前言:
我们有的时候,希望下方的内容能够显示到上方,达到类似于多个图层的效果,此时我们可以利用z-index这个属性。
介绍;
z-index属性值是用来设置元素的堆叠顺序(元素层级)。
覆盖原则:
<1>特殊情况
默认(或者position:static)情况下,z-index会失效,因此我们不会在此情况中使用z-index
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.a{
z-index: 1;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
position: static;
background-color: aqua;
}
.b{
z-index: 100;
background-color: rgb(222, 135, 135);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
</body>
</html>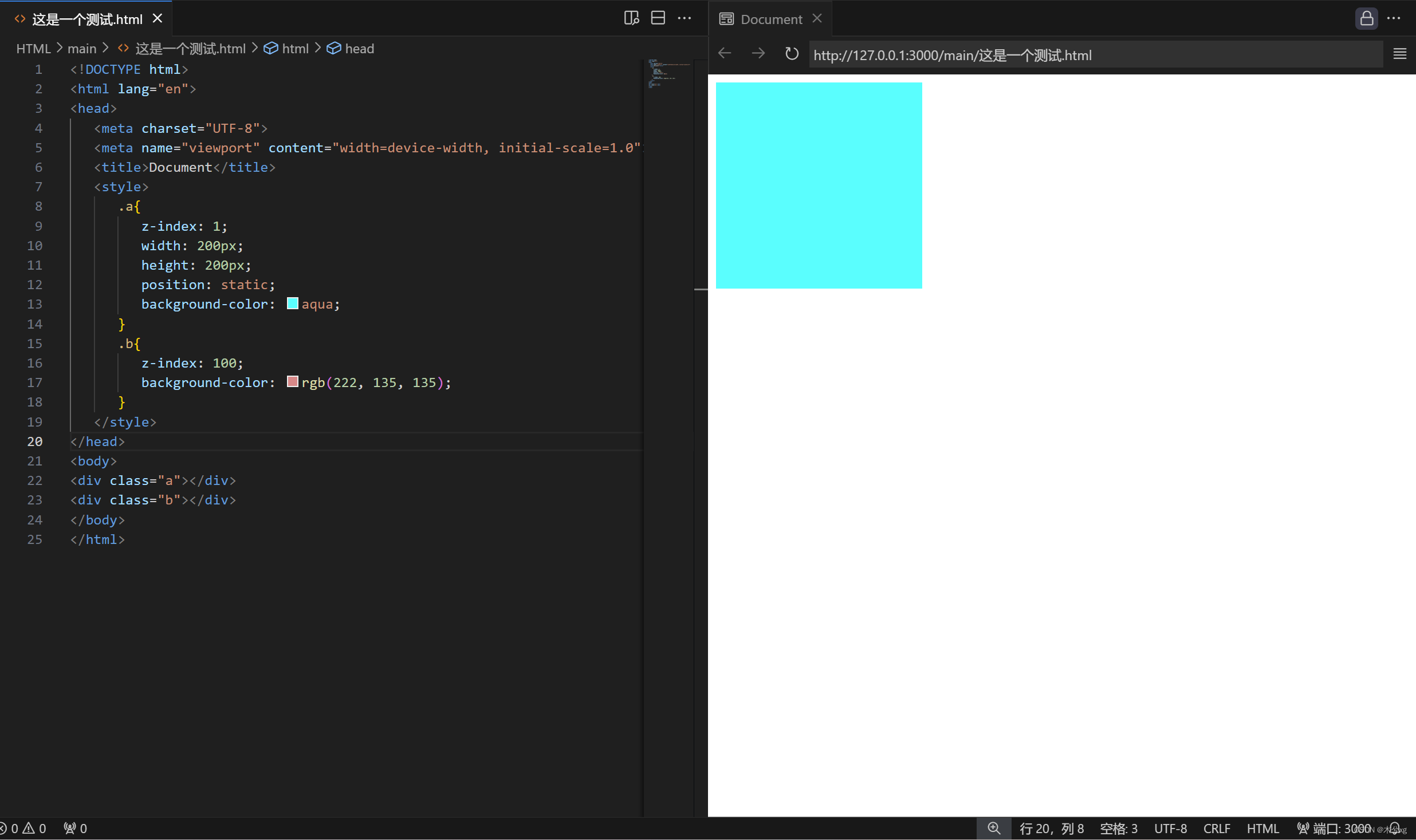
<2>同级元素之间
z-index级别大的在上,级别小的在下,z-index的默认值是0.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.a{
z-index: 1;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
position:absolute;
background-color:blue;
}
.b{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
z-index: 100;
position:absolute;
background-color: rgb(222, 135, 135);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a"></div>
<div class="b"></div>
</body>
</html>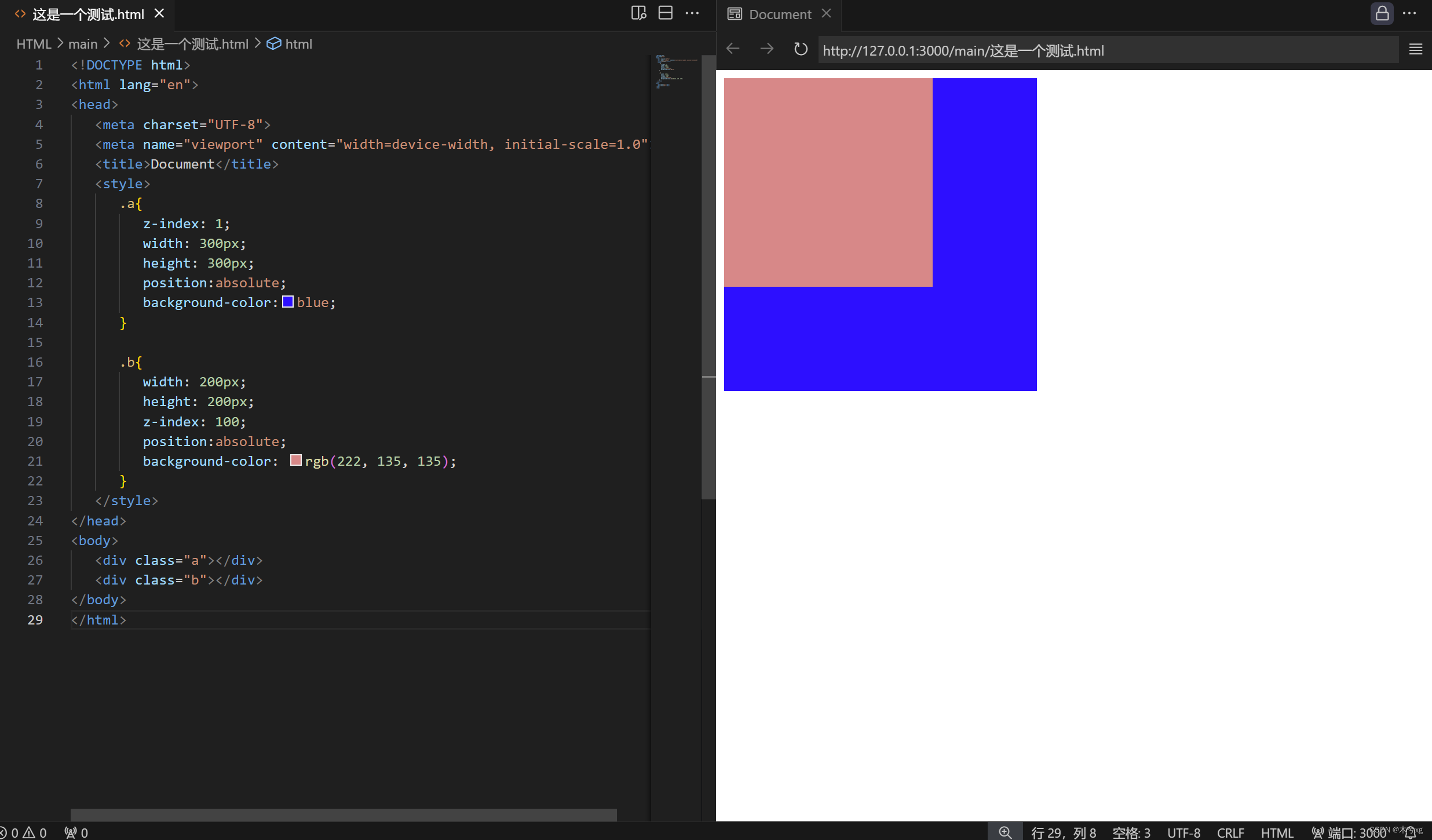
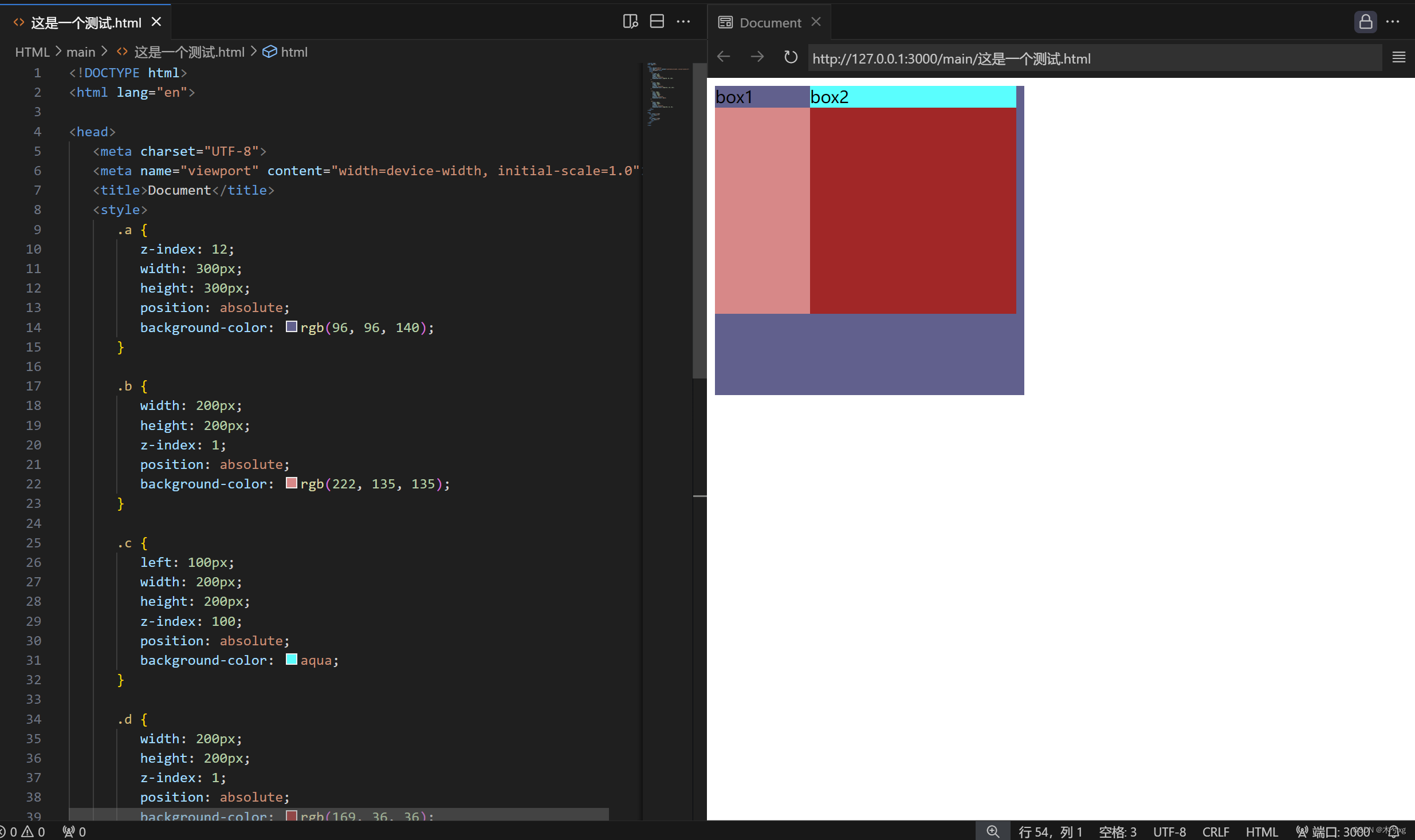
<2>非同级元素
对于非同级的元素,元素根据其父级元素的z-index来判别,与自身的z-index无关
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
.a {
z-index: 12;
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
position: absolute;
background-color: rgb(96, 96, 140);
}
.b {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
z-index: 1;
position: absolute;
background-color: rgb(222, 135, 135);
}
.c {
left: 100px;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
z-index: 100;
position: absolute;
background-color: aqua;
}
.d {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
z-index: 1;
position: absolute;
background-color: rgb(169, 36, 36);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="a">box1
<div class="b">
</div>
</div>
<div class="c">box2
<div class="d">
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>