立安装测试
* 依赖servlet-api
*/
public class BookControllerTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Before
public void setUp() {
//通过参数指定一组控制器,这样就不需要从上下文获取了
this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new BookController()).build();
}
@Test
public void testMockMvc() throws Exception {
System.out.println(mockMvc);
}
}
|
安装测试环境 方式二(集成Web环境方式)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | /**
* 集成Web环境方式
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations= {"classpath:spring-mvc.xml"})
//如果springmvc的配置文件在WEB-INF下使用下面这种写法
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"file:src/main/webapp/WEB-INF/springDispatcherServlet-servlet.xml"})
@WebAppConfiguration
public class BookControllerTest2 {
@Autowired
private WebApplicationContext wac;
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Before
public void setup() {
this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(this.wac).build();
}
@Test
public void testMockMvc() throws Exception {
System.out.println(mockMvc);
}
}
|
第3节 Mock的使用
3.1 方法的测试(返回值是JSON或者是字符串,方法无入参)
- 模型数据实体类
1 2 3 4 5
public class User { private Integer userId; private String userName; private Date hireDate; } - 测试的控制器方法
1 2 3 4 5 6
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/getUserJson",method = RequestMethod.GET) public User getUserJson(){ User user = new User(1001, "页", new Date()); return user; } - 单元测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
@Test public void getUserJson() throws Exception { ResultActions resultActions = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/getUserJson")); MvcResult mvcResult = resultActions.andReturn(); MockHttpServletResponse response = mvcResult.getResponse(); int status = response.getStatus();//响应状态码 String content = response.getContentAsString();//响应结果 System.out.println("响应状态码:"+status); System.out.println("响应内容:"+content); }
3.2 传统的(?)方式设置入参[GET请求]
- 测试的控制器方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/getUser",method = RequestMethod.GET) public User getUser(Integer userId,String userName){ User user = new User(); user.setUserId(userId); user.setUserName(userName); user.setHireDate(new Date()); return user; } - 单元测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
@Test public void getUser() throws Exception { ResultActions resultActions = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/getUser?userId={xyz}&userName={userName}", 100,"韩梅梅")); MvcResult mvcResult = resultActions.andReturn(); MockHttpServletResponse response = mvcResult.getResponse(); int status = response.getStatus();//响应状态码 String content = response.getContentAsString();//响应结果 System.out.println("响应状态码:"+status); System.out.println("响应内容:"+content); }
3.3 使用占位符{占位形参}设置入参[GET请求]
- 测试的控制器方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/getUser2/{userId}/{userName}",method = RequestMethod.GET) public User getUser2(@PathVariable("userId") Integer userId,@PathVariable("userName") String userName){ User user = new User(); user.setUserId(userId); user.setUserName(userName); user.setHireDate(new Date()); return user; } - 单元测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
@Test public void getUser2() throws Exception { ResultActions resultActions = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/getUser2/1000/李雷")); MvcResult mvcResult = resultActions.andReturn(); MockHttpServletResponse response = mvcResult.getResponse(); int status = response.getStatus();//响应状态码 String content = response.getContentAsString();//响应结果 System.out.println("响应状态码:"+status); System.out.println("响应内容:"+content); }
3.4 JSON作为入参参数设置
-
测试的控制器方法
1 2 3 4 5 6
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping(value = "/getUserForRequestJson",method = RequestMethod.POST) public String getUserForRequestJson(@RequestBody User user){ System.out.println("入参为: "+user); return "success"; } -
单元测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
@Test public void getUserForRequestJson() throws Exception { String var="{\"userId\":1001,\"userName\":\"李雷\",\"hireDate\":\"2020-12-12 22:22:22\"}"; /** * contentType: 设置传递参数的类型 * content: 设置传递的参数内容 */ ResultActions resultActions = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/getUserForRequestJson").contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8).content(var)); MvcResult mvcResult = resultActions.andReturn(); MockHttpServletResponse response = mvcResult.getResponse(); int status = response.getStatus();//响应状态码 String content = response.getContentAsString();//响应结果 System.out.println("响应状态码:"+status); System.out.println("响应内容:"+content); }3.5 控制器方法返回值为视图的测试
-
测试的控制器方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
@RequestMapping(value = "/testView",method = RequestMethod.GET) public String testView(Integer userId, Model model){ System.out.println("测试视图跳转... userId="+userId); //向模型中存储数据 model.addAttribute("userId",userId); //返回视图 return "testview"; } -
单元测试代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22
@Test public void testView() throws Exception { ResultActions resultActions = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/testView?userId={userId}", 10000)); //验证模型中是否存储此key的数据 resultActions.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.model().attributeExists("userId")); //验证模型是否存在此视图 resultActions.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.view().name("testview")); //验证请求状态 resultActions.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()); // 给他打印出来 resultActions.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print()); //返回结果 MvcResult result = resultActions.andReturn(); //上面的操作可以连接成串进行操作 //MvcResult result = mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/testView?userId={userId}", 10000)).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.model().attributeExists("userId")).andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.view().name("testview")).andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print()).andReturn(); } andExpect: 添加执行完成后的验证断言 andDo : 添加一个结果处理器 andReturn: 执行完成后返回响应的结果
第十三章 SpringMVC 运行流程