目录
一、STL的基本概念
二、vector容器
1.遍历
2.vector存放自定义数据类型
3.容器嵌套容器
4.构造函数
5.容量和大小
6.插入和删除
7.容器互换
三、string容器
1.string和char的区别
2.string的构造函数
3.赋值操作
4.字符串拼接
5.查找和替换
6.比较
7.字符串的存取和单个字符的修改
8.插入和删除
9.子串的获取
一、STL的基本概念
- STL(Standard Template Library,标准模板库),STL从广义上分为:容器(container),算法(algorithm),迭代器(iterator)。
- 迭代器是一个类对象,该类封装一个指针(迭代器可以理解为指针,对指针的操作基本都可以对迭代器操作),每个容器都有自己专属的迭代器
二、vector容器
- vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组
- vector与普通数组的区别:数组是静态空间,vector是可以动态扩展的,所谓的动态扩展是找更大的内存空间,然后将原有的数据拷贝给新的空间,释放原有的空间
1.遍历
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>//标准算法的头文件
using namespace std;
void print(int x)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
void text()
{
vector<int> v;//创建一个vector容器
v.push_back(1);//push_back()是插入函数
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
//通过迭代器访问容器中的数据
vector<int>::iterator itBegin = v.begin();//起始迭代器,指向容器中的第一个元素
vector<int>::iterator itEnd = v.end();//结束迭代器,指向容器中最后一个元素的下一个位置
//第一种遍历方式
while (itBegin != itEnd)
{
cout << *itBegin<< " ";
itBegin++;
}
cout << endl;
//第二种遍历方式
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//第三种方式利用STL提供的for_each()
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), print);
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
2.vector存放自定义数据类型
- vector存放自定义数据类型
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
Student(string n, int a)//构造函数,给name,age赋值
{
this->name = n;
this->age = a;
}
~Student()//析构函数
{
;
}
};
int main()
{
Student stu1("张三", 15);
Student stu2("李四", 17);
Student stu3("王五", 19);
vector<Student>v;
v.push_back(stu1);//向容器中插入数据
v.push_back(stu2);
v.push_back(stu3);
//遍历容器中的数据
for (vector<Student>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->name << " 年龄:" << it->age << endl;
}
return 0;
}- vector存放自定义数据类型的指针
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
string name;//姓名
int age;//年龄
Student(string n, int a)//构造函数,给name,age赋值
{
this->name = n;
this->age = a;
}
~Student()//析构函数
{
;
}
};
int main()
{
Student stu1("张三", 15);
Student stu2("李四", 17);
Student stu3("王五", 19);
vector<Student*>v;
v.push_back(&stu1);//向容器中存放数据的地址
v.push_back(&stu2);
v.push_back(&stu3);
//遍历容器中的数据
for (vector<Student*>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << (*it)->name << " 年龄:" << (*it)->age << endl;//it是指向数据地址的指针,*it是得到数据的地址,再通过->访问地址里面的内容
}
return 0;
}3.容器嵌套容器
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
vector<vector<int>>v;
//创建小容器
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
vector<int>v3;
vector<int>v4;
//小容器中添加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
v2.push_back(i + 2);
v3.push_back(i + 3);
v4.push_back(i + 4);
}
//将小容器插入到大容器中
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
v.push_back(v4);
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)//遍历所有数据
{
//*it-----vector<int>
for (vector<int>::iterator t = (*it).begin(); t != (*it).end(); t++)
{
cout << (*t) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}4.构造函数
vector<T> v;//采用类模板实现,默认构造函数
vector(v.begin(), v.end());//将v从v.begin()到v.end()区间之间的元素拷贝给本身
vector(n, elem);//构造函数将10个elem拷贝给本身
vector<T>v2(v);//拷贝构造,将v拷贝给v2#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void text()//vector容器的构造(实际是初始化vector的对象v1,v2...)
{
//方法1:默认构造,无参构造
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);//插入数据
}
print(v1);
//方法2:通过区间方式进行构造
vector<int>v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
print(v2);
//方法3:n个elem方式构造
vector<int>v3(10, 11);
print(v3);
//方法4:拷贝构造
vector<int>v4(v3);
print(v4);
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}5.容量和大小
v.capacity();//容器的容量
v.size();//返回容器中规定元数个数
v.resize(int num);//重新指定容器长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置
//若容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
v.resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem填充新位置
//若容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
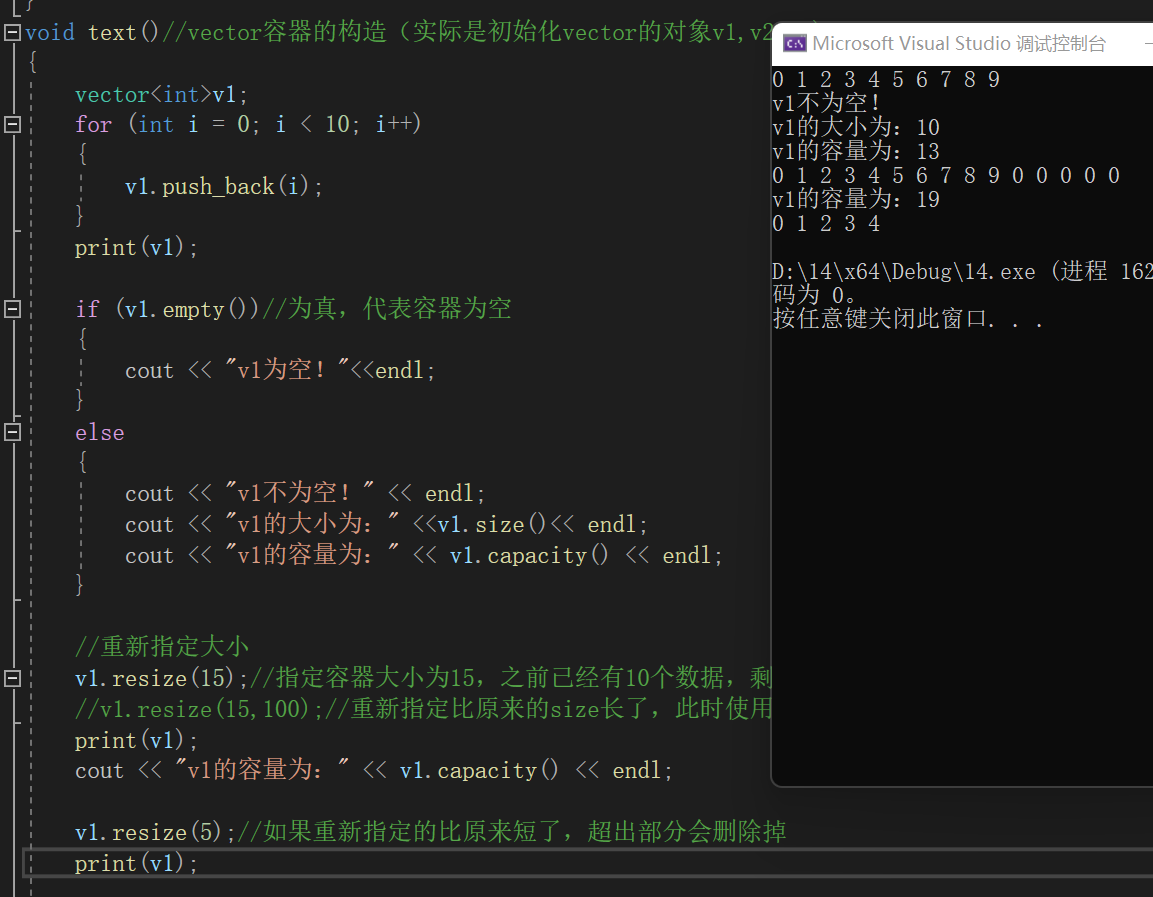
void text()//vector容器的构造(实际是初始化vector的对象v1,v2...)
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
print(v1);
if (v1.empty())//为真,代表容器为空
{
cout << "v1为空!"<<endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1不为空!" << endl;
cout << "v1的大小为:" <<v1.size()<< endl;
cout << "v1的容量为:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
}
//重新指定大小
v1.resize(15);//指定容器大小为15,之前已经有10个数据,剩下5个数据默认使用0填充
//v1.resize(15,100);//重新指定比原来的size长了,此时使用100填充
print(v1);
cout << "v1的容量为:" << v1.capacity() << endl;
v1.resize(5);//如果重新指定的比原来短了,超出部分会删除掉
print(v1);
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
6.插入和删除
v.push_back(elem);//尾部插入元素elem
v.pop_back();//删除尾部元素
v.insert(v.begin(), elem);//在迭代器的位置上,插入elem
v.erase(v.begin);//删除第一个元素
v.erase(v.begin(), v.end());//清空
v.clear();//清空#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void text()//vector容器的构造(实际是初始化vector的对象v1,v2...)
{
vector<int>v1;
//尾插
v1.push_back(11);
v1.push_back(22);
v1.push_back(33);
v1.push_back(44);
v1.push_back(55);
print(v1);
//尾删
v1.pop_back();
print(v1);
//插入
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);//在迭代器的位置上,插入100
print(v1);
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 2, 200);//在最前面插入两个200
print(v1);
//删除
v1.erase(v1.begin());//删除第一个元素
print(v1);
//清空
v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());//删除v1从头到尾所有元素
print(v1);
v1.clear();//第二种清空
print(v1);
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}7.容器互换
v1.swap(v2);//实现v1和v2的数据互换#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void text()
{
vector<int>v1;
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 10);
}
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
print(v1);
print(v2);
v1.swap(v2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
print(v1);
print(v2);
}
void text2()//巧用swap收缩内存
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
v.resize(3);//重新指定大小
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
//巧用swap收缩内存
vector<int>(v).swap(v);
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v的大小为:" << v.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
text2();
return 0;
}三、string容器
1.string和char的区别
- char* 是一个指针
- string是一个类,类内部封装了char* ,管理这个字符串,是一个char* 型的容器
2.string的构造函数
string(); //创造一个空的字符串,例如string str
string(const char* s);//使用字符串s初始化
string(const string& str);//使用string对象初始化string的另外一个对象
string(int n, char c);//使用n个字符c初始化#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
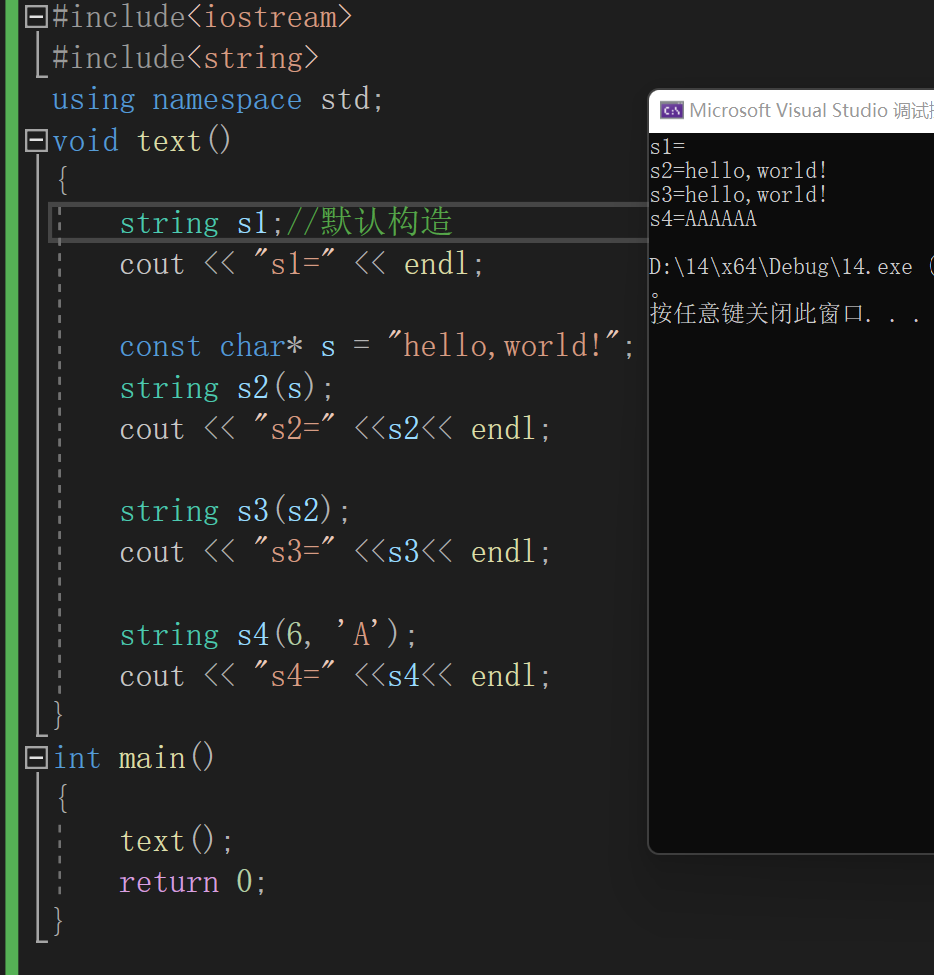
void text()
{
string s1;//创建空字符串,调用无参构造函数
cout << "s1=" << endl;
const char* s = "hello,world!";
string s2(s);
cout << "s2=" <<s2<< endl;
string s3(s2);
cout << "s3=" <<s3<< endl;
string s4(6, 'A');
cout << "s4=" <<s4<< endl;
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
3.赋值操作
string s1.assign(const char* s);//将字符串s赋值给s1
string s2.assign(const char* s, int n);//从字符串s中取前n个字符,赋值给s2
string s3.assign(const string s);//将s5赋值给s3
string s4.assign(int n, char c);//将n个字符c赋值给s4#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1;
str1 = "hello,world!"; //将字符串hello, world!赋值给str4
cout <<"str1 = "<< str1 << endl;
string str2;
str2 = str1;//将字符串str1赋值给str2
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
string str3;
str3 = 'A';//将字符A赋值给str3
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
string str4;
str4.assign("hello!");//将字符串hello!赋值给str4
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
string str5;
str5.assign("hello,world", 5);//取前5个字符
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
string str6;
str6.assign(str5);//将str5赋值给str6
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
string str7;
str7.assign(6, 'A');//将6个A赋值给str7
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
4.字符串拼接
string s1.append(string s)//将字符串s赋值给s1
string s2.append(string s,int n);//取字符串s的前n个字符连接在s2后面
string s3.append(string s, int pos, int n);//从字符串s下标为pos处开始取n个字符连接在s3后面#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1 = "c语言";
str1 += "程序设计";
cout << "st1 = " << str1<<endl;
string str2 = ",java";
str1 += str2;//将s2拼接在s1后面
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
string str3 ="中国";
str3.append(",美国");
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append("AAAAAAAA", 6);//取前6个字符连在字符串str3后面
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
str3.append(str2);//将字符串str2连在str3后面
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
string str4 = "complex,algorithm";
str4.append(str4,4, 5);//从字符串str4下标为4处开始取5个字符,然后连接在str4后面
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
}
5.查找和替换
string s1,s2,s3;
int pos = s1.find(s);//查找s在s1中第一次出现的位置(从左向右查找)
int pos_2 = s1.rfind(s);//查找s在s1中第一次出现的位置(从右向左查找)
int pos_3=s3.replace(int pos,int n,string s);//从下标为pos的位置开始的n个字符替换成s#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
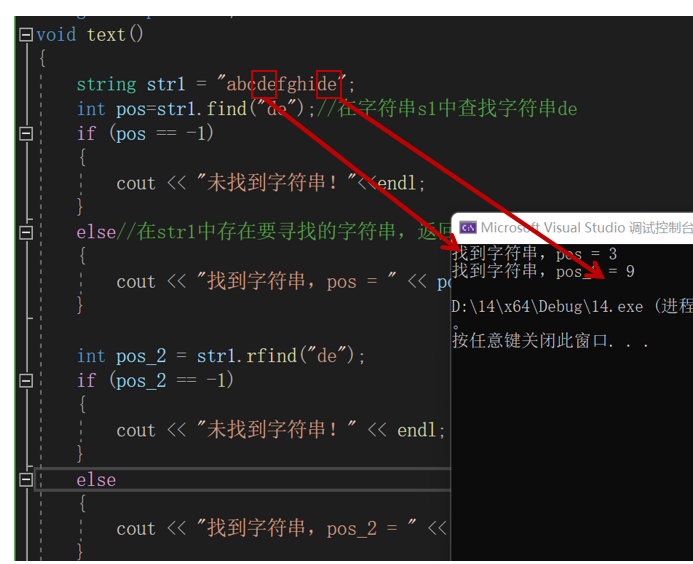
void text()
{
string str1 = "abcdefghide";
int pos=str1.find("de");//在字符串s1中查找字符串de
if (pos == -1)
{
cout << "未找到字符串!"<<endl;
}
else//在str1中存在要寻找的字符串,返回寻找的字符串的第一个字符的下标
{
cout << "找到字符串,pos = " << pos << endl;
}
int pos_2 = str1.rfind("de");
if (pos_2 == -1)
{
cout << "未找到字符串!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到字符串,pos_2 = " << pos_2 << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1 = "abcdefgh";
str1.replace(1, 3, "1111");//从下标为1的位置起的3个字符,替换为“1111”==>将bcd替换成1111
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
6.比较
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1 = "hello,world!";
string str2 = "hello,world";
if (str1.compare(str2) == 0)//compare按照两个字符串的assic码值逐个对比
{
cout << "str1等于str2" << endl;
}
else if (str1.compare(str2) > 0)
{
cout << "str1大于str2" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "str1小于str2" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}7.字符串的存取和单个字符的修改
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1 = "hello,world!";
//方法1:
for (int i = 0; i < str1.size(); i++)
{
cout << str1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//方法2:通过at方式访问单个字符
string str2 = "abcdefg";
for (int i = 0; i < str2.size(); i++)
{
cout << str2.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//修改单个字符
//方法1:
str1[0] = 'a';
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//方法2:
str2.at(0) = 'b';
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}
8.插入和删除
string s1, s2;
s1.insert(int pos, string s);//从下标为pos位置开始插入字符串s
s2.erase(int pos, int n);//从下标为pos位置开始删除n个字符#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1 = "hello,world!";
str1.insert(1, "111");//从下标为1的位置开始插入111
cout << "插入后,str1 = " << str1 << endl;//输出h111ello,world!
str1.erase(1, 3);//从下标为1的位置开始删除3个字符
cout << "删除后,str1 = " << str1 << endl;//输出hello,world!
}
int main()
{
text();
return 0;
}9.子串的获取
string sub,s1;
sub = s1.substr(int pos, int n);//从s1字符串的下标为pos的位置开始向后取n个字符#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void text()
{
string str1 = "hello,world!";
string Substr = str1.substr(1, 3);//从str1字符串的下标为1的位置开始向后取3个字符
cout << "Substr = " << Substr << endl;//输出ell
}
void text2()
{
string email = "zhangsan@qq.com";
int pos = email.find("@");
string name = email.substr(0, pos);
cout << "name = " <<name<< endl;//输出zhangsan
}
int main()
{
text();
text2();
return 0;
}