这里写目录标题
- 一、colmap解算数据放入高斯
- 1. 将稀疏重建的文件放入高斯
- 2. 将稠密重建的文件放入高斯
- 二、vkitti数据放入高斯
一、colmap解算数据放入高斯
运行Colmap.bat文件之后,进行稀疏重建和稠密重建之后可以得到如下文件结构。
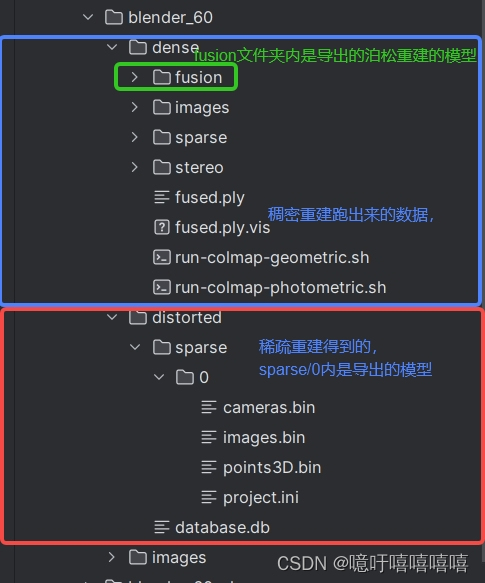
1. 将稀疏重建的文件放入高斯
按照以下文件结构将colmap中的数据放入高斯中,就可以执行 python train.py -s data/data_blender_60 -m data/data_blender_60/output 了
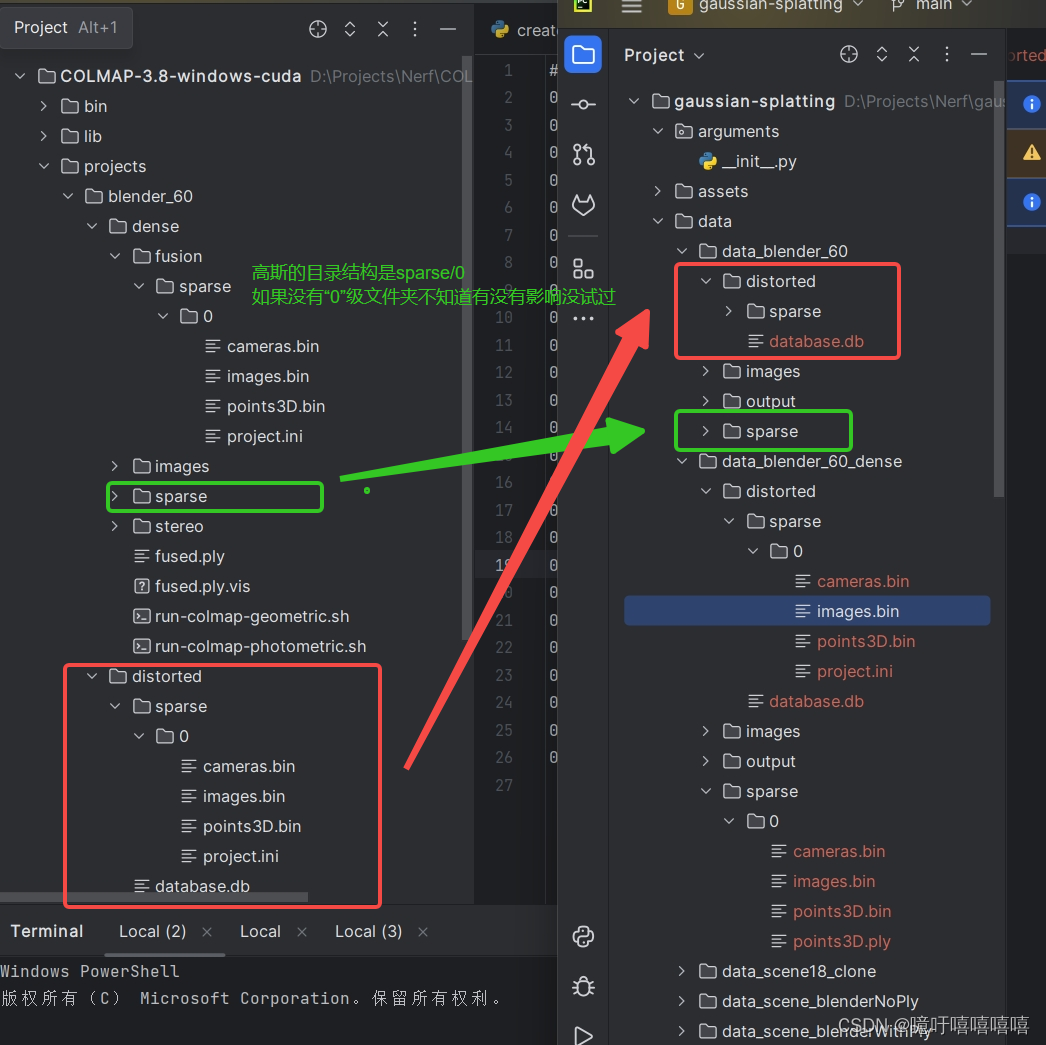
2. 将稠密重建的文件放入高斯
按照以下文件结构将colmap中的数据放入高斯中,
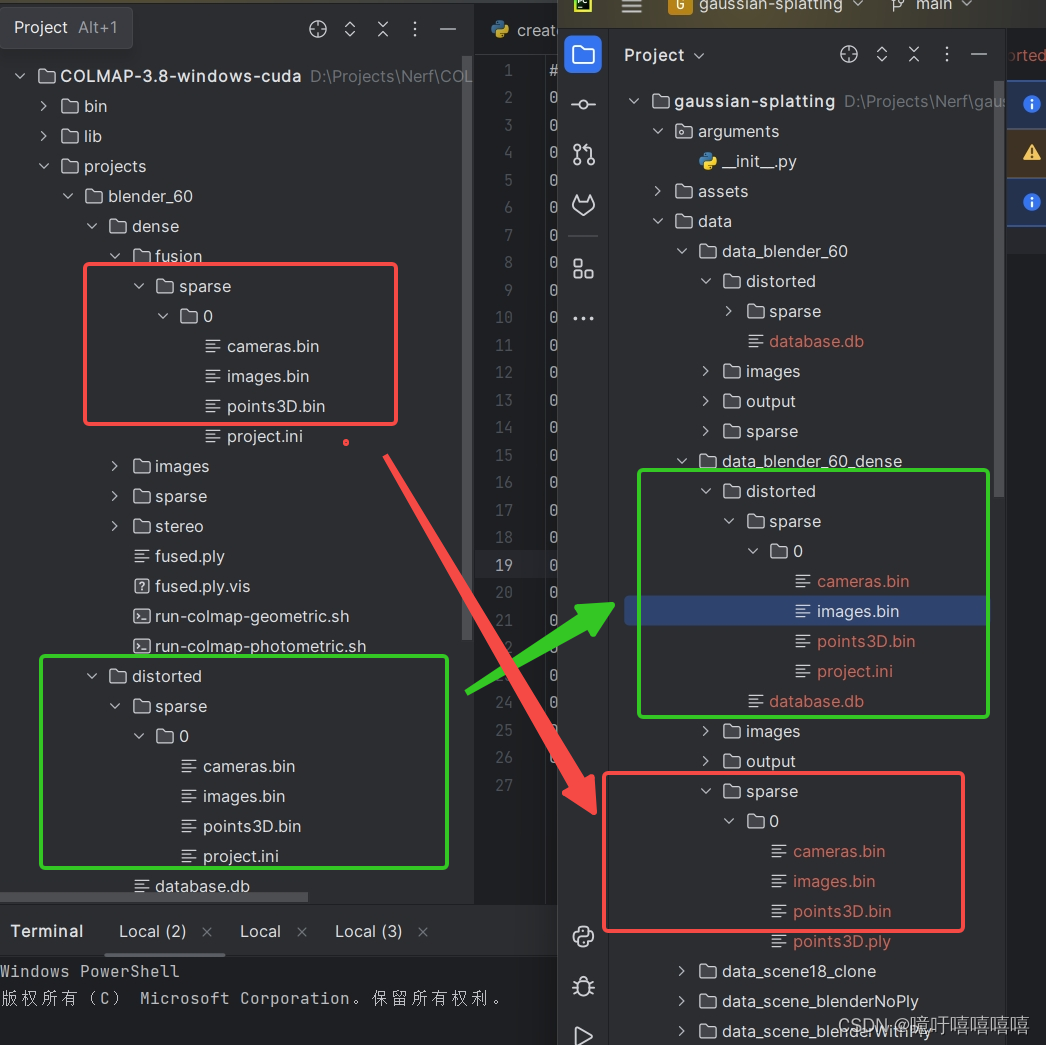
此时若直接运行train文件会有如下报错:
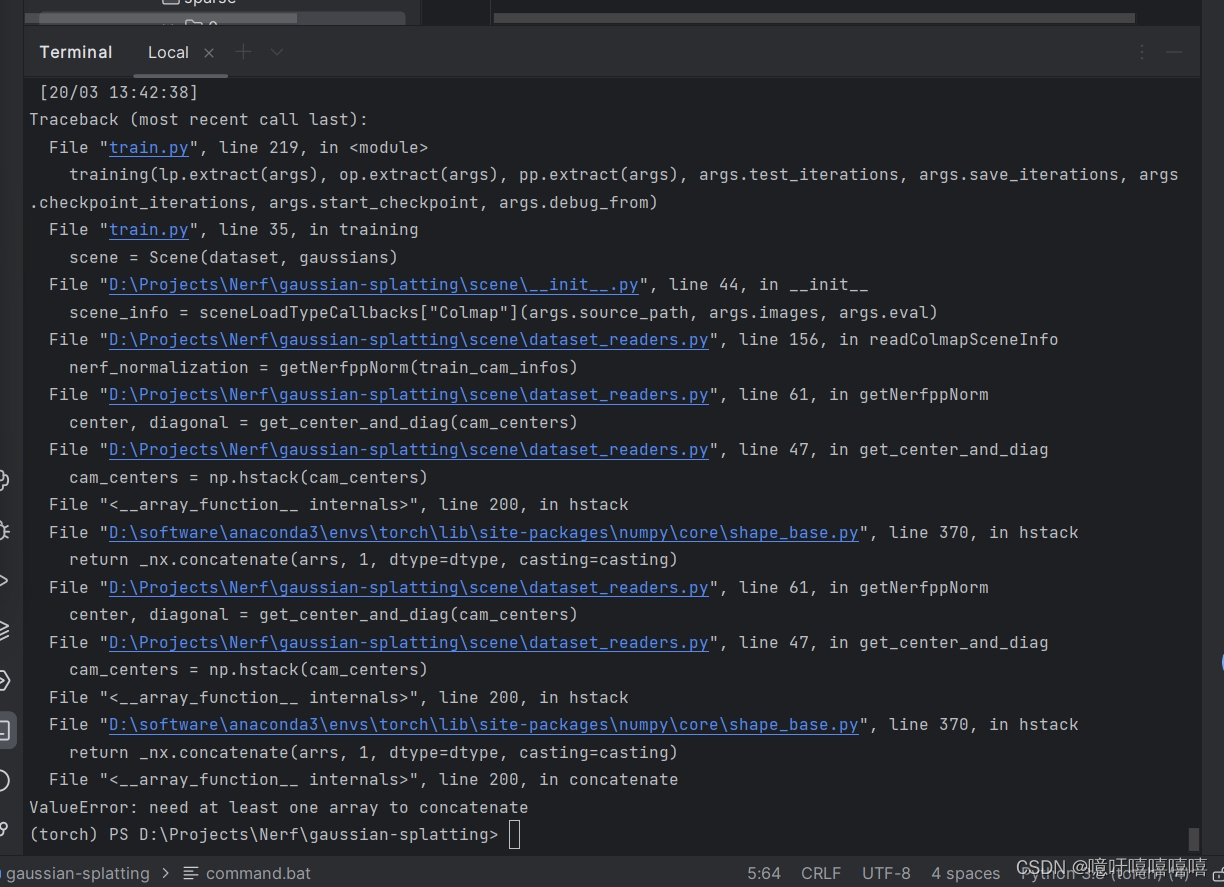
意思是没有获取到cameras,点开sparse/0中的cameras文件,发现全是null,此时,**先删除sparse/0中的cameras.bin和images.bin,再将distorted/sparse/0中的cameras.bin和images.bin文件复制到sparse/0中。**实在不行也可以在colmap中重新导出一下模型。
就可以执行 python train.py -s data/data_blender_60 -m data/data_blender_60/output 了
二、vkitti数据放入高斯
vkitti数据数据格式如下:
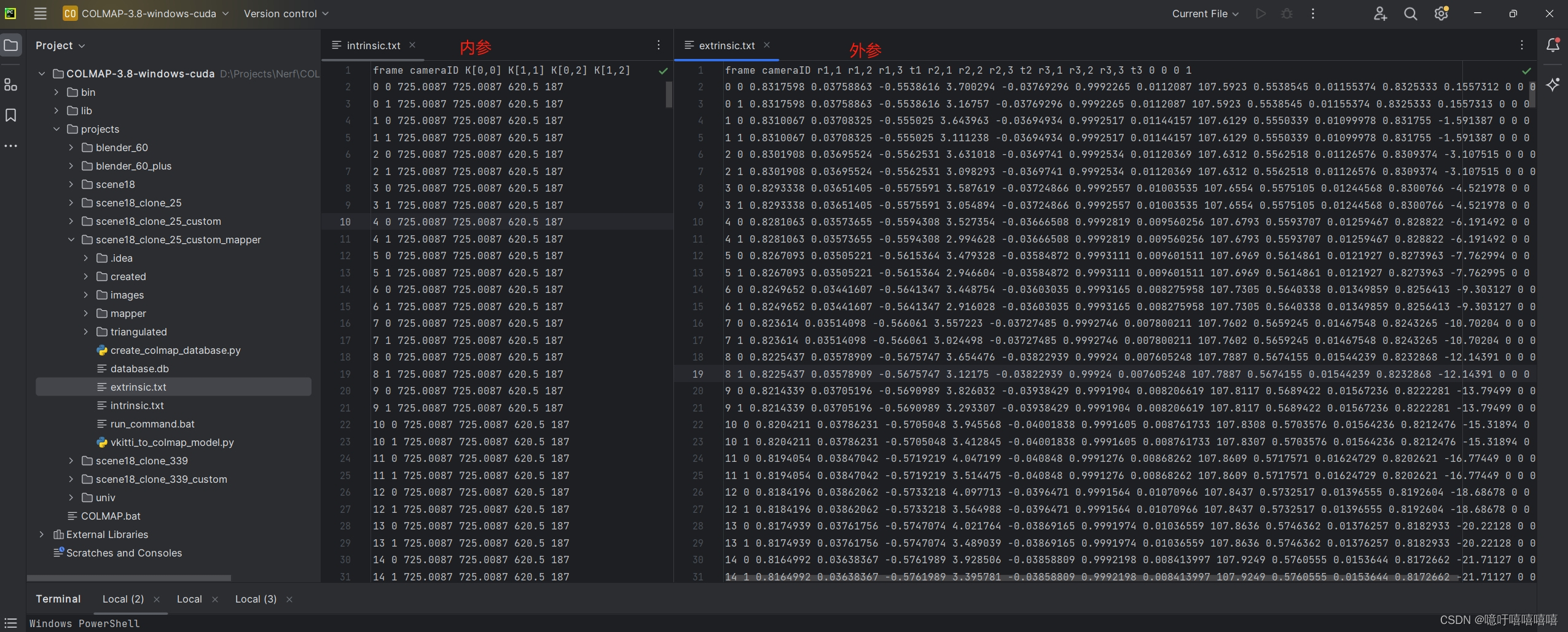
colmap数据数据格式如下(外参数据一定要空一行否则后续不会执行):
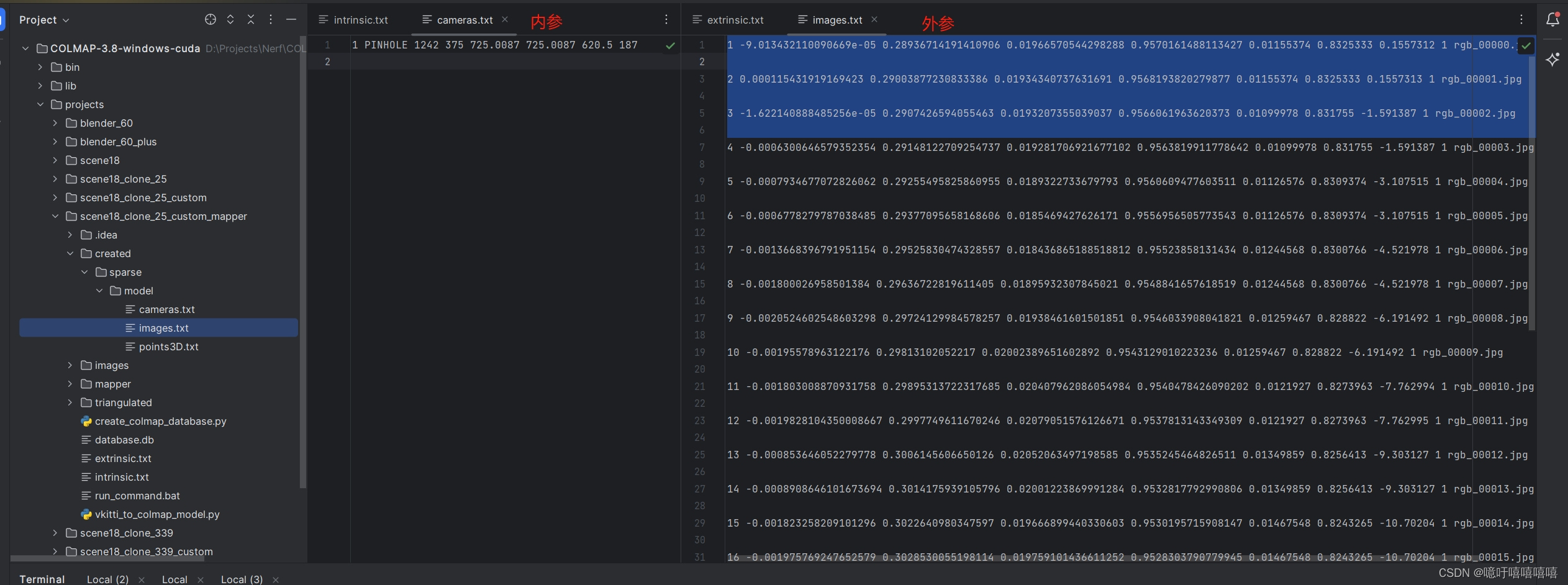
最后我的colmap中目录结构如下:
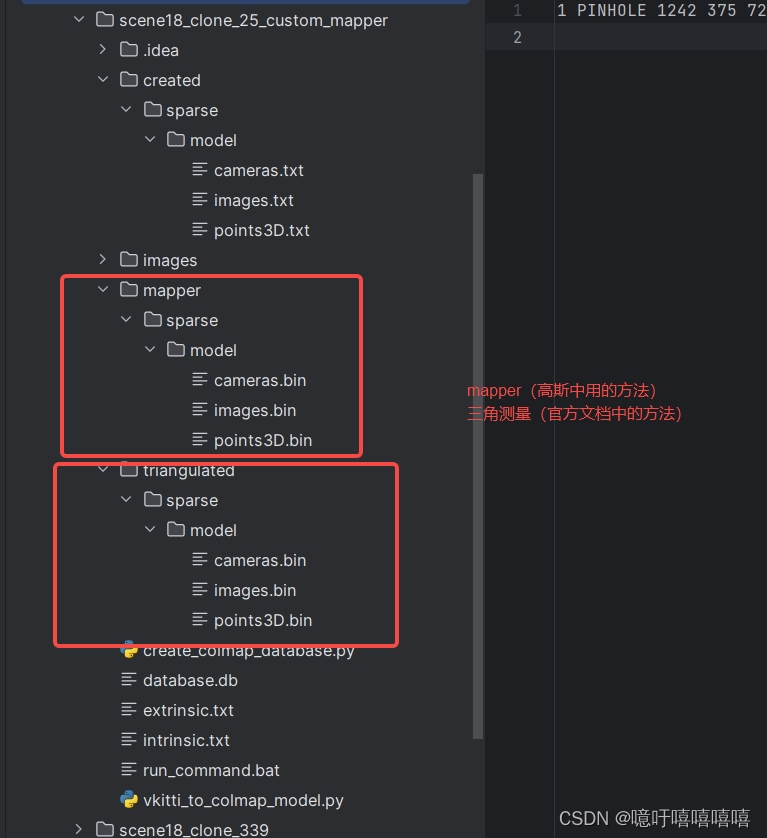
先自行创建以下几个文件夹:执行command.bat
@echo off
if not exist created\sparse\model (
mkdir created\sparse\model
echo Created directory: created\sparse\model
)
if not exist triangulated\sparse\model (
mkdir triangulated\sparse\model
echo Created directory: triangulated\sparse\model
)
if not exist mapper\sparse\model (
mkdir mapper\sparse\model
echo Created directory: mapper\sparse\model
)
接下来开始操作:
写了一个程序进行格式转换:vkitti_to_colmap_cameras.py
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial.transform import Rotation
index = 339 #要转换的图片张数
def cameras(input_path, output_path):
# 定义一个字典用于存储提取的数据
data_dict = {'frame': [], 'cameraID': [], 'PARAMS': []}
# 打开文件并读取内容
with open(input_path, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()[1:]
# # 删除 camera=1的行
# lines = [line for index, line in enumerate(lines) if index % 2 == 0]
# 遍历每一行数据
for line in lines:
# 分割每一行数据
elements = line.split()
# 提取frame和cameraID
frame = int(elements[0])
cameraID = int(elements[1])
if cameraID == 1:
continue
# 提取PARAMS
PARAMS = elements[2:6]
# 将提取的数据存入字典
data_dict['frame'].append(frame)
data_dict['cameraID'].append(frame + 1)
data_dict['PARAMS'].append(PARAMS)
width = 1242
height = 375
# 将处理后的内容写回文件
# 打开文件以写入数据
with open(output_path, 'w') as output_file:
# 写入文件头部信息
output_file.write(
"# Camera list with one line of data per camera:\n# CAMERA_ID, MODEL, WIDTH, HEIGHT, PARAMS[fx,fy,cx,cy]\n# Number of cameras: 1\n")
# 遍历每个数据点
for i in range(len(data_dict['frame'])):
# 获取相应的数据
if data_dict['frame'][i] > index - 1:
break
cameraID = data_dict['cameraID'][i]
PARAMS = data_dict['PARAMS'][i]
fx, fy, cx, cy = PARAMS
# 写入数据到文件
output_file.write(
f"{cameraID} PINHOLE {width} {height} {fx} {fy} {cx} {cy}\n")
def images(input_path, output_path):
# 定义一个字典用于存储提取的数据
data_dict = {'frame': [], 'cameraID': [], 'quaternions': []}
# 打开文件并读取内容
with open(input_path, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()[1:]
# 遍历每一行数据
for line in lines:
# 分割每一行数据
elements = line.split()
# 提取frame和cameraID
frame = int(elements[0])
cameraID = int(elements[1])
if cameraID == 1:
continue
# 提取旋转矩阵部分
rotation_matrix = np.array([[float(elements[i]) for i in range(2, 11, 4)],
[float(elements[i]) for i in range(3, 12, 4)],
[float(elements[i]) for i in range(4, 13, 4)]])
# 将旋转矩阵转换为四元数
rotation = Rotation.from_matrix(rotation_matrix)
quaternion = rotation.as_quat()
# 将提取的数据存入字典
data_dict['frame'].append(frame)
data_dict['cameraID'].append(frame + 1)
data_dict['quaternions'].append(quaternion)
# 打开文件以写入数据
with open(output_path, 'w') as output_file:
# 写入文件头部信息
output_file.write(
"# Image list with two lines of data per image:\n# IMAGE_ID, QW, QX, QY, QZ, TX, TY, TZ, CAMERA_ID, NAME\n# POINTS2D[] as (X, Y, POINT3D_ID)\n# Number of images: 339, mean observations per image: 1\n")
# 遍历每个数据点
for i in range(len(data_dict['frame'])):
# 获取相应的数据
if data_dict['frame'][i] > index - 1:
break
frame = data_dict['frame'][i]
cameraID = data_dict['cameraID'][i]
quaternion = data_dict['quaternions'][i]
# 将四元数和平移向量分开
qw, qx, qy, qz = quaternion
tx, ty, tz = [float(elem) for elem in lines[i].split()[11:14]]
# 写入数据到文件
output_file.write(
f"{frame + 1} {qw} {qx} {qy} {qz} {tx} {ty} {tz} {cameraID} rgb_{frame:05d}.jpg\n\n")
if __name__ == '__main__':
input_path = "./intrinsic.txt"
output_path = "./cameras.txt"
cameras(input_path, output_path)
input_path = "./extrinsic.txt"
output_path = "./images.txt"
images(input_path, output_path)
我的同学写了一个创建数据库的代码 ,这将cameras.txt和images.txt文件中的数据都放入database.db中:create_colmap_database.py
# Copyright (c) 2023, ETH Zurich and UNC Chapel Hill.
# All rights reserved.
#
# Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
# modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
#
# * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
#
# * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
# notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
# documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
#
# * Neither the name of ETH Zurich and UNC Chapel Hill nor the names of
# its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived
# from this software without specific prior written permission.
#
# THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
# AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
# IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE
# ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS OR CONTRIBUTORS BE
# LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
# CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF
# SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS
# INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
# CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE)
# ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
# POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
# This script is based on an original implementation by True Price.
import sys
import sqlite3
import numpy as np
IS_PYTHON3 = sys.version_info[0] >= 3
MAX_IMAGE_ID = 2 ** 31 - 1
CREATE_CAMERAS_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS cameras (
camera_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,
model INTEGER NOT NULL,
width INTEGER NOT NULL,
height INTEGER NOT NULL,
params BLOB,
prior_focal_length INTEGER NOT NULL)"""
CREATE_DESCRIPTORS_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS descriptors (
image_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rows INTEGER NOT NULL,
cols INTEGER NOT NULL,
data BLOB,
FOREIGN KEY(image_id) REFERENCES images(image_id) ON DELETE CASCADE)"""
CREATE_IMAGES_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS images (
image_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY AUTOINCREMENT NOT NULL,
name TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
camera_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
prior_qw REAL,
prior_qx REAL,
prior_qy REAL,
prior_qz REAL,
prior_tx REAL,
prior_ty REAL,
prior_tz REAL,
CONSTRAINT image_id_check CHECK(image_id >= 0 and image_id < {}),
FOREIGN KEY(camera_id) REFERENCES cameras(camera_id))
""".format(
MAX_IMAGE_ID
)
CREATE_TWO_VIEW_GEOMETRIES_TABLE = """
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS two_view_geometries (
pair_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rows INTEGER NOT NULL,
cols INTEGER NOT NULL,
data BLOB,
config INTEGER NOT NULL,
F BLOB,
E BLOB,
H BLOB,
qvec BLOB,
tvec BLOB)
"""
CREATE_KEYPOINTS_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS keypoints (
image_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rows INTEGER NOT NULL,
cols INTEGER NOT NULL,
data BLOB,
FOREIGN KEY(image_id) REFERENCES images(image_id) ON DELETE CASCADE)
"""
CREATE_MATCHES_TABLE = """CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS matches (
pair_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rows INTEGER NOT NULL,
cols INTEGER NOT NULL,
data BLOB)"""
CREATE_NAME_INDEX = (
"CREATE UNIQUE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS index_name ON images(name)"
)
CREATE_ALL = "; ".join(
[
CREATE_CAMERAS_TABLE,
CREATE_IMAGES_TABLE,
CREATE_KEYPOINTS_TABLE,
CREATE_DESCRIPTORS_TABLE,
CREATE_MATCHES_TABLE,
CREATE_TWO_VIEW_GEOMETRIES_TABLE,
CREATE_NAME_INDEX,
]
)
def image_ids_to_pair_id(image_id1, image_id2):
if image_id1 > image_id2:
image_id1, image_id2 = image_id2, image_id1
return image_id1 * MAX_IMAGE_ID + image_id2
def pair_id_to_image_ids(pair_id):
image_id2 = pair_id % MAX_IMAGE_ID
image_id1 = (pair_id - image_id2) / MAX_IMAGE_ID
return image_id1, image_id2
def array_to_blob(array):
if IS_PYTHON3:
return array.tobytes()
else:
return np.getbuffer(array)
def blob_to_array(blob, dtype, shape=(-1,)):
if IS_PYTHON3:
return np.fromstring(blob, dtype=dtype).reshape(*shape)
else:
return np.frombuffer(blob, dtype=dtype).reshape(*shape)
class COLMAPDatabase(sqlite3.Connection):
@staticmethod
def connect(database_path):
return sqlite3.connect(database_path, factory=COLMAPDatabase)
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super(COLMAPDatabase, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.create_tables = lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_ALL)
self.create_cameras_table = lambda: self.executescript(
CREATE_CAMERAS_TABLE
)
self.create_descriptors_table = lambda: self.executescript(
CREATE_DESCRIPTORS_TABLE
)
self.create_images_table = lambda: self.executescript(
CREATE_IMAGES_TABLE
)
self.create_two_view_geometries_table = lambda: self.executescript(
CREATE_TWO_VIEW_GEOMETRIES_TABLE
)
self.create_keypoints_table = lambda: self.executescript(
CREATE_KEYPOINTS_TABLE
)
self.create_matches_table = lambda: self.executescript(
CREATE_MATCHES_TABLE
)
self.create_name_index = lambda: self.executescript(CREATE_NAME_INDEX)
def add_camera(
self,
model,
width,
height,
params,
prior_focal_length=False,
camera_id=None,
):
params = np.asarray(params, np.float64)
cursor = self.execute(
"INSERT INTO cameras VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
(
camera_id,
model,
width,
height,
array_to_blob(params),
prior_focal_length,
),
)
return cursor.lastrowid
def add_image(
self,
name,
camera_id,
prior_q=np.full(4, np.NaN),
prior_t=np.full(3, np.NaN),
image_id=None,
):
cursor = self.execute(
"INSERT INTO images VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
(
image_id,
name,
camera_id,
prior_q[0],
prior_q[1],
prior_q[2],
prior_q[3],
prior_t[0],
prior_t[1],
prior_t[2],
),
)
return cursor.lastrowid
def add_keypoints(self, image_id, keypoints):
assert len(keypoints.shape) == 2
assert keypoints.shape[1] in [2, 4, 6]
keypoints = np.asarray(keypoints, np.float32)
self.execute(
"INSERT INTO keypoints VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)",
(image_id,) + keypoints.shape + (array_to_blob(keypoints),),
)
def add_descriptors(self, image_id, descriptors):
descriptors = np.ascontiguousarray(descriptors, np.uint8)
self.execute(
"INSERT INTO descriptors VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)",
(image_id,) + descriptors.shape + (array_to_blob(descriptors),),
)
def add_matches(self, image_id1, image_id2, matches):
assert len(matches.shape) == 2
assert matches.shape[1] == 2
if image_id1 > image_id2:
matches = matches[:, ::-1]
pair_id = image_ids_to_pair_id(image_id1, image_id2)
matches = np.asarray(matches, np.uint32)
self.execute(
"INSERT INTO matches VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?)",
(pair_id,) + matches.shape + (array_to_blob(matches),),
)
def add_two_view_geometry(
self,
image_id1,
image_id2,
matches,
F=np.eye(3),
E=np.eye(3),
H=np.eye(3),
qvec=np.array([1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]),
tvec=np.zeros(3),
config=2,
):
assert len(matches.shape) == 2
assert matches.shape[1] == 2
if image_id1 > image_id2:
matches = matches[:, ::-1]
pair_id = image_ids_to_pair_id(image_id1, image_id2)
matches = np.asarray(matches, np.uint32)
F = np.asarray(F, dtype=np.float64)
E = np.asarray(E, dtype=np.float64)
H = np.asarray(H, dtype=np.float64)
qvec = np.asarray(qvec, dtype=np.float64)
tvec = np.asarray(tvec, dtype=np.float64)
self.execute(
"INSERT INTO two_view_geometries VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)",
(pair_id,)
+ matches.shape
+ (
array_to_blob(matches),
config,
array_to_blob(F),
array_to_blob(E),
array_to_blob(H),
array_to_blob(qvec),
array_to_blob(tvec),
),
)
def example_usage():
import os
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--database_path", default="database.db")
args = parser.parse_args()
if os.path.exists(args.database_path):
print("ERROR: database path already exists -- will not modify it.")
return
# Open the database.
db = COLMAPDatabase.connect(args.database_path)
# For convenience, try creating all the tables upfront.
db.create_tables()
# Create dummy cameras.
model1, width1, height1, params1 = (
0,
1024,
768,
np.array((1024.0, 512.0, 384.0)),
)
model2, width2, height2, params2 = (
2,
1024,
768,
np.array((1024.0, 512.0, 384.0, 0.1)),
)
camera_id1 = db.add_camera(model1, width1, height1, params1)
camera_id2 = db.add_camera(model2, width2, height2, params2)
# Create dummy images.
image_id1 = db.add_image("image1.png", camera_id1)
image_id2 = db.add_image("image2.png", camera_id1)
image_id3 = db.add_image("image3.png", camera_id2)
image_id4 = db.add_image("image4.png", camera_id2)
# Create dummy keypoints.
#
# Note that COLMAP supports:
# - 2D keypoints: (x, y)
# - 4D keypoints: (x, y, theta, scale)
# - 6D affine keypoints: (x, y, a_11, a_12, a_21, a_22)
num_keypoints = 1000
keypoints1 = np.random.rand(num_keypoints, 2) * (width1, height1)
keypoints2 = np.random.rand(num_keypoints, 2) * (width1, height1)
keypoints3 = np.random.rand(num_keypoints, 2) * (width2, height2)
keypoints4 = np.random.rand(num_keypoints, 2) * (width2, height2)
db.add_keypoints(image_id1, keypoints1)
db.add_keypoints(image_id2, keypoints2)
db.add_keypoints(image_id3, keypoints3)
db.add_keypoints(image_id4, keypoints4)
# Create dummy matches.
M = 50
matches12 = np.random.randint(num_keypoints, size=(M, 2))
matches23 = np.random.randint(num_keypoints, size=(M, 2))
matches34 = np.random.randint(num_keypoints, size=(M, 2))
db.add_matches(image_id1, image_id2, matches12)
db.add_matches(image_id2, image_id3, matches23)
db.add_matches(image_id3, image_id4, matches34)
# Commit the data to the file.
db.commit()
# Read and check cameras.
rows = db.execute("SELECT * FROM cameras")
camera_id, model, width, height, params, prior = next(rows)
params = blob_to_array(params, np.float64)
assert camera_id == camera_id1
assert model == model1 and width == width1 and height == height1
assert np.allclose(params, params1)
camera_id, model, width, height, params, prior = next(rows)
params = blob_to_array(params, np.float64)
assert camera_id == camera_id2
assert model == model2 and width == width2 and height == height2
assert np.allclose(params, params2)
# Read and check keypoints.
keypoints = dict(
(image_id, blob_to_array(data, np.float32, (-1, 2)))
for image_id, data in db.execute("SELECT image_id, data FROM keypoints")
)
assert np.allclose(keypoints[image_id1], keypoints1)
assert np.allclose(keypoints[image_id2], keypoints2)
assert np.allclose(keypoints[image_id3], keypoints3)
assert np.allclose(keypoints[image_id4], keypoints4)
# Read and check matches.
pair_ids = [
image_ids_to_pair_id(*pair)
for pair in (
(image_id1, image_id2),
(image_id2, image_id3),
(image_id3, image_id4),
)
]
matches = dict(
(pair_id_to_image_ids(pair_id), blob_to_array(data, np.uint32, (-1, 2)))
for pair_id, data in db.execute("SELECT pair_id, data FROM matches")
)
assert np.all(matches[(image_id1, image_id2)] == matches12)
assert np.all(matches[(image_id2, image_id3)] == matches23)
assert np.all(matches[(image_id3, image_id4)] == matches34)
# Clean up.
db.close()
if os.path.exists(args.database_path):
os.remove(args.database_path)
def create_database():
import os
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--database_path", default="database.db")
args = parser.parse_args()
# if os.path.exists(args.database_path):
# print("ERROR: database path already exists -- will not modify it.")
# return
if os.path.exists(args.database_path):
os.remove(args.database_path)
# if not os.path.exists("distorted"):
# os.mkdir("distorted")
# Open the database.
db = COLMAPDatabase.connect(args.database_path)
# For convenience, try creating all the tables upfront.
db.create_tables()
# Create dummy cameras.
camModelDict = {'SIMPLE_PINHOLE': 0,
'PINHOLE': 1,
'SIMPLE_RADIAL': 2,
'RADIAL': 3,
'OPENCV': 4,
'FULL_OPENCV': 5,
'SIMPLE_RADIAL_FISHEYE': 6,
'RADIAL_FISHEYE': 7,
'OPENCV_FISHEYE': 8,
'FOV': 9,
'THIN_PRISM_FISHEYE': 10}
with open("created/sparse/model/cameras.txt", "r") as cameras_file:
cameras_instinct = cameras_file.read().replace("\n", "")
pass
cameras_instinct = cameras_instinct.split(" ")
# print(cameras_instinct)
model1 = camModelDict[cameras_instinct[1]]
width1, height1 = int(cameras_instinct[2]), int(cameras_instinct[3])
params1 = np.array([float(param) for param in cameras_instinct[4:]])
# print(model1,width1,height1,params1)
camera_id1 = db.add_camera(model1, width1, height1, params1)
# print(camera_id1)
# 图片
with open("created/sparse/model/images.txt", "r") as images_file:
images_list = images_file.readlines()
pass
for images_info in images_list:
if images_info == "\n":
continue
images_info = images_info.replace("\n", "").split(" ")
# print(images_info)
idx = int(images_info[0])
image_name = images_info[-1]
# images_info[1]-[4] QW, QX, QY, QZ
image_q = np.array([float(q_i) for q_i in images_info[1:5]])
# images_info[5]-[7] TX, TY, TZ
image_t = np.array([float(t_i) for t_i in images_info[5:8]])
image_id_from_db = db.add_image(image_name, camera_id1, prior_q=image_q, prior_t=image_t)
if idx != image_id_from_db:
print(f"{idx}!={image_id_from_db}")
pass
db.commit()
db.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# example_usage()
create_database()
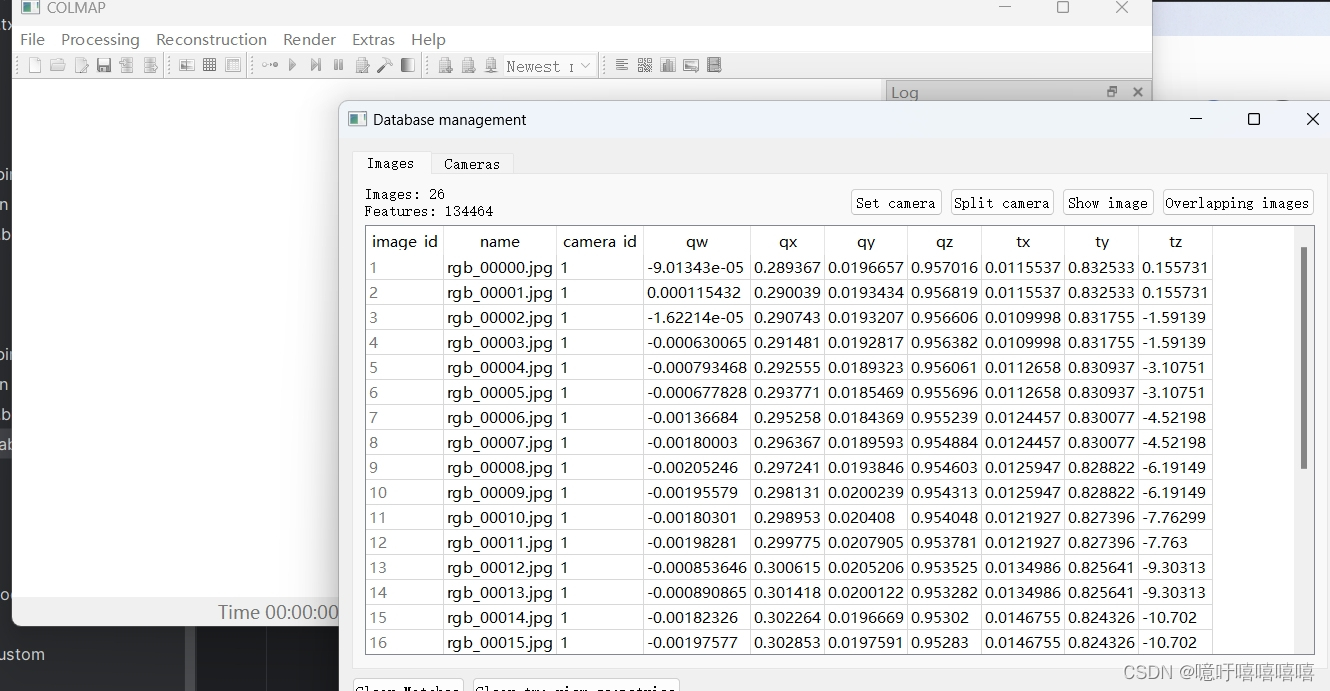
运行之后,你可以在colmap中新建项目,导入刚才的database.db文件,查看数据是否被加载进入:
执行:
colmap feature_extractor --database_path database.db --image_path images
colmap exhaustive_matcher --database_path database.db
colmap point_triangulator --database_path database.db --image_path images --input_path created\sparse\model --output_path triangulated\sparse\model
# 或者
colmap mapper --database_path database.db --image_path images --input_path created\sparse\model --output_path mapper\sparse\model
由于我的程序并没有给我 dense/stereo/ 目录下的 patch-match.cfg 等等,于是我自建:
执行程序:generate_fusion&patch_match.py
import numpy as np
import os
def main(folder_path):
# 获取文件夹中所有文件名
file_names = os.listdir(folder_path)
# 写入文件名到txt文件
output_file_path = 'patch-match.cfg'
with open(output_file_path, 'w') as file:
for file_name in file_names:
file.write(f"{file_name}\n__auto__, 20\n")
output_file_path = 'fusion.cfg'
with open(output_file_path, 'w') as file:
for file_name in file_names:
file.write(f"{file_name}\n")
if __name__ == '__main__':
folder_path = "images"
main(folder_path)
将数据移入高斯(我用的三角测量的):
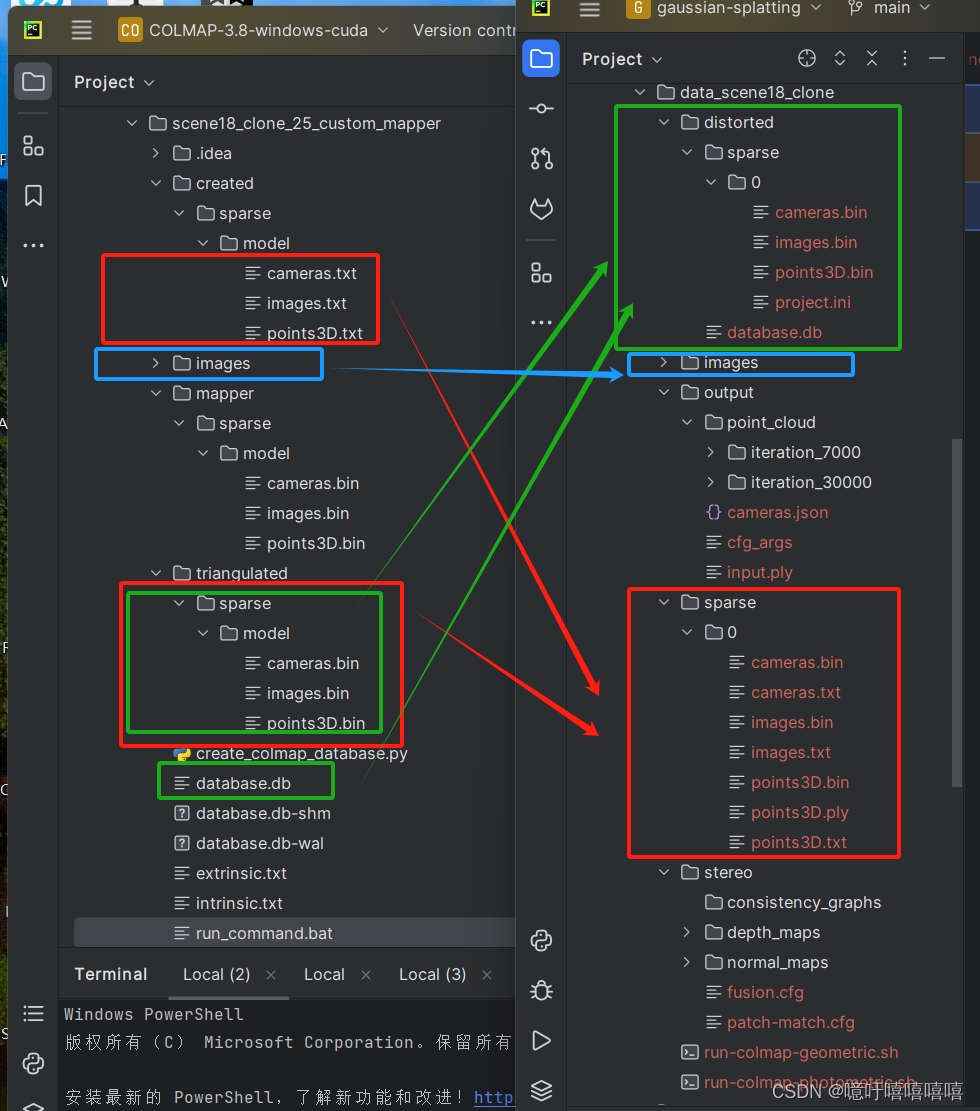
就可以在高斯中执行就 python train.py -s data/data_scene18 -m data/data_scene18 /output 了
但在可视化的时候老是会崩,而且colmap中进行系数重建和稠密重建的效果也不好。中间肯定还是有步骤出错了。