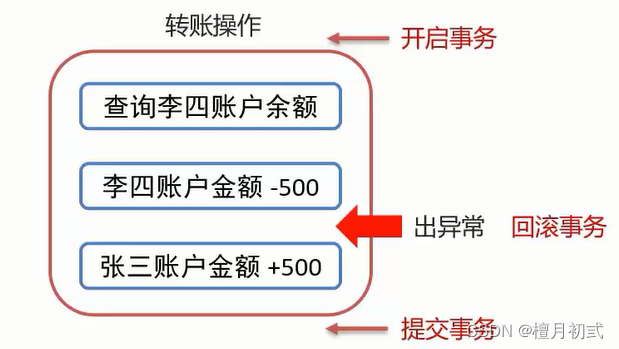
FrameLayout 是 Android 中常用的布局之一,它允许子视图堆叠在一起,可以在不同位置放置子视图。在这篇博客中,我们将详细介绍 FrameLayout 的属性及其作用。
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
在上面的代码中,我们定义了一个 FrameLayout,设置其宽度和高度均为 match_parent,使其填充其父视图的整个空间。
android:layout_width 和 android:layout_height
这两个属性决定了 FrameLayout 的宽度和高度。它们的取值可以是:
match_parent:视图的大小与其父视图相匹配。wrap_content:视图的大小根据其内容来确定。固定值(如100dp):设置固定的宽度或高度,不会随着内容或父视图的变化而变化。
android:layout_gravity
这个属性用于设置子视图在 FrameLayout 中的对齐方式。它的取值可以是:
top:子视图位于顶部。bottom:子视图位于底部。left:子视图位于左侧。right:子视图位于右侧。center:子视图位于中心。
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:text="This is TextView" />
在上面的示例中,TextView 的 android:layout_gravity 设置为 left,使其位于 FrameLayout 的左侧。
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
android:text="Button" />
而 Button 的 android:layout_gravity 设置为 right,使其位于 FrameLayout 的右侧。
通过合理地使用这些属性,可以轻松实现 FrameLayout 中子视图的灵活布局和对齐。 FrameLayout 在实现简单布局时非常方便,特别适用于叠加式布局,如显示叠加的图层或浮动按钮等。

希望这篇博客能帮助你更深入地理解 FrameLayout 布局及其属性的使用!