我们前面介绍了linux内存管理的三级架构,node->zone->page。本节就来介绍page。
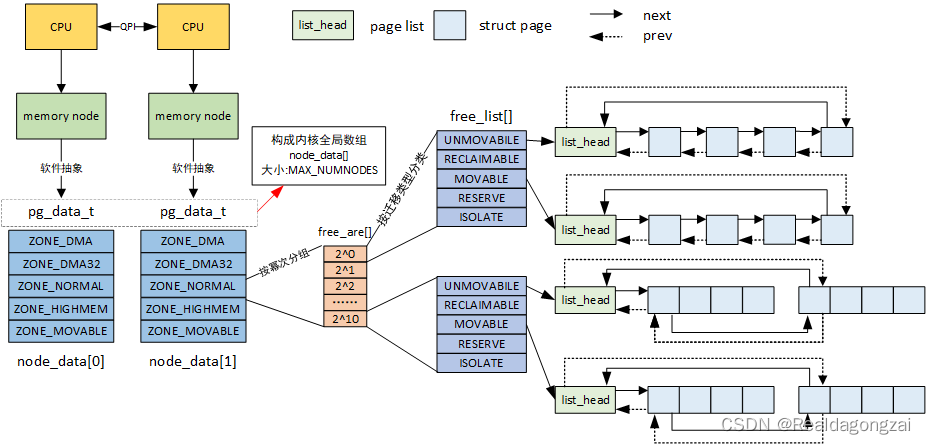
页是内核管理内存的基本单位,体系结构不同,支持的页大小也不尽相同,还有些体系结构甚至支持几种不同的页大小。大多数32位体系结构支持4KB的页,而64位体系结构一般会支持8KB的页。
内核用struct page结构描述系统中的每个物理页,
出于节省内存的考虑,struct page中使用了大量的联合体union,也导致page结构体理解起来比较复杂,对于不同的场景使用不同的union成员。最新版本的page结构体精简了好多。
struct page {
unsigned long flags; /* Atomic flags, some possibly
* updated asynchronously */ /* 描述page的状态和其他信息 */
/*
* Five words (20/40 bytes) are available in this union.
* WARNING: bit 0 of the first word is used for PageTail(). That
* means the other users of this union MUST NOT use the bit to
* avoid collision and false-positive PageTail().
*/
union {
struct { /* Page cache and anonymous pages */
/**
* @lru: Pageout list, eg. active_list protected by
* lruvec->lru_lock. Sometimes used as a generic list
* by the page owner.
*/
union {
struct list_head lru;
/* Or, for the Unevictable "LRU list" slot */
struct {
/* Always even, to negate PageTail */
void *__filler;
/* Count page's or folio's mlocks */
unsigned int mlock_count;
};
/* Or, free page */
struct list_head buddy_list;
struct list_head pcp_list;
};
/* See page-flags.h for PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS */
struct address_space *mapping;
pgoff_t index; /* Our offset within mapping. */
/**
* @private: Mapping-private opaque data.
* Usually used for buffer_heads if PagePrivate.
* Used for swp_entry_t if PageSwapCache.
* Indicates order in the buddy system if PageBuddy.
*/
unsigned long private;
};
... 删了一堆不常用的
/** @rcu_head: You can use this to free a page by RCU. */
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
};
union { /* This union is 4 bytes in size. */
/*
* If the page can be mapped to userspace, encodes the number
* of times this page is referenced by a page table.
*/
atomic_t _mapcount;
/*
* If the page is neither PageSlab nor mappable to userspace,
* the value stored here may help determine what this page
* is used for. See page-flags.h for a list of page types
* which are currently stored here.
*/
unsigned int page_type;
};
/* Usage count. *DO NOT USE DIRECTLY*. See page_ref.h */
atomic_t _refcount;
...省略了一堆开启配置才有的成员
} _struct_page_alignment;
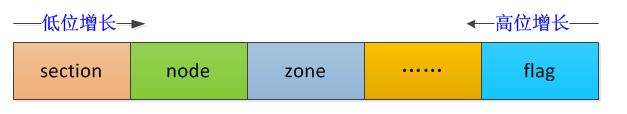
flags
第一个成员flags是所有page都有的
page的flags标识主要分为4部分,其中标志位flag向高位增长, 其余位字段向低位增长,中间存在空闲位
字段 描述
section 稀疏内存模型标识该page哪个section
node NUMA节点号, 标识该page属于哪一个节点
zone 内存域标志,标识该page属于哪一个zone
flag page的状态标识
配套的转换函数:
static inline void set_page_zone(struct page *page, enum zone_type zone)
{
page->flags &= ~(ZONES_MASK << ZONES_PGSHIFT);
page->flags |= (zone & ZONES_MASK) << ZONES_PGSHIFT;
}
static inline void set_page_node(struct page *page, unsigned long node)
{
page->flags &= ~(NODES_MASK << NODES_PGSHIFT);
page->flags |= (node & NODES_MASK) << NODES_PGSHIFT;
}
#ifdef SECTION_IN_PAGE_FLAGS
static inline void set_page_section(struct page *page, unsigned long section)
{
page->flags &= ~(SECTIONS_MASK << SECTIONS_PGSHIFT);
page->flags |= (section & SECTIONS_MASK) << SECTIONS_PGSHIFT;
}
static inline unsigned long page_to_section(const struct page *page)
{
return (page->flags >> SECTIONS_PGSHIFT) & SECTIONS_MASK;
}
#endif
page状态定义如下:
/*
* Don't use the pageflags directly. Use the PageFoo macros.
*
* The page flags field is split into two parts, the main flags area
* which extends from the low bits upwards, and the fields area which
* extends from the high bits downwards.
*
* | FIELD | ... | FLAGS |
* N-1 ^ 0
* (NR_PAGEFLAGS)
*
* The fields area is reserved for fields mapping zone, node (for NUMA) and
* SPARSEMEM section (for variants of SPARSEMEM that require section ids like
* SPARSEMEM_EXTREME with !SPARSEMEM_VMEMMAP).
*/
enum pageflags {
PG_locked, /* Page is locked. Don't touch. */
PG_referenced,
PG_uptodate,
PG_dirty,
PG_lru,
PG_active,
PG_workingset,
PG_waiters, /* Page has waiters, check its waitqueue. Must be bit #7 and in the same byte as "PG_locked" */
PG_error,
PG_slab,
PG_owner_priv_1, /* Owner use. If pagecache, fs may use*/
PG_arch_1,
PG_reserved,
PG_private, /* If pagecache, has fs-private data */
PG_private_2, /* If pagecache, has fs aux data */
PG_writeback, /* Page is under writeback */
PG_head, /* A head page */
PG_mappedtodisk, /* Has blocks allocated on-disk */
PG_reclaim, /* To be reclaimed asap */
PG_swapbacked, /* Page is backed by RAM/swap */
PG_unevictable, /* Page is "unevictable" */
#ifdef CONFIG_MMU
PG_mlocked, /* Page is vma mlocked */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_ARCH_USES_PG_UNCACHED
PG_uncached, /* Page has been mapped as uncached */
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_FAILURE
PG_hwpoison, /* hardware poisoned page. Don't touch */
#endif
#if defined(CONFIG_PAGE_IDLE_FLAG) && defined(CONFIG_64BIT)
PG_young,
PG_idle,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_64BIT
PG_arch_2,
#endif
#ifdef CONFIG_KASAN_HW_TAGS
PG_skip_kasan_poison,
#endif
__NR_PAGEFLAGS,
PG_readahead = PG_reclaim,
/*
* Depending on the way an anonymous folio can be mapped into a page
* table (e.g., single PMD/PUD/CONT of the head page vs. PTE-mapped
* THP), PG_anon_exclusive may be set only for the head page or for
* tail pages of an anonymous folio. For now, we only expect it to be
* set on tail pages for PTE-mapped THP.
*/
PG_anon_exclusive = PG_mappedtodisk,
/* Filesystems */
PG_checked = PG_owner_priv_1,
/* SwapBacked */
PG_swapcache = PG_owner_priv_1, /* Swap page: swp_entry_t in private */
/* Two page bits are conscripted by FS-Cache to maintain local caching
* state. These bits are set on pages belonging to the netfs's inodes
* when those inodes are being locally cached.
*/
PG_fscache = PG_private_2, /* page backed by cache */
/* XEN */
/* Pinned in Xen as a read-only pagetable page. */
PG_pinned = PG_owner_priv_1,
/* Pinned as part of domain save (see xen_mm_pin_all()). */
PG_savepinned = PG_dirty,
/* Has a grant mapping of another (foreign) domain's page. */
PG_foreign = PG_owner_priv_1,
/* Remapped by swiotlb-xen. */
PG_xen_remapped = PG_owner_priv_1,
/* SLOB */
PG_slob_free = PG_private,
/* Compound pages. Stored in first tail page's flags */
PG_double_map = PG_workingset,
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_FAILURE
/*
* Compound pages. Stored in first tail page's flags.
* Indicates that at least one subpage is hwpoisoned in the
* THP.
*/
PG_has_hwpoisoned = PG_error,
#endif
/* non-lru isolated movable page */
PG_isolated = PG_reclaim,
/* Only valid for buddy pages. Used to track pages that are reported */
PG_reported = PG_uptodate,
#ifdef CONFIG_MEMORY_HOTPLUG
/* For self-hosted memmap pages */
PG_vmemmap_self_hosted = PG_owner_priv_1,
#endif
};
第二个成员,比较复杂的联合体,此处我删除了一些不常用的场景,
先看第一个场景:用于page cache和匿名页。
什么是匿名页?
应用程序动态分配的堆内存称为匿名页(Anonymous Page)
堆内存很可能还要再次被访问,当然不能直接回收了。这些内存自然不能直接释放。什么是page cache?
磁盘中一个文件或者其他虚拟文件(shmem)加载到内存所对应的page。
这个页可能在lru上,可能在伙伴系统里,可能在pcp链表里,可能看到三种都是互斥的,这三种都是内核管理内存的方式,只是用于不同的场景需要。这么来看,还是挺清晰的。
/*
* Five words (20/40 bytes) are available in this union.
* WARNING: bit 0 of the first word is used for PageTail(). That
* means the other users of this union MUST NOT use the bit to
* avoid collision and false-positive PageTail().
*/
union {
struct { /* Page cache and anonymous pages */
/**
* @lru: Pageout list, eg. active_list protected by
* lruvec->lru_lock. Sometimes used as a generic list
* by the page owner.
*/
union {
struct list_head lru;
/* Or, for the Unevictable "LRU list" slot */
struct {
/* Always even, to negate PageTail */
void *__filler;
/* Count page's or folio's mlocks */
unsigned int mlock_count;
};
/* Or, free page */
struct list_head buddy_list;
struct list_head pcp_list;
};
/* See page-flags.h for PAGE_MAPPING_FLAGS */
struct address_space *mapping;
pgoff_t index; /* Our offset within mapping. */
/**
* @private: Mapping-private opaque data.
* Usually used for buffer_heads if PagePrivate.
* Used for swp_entry_t if PageSwapCache.
* Indicates order in the buddy system if PageBuddy.
*/
unsigned long private;
};
...
struct { /* Page table pages */
unsigned long _pt_pad_1; /* compound_head */
pgtable_t pmd_huge_pte; /* protected by page->ptl */
unsigned long _pt_pad_2; /* mapping */
union {
struct mm_struct *pt_mm; /* x86 pgds only */
atomic_t pt_frag_refcount; /* powerpc */
};
#if ALLOC_SPLIT_PTLOCKS
spinlock_t *ptl;
#else
spinlock_t ptl;
#endif
};
/** @rcu_head: You can use this to free a page by RCU. */
struct rcu_head rcu_head;
};
上面有一个非常非常重要的成员,struct address_space *mapping;,磁盘中一个文件或者其他虚拟文件(shmem)所对应的page每次都是经过同一个struct address_space来进行管理。
index在映射的虚拟空间(vma_area)内的偏移;一个文件可能只映射一部分,假设映射了1M的空间,index指的是在1M空间内的偏移,而不是在整个文件内的偏移
private私有数据指针,由应用场景确定其具体的含义
- 如果设置了PG_private标志,则private字段指向struct buffer_head
- 如果设置了PG_swapcache标志,private存储了该page在交换分区中对应的位置信息swp_entry_t。
- 如果设置了PageBuddy标志,说明该page位于伙伴系统,private存储该伙伴的阶
页的第二个场景,用于存放页表。
第三个成员,联合体:
union { /* This union is 4 bytes in size. */
/*
* If the page can be mapped to userspace, encodes the number
* of times this page is referenced by a page table.
*/
atomic_t _mapcount;
/*
* If the page is neither PageSlab nor mappable to userspace,
* the value stored here may help determine what this page
* is used for. See page-flags.h for a list of page types
* which are currently stored here.
*/
unsigned int page_type;
};
被页表映射的次数,也就是说该page同时被多少个进程共享。初始值为-1,如果只被一个进程的页表映射了,该值为0. 如果该page处于伙伴系统中,该值为PAGE_BUDDY_MAPCOUNT_VALUE(-128),内核通过判断该值是否为PAGE_BUDDY_MAPCOUNT_VALUE来确定该page是否属于伙伴系统
第四个成员,所有page都有的成员:
atomic_t _refcount;
引用计数,表示内核中引用该page的次数, 如果要操作该page, 引用计数会+1, 操作完成-1. 当该值为0时, 表示没有引用该page的位置,所以该page可以被解除映射,这往往在内存回收时是有用的
page_ref.h定义了配套的操作函数:
static inline int page_ref_count(const struct page *page)
{
return atomic_read(&page->_refcount);
}
static inline void set_page_count(struct page *page, int v)
{
atomic_set(&page->_refcount, v);
if (page_ref_tracepoint_active(page_ref_set))
__page_ref_set(page, v);
}
...


![[数据结构]栈和队列](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/87aa07754158440fa6fa92046f49d6b4.png)


![[Android]序列化原理Parcelable](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/99a589e6f99a43c19b8bc47b8e19a2be.png)